VisionPro之脚本(一文读懂VisionPro脚本原理与使用方法)
一、脚本简介
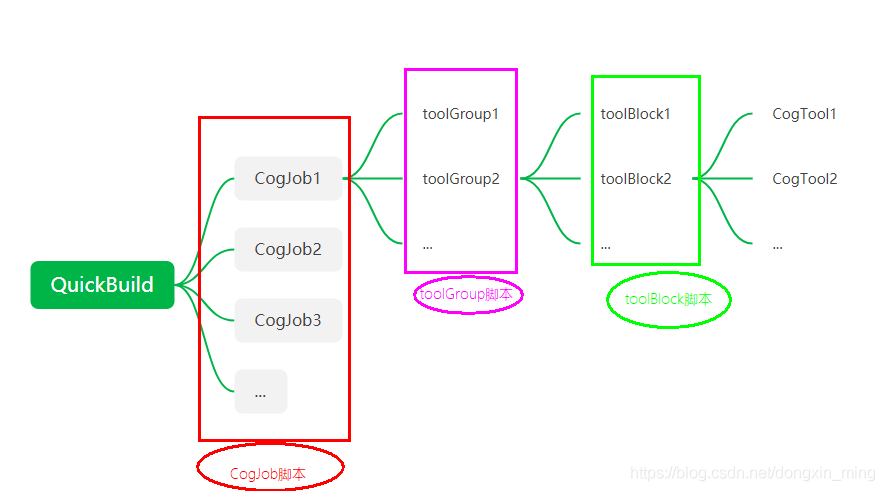
1.1 VisionPro项目组成简介
在介绍脚本之前先简单介绍一下VisionPro开发环境(QuickBuild)的项目结构,Job是QuickBuild工程的基本组成单位,一个QucikBuild工程至少含有一个Job,工程中所有的Job是并行结构,各个Job之间不会相互影响。每个Job中默认包含一个toolGroup,用户可以在默认的toolGroup中添加项目所需的工具和工具块。工具块(toolBlock)与工具组(toolGroup)都是工具的**“容器”**,通过使用工具块与工具组可以将完成某一功能的工具进行封装,实现项目模块化,同时亦可将某一特定功能的工具块或工具组导出实现重复使用,类似于编程语言中“函数”功能。工具块中亦可以包含工具块与工具组,两者之间的包含关系没有明确层次关系。
关于toolGroup与toolBlock的区别,请参考链接: https://blog.csdn.net/dongxin_ming/article/details/104926910.
1.2 VisionPro脚本简介
VisionPro工具封装了视觉算法与用户交互界面,toolGroup与toolBlock提供了组合工具的容器,但是并非所有的功能都能通过既定交互界面实现。为了让用户实现客制化功能更加“随心所欲”,实现VisionPro本身无法实现的逻辑功能,VisionPro预留了脚本功能。脚本的类型、作用与支持语言如下图所示:

二、脚本类与方法
VisionPro通过”多态”技术实现脚本功能,VisionPro 的每一Job、toolGroup、toolBlock对象都含有一个接口对象,用户通过重写接口方法实现自定义拓展功能。以toolGroup为例, ICogToolGroupScript接口中定义了子类中必须实现的函数,当toolGruoup执行到某一节点(工具准备运行、工具运行完成等)时会调用相应的接口函数实现用户指定的功能。
如果你对接口、多态理解不够深入,你只需要明白脚本就是**“填空题”**,VisionPro在适当的位置给你留下空白,在这个空白区域你可以在满足条件的情况下“自由发挥”,实现你想要实现的功能。
2.1 toolGroup脚本类
以ToolGroup脚本为例展开,toolGroup 脚本是继承于CogToolGroupBaseScript,实现了ICogToolGroupScript接口,该接口有四个方法,详细介绍如下:
public class CogToolGroupBaseScript : ICogToolGroupScript { // public virtual bool GroupRun(ref string message,ref Cognex.VisionPro.CogToolResultConstants result) { return true; } public virtual void ModifyCurrentRunRecord(ICogRecord currentRecord) {} public virtual void ModifyLastRunRecord(ICogRecord lastRecord) {} public virtual void Initialize(Cognex.VisionPro.ToolGroup.CogToolGroup host) { toolGroup = host; } protected Cognex.VisionPro.ToolGroup.CogToolGroup toolGroup=null; }
》Initialize() 顾名思义,该方法用于对toolGroup工具进行初始化,当退出脚本编辑工具时脚本会进行编译并进行初始化,此时该方法会被调用。此外,在对该group通过*.vpp文件进行加载时也会被立即调用。所以,所有的“一次性”的初始化工作都应该写在该方法中。
》GroupRun()方法运行该Group中的工具,如果该方法返回值为true,所有的属于当前Group的视觉工具都将运行,如果返回值为false,用户可以自定义工具的执行顺序,返回值为false为常见情况。
》ModifyCurrentRunRecord() 方法用于修改CurrentRecord,在toolGroup的CurrentRecord被创建后调用。
》ModifyLastRunRecord() 方法用于修改LastRunRecord,在toolGroup的LastRunRecord被创建后调用,例如:在最终生成图像中添加标签、该表颜色、用不同几何图像标记目标区域。
成员变量toolGroup为CogToolGroup类型,该类的runTool方法用于运行指定视觉工具;Tools 属性为当前Group的工具集合,一般用于获取当前工具组中某一工具的引用;DefineScriptTerminal、GetScriptTerminalData、SetScriptTerminalData 方法用于定义、获取、设置输入输出终端。
//对于当前Group存在的视觉工具的程序集与命名空间会自动添加,如果用户想要使用当前Group不存在的工具或者添加自定义程序集可以手动添加 //详细的操作步骤会在后续实例中进行介绍 using System; using Cognex.VisionPro; using Cognex.VisionPro3D; using Cognex.VisionPro.ToolGroup; public class UserScript : CogToolGroupBaseScript { //默认情况下遍历group中所有的工具并运行,用户可以根据实际情况自定义运行逻辑与顺序 public override bool GroupRun(ref string message, ref CogToolResultConstants result) for (Int32 toolIdx = 0; toolIdx < toolGroup.Tools.Count; toolIdx++) toolGroup.RunTool(toolGroup.Tools[toolIdx], ref message, ref result); return false;//默认情况下为false表示用户可以控制工具的运行顺序,返回值为true则运行当前Group中所有工具。 } public override void ModifyCurrentRunRecord(Cognex.VisionPro.ICogRecord currentRecord) { //在此处添加用户代码实现自定义修改CurrentRunRecord的功能 } public override void ModifyLastRunRecord(Cognex.VisionPro.ICogRecord lastRecord) { //在此处添加用户代码用于所有工具运行完成后根据用户需求创建Record或者在既有Record中添加标记等 } public override void Initialize(CogToolGroup host) { //调用父类初始化函数,初始化toolGroup对象 base.Initialize(host); } }
2.2 toolBlcok脚本类
与toolGroup脚本类似,toolBlock的脚本父类CogToolBlockAdvancedScriptBase,该类实现的接口与toolGroup相同,都是ICogToolGroupScript,不同之处在于toolBlock与两个脚本基类,CogToolBlockSimpleScript 与 CogToolBlockAdvancedScript 分别用于“简单脚”与“复杂”脚本,两者之间的区别在于复杂脚本能够实现:①动态定义toolBlock的输入输出终端,② 能够访问当前工具块所包含工具的所有属性与方法 ,为保证与toolGroup脚本使用的统一性,推荐直接使用复杂脚本。
存在即合理,简单脚本具有使用的便利性,在访问工具块的输入输出终端时,两者的具体访问方式如下:
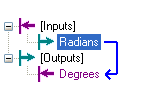
//使用简单脚本为输出赋值 Outputs.Degrees = Inputs.Radians * 180 / Math.PI; //使用复杂脚本为输出赋值 this.mToolBlock.Outputs["Degrees"].Value = ((double) this.mToolBlock.Inputs["Radians"].Value) * 180 / Math.PI;
既然与toolGroup实现了相同的接口,toolBlock脚本基类的方法与toolGroup必然相同,功能基本无异,不再赘述。
2.3Job脚本类
Job脚本用于控制与图像获取相关的设备属性与参数,基类为CogJobBaseScript,实现ICogJobScript接口。
public class CogJobBaseScript : ICogJobScript { public virtual void Initialize(CogJob jobParam) { job = jobParam; } public virtual void AcqFifoConstruction(ICogAcqFifo fifo) {} public virtual void PreAcquisition() {} public virtual void PostAcquisition(ICogImage image) {} public virtual bool PostAcquisitionRef(ref ICogImage image) { PostAcquisition(image); return true; } public virtual bool PostAcquisitionRefInfo(ref ICogImage image, ICogAcqInfo info) { return PostAcquisitionRef(ref image); } protected CogJob job = null; } }
》Initialize() 初始化方法,获取当前job引用以及用户需要的初始化数据。
》PreAcquisition() 在FIFO的StartAcquire()方法调用之前被调用,即在进行图像采集之前调用,如在图像采集之前设置曝光、增益、对比度等图像参数。
》PostAcquisition() 在图像采集完成之后被调用。
》PostAcquisitionRef() 该方法与 PostAcquisition 类似,不同之处在于 image 是以引用的方式传递,如果这个方法返回 Ture , VisionPro 将处理这个 image,如果这个方法返回 False ,这个 image 将不会被立即进行处理 ,而是采集下一幅图像,这可以使你能够在处理所取的多个 image 之前将它们联合在一起.(如果 PostAcquisition 和 PostAcquisitionRef 都被重写,PostAcquisition 将被忽略)。例如你需要同一个相机采集多张不同曝光的图像进行合成,并不是每次采集后都立即进行处理,而是采集到固定数量或者满足某一条件时进行处理。
》PostAcquisitionRefInfo() 与PostAcquisiitonRef相似,多了一个参数,用户可以通过ICogAcqInfo获取图像的时间戳,重写该方法后 PostAcquisition 、PostAcquisitionRef、 PostAcquisitionRef会被忽略。
三、脚本使用案例
3.1 job本实用实例-----自动调节曝光时间
setp1.新建Job,双击进入job中。
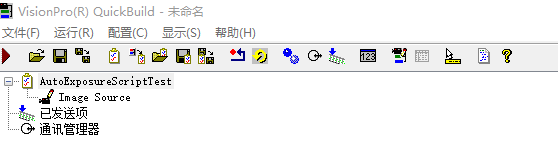
step2 配置->作业属性->编辑脚本->C#脚本,进入Job脚本编辑环境
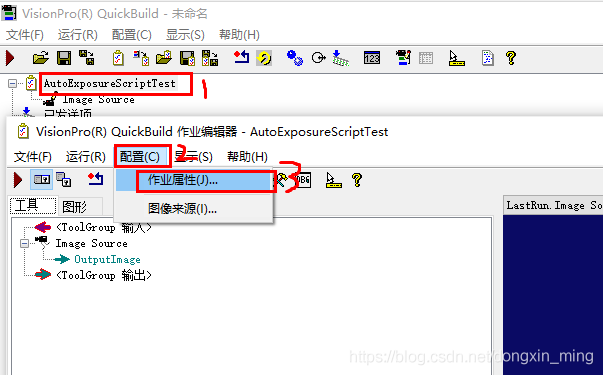
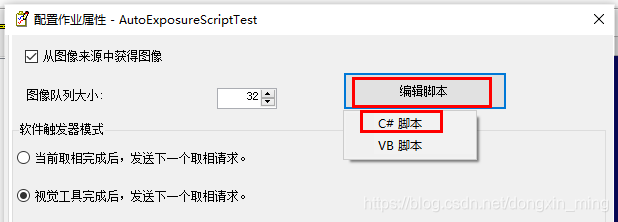
using System; using Cognex.VisionPro; using Cognex.VisionPro.QuickBuild; using Cognex.VisionPro.ImageProcessing; public class UserScript : CogJobBaseScript { double exposure = 10; #region "When an Acq Fifo Has Been Constructed and Assigned To The Job" // This function is called when a new fifo is assigned to the job. This usually // occurs when the "Initialize Acquisition" button is pressed on the image source // control. This function is where you would perform custom setup associated // with the fifo. public override void AcqFifoConstruction(Cognex.VisionPro.ICogAcqFifo fifo) { } #endregion #region "When an Acquisition is About To Be Started" // Called before an acquisition is started for manual and semi-automatic trigger // models. If "Number of Software Acquisitions Pre-queued" is set to 1 in the // job configuration, then no acquisitions should be in progress when this // function is called. public override void PreAcquisition() { // To let the execution stop in this script when a debugger is attached, uncomment the following lines. // #if DEBUG // if (System.Diagnostics.Debugger.IsAttached) System.Diagnostics.Debugger.Break(); // #endif ICogAcqExposure IExposure = job.AcqFifo.OwnedExposureParams; IExposure.Exposure = exposure; } #endregion #region "When an Acquisition Has Just Completed" // Called immediately after an acquisition has completed. // Return true if the image should be inspected. // Return false to skip the inspection and acquire another image. public override bool PostAcquisitionRefInfo(ref Cognex.VisionPro.ICogImage image, Cognex.VisionPro.ICogAcqInfo info) { // To let the execution stop in this script when a debugger is attached, uncomment the following lines. // #if DEBUG // if (System.Diagnostics.Debugger.IsAttached) System.Diagnostics.Debugger.Break(); // #endif CogHistogram curImageHist = new CogHistogram(); CogHistogramResult curHistResult = curImageHist.Execute(image,null); if(curHistResult.Mean>150) exposure *= 0.75; if(curHistResult.Mean < 50) exposure *= 1.5; if(exposure<0.1) exposure = 0.1; return true; } #endregion //Perform any initialization required by your script here. public override void Initialize(CogJob jobParam) { //DO NOT REMOVE - Call the base class implementation first - DO NOT REMOVE base.Initialize(jobParam); } #endregion }
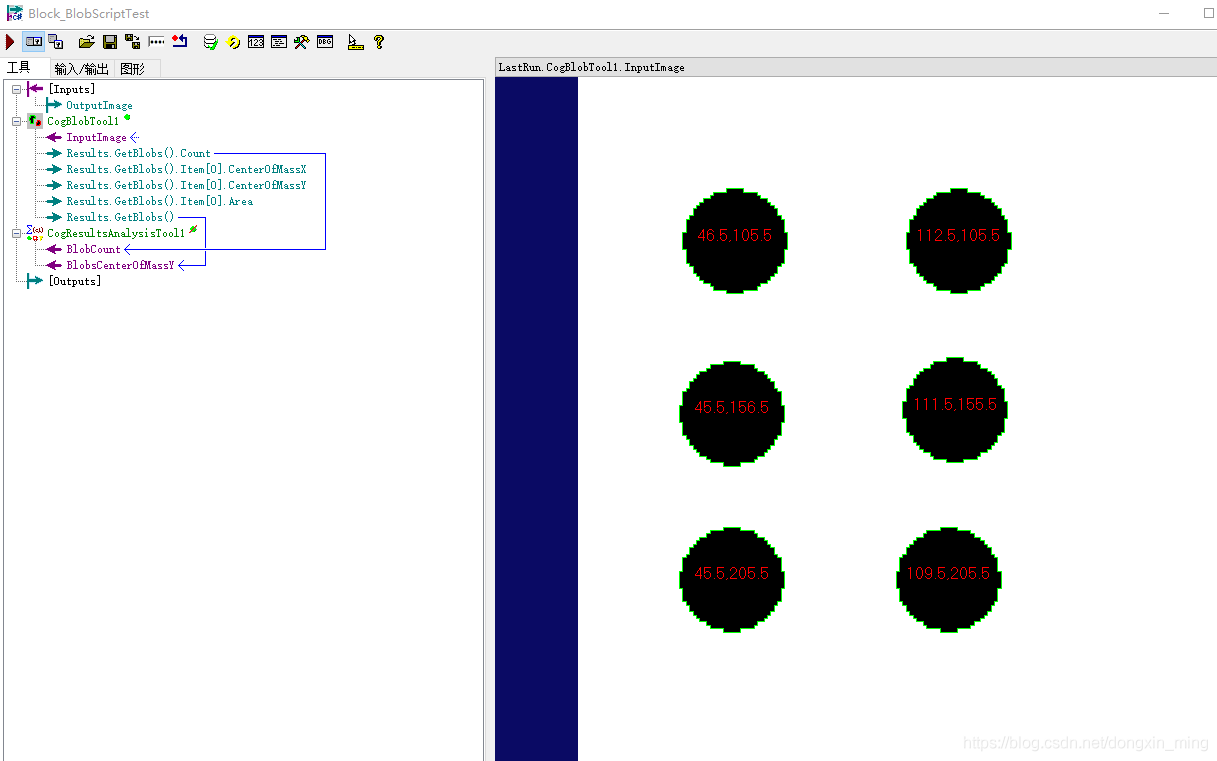
3.2 toolBlock脚本使用实例-----显示Blob区域的中心坐标于当前Blob区域
toolBlock脚本的应用最为广泛,用于控制工具的运行逻辑,修改生成的record,拓展数据逻辑等。本例以最简单的方式介绍toolBloc脚本使用方法,本例的具体应用为在各个独立的Blob区域显示其中心坐标值。
在进行脚本编辑之前,根据用户需要添加程序集以及命名空间 ,添加引用程序集的具体过程如下图所示:
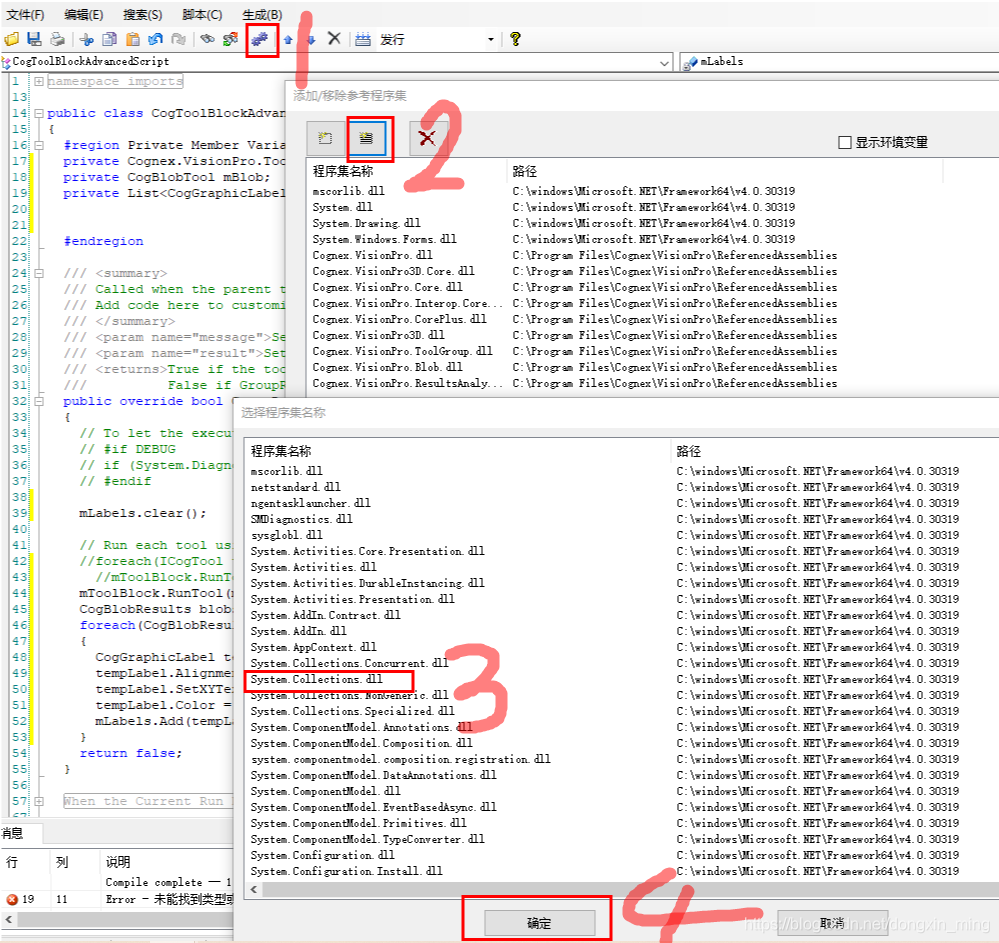
在编写C#toolBlock脚本时,其常规流程为:
step1. 根据需求添加程序集以及命名空间
step2. 声明对应toolBlock的相关变量以及用户自定义变量
step3. 在Initialize()函数中获取toolBlock中工具的引用
step4. 在GroupRun()方法中通过工具变量控制工具的执行顺序以及获取所需用户数据
step5. 修改Record得到用户所需效果
//==========================step1=================================== #region namespace imports using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Drawing; using System.IO; using System.Windows.Forms; using Cognex.VisionPro; using Cognex.VisionPro.ToolBlock; using Cognex.VisionPro3D; using Cognex.VisionPro.Blob; using Cognex.VisionPro.ResultsAnalysis; #endregion public class CogToolBlockAdvancedScript : CogToolBlockAdvancedScriptBase { //==========================step2=================================== #region Private Member Variables private Cognex.VisionPro.ToolBlock.CogToolBlock mToolBlock; private CogBlobTool mBlob; private List<CogGraphicLabel> mLabels; #endregion /// <summary> /// Called when the parent tool is run. /// Add code here to customize or replace the normal run behavior. /// </summary> /// <param name="message">Sets the Message in the tool's RunStatus.</param> /// <param name="result">Sets the Result in the tool's RunStatus</param> /// <returns>True if the tool should run normally, /// False if GroupRun customizes run behavior</returns> public override bool GroupRun(ref string message, ref CogToolResultConstants result) { // To let the execution stop in this script when a debugger is attached, uncomment the following lines. // #if DEBUG // if (System.Diagnostics.Debugger.IsAttached) System.Diagnostics.Debugger.Break(); // #endif //==========================step4=================================== mLabels.Clear(); // Run each tool using the RunTool function //foreach(ICogTool tool in mToolBlock.Tools) //mToolBlock.RunTool(tool, ref message, ref result); mToolBlock.RunTool(mBlob, ref message, ref result); CogBlobResultCollection blobs = mBlob.Results.GetBlobs(); foreach(CogBlobResult blob in blobs) { CogGraphicLabel tempLabel = new CogGraphicLabel(); tempLabel.Alignment = CogGraphicLabelAlignmentConstants.BaselineCenter; tempLabel.SetXYText(blob.CenterOfMassX, blob.CenterOfMassY, Convert.ToString(blob.CenterOfMassX)+","+Convert.ToString(blob.CenterOfMassY)); tempLabel.Color = CogColorConstants.Red; mLabels.Add(tempLabel); } return false; } #region When the Current Run Record is Created /// <summary> /// Called when the current record may have changed and is being reconstructed /// </summary> /// <param name="currentRecord"> /// The new currentRecord is available to be initialized or customized.</param> public override void ModifyCurrentRunRecord(Cognex.VisionPro.ICogRecord currentRecord) { } #endregion #region When the Last Run Record is Created /// <summary> /// Called when the last run record may have changed and is being reconstructed /// </summary> /// <param name="lastRecord"> /// The new last run record is available to be initialized or customized.</param> public override void ModifyLastRunRecord(Cognex.VisionPro.ICogRecord lastRecord) { //==========================step5=================================== foreach(CogGraphicLabel label in mLabels) { mToolBlock.AddGraphicToRunRecord(label, lastRecord, "CogBlobTool1.InputImage"," "); } } #endregion #region When the Script is Initialized /// <summary> /// Perform any initialization required by your script here /// </summary> /// <param name="host">The host tool</param> public override void Initialize(Cognex.VisionPro.ToolGroup.CogToolGroup host) { // DO NOT REMOVE - Call the base class implementation first - DO NOT REMOVE base.Initialize(host); // Store a local copy of the script host //==========================step3=================================== this.mToolBlock = ((Cognex.VisionPro.ToolBlock.CogToolBlock)(host)); mBlob = this.mToolBlock.Tools["CogBlobTool1"] as CogBlobTool; mLabels = new List<CogGraphicLabel>(); } #endregion }
效果图为:
四、脚本进阶
4.1 脚本是“插件”程序集
无论你是通过Job脚本、ToolGroup脚本还是ToolBlock脚本拓展QuickBuild程序功能时,实际上是完善了继承于某一接口的脚本类(继承于CogToolGroupBaseScript、CogJobBaseScript或者CogToolBlockAdvancedScriptBase类),在退出脚本编辑环境时QuickBuild对你完善的子类进行编译,如果出现语法错误会报错提示,在语法错误改正前当前脚本的所有内容都不会被调用,因为没有通过编译。如果出现逻辑错误不会提示,需要在VS环境下进行调试,调试方法后续会详细介绍。QuickBuild程序运行时通过接口实现对脚本子类成员函数的调用,从而将脚本函数的拓展功能进行实现。
关于脚本,你还需要明白以下几点:
用户在脚本中编写的代码会成为VisionPro程序的一部分,其中的bug也不可避免影响到VisionPro 的运行。
用户实现的脚本类会被编译为程序集加载到内存当中,而且每次对脚本进行编辑之后会重新编译,但是旧版本的程序集会一致在内存中直到你重新启动QuickBuild,因此频繁修改脚本会增加一点点的内存消耗。
脚本程序集被加载到内存之后,VisionPro会创建一个该脚本类的接口对象。脚本重新编辑之后接口对象会释放Dispose之前对象,运行GC进行垃圾回收,创建新脚本类的接口实例。
在进行脚本编辑时,如果脚本内容比较多,最好经常进行保存,保存时需要退出脚本编辑环境对整个QuickBuild工程进保存。补充一点,在QuickBuild环境下进行工具编辑时亦需要进行随手保存,工具Block误删除之后好像是无法恢复的只有退出QuickBuild时选择不保存,前提是你误删除之前刚好保存过,惨痛的经历已不止一次。
4.2 脚本实现事件与委托
事件响应函数中要增加异常处理机制(Try …Catch),否则容易导致VisionPro运行出现异常;
不要在事件处理函数中产生当前的事件,否则会造成无限循环
重写实现Dispose(),取消事件注册。脚本每次修改退出后都会进行编译,运行时重新注册事件,如果没有在Dispose总取消注册会造成多次注册。
当前事件的响应函数可能不止你在脚本中实现,在VisionPro内部机制中可能也有实现,这些事件的响应函数执行顺序是不确定的。
备注:但又多个Tool BLock或多个Tool Group时脚本中的写法:
一般来说,搭建工程的toolBlock与ToolGroup的数量是明确已知的,如果你用了3个Block就声明3个对应的变量。 声明: private CogToolGroup mToolGroup1; private CogToolGroup mToolGroup2; private CogToolGroup mToolGroup3; 初始化: public override void Initialize(CogToolGroup host) { base.Initialize(host); mToolGroup1= host.Tools["CogToolGroup1"] as CogToolGroup; mToolGroup2= host.Tools["CogToolGroup2"] as CogToolGroup; mToolGroup3= host.Tools["CogToolGroup3"] as CogToolGroup; } public override bool GroupRun(ref string message, ref CogToolResultConstants result) { //此处为默认遍历 for (Int32 toolIdx = 0; toolIdx < toolGroup.Tools.Count; toolIdx++) toolGroup.RunTool(toolGroup.Tools[toolIdx], ref message, ref result); //添加自定义访问 toolGroup.RunTool(mToolGroup1, ref message, ref result); return false; }
------------------------------------------------------------
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「一直在模仿,从没有超越」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/dongxin_ming/article/details/104932352



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号