外微分 全微分 极限 连续 可导 可微






判别可微方法


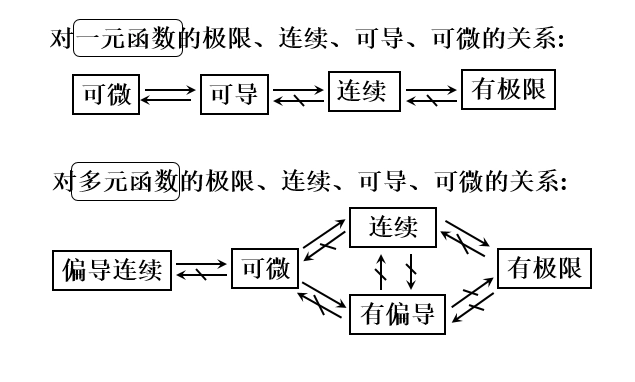
外微分_百度百科 https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E5%A4%96%E5%BE%AE%E5%88%86/1802695?fr=aladdin
The exterior derivative of a differential form of degree k is a differential form of degree k + 1.
If f is a smooth function (a 0-form), then the exterior derivative of f is the differential of f . That is, df is the unique 1-form such that for every smooth vector field X, df (X) = dX f , where dX f is the directional derivative of f in the direction of X.
There are a variety of equivalent definitions of the exterior derivative of a general k-form.
In terms of axioms
The exterior derivative is defined to be the unique ℝ-linear mapping from k-forms to (k + 1)-forms satisfying the following properties:
- df is the differential of f for smooth functions f .
- d(df ) = 0 for any smooth function f .
- d(α ∧ β) = dα ∧ β + (−1)p (α ∧ dβ) where α is a p-form. That is to say, d is an antiderivation of degree 1 on the exterior algebra of differential forms.
The second defining property holds in more generality: in fact, d(dα) = 0 for any k-form α; more succinctly, d2 = 0. The third defining property implies as a special case that if f is a function and α a k-form, then d( fα) = d( f ∧ α) = df ∧ α + f ∧ dα because functions are 0-forms, and scalar multiplication and the exterior product are equivalent when one of the arguments is a scalar.



