What’s New in MySQL 8.0? (Generally Available) 新特性
CATS事务调度算法
CATS(Contention Aware Transaction Schedule)是MySQL 8.0的一个新特性,相关论文发表在VLDB 2018。它的作用是在高冲突场景下,一个事务在释放一个锁后决定这把锁给哪个等待的事务。CATS将等待的事务按照权重排序,权重最高的事务拥有最高的优先级获得等待的锁。事务的权重取决于等待这个事务的事务数量。换句话说,一个事务有越多的等待事务,那么它获取锁的优先级越高。
We proudly announce General Availability of MySQL 8.0. Download now! MySQL 8.0 is an extremely exciting new version of the world’s most popular open source database with improvements across the board. Some key enhancements include:
- SQL Window functions, Common Table Expressions, NOWAIT and SKIP LOCKED, Descending Indexes, Grouping, Regular Expressions, Character Sets, Cost Model, and Histograms.
- JSON Extended syntax, new functions, improved sorting, and partial updates. With JSON table functions you can use the SQL machinery for JSON data.
- GIS Geography support. Spatial Reference Systems (SRS), as well as SRS aware spatial datatypes, spatial indexes, and spatial functions.
- Reliability DDL statements have become atomic and crash safe, meta-data is stored in a single, transactional data dictionary. Powered by InnoDB!
- Observability Significant enhancements to Performance Schema, Information Schema, Configuration Variables, and Error Logging.
- Manageability Remote management, Undo tablespace management, and new instant DDL.
- Security OpenSSL improvements, new default authentication, SQL Roles, breaking up the super privilege, password strength, and more.
- Performance InnoDB is significantly better at Read/Write workloads, IO bound workloads, and high contention “hot spot” workloads. Added Resource Group feature to give users an option optimize for specific workloads on specific hardware by mapping user threads to CPUs.
The above represents some of the highlights and I encourage you to further drill into the complete series of Milestone blog posts—8.0.0, 8.0.1, 8.0.2, 8.0.3, and 8.0.4 —and even further down in to the individual worklogs with their specifications and implementation details. Or perhaps you prefer to just look at the source code at github.com/mysql.
Developer features
MySQL Developers want new features and MySQL 8.0 delivers many new and much requested features in areas such as SQL, JSON, Regular Expressions, and GIS. Developers also want to be able to store Emojis, thus UTF8MB4 is now the default character set in 8.0. Finally there are improvements in Datatypes, with bit-wise operations on BINARY datatypes and improved IPv6 and UUID functions.
SQL
Window Functions
MySQL 8.0 delivers SQL window functions. Similar to grouped aggregate functions, window functions perform some calculation on a set of rows, e.g. COUNT or SUM. But where a grouped aggregate collapses this set of rows into a single row, a window function will perform the aggregation for each row in the result set.
Window functions come in two flavors: SQL aggregate functions used as window functions and specialized window functions. This is the set of aggregate functions in MySQL that support windowing: COUNT, SUM, AVG, MIN, MAX, BIT_OR, BIT_AND, BIT_XOR, STDDEV_POP (and its synonyms STD, STDDEV), STDDEV_SAMP, VAR_POP (and its synonym VARIANCE) and VAR_SAMP. The set of specialized window functions are: RANK, DENSE_RANK, PERCENT_RANK, CUME_DIST, NTILE, ROW_NUMBER, FIRST_VALUE, LAST_VALUE, NTH_VALUE, LEAD and LAG
Support for window functions (a.k.a. analytic functions) is a frequent user request. Window functions have long been part of standard SQL (SQL 2003). See blog post by Dag Wanvik here as well as blog post by Guilhem Bichot here.
Common Table Expression
MySQL 8.0 delivers [Recursive] Common Table Expressions (CTEs). Non-recursive CTEs can be explained as “improved derived tables” as it allow the derived table to be referenced more than once. A recursive CTE is a set of rows which is built iteratively: from an initial set of rows, a process derives new rows, which grow the set, and those new rows are fed into the process again, producing more rows, and so on, until the process produces no more rows. CTE is a commonly requested SQL feature, see for example feature request 16244 and 32174 . See blog posts by Guilhem Bichot here, here, here, and here.
NOWAIT and SKIP LOCKED
MySQL 8.0 delivers NOWAIT and SKIP LOCKED alternatives in the SQL locking clause. Normally, when a row is locked due to an UPDATEor a SELECT ... FOR UPDATE, any other transaction will have to wait to access that locked row. In some use cases there is a need to either return immediately if a row is locked or ignore locked rows. A locking clause using NOWAIT will never wait to acquire a row lock. Instead, the query will fail with an error. A locking clause using SKIP LOCKED will never wait to acquire a row lock on the listed tables. Instead, the locked rows are skipped and not read at all. NOWAIT and SKIP LOCKED are frequently requested SQL features. See for example feature request 49763 . We also want to say thank you to Kyle Oppenheim for his code contribution! See blog post by Martin Hansson here.
Descending Indexes
MySQL 8.0 delivers support for indexes in descending order. Values in such an index are arranged in descending order, and we scan it forward. Before 8.0, when a user create a descending index, we created an ascending index and scanned it backwards. One benefit is that forward index scans are faster than backward index scans. Another benefit of a real descending index is that it enables us to use indexes instead of filesort for an ORDER BY clause with mixed ASC/DESC sort key parts. Descending Indexes is a frequently requested SQL feature. See for example feature request 13375 . See blog post by Chaithra Gopalareddy here.
GROUPING
MySQL 8.0 delivers GROUPING(), SQL_FEATURE T433. The GROUPING() function distinguishes super-aggregate rows from regular grouped rows. GROUP BY extensions such as ROLLUP produce super-aggregate rows where the set of all values is represented by null. Using the GROUPING() function, you can distinguish a null representing the set of all values in a super-aggregate row from a NULL in a regular row. GROUPING is a frequently requested SQL feature. See feature requests 3156 and 46053. Thank you to Zoe Dong and Shane Adams for code contributions in feature request 46053 ! See blog post by Chaithra Gopalareddy here.
Optimizer Hints
In 5.7 we introduced a new hint syntax for optimizer hints. With the new syntax, hints can be specified directly after the SELECT | INSERT | REPLACE | UPDATE | DELETE keywords in an SQL statement, enclosed in /*+ */ style comments. (See 5.7 blog post by Sergey Glukhov here). In MySQL 8.0 we complete the picture by fully utilizing this new style:
- MySQL 8.0 adds hints for
INDEX_MERGEandNO_INDEX_MERGE. This allows the user to control index merge behavior for an individual query without changing the optimizer switch. - MySQL 8.0 adds hints for
JOIN_FIXED_ORDER,JOIN_ORDER,JOIN_PREFIX, andJOIN_SUFFIX. This allows the user to control table order for the join execution. - MySQL 8.0 adds a hint called
SET_VAR. TheSET_VARhint will set the value for a given system variable for the next statement only. Thus the value will be reset to the previous value after the statement is over. See blog post by Sergey Glukhov here.
We prefer the new style of optimizer hints as preferred over the old-style hints and setting of optimizer_switch values. By not being inter-mingled with SQL, the new hints can be injected in many places in a query string. They also have clearer semantics in being a hint (vs directive).
JSON
MySQL 8.0 adds new JSON functions and improves performance for sorting and grouping JSON values.
Extended Syntax for Ranges in JSON path expressions
MySQL 8.0 extends the syntax for ranges in JSON path expressions. For example SELECT JSON_EXTRACT('[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]', '$[1 to 3]'); results in [2, 3, 4]. The new syntax introduced is a subset of the SQL standard syntax, described in SQL:2016, 9.39 SQL/JSON path language: syntax and semantics. See also Bug#79052 reported by Roland Bouman.
JSON Table Functions
MySQL 8.0 adds JSON table functions which enables the use of the SQL machinery for JSON data. JSON_TABLE() creates a relational view of JSON data. It maps the result of a JSON data evaluation into relational rows and columns. The user can query the result returned by the function as a regular relational table using SQL, e.g. join, project, and aggregate.
JSON Aggregation Functions
MySQL 8.0 adds the aggregation functions JSON_ARRAYAGG() to generate JSON arrays and JSON_OBJECTAGG() to generate JSON objects . This makes it possible to combine JSON documents in multiple rows into a JSON array or a JSON object. See blog post by Catalin Besleaga here.
JSON Merge Functions
The JSON_MERGE_PATCH() function implements the semantics of JavaScript (and other scripting languages) specified by RFC7396, i.e. it removes duplicates by precedence of the second document. For example, JSON_MERGE('{"a":1,"b":2 }','{"a":3,"c":4 }'); #returns {"a":3,"b":2,"c":4}.
The JSON_MERGE_PRESERVE() function has the semantics of JSON_MERGE() implemented in MySQL 5.7 which preserves all values, for example JSON_MERGE('{"a": 1,"b":2}','{"a":3,"c":4}'); # returns {"a":[1,3],"b":2,"c":4}.
The existing JSON_MERGE() function is deprecated in MySQL 8.0 to remove ambiguity for the merge operation. See also proposal in Bug#81283 and blog post by Morgan Tocker here.
JSON Pretty Function
MySQL 8.0 adds a JSON_PRETTY() function in MySQL. The function accepts either a JSON native data-type or string representation of JSON and returns a JSON formatted string in a human-readable way with new lines and indentation.
JSON Size Functions
MySQL 8.0 adds JSON functions related to space usage for a given JSON object. The JSON_STORAGE_SIZE() returns the actual size in bytes for a JSON datatype. The JSON_STORAGE_FREE() returns the free space of a JSON binary type in bytes, including fragmentation and padding saved for inplace update.
JSON Improved Sorting
MySQL 8.0 gives better performance for sorting/grouping JSON values by using variable length sort keys. Preliminary benchmarks shows from 1.2 to 18 times improvement in sorting, depending on use case.
JSON Partial Update
MySQL 8.0 adds support for partial update for the JSON_REMOVE(), JSON_SET() and JSON_REPLACE() functions. If only some parts of a JSON document are updated, we want to give information to the handler about what was changed, so that the storage engine and replication don’t need to write the full document. In a replicated environment, it cannot be guaranteed that the layout of a JSON document is exactly the same on the slave and the master, so the physical diffs cannot be used to reduce the network I/O for row-based replication. Thus, MySQL 8.0 provides logical diffs that row-based replication can send over the wire and reapply on the slave. See blog post by Knut Anders Hatlen here.
GIS
MySQL 8.0 delivers geography support. This includes meta-data support for Spatial Reference System (SRS), as well as SRS aware spatial datatypes, spatial indexes, and spatial functions. In short, MySQL 8.0 understands latitude and longitude coordinates on the earth’s surface and can, for example, correctly calculate the distances between two points on the earths surface in any of the about 5000 supported spatial reference systems.
Spatial Reference System (SRS)
The ST_SPATIAL_REFERENCE_SYSTEMS information schema view provides information about available spatial reference systems for spatial data. This view is based on the SQL/MM (ISO/IEC 13249-3) standard. Each spatial reference system is identified by an SRID number. MySQL 8.0 ships with about 5000 SRIDs from the EPSG Geodetic Parameter Dataset, covering georeferenced ellipsoids and 2d projections (i.e. all 2D spatial reference systems).
SRID aware spatial datatypes
Spatial datatypes can be attributed with the spatial reference system definition, for example with SRID 4326 like this: CREATE TABLE t1 (g GEOMETRY SRID 4326); The SRID is here a SQL type modifier for the GEOMETRY datatype. Values inserted into a column with an SRID property must be in that SRID. Attempts to insert values with other SRIDs results in an exception condition being raised. Unmodified types, i.e., types with no SRID specification, will continue to accept all SRIDs, as before.
MySQL 8.0 adds the INFORMATION_SCHEMA.ST_GEOMETRY_COLUMNS view as specified in SQL/MM Part 3, Sect. 19.2. This view will list all GEOMETRY columns in the MySQL instance and for each column it will list the standard SRS_NAME , SRS_ID , and GEOMETRY_TYPE_NAME.
SRID aware spatial indexes
Spatial indexes can be created on spatial datatypes. Columns in spatial indexes must be declared NOT NULL. For example like this: CREATE TABLE t1 (g GEOMETRY SRID 4326 NOT NULL, SPATIAL INDEX(g));
Columns with a spatial index should have an SRID type modifier to allow the optimizer to use the index. If a spatial index is created on a column that doesn’t have an SRID type modifier, a warning is issued.
SRID aware spatial functions
MySQL 8.0 extends spatial functions such as ST_Distance() and ST_Length() to detect that its parameters are in a geographic (ellipsoidal) SRS and to compute the distance on the ellipsoid. So far, ST_Distance and spatial relations such as ST_Within, ST_Intersects, ST_Contains, ST_Crosses, etc. support geographic computations. The behavior of each ST function is as defined in SQL/MM Part 3 Spatial.
Character Sets
MySQL 8.0 makes UTF8MB4 the default character set. SQL performance – such as sorting UTF8MB4 strings – has been improved by a factor of 20 in 8.0 as compared to 5.7. UTF8MB4 is the dominating character encoding for the web, and this move will make life easier for the vast majority of MySQL users.
- The default character set has changed from
latin1toutf8mb4and the default collation has changed fromlatin1_swedish_citoutf8mb4_800_ci_ai. - The changes in defaults applies to libmysql and server command tools as well as the server itself.
- The changes are also reflected in MTR tests, running with new default charset.
- The collation weight and case mapping are based on Unicode 9.0.0 , announced by the Unicode committee on Jun 21, 2016.
- The 21 language specific case insensitive collations available for latin1 (MySQL legacy) have been implemented for
utf8mb4collations, for example the Czech collation becomes utf8mb4_cs_800_ai_ci. See complete list in WL#9108 . See blog post by Xing Zhang here . - Added support for case and accent sensitive collations. MySQL 8.0 supports all 3 levels of collation weight defined by DUCET (Default Unicode Collation Entry Table). See blog post by Xing Zhang here.
- Japanese
utf8mb4_ja_0900_as_cscollation forutf8mb4which sorts characters by using three levels’ weight. This gives the correct sorting order for Japanese. See blog post by Xing Zhang here. - Japanese with additional kana sensitive feature,
utf8mb4_ja_0900_as_cs_ks, where ‘ks’ stands for ‘kana sensitive’. See blog post by Xing Zhang here. - Changed all new collations, from Unicode 9.0.0 forward, to be
NO PADinstead ofPAD STRING, ie., treat spaces at the end of a string like any other character. This is done to improve consistency and performance. Older collations are left in place.
See also blog posts by Bernt Marius Johnsen here, here and here.
Datatypes
Bit-wise operations on binary data types
MySQL 8.0 extends the bit-wise operations (‘bit-wise AND’, etc) to also work with [VAR]BINARY/[TINY|MEDIUM|LONG]BLOB. Prior to 8.0 bit-wise operations were only supported for integers. If you used bit-wise operations on binaries the arguments were implicitly cast to BIGINT (64 bit) before the operation, thus possibly losing bits. From 8.0 and onward bit-wise operations work for all BINARYand BLOB data types, casting arguments such that bits are not lost.
IPV6 manipulation
MySQL 8.0 improves the usability of IPv6 manipulation by supporting bit-wise operations on BINARY data types. In MySQL 5.6 we introduced the INET6_ATON() and INET6_NTOA() functions which convert IPv6 addresses between text form like 'fe80::226:b9ff:fe77:eb17' and VARBINARY(16). However, until now we could not combine these IPv6 functions with bit-wise operations since such operations would – wrongly – convert output to BIGINT. For example, if we have an IPv6 address and want to test it against a network mask, we can now use INET6_ATON(address) because
& INET6_ATON(network)INET6_ATON() correctly returns the VARBINARY(16) datatype (128 bits). See blog post by Catalin Besleaga here.
UUID manipulations
MySQL 8.0 improves the usability of UUID manipulations by implementing three new SQL functions: UUID_TO_BIN(), BIN_TO_UUID(), and IS_UUID(). The first one converts from UUID formatted text to VARBINARY(16), the second one from VARBINARY(16) to UUID formatted text, and the last one checks the validity of an UUID formatted text. The UUID stored as a VARBINARY(16) can be indexed using functional indexes. The functions UUID_TO_BIN() and UUID_TO_BIN() can also shuffle the time-related bits and move them at the beginning making it index friendly and avoiding the random inserts in the B-tree, this way reducing the insert time. The lack of such functionality has been mentioned as one of the drawbacks of using UUID’s. See blog post by Catalin Besleaga here.
Cost Model
Query Optimizer Takes Data Buffering into Account
MySQL 8.0 chooses query plans based on knowledge about whether data resides in-memory or on-disk. This happens automatically, as seen from the end user there is no configuration involved. Historically, the MySQL cost model has assumed data to reside on spinning disks. The cost constants associated with looking up data in-memory and on-disk are now different, thus, the optimizer will choose more optimal access methods for the two cases, based on knowledge of the location of data. See blog post by Øystein Grøvlen here.
Optimizer Histograms
MySQL 8.0 implements histogram statistics. With Histograms, the user can create statistics on the data distribution for a column in a table, typically done for non-indexed columns, which then will be used by the query optimizer in finding the optimal query plan. The primary use case for histogram statistics is for calculating the selectivity (filter effect) of predicates of the form “COLUMN operator CONSTANT”.
The user creates a histogram by means of the ANALYZE TABLE syntax which has been extended to accept two new clauses: UPDATE HISTOGRAM ON column [, column] [WITH n BUCKETS] and DROP HISTOGRAM ON column [, column]. The number of buckets is optional, the default is 100. The histogram statistics are stored in the dictionary table “column_statistics” and accessible through the view information_schema.COLUMN_STATISTICS. The histogram is stored as a JSON object due to the flexibility of the JSON datatype. ANALYZE TABLE will automatically decide whether to sample the base table or not, based on table size. It will also decide whether to build a singleton or a equi-height histogram based on the data distribution and the number of buckets specified. See blog post by Erik Frøseth here.
Regular Expressions
MySQL 8.0 supports regular expressions for UTF8MB4 as well as new functions like REGEXP_INSTR(), REGEXP_LIKE(), REGEXP_REPLACE(), and REGEXP_SUBSTR(). The system variables regexp_stack_limit (default 8000000 bytes) and regexp_time_limit(default 32 steps) have been added to control the execution. The REGEXP_REPLACE() function is one of the most requested features by the MySQL community, for example see feature request reported as BUG #27389 by Hans Ginzel. See also blog posts by Martin Hansson here and Bernt Marius Johnsen here.
Dev Ops features
Dev Ops care about operational aspects of the database, typically about reliability, availability, performance, security, observability, and manageability. High Availability comes with MySQL InnoDB Cluster and MySQL Group Replication which will be covered by a separate blog post. Here follows what 8.0 brings to the table in the other categories.
Reliability
MySQL 8.0 increases the overall reliability of MySQL because :
- MySQL 8.0 stores its meta-data into InnoDB, a proven transactional storage engine. System tables such as Users and Privileges as well as Data Dictionary tables now reside in InnoDB.
- MySQL 8.0 eliminates one source of potential inconsistency. In 5.7 and earlier versions there are essentially two data dictionaries, one for the Server layer and one for the InnoDB layer, and these can get out of sync in some crashing scenarios. In 8.0 there is only one data dictionary.
- MySQL 8.0 ensures atomic, crash safe DDL. With this the user is guaranteed that any DDL statement will either be executed fully or not at all. This is particularly important in a replicated environment, otherwise there can be scenarios where masters and slaves (nodes) get out of sync, causing data-drift.
This work is done in the context of the new, transactional data dictionary. See blog posts by Staale Deraas here and here.
Observability
Information Schema (speed up)
MySQL 8.0 reimplements Information Schema. In the new implementation the Information Schema tables are simple views on data dictionary tables stored in InnoDB. This is by far more efficient than the old implementation with up to 100 times speedup. This makes Information Schema practically usable by external tooling. See blog posts by Gopal Shankar here and here , and the blog post by Ståle Deraas here.
Performance Schema (speed up)
MySQL 8.0 speeds up performance schema queries by adding more than 100 indexes on performance schema tables. The indexes on performance schema tables are predefined. They cannot be deleted,added or altered. A performance schema index is implemented as a filtered scan across the existing table data, rather than a traversal through a separate data structure. There are no B-trees or hash tables to be constructed, updated or otherwise managed. Performance Schema tables indexes behave like hash indexes in that a) they quickly retrieve the desired rows, and b) do not provide row ordering, leaving the server to sort the result set if necessary. However, depending on the query, indexes obviate the need for a full table scan and will return a considerably smaller result set. Performance schema indexes are visible with SHOW INDEXES and are represented in the EXPLAINoutput for queries that reference indexed columns. See comment from Simon Mudd. See blog post by Marc Alff here.
Configuration Variables
MySQL 8.0 adds useful information about configuration variables, such as the variable name, min/max values, where the current value came from, who made the change and when it was made. This information is found in a new performance schema table called variables_info. See blog post by Satish Bharathy here.
Client Error Reporting – Message Counts
MySQL 8.0 makes it possible to look at aggregated counts of client error messages reported by the server. The user can look at statistics from 5 different tables: Global count, summary per thread, summary per user, summary per host, or summary per account. For each error message the user can see the number of errors raised, the number of errors handled by the SQL exception handler, “first seen” timestamp, and “last seen” timestamp. Given the right privileges the user can either SELECT from these tables or TRUNCATE to reset statistics. See blog post by Mayank Prasad here.
Statement Latency Histograms
MySQL 8.0 provides performance schema histograms of statements latency, for the purpose of better visibility of query response times. This work also computes “P95”, “P99” and “P999” percentiles from collected histograms. These percentiles can be used as indicators of quality of service. See blog post by Frédéric Descamps here.
Data Locking Dependencies Graph
MySQL 8.0 instruments data locks in the performance schema. When transaction A is locking row R, and transaction B is waiting on this very same row, B is effectively blocked by A. The added instrumentation exposes which data is locked (R), who owns the lock (A), and who is waiting for the data (B). See blog post by Frédéric Descamps here.
Digest Query Sample
MySQL 8.0 makes some changes to the events_statements_summary_by_digest performance schema table to capture a full example query and some key information about this query example. The column QUERY_SAMPLE_TEXT is added to capture a query sample so that users can run EXPLAIN on a real query and to get a query plan. The column QUERY_SAMPLE_SEEN is added to capture the query sample timestamp. The column QUERY_SAMPLE_TIMER_WAIT is added to capture the query sample execution time. The columns FIRST_SEEN and LAST_SEEN have been modified to use fractional seconds. See blog post by Frédéric Descamps here.
Meta-data about Instruments
MySQL 8.0 adds meta-data such as properties, volatility, and documentation to the performance schema table setup_instruments. This read only meta-data act as online documentation for instruments, to be looked at by users or tools. See blog post by Frédéric Descamps here.
Error Logging
MySQL 8.0 delivers a major overhaul of the MySQL error log. From a software architecture perspective the error log is made a component in the new service infrastructure. This means that advanced users can write their own error log implementation if desired. Most users will not want to write their own error log implementation but still want some flexibility in what to write and where to write it. Hence, 8.0 offers users facilities to add sinks (where) and filters (what). MySQL 8.0 implements a filtering service (API) and a default filtering service implementation (component). Filtering here means to suppress certain log messages (selection) and/or fields within a given log message (projection). MySQL 8.0 implements a log writer service (API) and a default log writer service implementation (component). Log writers accept a log event and write it to a log. This log can be a classic file, syslog, EventLog and a new JSON log writer.
By default, without any configuration, MySQL 8.0 delivers many out-of-the-box error log improvements such as:
- Error numbering: The format is a number in the 10000 series preceded by “MY-“, for example “MY-10001”. Error numbers will be stable in a GA release, but the corresponding error texts are allowed to change (i.e. improve) in maintenance releases.
- System messages: System messages are written to the error log as [System] instead of [Error], [Warning], [Note]. [System] and [Error] messages are printed regardless of verbosity and cannot be suppressed. [System] messages are only used in a few places, mainly associated with major state transitions such as starting or stopping the server.
- Reduced verbosity: The default of log_error_verbosity changes from 3 (Notes) to 2 (Warning). This makes MySQL 8.0 error log less verbose by default.
- Source Component: Each message is annotated with one of three values [Server], [InnoDB], [Replic] showing which sub-system the message is coming from.
This is what is written to the error log in 8.0 GA after startup :
|
1
2
3
4
|
2018-03-08T10:14:29.289863Z 0 [System] [MY-010116] [Server] /usr/sbin/mysqld (mysqld 8.0.5) starting as process 8063
2018-03-08T10:14:29.745356Z 0 [Warning] [MY-010068] [Server] CA certificate ca.pem is self signed.
2018-03-08T10:14:29.765159Z 0 [System] [MY-010931] [Server] /usr/sbin/mysqld: ready for connections. Version: '8.0.5' socket: '/tmp/mysql.sock' port: 3306 Source distribution.
2018-03-08T10:16:51.343979Z 0 [System] [MY-010910] [Server] /usr/sbin/mysqld: Shutdown complete (mysqld 8.0.5) Source distribution.
|
The introduction of error numbering in the error log allows MySQL to improve an error text in upcoming maintenance releases (if needed) while keeping the error number (ID) unchanged. Error numbers also act as the basis for filtering/suppression and internationalization/localization.
Manageability
INVISIBLE Indexes
MySQL 8.0 adds the capability of toggling the visibility of an index (visible/invisible). An invisible index is not considered by the optimizer when it makes the query execution plan. However, the index is still maintained in the background so it is cheap to make it visible again. The purpose of this is for a DBA / DevOp to determine whether an index can be dropped or not. If you suspect an index of not being used you first make it invisible, then monitor query performance, and finally remove the index if no query slow down is experienced. This feature has been asked for by many users, for example through Bug#70299. See blog post by Martin Hansson here.
Flexible Undo Tablespace Management
MySQL 8.0 gives the user full control over Undo tablespaces, i.e. how many tablespaces, where are they placed, and how many rollback segments in each.
- No more Undo log in the System tablespace. Undo log is migrated out of the System tablespace and into Undo tablespaces during upgrade. This gives an upgrade path for existing 5.7 installation using the system tablespace for undo logs.
- Undo tablespaces can be managed separately from the System tablespace. For example, Undo tablespaces can be put on fast storage.
- Reclaim space taken by unusually large transactions (online). A minimum of two Undo tablespaces are created to allow for tablespace truncation. This allows InnoDB to shrink the undo tablespace because one Undo tablespace can be active while the other is truncated.
- More rollback segments results in less contention. The user might choose to have up to 127 Undo tablespaces, each one having up to 128 rollback segments. More rollback segments mean that concurrent transactions are more likely to use separate rollback segments for their undo logs which results in less contention for the same resources.
See blog post by Kevin Lewis here.
SET PERSIST for global variables
MySQL 8.0 makes it possible to persist global, dynamic server variables. Many server variables are both GLOBAL and DYNAMIC and can be reconfigured while the server is running. For example: SET GLOBAL sql_mode='STRICT_TRANS_TABLES'; However, such settings are lost upon a server restart.
This work makes it possible to write SET PERSIST sql_mode='STRICT_TRANS_TABLES'; The effect is that the setting will survive a server restart. There are many usage scenarios for this functionality but most importantly it gives a way to manage server settings when editing the configuration files is inconvenient or not an option. For example in some hosted environments you don’t have file system access, all that you have is the ability to connect to one or more servers. As for SET GLOBAL you need the super privilege for SET PERSIST.
There is also the RESET PERSIST command. The RESET PERSIST command has the semantic of removing the configuration variable from the persist configuration, thus converting it to have similar behavior as SET GLOBAL.
MySQL 8.0 allows SET PERSIST to set most read-only variables as well, the new values will here take effect at the next server restart. Note that a small subset of read-only variables are left intentionally not settable. See blog post by Satish Bharathy here.
Remote Management
MySQL 8.0 implements an SQL RESTART command. The purpose is to enable remote management of a MySQL server over an SQL connection, for example to set a non-dynamic configuration variable by SET PERSIST followed by a RESTART. See blog post MySQL 8.0: changing configuration easily and cloud friendly ! by Frédéric Descamps.
Rename Tablespace (SQL DDL)
MySQL 8.0 implements ALTER TABLESPACE s1 RENAME TO s2; A shared/general tablespace is a user-visible entity which users can CREATE, ALTER, and DROP. See also Bug#26949, Bug#32497, and Bug#58006.
Rename Column (SQL DDL)
MySQL 8.0 implements ALTER TABLE ... RENAME COLUMN old_name TO new_name;This is an improvement over existing syntax ALTER TABLE <table_name> CHANGE … which requires re-specification of all the attributes of the column. The old/existing syntax has the disadvantage that all the column information might not be available to the application trying to do the rename. There is also a risk of accidental data type change in the old/existing syntax which might result in data loss.
Security features
New Default Authentication Plugin
MySQL 8.0 changes the default authentication plugin from mysql_native_password to caching_sha2_password. Correspondingly, libmysqlclient will use caching_sha2_password as the default authentication mechanism, too. The new caching_sha2_password combines better security (SHA2 algorithm) with high performance (caching). The general direction is that we recommend all users to use TLS/SSL for all their network communication. See blog post by Harin Vadodaria here.
OpenSSL by Default in Community Edition
MySQL 8.0 is unifying on OpenSSL as the default TLS/SSL library for both MySQL Enterprise Edition and MySQL Community Edition. Previously, MySQL Community Edition used YaSSL. Supporting OpenSSL in the MySQL Community Edition has been one of the most frequently requested features. See blog post by Frédéric Descamps here.
OpenSSL is Dynamically Linked
MySQL 8.0 is linked dynamically with OpenSSL. Seen from the MySQL Repository users perspective , the MySQL packages depends on the OpenSSL files provided by the Linux system at hand. By dynamically linking, OpenSSL updates can be applied upon availability without requiring a MySQL upgrade or patch. See blog post by Frédéric Descamps here.
Encryption of Undo and Redo log
MySQL 8.0 implements data-at-rest encryption of UNDO and REDO logs. In 5.7 we introduced Tablespace Encryption for InnoDB tables stored in file-per-table tablespaces. This feature provides at-rest encryption for physical tablespace data files. In 8.0 we extend this to include UNDO and REDO logs. See documentation here.
SQL roles
MySQL 8.0 implements SQL Roles. A role is a named collection of privileges. The purpose is to simplify the user access right management. One can grant roles to users, grant privileges to roles, create roles, drop roles, and decide what roles are applicable during a session. See blog post by Frédéric Descamps here.
Allow grants and revokes for PUBLIC
MySQL 8.0 introduces the configuration variable mandatory-roles which can be used for automatic assignment and granting of default roles when new users are created. Example: role1@%,role2,role3,role4@localhostactivate-all-roles-on-login is set to “ON”, all granted roles are always activated after the user has authenticated.
Breaking up the super privileges
MySQL 8.0 defines a set of new granular privileges for various aspects of what SUPER is used for in previous releases. The purpose is to limit user access rights to what is needed for the job at hand and nothing more. For example BINLOG_ADMIN, CONNECTION_ADMIN, and ROLE_ADMIN.
Authorization model to manage XA-transactions
MySQL 8.0 introduces a new system privilege XA_RECOVER_ADMIN which controls the capability to execute the statement XA RECOVER. An attempt to do XA RECOVER by a user who wasn’t granted the new system privilege XA_RECOVER_ADMIN will cause an error.
Password rotation policy
MySQL 8.0 introduces restrictions on password reuse. Restrictions can be configured at global level as well as individual user level. Password history is kept secure because it may give clues about habits or patterns used by individual users when they change their password. The password rotation policy comes in addition to other, existing mechanisms such as the password expiration policyand allowed password policy. See Password Management.
Slow down brute force attacks on user passwords
MySQL 8.0 introduces a delay in the authentication process based on consecutive unsuccessful login attempts. The purpose is to slow down brute force attacks on user passwords. It is possible to configure the number of consecutive unsuccessful attempts before the delay is introduced and the maximum amount of delay introduced.
Retire skip-grant-tables
MySQL 8.0 disallows remote connections when the server is started with –skip-grant-tables. See also Bug#79027 reported by Omar Bourja.
Add mysqld_safe-functionality to server
MySQL 8.0 implement parts of the logic currently found in the mysqld_safe script inside the server. The work improves server usability in some scenarios for example when using the --daemonize startup option. The work also make users less dependent upon the mysqld_safe script, which we hope to remove in the future. It also fixes Bug#75343 reported by Peter Laursen.
Performance
MySQL 8.0 comes with better performance for Read/Write workloads, IO bound workloads, and high contention “hot spot” workloads. In addition, the new Resource Group feature gives users an option to optimize for specific workloads on specific hardware by mapping user threads to CPUs.
Scaling Read/Write Workloads
Utilizing IO Capacity (Fast Storage)
fil_system_mutex global lock.Better Performance upon High Contention Loads (“hot rows”)
MySQL 8.0 significantly improves the performance for high contention workloads. A high contention workload occurs when multiple transactions are waiting for a lock on the same row in a table, causing queues of waiting transactions. Many real world workloads are not smooth over for example a day but might have bursts at certain hours (Pareto distributed). MySQL 8.0 deals much better with such bursts both in terms of transactions per second, mean latency, and 95th percentile latency. The benefit to the end user is better hardware utilization (efficiency) because the system needs less spare capacity and can thus run with a higher average load. The original patch was contributed by Jiamin Huang (Bug#84266). Please study the Contention-Aware Transaction Scheduling (CATS) algorithm and read the MySQL blog post by Jiamin Huang and Sunny Bains here.
Resource Groups
MySQL 8.0 introduces global Resource Groups to MySQL. With Resource Groups, DevOps/DBAs can manage the mapping between user/system threads and CPUs. This can be used to split workloads across CPUs to obtain better efficiency and/or performance in some use cases. Thus, Resource Groups adds a tool to the DBA toolbox, a tool which can help the DBA to increase hardware utilization or to increase query stability. As an example, with a Sysbench RW workload running on a Intel(R) Xeon (R) CPU E7-4860 2.27 GHz 40 cores-HT box we doubled the overall throughput by limiting the Write load to 10 cores. Resource Groups is a fairly advanced tool which requires skilled DevOps/DBA to be used effectively as effects will vary with type of load and with the hardware at hand.
Other Features
Better Defaults
In the MySQL team we pay close attention to the default configuration of MySQL, and aim for users to have the best out of the box experience possible. MySQL 8.0 has changed more than 30 default values to what we think are better values. See blog post New Defaults in MySQL 8.0. The motivation for this is outlined in a blog post by Mogan Tocker here.
Protocol
MySQL 8.0 adds an option to turn off metadata generation and transfer for resultsets. Constructing/parsing and sending/receiving resultset metadata consumes server, client and network resources. In some cases the metadata size can be much bigger than actual result data size and the metadata is just not needed. We can significantly speed up the query result transfer by completely disabling the generation and storage of these data. Clients can set the CLIENT_OPTIONAL_RESULTSET_METADATA flag if they do not want meta-data back with the resultset.
C Client API
MySQL 8.0 extends libmysql’s C API with a stable interface for getting replication events from the server as a stream of packets. The purpose is to avoid having to call undocumented APIs and package internal header files in order to implement binlog based programs like the MySQL Applier for Hadoop.
Memcached
MySQL 8.0 enhances the InnoDB Memcached functionalities with multiple get operations and support for range queries. We added support for the multiple get operation to further improve the read performance, i.e. the user can fetch multiple key value pairs in a single memcached query. Support for range queries has been requested by Yoshinori @ Facebook. With range queries, the user can specify a particular range, and fetch all the qualified values in this range. Both features can significantly reduce the number of roundtrips between the client and the server.
Persistent Autoinc Counters
MySQL 8.0 persists the AUTOINC counters by writing them to the redo log. This is a fix for the very old Bug#199. The MySQL recovery process will replay the redo log and ensure correct values of the AUTOINC counters. There won’t be any rollback of AUTOINCcounters. This means that database recovery will reestablish the last known counter value after a crash. It comes with the guarantee that the AUTOINC counter cannot get the same value twice. The counter is monotonically increasing, but note that there can be gaps (unused values). The lack of persistent AUTOINC has been seen as troublesome in the past, e.g. see Bug#21641reported by Stephen Dewey in 2006 or this blog post .
Summary
As shown above, MySQL 8.0 comes with a large set of new features and performance improvements. Download it from dev.mysql.com and try it out !
You can also upgrade an existing MySQL 5.7 to MySQL 8.0. In the process you might want to try our new Upgrade Checker that comes with the new MySQL Shell (mysqlsh). This utility will analyze your existing 5.7 server and tell you about potential 8.0 incompatibilities. Another good resource is the blog post Migrating to MySQL 8.0 without breaking old application by Frédéric Descamps.
In this blog post we have covered Server features. There is much more! We will also publish blog posts for other features such as Replication, Group Replication, InnoDB Cluster, Document Store, MySQL Shell, DevAPI, and DevAPI based Connectors (Connector/Node.js, Connector/Python, PHP, Connector/NET, Connector/ODBC, Connector/C++, and Connector/J).
That’s it for now, and thank you for using MySQL !
【Mysql】Mysq8.0新特性 - songguojun - 博客园 https://www.cnblogs.com/songgj/p/10658916.html
一.MySQL8.0简介
mysql8.0现在已经发布,2016-09-12第一个DM(development milestone)版本8.0.0发布。新的版本带来很多新功能和新特性,对性能也得到了很大对提升。官方表示 MySQL 8 比之前mysql版本有很大提升,它的速度是 MySQL 5.7 2 倍,如下图对比所示

mysql8.0官方文档: https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/
二.MySQL8.0新增的特性
mysql8.0新增的特性主要有以下几个方面:
1.账户与安全
1)用户创建和授权是分开的,并修改了默认的认证插件。
2)增加了密码重用策略,支持修改密码时要求用户输入当前密码。
3)支持角色功能。
提高了用户和密码管理的安全性,方便了权限的管理。
2.优化器索引
三种新的索引方式
1)支持隐藏索引,方便索引的维护和性能调试。
2)支持降序索引,提高了特定场景的查询性能。
3)支持函数索引,扩展了索引支持的数据类型,可以对更多的数据类型进行索引。
3.通用表表达式(Common Table Expressions:CTE)
1)非递归CTE,提高查询的性能和代码的可读性。
2)递归CTE,支持通过对数据遍历和递归的实现完成SQL实现强大复杂的功能。
4.窗口函数(Window Functions)
是一种新的查询方式。窗口函数有两类,一类上传统的聚合函数作为窗口函数使用,另一类是专用的窗口函数。可以实现复杂的数据分析能力。
5.InnoDB存储引擎增强
1)新的数据字典可以对元数据统一的管理,同时也提高了更好的查询性能和可靠性。
2)原子DDL的操作,提供了更加可靠的管理。
3)自增列的持久化,解决了长久以来自增列重复值的bug。
4)死锁检查控制,可以选择在高并发的场景中关闭,提高对高并发场景的性能。
5)锁定语句选项,可以根据不同业务需求来选择锁定语句级别。
6.JSON增强
新的运算符及JSON相关函数。
mysql8.0新特性更多可以查看这篇:https://mysqlserverteam.com/whats-new-in-mysql-8-0-generally-available/
二.本机操作环境
先看下本机mysql环境和状态
mysql> show variables like '%%version%';
+--------------------------+------------------------------+ | Variable_name | Value | +--------------------------+------------------------------+ | immediate_server_version | 999999 | | innodb_version | 8.0.16 | | original_server_version | 999999 | | protocol_version | 10 | | slave_type_conversions | | | tls_version | TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2 | | version | 8.0.16 | | version_comment | MySQL Community Server - GPL | | version_compile_machine | x86_64 | | version_compile_os | Linux | | version_compile_zlib | 1.2.11 | +--------------------------+------------------------------+
查看状态
mysql80>status -------------- mysql Ver 14.14 Distrib 5.7.26, for Linux (x86_64) using EditLine wrapper Connection id: 2 Current database: Current user: root@localhost SSL: Not in use Current pager: stdout Using outfile: '' Using delimiter: ; Server version: 5.7.26 MySQL Community Server (GPL) Protocol version: 10 Connection: Localhost via UNIX socket Server characterset: latin1 Db characterset: latin1 Client characterset: latin1 Conn. characterset: latin1 UNIX socket: /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock Uptime: 27 min 38 sec
三.MySQL8.0新特性
账户与安全变更:增加新的安全策略,增加角色功能。
1.创建用户和用户授权的命令是分开执行。
先看下mysql5.7是如何创建用户和授权的。
mysql5.7中查询默认用户,以下是mysql5.7中的默认的三个用户。
mysql5.7> select user,host from mysql.user; +---------------+-----------+ | user | host | +---------------+-----------+ | mysql.session | localhost | | mysql.sys | localhost | | root | localhost | +---------------+-----------+
mysq5.7grant可以完成用户创建和授权同时操作。
mysql> grant all privileges on *.* to 'song'@'%' identified by 'song@2019'; #创建新的用户并赋予在所有主机登陆及密码 mysql> select user,host from mysql.user; +---------------+-----------+ | user | host | +---------------+-----------+ | root | % | | song | % | | mysql.session | localhost | | mysql.sys | localhost | | root | localhost | +---------------+-----------+
mysql8.0创建用户和授权命令如下,分两步进行。
create user 'song'@'%' identified by 'Song@2019'; //创建用户 grant all privileges on *.* to 'song'@'%'; //授权
mysql8.0
mysql> select host,user from mysql.user; +-----------+------------------+ | host | user | +-----------+------------------+ | localhost | mysql.infoschema | | localhost | mysql.session | | localhost | mysql.sys | | localhost | root | +-----------+------------------+
创建用户
mysql> create user 'song'@'%' identified by 'song@2019'; mysql> select host,user from mysql.user; +-----------+------------------+ | host | user | +-----------+------------------+ | % | song | | localhost | mysql.infoschema | | localhost | mysql.session | | localhost | mysql.sys | | localhost | root |
授权
mysql> grant all privileges on *.* to 'song'@'%';
这样分两次的好处是语句的语义更加清晰点。
2.认证的插件更新
mysql8.0中默认的身份认证插件是caching_sha2_password,替代了之前的mysql_navtive_password,这个新的认证会更加安全。
通过系统变量查询,下面这是mysql5.7的,发现mysql5.7还是使用mysql_native_password这个插件。
mysql> show variables like 'default_authentication%'; +-------------------------------+-----------------------+ | Variable_name | Value | +-------------------------------+-----------------------+ | default_authentication_plugin | mysql_native_password | +-------------------------------+-----------------------+
看下mysq8.0
mysql> show variables like 'default_authentication%'; +-------------------------------+-----------------------+ | Variable_name | Value | +-------------------------------+-----------------------+ | default_authentication_plugin | caching_sha2_password | +-------------------------------+-----------------------+
也可以通过用户表user查看plugin这一列。
mysql> select user,host,plugin from mysql.user; +------------------+-----------+-----------------------+ | user | host | plugin | +------------------+-----------+-----------------------+ | root | % | caching_sha2_password | | mysql.infoschema | localhost | caching_sha2_password | | mysql.session | localhost | caching_sha2_password | | mysql.sys | localhost | caching_sha2_password | | root | localhost | caching_sha2_password | +------------------+-----------+-----------------------+
不过如果连接客户端比较老旧没有升级,在连接mysql8.0时候可能会认证错误。如果想要使用之前老的认证方式可以在配置文件里将default-authentication-plugin这段开启,然后重启数据库。

如果想对某个用户使用老的认证方式,可以使用下面语句
alter user 'song'@'%' identified with mysql_native_password by 'Songpasswd';
with后面可以跟新的认证插件也可以是老的认证插件。
3.密码管理策略增强
mysql8.0开始允许限制重复使用以前的密码。也就是说在修改密码的时候不能改为以前使用过的密码。
mysql8.0中有几个系统变量来实现控制密码修改策略。
1)password_history:该参数数值用于设置历史密码可以再次使用之前需要进行密码修改的次数。比如password_history = 3 就是代表新密码不能和最近使用过3次的密码相同。设置为0则不会对历史密码是否可以重用进行限制。
2)password_reuse_interval:按照日期指定来限制,比如 password_reuse_interval = 60 表示新密码不能和60天之内的密码相同,默认值为0,设置为0则不会对历史密码重用进行时间间隔设置。
3)password_require_current:默认值是OFF,当值为ON时候用户修改密码时候是否需要提供当前密码。
查看变量,都是以password开头的。
mysql> show variables like 'password%'; +--------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +--------------------------+-------+ | password_history | 0 | | password_require_current | OFF | | password_reuse_interval | 0 | +--------------------------+-------+
默认情况下password_history和password_reuse_interval的值是0,表示不做限制,而password_require_current的值是off,也就是说默认情况下这些值都是没有启用的。
设置方式,在之前mysql版本中如果给运行中mysql修改参数只能在当前mysql进程中设置,但是mysql重启后就会失效,二如果写入配置文件my.cnf里则需要重启服务,这两种方法都不太方便,而在mysql8.0增加了新特性就是在线修改系统变量,并将修改后的持久化到磁盘,重启服务依然有效。它在mysql目录下增加了一个配置文件mysqld-auto.cnf。
mysql> set persist password_history=6; mysql> show variables like 'password%'; +--------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +--------------------------+-------+ | password_history | 6 | | password_require_current | OFF | | password_reuse_interval | 0 | +--------------------------+-------+
查看mysqld-auto.cnf,这是一个json格式的配置文件。mysql服务器在重启的时候就会读取这个文件。
root@f488b1c2586a:/# cat /var/lib/mysql/mysqld-auto.cnf
{ "Version" : 1 , "mysql_server" : { "password_history" : { "Value" : "6" , "Metadata" : { "Timestamp" : 1563796829915492 , "User" : "root" , "Host" : "localhost" } } } }
对于的修改也可以针对用户去修改。
mysql> select user,host,Password_reuse_history from mysql.user; #先查看 +------------------+-----------+------------------------+ | user | host | Password_reuse_history | +------------------+-----------+------------------------+ | root | % | NULL | | song | % | NULL | | mysql.infoschema | localhost | NULL | | mysql.session | localhost | NULL | | mysql.sys | localhost | NULL | | root | localhost | NULL | +------------------+-----------+------------------------+ mysql> alter user 'song'@'%' password history 10; #设置10 mysql> select user,host,Password_reuse_history from mysql.user; #查看设置成功 +------------------+-----------+------------------------+ | user | host | Password_reuse_history | +------------------+-----------+------------------------+ | root | % | NULL | | song | % | 10 | | mysql.infoschema | localhost | NULL | | mysql.session | localhost | NULL | | mysql.sys | localhost | NULL | | root | localhost | NULL | +------------------+-----------+------------------------+
设置成功可以测试下,发现密码不可修改并报错。
mysql> alter user 'song'@'%' identified by 'song_passwd'; ERROR 3689 (HY000): Cannot use these credentials for 'song'@'%' because they contradict the password history policy
4.角色管理
mysql8.0提供了角色管理新功能,角色是一组权限的集合。
在之前的mysql版本中,要给某些用户分配权限需要一个个分配。如果用户比较多,角色也比较多,手动分配管理起来就比较麻烦。
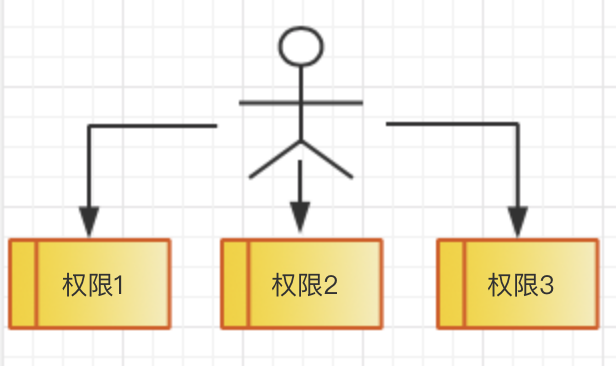
新的版本有了角色功能之后,在权限和用户之间加了一层角色。可以将一组定义好的权限赋予某个角色,可以在将角色分配给需要的用户。这样可以简化用户权限的管理。
步骤:
1.先创建角色
2.给这个角色赋予事先定义好的权限。
3.给角色授权给某个用户。
操作流程:
| 操作步骤 | 说明 |
| mysql> create database roleDB ; | 创建一个数据库 |
| create table roleDB.table_auth(id int); | 创建一张表 |
| create role 'write_role'; | 创建一个角色 |
| mysql> select host,user,authentication_string from mysql.user; +-----------+------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | host | user | authentication_string | +-----------+------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | % | root | $A$005$OI6M7iPSa8RTaSQ4NXvRjLWQ2Qf3JUMlS1NrQTPdvhEUh/bfIIdBj. | | % | song | $A$005$GAy/g`mMyQa.gojqBMnFSqaTpD6DZFZPExMVjFmxVDU45RkiAvsH4qFb9Y9 | | % | write_role | | | localhost | mysql.infoschema | $A$005$THISISACOMBINATIONOFINVALIDSALTANDPASSWORDTHATMUSTNEVERBRBEUSED | | localhost | mysql.session | $A$005$THISISACOMBINATIONOFINVALIDSALTANDPASSWORDTHATMUSTNEVERBRBEUSED | | localhost | mysql.sys | $A$005$THISISACOMBINATIONOFINVALIDSALTANDPASSWORDTHATMUSTNEVERBRBEUSED | | localhost | root | $A$005$rX oqug@ ~HH%H XLsY.hAnb2p8G5JXazsp/2qDxaSLEZpDVVfRnSKrre6 | +-----------+------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
查看用户信息表, 这里write_role是一个没有密码的用户, 可以看出mysql里的角色其实是一个用户。 是用用户来模拟角色的效果。 |
| mysql> grant select,insert,update,delete on roleDB.* to 'write_role'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) |
授权,授予roleDB库上的增删改查权限, 这里对角色和用户的授权语法都是 一样的。 |
| mysql> create user 'yonhu_role1' identified by 'password123'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) |
创建用户并赋予密码 |
| mysql> grant 'write_role' to 'yonhu_role1'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) |
将角色授予用户 |
| mysql> show grants for 'yonhu_role1'; +---------------------------------------------+ | Grants for yonhu_role1@% | +---------------------------------------------+ | GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO `yonhu_role1`@`%` | | GRANT `write_role`@`%` TO `yonhu_role1`@`%` | +---------------------------------------------+ |
显示用户的权限 第一条是默认使用权限 第二条就是刚刚赋予的角色 |
| mysql> show grants for 'yonhu_role1' using 'write_role'; +-----------------------------------------------------------------+ | Grants for yonhu_role1@% | +-----------------------------------------------------------------+ | GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO `yonhu_role1`@`%` | | GRANT SELECT,INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE ON `roleDB`.* TO `yonhu_role1`@`%` | | GRANT `write_role`@`%` TO `yonhu_role1`@`%` | +-----------------------------------------------------------------+ |
具体查看用户角色拥有的权限 |
| exit |
退出 |
|
root@f488b1c2586a:/# mysql -uyonhu_role1 -p mysql> select user(); |
用yonhu_role1用户登陆 |
|
|
实际table_auth表上存在的,也 拥有权限去查询。 |
|
mysql> select current_role(); |
查看当前角色,默认没有激活 这就是没法查询原因。
|
|
mysql> set role 'write_role'; mysql> select * from roleDB.table_auth; |
设置角色,再次查询就可以 |
|
root@f488b1c2586a:/# mysql -uroot -p mysql> set default role 'write_role' to 'yonhu_role1'; |
为每个用户设置默认角色 |
|
mysql> select * from mysql.default_roles; mysql> select * from mysql.role_edges; |
查看用户角色信息,这个是mysql8 新增加的表。 下面是用户锁设计到角色的信息。 |
也可以撤销角色
mysql> revoke insert,update,delete on roleDB.* from 'write_role'; mysql> show grants for 'write_role'; +------------------------------------------------+ | Grants for write_role@% | +------------------------------------------------+ | GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO `write_role`@`%` | | GRANT SELECT ON `roleDB`.* TO `write_role`@`%` | +------------------------------------------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> show grants for yonhu_role1; +---------------------------------------------+ | Grants for yonhu_role1@% | +---------------------------------------------+ | GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO `yonhu_role1`@`%` | | GRANT `write_role`@`%` TO `yonhu_role1`@`%` |
优化器索引
mysq8.0增加了三种新的索引方式,降序索引,影藏索引,函数索引。
1.隐藏索引(invisiable index):也叫做不可见索引,它不会被优化器使用,也就是对优化器不可见,但是但仍然需要维护。
应用场景:
1)软删除:可以先隐藏索引,查询优化器不会使用该索引,但是索引还是在维护,当最终确认删除后系统不受影响,就可以彻底删除索引)。
2)灰度发布:测试一些索引功能,在线上测试,查询不会影响,确认索引有效,某些功能受能用到的,在将索引可见)。
3)新索引替换老索引。
mysql> create table user(i int,j int); mysql> create index i_index on user(i); mysql> create index j_index on user(j) invisible;
显示索引信息
mysql> show index from user\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: user
Non_unique: 1
Key_name: i_index
Seq_in_index: 1
Column_name: i
Collation: A
Cardinality: 0
Sub_part: NULL
Packed: NULL
Null: YES
Index_type: BTREE
Comment:
Index_comment:
Visible: YES
Expression: NULL
*************************** 2. row ***************************
Table: user
Non_unique: 1
Key_name: j_index
Seq_in_index: 1
Column_name: j
Collation: A
Cardinality: 0
Sub_part: NULL
Packed: NULL
Null: YES
Index_type: BTREE
Comment:
Index_comment:
Visible: NO
Expression: NULL
2 rows in set (0.06 sec)
查看执行计划任务
mysql> explain select * from user where i=1; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | user | NULL | ref | user_index | i_index | 5 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ mysql> explain select * from user where j=1; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | user | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | Using where | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
查看查询优化器开关
mysql> select @@optimizer_switch\G; *************************** 1. row *************************** @@optimizer_switch: index_merge=on,index_merge_union=on,index_merge_sort_union=on,index_merge_intersection=on,
engine_condition_pushdown=on,index_condition_pushdown=on,mrr=on,mrr_cost_based=on,block_nested_loop=on,batched_key_access=off,
materialization=on,semijoin=on,loosescan=on,firstmatch=on,duplicateweedout=on,subquery_materialization_cost_based=on,
use_index_extensions=on,condition_fanout_filter=on,derived_merge=on,use_invisible_indexes=off,skip_scan=on 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
在会话级别打开它
mysql> set session optimizer_switch="use_invisible_indexes=on"; mysql> select @@optimizer_switch\G; *************************** 1. row *************************** @@optimizer_switch: index_merge=on,index_merge_union=on,index_merge_sort_union=on,index_merge_intersection=on,
engine_condition_pushdown=on,index_condition_pushdown=on,mrr=on,mrr_cost_based=on,block_nested_loop=on,batched_key_access=off,
materialization=on,semijoin=on,loosescan=on,firstmatch=on,duplicateweedout=on,subquery_materialization_cost_based=on,
use_index_extensions=on,condition_fanout_filter=on,derived_merge=on,use_invisible_indexes=on,skip_scan=on
设置成功,查询发现已经打开.
在此查看,可以使用不可见索引
mysql> explain select * from user where j=1; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | user | NULL | ref | j_index | j_index | 5 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
我们可以在某个特定的会话中,打开开关测试语句。
修改可见/不可见属性
mysql> alter table user alter index i_index visible;
注意:
主键不可以设置不可见。因为也没啥意义。
2.降序索引(descending index)
1)mysql8.0开始真正支持降序索引,在之前的mysql版本中也支持这种降序(DESC)索语法定义,但实际上mysql server会忽略这个定义,创建的还是升序索引(ASC)。
我们通常使用下面的语句来创建一个索引:
create index idx_t1_bcd on t1(b,c,d);
上面sql的意思是在t1表中,针对b,c,d三个字段创建一个联合索引。
但是大家不知道的是,上面这个sql实际上和下面的这个sql是等价的:
create index idx_t1_bcd on t1(b asc,c asc,d asc);
2)目前只有innodb存储引擎支持降序索引,只支持BTREE降序索引。
3)由于降序索引引入,mysql8.0不再对group by 操作进行隐式排序,如果需要进行order by指明处理。
4)降序索引带来了性能的改进。
mysql5.7中
mysql> create table tablename1 (a int , b int, index idx1 (a asc,b desc)); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec) mysql> show create table tablename1; +------------+----------------------------------------------------+ | Table | Create Table | +------------+----------------------------------------------------+ | tablename1 | CREATE TABLE `tablename1` ( `a` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `b` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, KEY `idx1` (`a`,`b`) #虽然在语句中指定来a升序,b字段降序,但是这里都是默认升序 ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1 | +------------+----------------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql8.0
mysql8> create table user2(a1 int,a2 int,index(a1 asc,a2 desc));
mysql> show create table user2\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: user2
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `user2` (
`a1` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`a2` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
KEY `a1` (`a1`,`a2` DESC) #a2 后面有个desc 是真正的降序
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
插入一些数据
mysql8> insert into user2(a1,a2) values(1,100),(2,200),(3,150),(4,50); Query OK, 4 rows affected (0.02 sec) Records: 4 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> select * from user2; +------+------+ | a1 | a2 | +------+------+ | 1 | 100 | | 2 | 200 | | 3 | 150 | | 4 | 50 | +------+------+
执行优化器,查询使用a1升序,a2降序,查看索引使用情况。
mysql8> explain select * from user2 order by a1,a2 desc; +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | user2 | NULL | index | NULL | a1 | 10 | NULL | 4 | 100.00 | Using index | 组合排序仍然可以使用到索引a1 +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
可以使用到索引
mysql5.7
mysql> explain select * from user2 order by a1,a2 desc; +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | user2 | NULL | index | NULL | a1 | 10 | NULL | 4 | 100.00 | Using index; Using filesort | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql5.7中虽然使用到了索引,但是还需要额外的排序操作,不能直接通过索引来得到我们锁需要的顺序。
当在mysql8.0执行相反查询的时候。
mysql> explain select * from user2 order by a1 desc ,a2 ; +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | user2 | NULL | index | NULL | a1 | 10 | NULL | 4 | 100.00 | Backward index scan; Using index | #从大到小的扫描 +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------+
不仅用到了索引,还用到反向索引扫描。
上面就是新的降序索引带来的性能的改进。
另外对group by不会默认的排序。随机返回。
mysql8> select count(*) , a2 from user2 group by a2; +----------+------+ | count(*) | a2 | +----------+------+ | 1 | 100 | | 1 | 200 | | 1 | 150 | | 1 | 50 | +----------+------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql8增加order by才有排序效果
mysql5.7默认增加order by排序
mysql5.7> select count(*) , a2 from user2 group by a2; +----------+------+ | count(*) | a2 | +----------+------+ | 1 | 50 | | 1 | 100 | | 1 | 150 | | 1 | 200 | +----------+------+
mysql8 增加order by 就和mysql5.7一样,有排序的效果。
mysql8> select count(*) , a2 from user2 group by a2 order by a2; +----------+------+ | count(*) | a2 | +----------+------+ | 1 | 50 | | 1 | 100 | | 1 | 150 | | 1 | 200 | +----------+------+
3.函数索引
mysql8.0.13开始支持在索引中使用函数(表达式)的值,之前是使用列值,现在可以使用函数表达式的值使用索引,同时也支持降序索引,json数据的索引。之前版本的数据库是没法对json里各个节点的数据索引,函数索引是基于虚拟计算列功能来实现的。可以方便对json格式数据的查询。
mysql> create table user3(c1 varchar(10),c2 varchar(10)); mysql> create index index1 on user3(c1); mysql> create index func_index on user3( (UPPER(c2)) ); #函数索引用大括号包起来
查看索引情况
mysql> show index from user3\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: user3
Non_unique: 1
Key_name: index1
Seq_in_index: 1
Column_name: c1
Collation: A
Cardinality: 0
Sub_part: NULL
Packed: NULL
Null: YES
Index_type: BTREE
Comment:
Index_comment:
Visible: YES
Expression: NULL
*************************** 2. row ***************************
Table: user3
Non_unique: 1
Key_name: func_index
Seq_in_index: 1
Column_name: NULL
Collation: A
Cardinality: 0
Sub_part: NULL
Packed: NULL
Null: YES
Index_type: BTREE
Comment:
Index_comment:
Visible: YES
Expression: upper(`c2`)
2 rows in set (0.11 sec)
mysql> explain select * from user3 where upper(c1)='ABC'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | user3 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | Using where | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ mysql> explain select * from user3 where upper(c2)='ABC'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | user3 | NULL | ref | func_index | func_index | 43 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
分析:虽然有c1索引,但是还是全表扫描
针对json节点的索引
mysql> create table table_json (data json , index ((CAST(data->>'$.name' as char(30)) ))); mysql> show index from table_json; +------------+------------+------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+---------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment | Visible | Expression | +------------+------------+------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+---------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | table_json | 1 | functional_index | 1 | NULL | A | 0 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | | YES | cast(json_unquote(json_extract(`data`,_latin1\'$.name\')) as char(30) charset latin1) | +------------+------------+------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+---------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
cast函数作为类型转换 成char(30) ->>是新的json运算符,就是去name的值
mysql> explain select * from table_json where CAST(data->>'$.name' as char(30)) = 'aaa'; +----+-------------+------------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+------------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | table_json | NULL | ref | functional_index | functional_index | 33 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+------------+------------+------+------------------+------------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
函数计算列
mysql> create table user3 (a1 varchar(10),a2 varchar(10)); mysql> desc user3; +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | a1 | varchar(10) | YES | | NULL | | | a2 | varchar(10) | YES | | NULL | | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
添加数据
mysql> alter table user3 add column a3 varchar(10) generated always as (upper(a1));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> insert into user3(a1,a2) values ('abc','abc');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from user3;
+------+------+------+
| a1 | a2 | a3 |
+------+------+------+
| abc | abc | ABC |
+------+------+------+
c3列是基于c1列大写的形式计算出来的。
mysql> create index idx3 on user3(a3); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> explain select * from user3 where upper(a1) = 'ABC'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | user3 | NULL | ref | idx3 | idx3 | 43 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
达到了与函数索引一样的效果

通用表表达式(CTE):
即with子句,是sql语句的增强,通用表达式在sql2003标准(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SQL:2003)中就引入了,很多主流数据库都有该功能,mysql8.0也是拥有了该功能。
1.非递归CTE
派生表:select * from (select 1) as dt;
通用表表达式:with cte as (select 1)select * from cte;就相当于一个变量,在后面语句中使用。
mysql> select * from (select 1) as dt;
+---+
| 1 |
+---+
| 1 |
+---+
mysql> with dt as (select 1)
-> select * from dt;
+---+
| 1 |
+---+
| 1 |
+---+
写法更加清晰
mysql> with cte1(id) as (select 1),
-> cte2(id) as (select id+1 from cte1)
-> select * from cte1 join cte2;
+----+----+
| id | id |
+----+----+
| 1 | 2 |
+----+----+
2.递归CTE
在查询中引用自己的定义,使用RECURSIVE表示。和编程语言中的递归函数调用差不多。生成一些模拟数据也比较方便
mysql> with recursive cte (n) as
-> (
-> select 1
-> union all
-> select n + 1 from cte where n <10
-> )
-> select * from cte;
+------+
| n |
+------+
| 1 |
| 2 |
| 3 |
| 4 |
| 5 |
| 6 |
| 7 |
| 8 |
| 9 |
| 10 |
+------+
无限级分类表
mysql> create table employee (id int,name varchar(20),manager_id int); mysql> insert into employee values(29,'song',198),(72,'lucy',29),(123,'adil',692),(198,'join',333),(333,'yaml',NULL),(692,'cady',333),(700,'sarac',29); mysql> select * from employee; +------+-------+------------+ | id | name | manager_id | +------+-------+------------+ | 29 | song | 198 | | 72 | lucy | 29 | | 123 | adil | 692 | | 198 | join | 333 | | 333 | yaml | NULL | | 692 | cady | 333 | | 700 | sarac | 29 | +------+-------+------------+
实例
mysql> with recursive employee_paths(id,name,path) as
-> (
-> select id,name,cast(id as char(200))
-> from employee
-> where manager_id is null
-> union all
-> select e.id,e.name,concat(ep.path,',',e.id)
-> from employee_paths as ep join employee as e
-> on ep.id = e.manager_id
-> )
-> select * from employee_paths order by path;
+------+-------+----------------+
| id | name | path |
+------+-------+----------------+
| 333 | yaml | 333 |
| 198 | join | 333,198 |
| 29 | song | 333,198,29 |
| 700 | sarac | 333,198,29,700 |
| 72 | lucy | 333,198,29,72 |
| 692 | cady | 333,692 |
| 123 | adil | 333,692,123 |
+------+-------+----------------+
递归cte注意次数限制,递归表达式要包含一个终止递归的条件,避免死循环。
mysql8.0提供了参数cte_max_recursion_depth:最大递归深度, max_execution_time:sql语句最大执行时间。
mysql> with recursive cte(n) as
-> (
-> select 1
-> union all
-> select n+1 from cte
-> )
-> select * from cte;
ERROR 3636 (HY000): Recursive query aborted after 1001 iterations. Try increasing @@cte_max_recursion_depth to a larger value.
在第1001次阻断
mysql> show variables like 'cte_max%'; +-------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +-------------------------+-------+ | cte_max_recursion_depth | 1000 | +-------------------------+-------+ mysql> set session cte_max_recursion_depth=10;

0表示无限制 1000毫秒=1秒
通用表表达式和派生表很类似,就像语句级别的临时表和试图,用派生表的地方就可以用通用表表达式,语意更加清晰点。
cte可以在查询中多次引用,也可以引用其他的cte
cte支持select/insert/update/delete等语句
比如使用递归CTE生成斐波那契数列。
窗口函数(window function)
也称呼为分析函数,为sql语句提供强大的数据分析功能,可以通过sql语句做一些数据分析。
窗口函数与分组聚合函数类似,但是每一行数据都生成一个结果,就是主要对数据进行分组group by操作,然后对每一个组聚合产生一个结果,比如组内的平均数,组内的组合等等。窗口函数与之相似也可以分组,不同的地方在于,针对分组内的每一个行都会生成相应的一个结果,所以结果和行数上相同的。
窗口函数定义

over是关键字,用来指定函数执行的窗口范围,内部可以指定三个选项,第一个是先对数据进行分组,第二个是对分组的数据进行排序,第三个进一步操作。
常见聚合窗口函数:SUM / AVG / COUNT / MAX / MIN 等等。
mysql> insert into sales values (2000,'Finland','Computer',1500),(2001,'USA','Phone',1200),(2001,'Finland','Phone',10),(2000,'India','Calculator',75),
(2001,'USA','TV',150),(2000,'India','Computer',1200),(2000,'USA','Calculator',5),(2000,'USA','Computer',1500),(2000,'Finland','Phone',100),
(2001,'USA','Calculator',50),(2001,'USA ',' TV',100); mysql> select * from sales; +------+---------+------------+--------+ | year | country | product | profit | +------+---------+------------+--------+ | 2000 | Finland | Computer | 1500 | | 2001 | USA | Phone | 1200 | | 2001 | Finland | Phone | 10 | | 2000 | India | Calculator | 75 | | 2001 | USA | TV | 150 | | 2000 | India | Computer | 1200 | | 2000 | USA | Calculator | 5 | | 2000 | USA | Computer | 1500 | | 2000 | Finland | Phone | 100 | | 2001 | USA | Calculator | 50 | | 2001 | USA | Computer | 1500 | | 2000 | India | Calculator | 75 | | 2001 | USA | TV | 100 | +------+---------+------------+--------+
mysql> select country,sum(profit) as country_profit
-> from sales
-> group by country
-> order by country;
+---------+----------------+
| country | country_profit |
+---------+----------------+
| Finland | 1610 |
| India | 1350 |
| USA | 4505 |
mysql> select year,country,product,profit,
-> sum(profit) OVER (partition by country) as country_profit
-> from sales
-> order by country,year,product,profit;
+------+---------+------------+--------+----------------+
| year | country | product | profit | country_profit |
+------+---------+------------+--------+----------------+
| 2000 | Finland | Computer | 1500 | 1610 |
| 2000 | Finland | Phone | 100 | 1610 |
| 2001 | Finland | Phone | 10 | 1610 |
| 2000 | India | Calculator | 75 | 1350 |
| 2000 | India | Calculator | 75 | 1350 |
| 2000 | India | Computer | 1200 | 1350 |
| 2000 | USA | Calculator | 5 | 4505 |
| 2000 | USA | Computer | 1500 | 4505 |
| 2001 | USA | Calculator | 50 | 4505 |
| 2001 | USA | Computer | 1500 | 4505 |
| 2001 | USA | Phone | 1200 | 4505 |
| 2001 | USA | TV | 100 | 4505 |
| 2001 | USA | TV | 150 | 4505 |
+------+---------+------------+--------+----------------+
使用窗口函数,每一行都出现,保留了原来的数据结构,在原来基础上增加一些分析出来结果列,而不像分组聚合函数那样。分析数据可以使用
前四列是原始数据
窗口函数不需要在加group by了。
专用窗口函数
获取排名函数
ROW_NUMBER() / RANK() /DENSE_RANK() / PERCENT_RANK()
FIRST_VALUE() / LAST_VALUE() / LEAD() / LAG()
CUME_DIST() / NTH_VALUE() / NTILE()
mysql> insert into numbers values (1),(1),(2),(3),(3),(3),(3),(4),(4),(5); Query OK, 10 rows affected (0.01 sec) Records: 10 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> select * from numbers; +------+ | nums | +------+ | 1 | | 1 | | 2 | | 3 | | 3 | | 3 | | 3 | | 4 | | 4 | | 5 | +------+
排名
mysql> select nums , row_number() OVER (order by nums) as 'row_number' from numbers; +------+------------+ | nums | row_number | +------+------------+ | 1 | 1 | | 1 | 2 | | 2 | 3 | | 3 | 4 | | 3 | 5 | | 3 | 6 | | 3 | 7 | | 4 | 8 | | 4 | 9 | | 5 | 10 | +------+------------+
mysql> select nums,
-> first_value(nums) over (order by nums) as 'first',
-> lead(nums,1) over (order by nums) as 'lead'
-> from numbers;
+------+-------+------+
| nums | first | lead |
+------+-------+------+
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 1 | 3 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 |
| 3 | 1 | 4 |
| 4 | 1 | 4 |
| 4 | 1 | 5 |
| 5 | 1 | NULL |
+------+-------+------+
Innodb存储引擎改进
Innodb存储引擎成为mysql默认存储引擎后,功能一直在改进,mysql8.0中innodb的功能也得到增强。
1.集成数据字典
mysql8.0重新重构了数据字典
1)删除了之前元数据文件关于数据库等信息,例如.frm .opt等基于文件等数据库信息。
mysql5.7
root@4a68d9279589:/# cd /var/lib/mysql root@4a68d9279589:/var/lib/mysql# ls auto.cnf client-cert.pem ib_logfile0 ibtmp1 private_key.pem server-key.pem ca-key.pem client-key.pem ib_logfile1 mysql public_key.pem sys ca.pem ib_buffer_pool ibdata1 performance_schema server-cert.pem testDB root@4a68d9279589:/var/lib/mysql# ls mysql columns_priv.MYD gtid_executed.ibd proc.MYI slow_log.CSV columns_priv.MYI help_category.frm proc.frm slow_log.frm columns_priv.frm help_category.ibd procs_priv.MYD tables_priv.MYD db.MYD help_keyword.frm procs_priv.MYI tables_priv.MYI db.MYI help_keyword.ibd procs_priv.frm tables_priv.frm db.frm help_relation.frm proxies_priv.MYD time_zone.frm db.opt help_relation.ibd proxies_priv.MYI time_zone.ibd engine_cost.frm help_topic.frm proxies_priv.frm time_zone_leap_second.frm engine_cost.ibd help_topic.ibd server_cost.frm time_zone_leap_second.ibd event.MYD innodb_index_stats.frm server_cost.ibd time_zone_name.frm event.MYI innodb_index_stats.ibd servers.frm time_zone_name.ibd event.frm innodb_table_stats.frm servers.ibd time_zone_transition.frm func.MYD innodb_table_stats.ibd slave_master_info.frm time_zone_transition.ibd func.MYI ndb_binlog_index.MYD slave_master_info.ibd time_zone_transition_type.frm func.frm ndb_binlog_index.MYI slave_relay_log_info.frm time_zone_transition_type.ibd general_log.CSM ndb_binlog_index.frm slave_relay_log_info.ibd user.MYD general_log.CSV plugin.frm slave_worker_info.frm user.MYI general_log.frm plugin.ibd slave_worker_info.ibd user.frm gtid_executed.frm proc.MYD slow_log.CSM
mysql8.0
root@8de6e5139f7d:/# cd /var/lib/mysql/ root@8de6e5139f7d:/var/lib/mysql# ls mysql general_log.CSM general_log.CSV general_log_197.sdi slow_log.CSM slow_log.CSV slow_log_198.sdi root@8de6e5139f7d:/var/lib/mysql# ls -l mysql total 28 -rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 35 Jul 15 11:19 general_log.CSM -rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 0 Jul 15 11:19 general_log.CSV -rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 5561 Jul 15 11:19 general_log_197.sdi -rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 35 Jul 15 11:19 slow_log.CSM -rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 0 Jul 15 11:19 slow_log.CSV -rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 11786 Jul 15 11:19 slow_log_198.sdi
mysql8.0主要存放在这个目录下
root@8de6e5139f7d:/var/lib/mysql# ls #innodb_temp binlog.000003 ca-key.pem ib_buffer_pool ibtmp1 private_key.pem sys auto.cnf binlog.000004 ca.pem ib_logfile0 mysql public_key.pem testDB binlog.000001 binlog.000005 client-cert.pem ib_logfile1 mysql.ibd server-cert.pem undo_001 binlog.000002 binlog.index client-key.pem ibdata1 performance_schema server-key.pem undo_002 root@8de6e5139f7d:/var/lib/mysql# ls -l mysql.ibd -rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 31457280 Jul 15 12:50 mysql.ibd
mysql8将系统表(mysql)和数据字典全部改为innodb。
2.原子ddl操作,基于innodb事务特性。
由于采用了新的数据字典, MySQL 8.0 现在支持原子数据定义语句 (Atomic DDLs)。 这意味着执行 DDL 时,数据字典更新,存储引擎操作以及二进制日志文件中的写入操作会合并到单个原子事务中,该事务要么完全执行,要么根本不执行。这提高了 DDL 的稳定性保证未完成的 DDL 不会留下任何不完整的数据。
mysql8.0开始支持原子DDL操作,原子DDL操作又很多种,但其中与表相关的原子DDL只支持Innodb存储引擎,比如创建表,删除表。一个原子DDL操作包括:更新数据字典,存储引擎层的操作,在binlog二进制日志中记录DDL操作,
支持与表相关的DDL:数据库,表空间,表,索引的create,alter,drop以及truncate table。
支持的其他DDL:存储过程,触发器,视图,UDF(用户定义函数)的create,drop以及alter语句。
支持账户管理相关DDL:用户和角色的create,alter,drop以及适用的rename,以及GRANT(授权)和REVOKE(撤销授权)语句。
mysql> show tables; +------------------+ | Tables_in_testDB | +------------------+ | table1 | +------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> drop table table1,table2; ERROR 1051 (42S02): Unknown table 'testDB.table2' mysql> show tables; Empty set (0.00 sec)
虽然错误,但是t1表已经被删除了,所以这个操作不具有原子性。
在mysql8.0进行相同操作
mysql> show tables; +------------------+ | Tables_in_testDB | +------------------+ | employee | | user | | user2 | | user3 | +------------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> drop table user3,user4; ERROR 1051 (42S02): Unknown table 'testDB.user4' mysql> show tables; +------------------+ | Tables_in_testDB | +------------------+ | employee | | user | | user2 | | user3 | 表user3依然存在 +------------------+
新版本功能对复制的影响:
主从复制时候,主节点上mysql5.7,从节点上mysql8.0,由于实现原理不一样,主节点drop语句有可能成功一部分,而mysql8.0会全部失败,可以通过判断drop if exists t1,t2。
3.自增列持久化
mysql5.7及早期版本,Innodb自增列计数器(AUTH_INCREMENT)的只值存储在内存中,它值的更新只会在内存中更新,当系统出现故障或者重启,它需要重新去扫描表中的自增列,找到当前最大列,然后基于这个值在自增,在某些情况下它这个值有可能是之前使用过的值,也就是说会出现重复的值,对于主键来说是不允许有重复的值。
基于以上原因mysql8.0做了修改,mysql8.0每次变化时将自增计数器的最大值写入redo log,同时每次在检查点将其写入引擎私有的系统表。系统在下次重启或者恢复时候可以找到曾经使用过的最大值,避免新生成的值和以前的值重复的情况。
mysql57> create table table1(id int auto_increment primary key, name varchar(10));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql57> insert into table1(name) values('tom'),('lucy'),('make');
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.02 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql57> select * from table1;
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 1 | tom |
| 2 | lucy |
| 3 | make |
+----+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql57> delete from table1 where id=3;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.02 sec)
mysql57> select * from table1;
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 1 | tom |
| 2 | lucy |
+----+------+
2 rows in set (0.01 sec)
删除并重启
songguojundeMBP:~ songguojun$ docker stop song-mysql57 song-mysql57 songguojundeMBP:~ songguojun$ docker start song-mysql57 song-mysql57 songguojundeMBP:~ songguojun$ docker exec -it song-mysql57 /bin/bash
mysql> select * from table1;
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 1 | tom |
| 2 | lucy |
+----+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into table1(name) values('salary');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from table1;
+----+--------+
| id | name |
+----+--------+
| 1 | tom |
| 2 | lucy |
| 3 | salary |
+----+--------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> update table1 set id=5 where name = 'tom';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from table1;
+----+--------+
| id | name |
+----+--------+
| 2 | lucy |
| 3 | salary |
| 5 | tom |
+----+--------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into table1(name) values ('song');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from table1;
+----+--------+
| id | name |
+----+--------+
| 2 | lucy |
| 3 | salary |
| 4 | song |
| 5 | tom |
+----+--------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into table1(name) values ('song2');
ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '5' for key 'PRIMARY'
接下来看mysql8.0是如何解决这个问题的
按照上面的步骤操作即可
mysql> show variables like 'innodb_autoinc%'; +--------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +--------------------------+-------+ | innodb_autoinc_lock_mode | 2 | +--------------------------+-------+
参数解释:
mysql8.0这个值默认是2 mysql5.7这个默认值是1, 2是交叉模式,这个锁是交叉生成的,1表示连续模式,这两个值差别在于复制的时候,比如说之前 复制说基于语句的复制,比如一条语句生成10条记录,在这条语句中生成的记录都是顺序的,如果从主节点复制到从节点也要保证说顺序的话就要使用这个值为1,可以保证语句级别的增长都是连续的,最新的复制模式改为行的复制模式,意味着将行的实际数据值复制,所以不关心自增列是怎么生成的,也不能保证生成的id一致性,因为不像之前版本加上锁,这样的好处可以支持更高的并发和扩展。如果还想要之前那样基于语句就要注意这个参数设置下。
4.死锁检查控制
死锁:有两个事务都需要对数据进行修改,修改的过程中都需要等待对方释放资源,由于互相没有感知,在没有外界的介入下它们会一直等待下去,就形成了死锁。mysql后台有个死锁检测程序,在后台发现了会让一个事务失败,让另一个事务进行下去,当然死锁检测需要一定的代价,需要占用一定的系统资源。
mysql8.0及mysql5.7.15增加了一个新的动态变量,用于控制系统是否执行Innodb的死锁检测。
innodb_deadlock_detect 默认情况说打开的,会进行死锁检测。
对于高并发的系统,死锁检测会占用系统资源,所以禁用死锁检测可能会带来性能的提高。
mysql8> show variables like 'innodb_deadlock_detect'; +------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +------------------------+-------+ | innodb_deadlock_detect | ON | +------------------------+-------+
下面开启两个事务,然后在两个事务之间互相锁定各自的资源,来等待对方的锁。
先创建一张表
mysql> create table table_t1 (i int); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec) mysql> insert into table_t1(i) values(1); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
| 事务1 | 说明 | 事务2 | 说明 |
mysql> start transaction; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) mysql> select * from table_t1 where i=1 for share; +------+ | i | +------+ | 1 | +------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) |
for share获取记录上的一个共享锁 | mysql> start transaction; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> delete from table_t1 where i=1; |
删除需要排它锁 ,由于前面一个会话已经占用了一个共享锁,这时候在等待资源的释放。 |
| mysql> delete from table_t1 where i=1; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) |
第二个窗口 删除时候也需要排它锁,这个时候它也需要第二个会话事务释放锁才能进行下去,发现了死锁 。 因为系统发现了死锁并解除死锁,这里可以进行下去。 |
mysql> delete from table_t1 where i=1; ERROR 1213 (40001): Deadlock found when trying to get lock; try restarting transaction |
死锁被发现,系统将它会滚掉,让第一个事务进行下去 |
| mysql> select * from table_t1; Empty set (0.00 sec) |
数据被删除 |
以上是innodb_deadlock_detect默认打开情况下掉行为。
那么我们将这个参数关闭测试看看如何处理死锁的
mysql> set global innodb_deadlock_detect = off; #关闭死锁检测 Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> show variables like 'innodb_deadlock_detect'; +------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +------------------------+-------+ | innodb_deadlock_detect | OFF | +------------------------+-------+
还有一个参数 锁等待超时 这个参数会影响实验
mysql> show variables like 'innodb_lock_wait%'; +--------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +--------------------------+-------+ | innodb_lock_wait_timeout | 50 | #默认是50秒 +--------------------------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> set global innodb_lock_wait_timeout=5; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
50秒设置为5秒
| 事务1 | 说明 | 事务2 | 说明 |
| mysql> start transaction; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) mysql> select * from table_t1 where i=1 for share; +------+ | i | +------+ | 1 | +------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) |
mysql> start transaction;
|
||
|
mysql> delete from table_t1 where i=1; |
执行删除操作,在等待中 | ||
| mysql> delete from table_t1 where i=1; Query OK, 1 row affected (31.99 sec) |
这个事务也在等待中, 如果死锁检测打开,就会提示死锁错误信息,但是这里没有提示 |
||
| ERROR 1205 (HY000): Lock wait timeout exceeded; try restarting transaction | 通过超时来回滚事务,让事务二失败 |
注意:
1.死锁检测关闭的前提是我们系统不会发生死锁的情况,所以在我们写代码写sql语句要注意点死锁的发生。
2.锁等待超时时间不要设置太长,防止对系统的影响。
5.锁定语句选项
mysql里面有两种为查询语句加锁的语句
1. select....... for update
2. select ....... for share
这两个语句分别是为我们查询出来的语句加上共享锁和排它锁,如果查出来的数据在其他事物中以及占用了相应的锁,那么我们的语句需要进行相应的等待直到响应的事务释放锁直到超时。
mysql8.0为这两个语句增加了两个新的选项。
1) NOWAIT:如果请求的行被其他事物锁定,语句立即返回,不等待。
2)SKIP LOCKED:从返回的结果中移除锁定的行,只返回没有被锁定的行。应用场景,比如在线票务系统,有很多并发请求,如果票被其他线程占用,这时候可以选择不等待,返回可以使用的票。
mysql> create table table6 (i int ,primary key(i)); mysql> insert into table6 values (1),(2),(3);
| 事务1 | 说明 | 事务2 | 说明 |
| mysql> start transaction; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> update table6 set i=0 where i=2; |
加上排它锁,不进行提交 | ||
|
start transaction; select * from table6 where i=2 for update; ERROR 1205 (HY000): Lock wait timeout exceeded; try restarting transaction |
由于前面会话占用了锁,会一直等待直到语句超时 | ||
| mysql> start transaction; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from table6 where i=2 for update nowait; ERROR 3572 (HY000): Statement aborted because lock(s) could not be acquired immediately and NOWAIT is set. |
如果加上nowait选项选择不等待锁会返回一个错误,相应数据被占用,直接返回错误。 | ||
| mysql> select * from table6 for update skip locked; +---+ | i | +---+ | 1 | | 3 | +---+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
加上skip locked选项选择跳过锁定的数据,返回别的没被锁定的数据。 |
注意:
1.这两个参数锁针对行级锁。
2.这两个锁针对行级锁,对每一条行记录起作用。
主从复制,主从当时运行环境情况的各不一样,导致数据的不确定性,对于语句级别会带来不一致性问题。
3.简化了INFORMATION_SCHEMA的实现,提高了访问性能。
4.针对innodb存储引擎提供了序列化字典信息(SDL)的支持,以及ibd2sdi工具。SDI是一个文本文件,存储了数据字典信息。ibd2sdi工具可以将innodb相关表信息导出成文本信息。
root@f488b1c2586a:/# cd /var/lib/mysql/ root@f488b1c2586a:/var/lib/mysql# ls #innodb_temp ca.pem ibdata1 private_key.pem undo_001 auto.cnf client-cert.pem ibtmp1 public_key.pem undo_002 binlog.000001 client-key.pem mysql server-cert.pem binlog.000002 ib_buffer_pool mysql.ibd server-key.pem binlog.index ib_logfile0 mysqld-auto.cnf sys ca-key.pem ib_logfile1 performance_schema testDB root@f488b1c2586a:/var/lib/mysql# cd testDB/ root@f488b1c2586a:/var/lib/mysql/testDB# ls numbers.ibd sales.ibd table_json.ibd user2.ibd user3.ibd
root@f488b1c2586a:/var/lib/mysql/testDB# ibd2sdi table_json.ibd > sales.ibd
root@f488b1c2586a:/var/lib/mysql/testDB# ls
numbers.ibd sales.ibd table_json.ibd user2.ibd user3.ibd
root@f488b1c2586a:/var/lib/mysql/testDB# cat sales.ibd
["ibd2sdi"
,
{
"type": 1,
"id": 342,
"object":
{
"mysqld_version_id": 80016,
"dd_version": 80016,
"sdi_version": 80016,
"dd_object_type": "Table",
"dd_object": {
"name": "table_json",
"mysql_version_id": 80016,
"created": 20190722122718,
"last_altered": 20190722122718,
"hidden": 1,
"options": "avg_row_length=0;encrypt_type=N;key_block_size=0;keys_disabled=0;pack_record=1;stats_auto_recalc=0;stats_sample_pages=0;",
"columns": [
{
"name": "data",
"type": 31,
"is_nullable": true,
"is_zerofill": false,
"is_unsigned": false,
"is_auto_increment": false,
"is_virtual": false,
"hidden": 1,
"ordinal_position": 1,
"char_length": 4294967295,
"numeric_precision": 0,
"numeric_scale": 0,
"numeric_scale_null": true,
"datetime_precision": 0,
"datetime_precision_null": 1,
"has_no_default": false,
"default_value_null": true,
"srs_id_null": true,
"srs_id": 0,
"default_value": "",
"default_value_utf8_null": true,
"default_value_utf8": "",
"default_option": "",
"update_option": "",
"comment": "",
"generation_expression": "",
"generation_expression_utf8": "",
"options": "interval_count=0;",
"se_private_data": "table_id=1066;",
"column_key": 1,
"column_type_utf8": "json",
"elements": [],
"collation_id": 63,
"is_explicit_collation": true
},
比如当数据表损坏的时候可以用这些文本信息恢复。
由于新的数据字典的引入,会导致之前使用上的差异,例如innodb_read_only影响所有所有的存储引擎。数据字典不可见,不能直接修改和查询。
6.索引跳跃扫描(index skip scan)
mysql> CREATE TABLE table_scan (i1 int, i2 int , PRIMARY KEY(i1, i2)); mysql> INSERT INTO table_scan VALUES (1,1), (1,2), (1,3), (1,4), (1,5),(2,1), (2,2), (2,3), (2,4), (2,5); mysql> INSERT INTO table_scan SELECT i1, i2 + 5 FROM table_scan; mysql> INSERT INTO table_scan SELECT i1, i2 + 10 FROM table_scan; mysql> INSERT INTO table_scan SELECT i1, i2 + 20 FROM table_scan; mysql> INSERT INTO table_scan SELECT i1, i2 + 40 FROM table_scan; mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT i1, i2 FROM table_scan WHERE i2 > 40; +----+-------------+------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | table_scan | NULL | index | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 8 | NULL | 160 | 33.33 | Using where; Using index | +----+-------------+------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------+mysql> ANALYZE TABLE table_scan; +-------------------+---------+----------+----------+ | Table | Op | Msg_type | Msg_text | +-------------------+---------+----------+----------+ | testDB.table_scan | analyze | status | OK | +-------------------+---------+----------+----------+ mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT i1, i2 FROM table_scan WHERE i2 > 40; +----+-------------+------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | table_scan | NULL | range | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 8 | NULL | 53 | 100.00 | Using where; Using index for skip scan | +----+-------------+------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------------------------------+
mysql> show variables like 'optimizer_trace%'; +------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Variable_name | Value | +------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | optimizer_trace | enabled=off,one_line=off | | optimizer_trace_features | greedy_search=on,range_optimizer=on,dynamic_range=on,repeated_subselect=on | | optimizer_trace_limit | 1 | | optimizer_trace_max_mem_size | 1048576 | | optimizer_trace_offset | -1 | +------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
开启 optimizer_trace
SET optimizer_trace='enabled=on';
执行需要执行的 sql
SELECT i1, i2 FROM table_scan WHERE i2 > 40;
可以从optimizer trace里看到如何选择的skip scan
mysql> select trace from `information_schema`.`optimizer_trace`\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
trace: {
"steps": [
{
"join_preparation": {
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
{
"expanded_query": "/* select#1 */ select `table_scan`.`i1` AS `i1`,`table_scan`.`i2` AS `i2` from `table_scan` where (`table_scan`.`i2` > 40)"
}
]
}
},
{
#此处省略.....
"group_index_range": {
"chosen": false,
"cause": "not_group_by_or_distinct"
},
"skip_scan_range": {
"potential_skip_scan_indexes": [
{
"index": "PRIMARY",
"tree_travel_cost": 0.4,
"num_groups": 3,
"rows": 53,
"cost": 10.625
}
]
},
"best_skip_scan_summary": {
"type": "skip_scan",
"index": "PRIMARY",
"key_parts_used_for_access": [
"i1",
"i2"
],
"range": [
"40 < i2"
],
"chosen": true
},
"rows_for_plan": 53,
"cost_for_plan": 10.625,
"chosen": true
}
}
}
]
#此处省略.....
}
},
{
"join_execution": {
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
]
}
}
]
}
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> show variables like 'optimizer_switch%'; +------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Variable_name | Value | +------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | optimizer_switch | index_merge=on,index_merge_union=on,index_merge_sort_union=on,index_merge_intersection=on,engine_condition_pushdown=on,
index_condition_pushdown=on,mrr=on,mrr_cost_based=on,block_nested_loop=on,batched_key_access=off,materialization=on,semijoin=on,loosescan=on,
firstmatch=on,duplicateweedout=on,subquery_materialization_cost_based=on,use_index_extensions=on,condition_fanout_filter=on,derived_merge=on,
use_invisible_indexes=off,skip_scan=on | +------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
innodb其他的改进
1)支持部门快速DDL alter table .......ALGORITHM=INSTANT
比如快速增加某一列,可以使用INSTANT这种算法。就是修改相应数据字典的信息,而不是像以前重新创建一张表进行数据复制,这个比以前快很多,尤其线上系统非常实用。(这个功能锁腾讯开发合并到主分支上)
2)innodb临时表使用的共享临时表空间ibtmp1,改变之前使用分散的表空间的问题,存储在ibtmp1。临时表使用完就删除了,现在统一放在ibtmp1,统一的维护。
3)新增静态变量innodb_dedicated_server,如果有一台服务器是专门用于mysql数据库的,可以打开这个配置变量,系统会自动配置innodb相关等内存配置参数, 自动配置Innodb内存参数:innodb_buffer_pool_size/innodb_log_file_size等,尽量合理占用系统资源来提高系统等利用率。
4)新增表INFORMATION_SCHEMA.INNODB_CACHED_INDEXES显示每个索引缓存在innodb缓冲池中的索引页数,通过这个参数也可以了解索引缓存使用情况。
5)新增视图INFORMATION_SCHEMA.INNODB_TABLESPACES_BRIEF,为innodb表空间提供相关元数据信息。
6)mysql8.0默认创建2个undo表空间,不再使用系统表空间。以前undo表空间会占用系统表空间资源,单独存储会是系统表空间独立点。
7)支持alter tablespace......rename to重命名通用表空间。
8)支持使用innodb_directories选项在服务器停止时将表空间文件移动到新的位置。这个参数是表空间文件所在的路径,通过修改参数
9)innodb表空间加密特性支持重做日志和撤销日志,innodb_undo_log_encrypt和innodb_undo_log_encrypt参数。加密会更加安全。
JSON增强
json数据格式和关系型数据库的数据格式是不一样的,它是一个结构不固定的数据结构方式,也算是属于nosql范畴,mysql针对json不断的增强。mysql8.0关于json有了一些增强,主要是增加了一些内置的运算符和数据处理函数。
1.内联路径操作符
主要用于获取json对象在某一些节点或者某些路径上的数据。
内联操作符的表达式:
column->>path 等价于JSON_UNQUOTE( column -> path) JSON_UNQUOTE(JSON_EXTRACT(column,path))
示例演示
mysql> with doc(data) as
-> ( select json_object('id','1','name','tom')) #创建一个json对象 有两个字段 id name
-> select json_unquote(data->'$.name') from doc; #获得节点name的值
+------------------------------+
| json_unquote(data->'$.name') |
+------------------------------+
| tom |
+------------------------------+
还有一种方式也是之前版本支持的,这里实用另外一个函数json_extract
mysql> with doc(data) as
-> ( select json_object('id','1','name','tom'))
-> select json_unquote(json_extract(data,'$.name')) from doc; +-------------------------------------------+ | json_unquote(json_extract(data,'$.name')) | +-------------------------------------------+ | tom | +-------------------------------------------+
以上是mysql8之前写法
下面看mysql8.0内联路径操作符的写法
mysql> with doc(data) as ( select json_object('id','1','name','tom')) select data->>'$.name' from doc;
+-----------------+
| data->>'$.name' |
+-----------------+
| tom |
+-----------------+
mysql8.0还扩展了这个路径表达式的语法,可以支持范围的操作。
mysql> select json_extract('["a","b","c"]','$[1]');
+--------------------------------------+
| json_extract('["a","b","c"]','$[1]') |
+--------------------------------------+
| "b" |
+--------------------------------------+
mysql> select json_extract('["a","b","c"]','$[1 to 3]'); #这个是新版本写法 支持范围查找
+-------------------------------------------+
| json_extract('["a","b","c"]','$[1 to 3]') |
+-------------------------------------------+
| ["b", "c"] |
+-------------------------------------------+
2.json聚合函数
可以将表中列的数据聚合成对应的json数组或者json对象。
mysql8.0增加了两个聚合函数,mysql5.7.22也增加了相同的函数。
1)JSON_ARRAYAGG() ,用于将多行数据组合生成JSON数组。
2) JSON_OBJECTAGG(),用于生成json对象。
示例演示
mysql> create table jsontable(i int,attribute varchar(100),value varchar(100)); mysql> insert into jsontable values(2,'color','red'),(2,'fabric','silk'),(3,'color','green'),(3,'shape','square');
json聚合函数和普通聚合函数是一样的。
先看数组聚合函数
mysql> select i,json_arrayagg(attribute) as attributes from jsontable group by i; +------+---------------------+ | i | attributes | +------+---------------------+ | 2 | ["color", "fabric"] | | 3 | ["color", "shape"] | +------+---------------------+
json_objectagg支持多个列
mysql> select i,json_objectagg(attribute,value) as attributes from jsontable group by i;
+------+---------------------------------------+
| i | attributes |
+------+---------------------------------------+
| 2 | {"color": "red", "fabric": "silk"} |
| 3 | {"color": "green", "shape": "square"} |
+------+---------------------------------------+
如果存在重复值是如何处理的
mysql> insert into jsontable values(3,'color','yellow');
mysql> select * from jsontable;
+------+-----------+--------+
| i | attribute | value |
+------+-----------+--------+
| 2 | color | red |
| 2 | fabric | silk |
| 3 | color | green |
| 3 | shape | square |
| 3 | color | yellow |
+------+-----------+--------+
mysql> select i,json_objectagg(attribute,value) as attributes from jsontable group by i;
+------+----------------------------------------+
| i | attributes |
+------+----------------------------------------+
| 2 | {"color": "red", "fabric": "silk"} |
| 3 | {"color": "yellow", "shape": "square"} | #最后面的值覆盖前面的值
+------+----------------------------------------+
3.json实用函数
用于对json对象的输出或者获取json所占用的存储空间。
mysql8.0 (mysql5.7.22)增加了JSON_PRETTY()。这个函数用于在输出json对象内容的时候进行格式化或者美化的输出。
mysql8.0 (mysql5.7.22)增加了JSON_STORAGE_SIZE(),返回json数据所占用的空间大小。
JSON_STORAGE_FREE(),用于更新某些json列之后,相应的一些字段它可能释放的存储空间。
mysql> select json_object('id','1','name','jack'); #先构造一个json对象
+-------------------------------------+
| json_object('id','1','name','jack') |
+-------------------------------------+
| {"id": "1", "name": "jack"} |
+-------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select json_pretty(json_object('id','1','name','jack')); #内容一样,格式被处理了
+--------------------------------------------------+
| json_pretty(json_object('id','1','name','jack')) |
+--------------------------------------------------+
| {
"id": "1",
"name": "jack"
} |
mysql> create table json_table2 (j_field varchar(200));
mysql> insert into json_table2 values('{"a":1000,"b":"aaa","c":"[1,2,3,4,5,6]"}');
mysql> select * from json_table2;
+------------------------------------------+
| j_field |
+------------------------------------------+
| {"a":1000,"b":"aaa","c":"[1,2,3,4,5,6]"} |
+------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select j_field , json_storage_size(j_field) from json_table2; #查看空间大小
+------------------------------------------+----------------------------+
| j_field | json_storage_size(j_field) |
+------------------------------------------+----------------------------+
| {"a":1000,"b":"aaa","c":"[1,2,3,4,5,6]"} | 47 | #47个字节
+------------------------------------------+----------------------------+
mysql> select j_field , json_storage_free(j_field) from json_table2;
+------------------------------------------+----------------------------+
| j_field | json_storage_free(j_field) |
+------------------------------------------+----------------------------+
| {"a":1000,"b":"aaa","c":"[1,2,3,4,5,6]"} | 0 | #默认上面表数据没有更新 所以这里数据显示释放的空间为0
+------------------------------------------+----------------------------+
mysql> update json_table2 set j_field = json_set(j_field,"$.a",10,"$.b","bb","$.c",1);
4.json合并函数
主要是将两个json对象合并成一个。
5.json表函数
和json聚合函数执行相反的操作。将这种json对象扩展成关系型数据表行和列组织的数据形式。
四.mysql8.0其它的新的特性
1. 默认字符集由latin1变为utf8mb4。
2. 统计直方图,是一种统计信息,统计表中字段各值的分布情况。由于有时候查询优化器会走不到最优的执行计划,所以利用统计直方图,用户可以对一张表的一列做数据分布的统计,尤其是针对没有索引的字段。这可以帮助查询优化器找到更优的执行计划。统计直方图的主要使用场景是用来计算字段选择性。
3.新增mysql-auto.cnf文件,比my.cnf具有更高优先权。
五.mysql8.0去掉的特性
有增加的新特性,也会有去掉不适用老的功能
1.取消 Query Cache
现在性能审计中第一件事就是禁用 Query Cache ,因为他给数据库设计带来很多麻烦。 MySQL QC 造成的问题比他解决问题要多得多。 因此我们决定在 MySQL 8.0 中取消他,因为大家就不应该使用它。 如果你工作中需要使用 Query Cache,你应该用 ProxySQL as Query Cache 替代 Query Cache。
但是大多数情况下我会建议你不要使用查询缓存,为什么呢?因为查询缓存往往弊大于利。
查询缓存的失效非常频繁,只要有对一个表的更新,这个表上所有的查询缓存都会被清空。因此很可能你费劲地把结果存起来,还没使用呢,就被一个更新全清空了。对于更新压力大的数据库来说,查询缓存的命中率会非常低。除非你的业务就是有一张静态表,很长时间才会更新一次。比如,一个系统配置表,那这张表上的查询才适合使用查询缓存。
好在MySQL也提供了这种“按需使用”的方式。你可以将参数query_cache_type设置成DEMAND,这样对于默认的SQL语句都不使用查询缓存。而对于你确定要使用查询缓存的语句,可以用SQL_CACHE显式指定,像下面这个语句一样:
mysql> select SQL_CACHE * from T where ID=10;
需要注意的是,MySQL 8.0版本直接将查询缓存的整块功能删掉了,也就是说8.0开始彻底没有这个功能了。
mysql5.7 mysql8都是默认关闭的
mysql> show variables like '%query_cache%' ; +------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +------------------+-------+ | have_query_cache | NO | +------------------+-------+
2.取消默认MyISAM系统表:并发程度低,资源利用率低。
3.移除PASSWORD()函数,无法再用SET PASSWORD=PASSWORD(密码)去加密。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号