tee MultiWriter creates a writer that duplicates its writes to all the // provided writers, similar to the Unix tee(1) command.
https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tee
在计算机科学中,tee是一个常见的指令,它能够将某个指令的标准输出,导向、存入某个档案中。许多不同的命令行界面(Shell)都提供这个功能,如 Unix shell、Windows PowerShell。
tee的功能通常是用管道,让它不但能在萤幕输出,而且也能够将它储存在档案中。当一个资料在被另一个指令或程式改变之前的中间输出,也能够用tee来捕捉它。tee命令能够读取标准输入,之后将它的内容写入到标准输出,同时将它的副本写入特定的档案或变数中。
tee [ -a ] [ -i ] [檔案 ... ]
参数:
檔案一个或多个档案,能够接收 tee-d 的输出。
Flags:
-a追加(append)到目标文件而不是覆盖-i忽略中断。
[cpy@public ~]$ ll -as 总用量 32 0 drwx------ 10 cpy cpy 206 12月 25 17:50 . 0 drwxr-xr-x. 8 root root 111 12月 25 15:45 .. 12 -rw------- 1 cpy cpy 12194 12月 23 19:58 .bash_history 4 -rw-r--r-- 1 cpy cpy 18 8月 3 2016 .bash_logout 4 -rw-r--r-- 1 cpy cpy 193 8月 3 2016 .bash_profile 4 -rw-r--r-- 1 cpy cpy 231 8月 3 2016 .bashrc 0 drwxrwxr-x 4 cpy cpy 34 12月 9 19:12 .cache 0 drwxrwxr-x 3 cpy cpy 18 11月 25 11:53 .config 4 -rw-rw-r-- 1 cpy cpy 35 12月 25 17:50 file 0 drwxrwxr-x 7 cpy cpy 120 12月 23 16:59 game_manager 0 drwxrwxr-x 4 cpy cpy 28 12月 9 19:12 go 4 drwxrwxr-x 10 cpy cpy 4096 11月 26 12:25 perfCCpp 0 drwxrw---- 3 cpy cpy 19 12月 9 19:12 .pki 0 drwxrwxr-x 5 cpy cpy 176 12月 14 11:53 soft 0 drwx------ 2 cpy cpy 25 11月 25 12:21 .ssh [cpy@public ~]$ ll -as | tee file | cat 总用量 28 0 drwx------ 10 cpy cpy 206 12月 25 17:50 . 0 drwxr-xr-x. 8 root root 111 12月 25 15:45 .. 12 -rw------- 1 cpy cpy 12194 12月 23 19:58 .bash_history 4 -rw-r--r-- 1 cpy cpy 18 8月 3 2016 .bash_logout 4 -rw-r--r-- 1 cpy cpy 193 8月 3 2016 .bash_profile 4 -rw-r--r-- 1 cpy cpy 231 8月 3 2016 .bashrc 0 drwxrwxr-x 4 cpy cpy 34 12月 9 19:12 .cache 0 drwxrwxr-x 3 cpy cpy 18 11月 25 11:53 .config 0 -rw-rw-r-- 1 cpy cpy 0 12月 25 17:51 file 0 drwxrwxr-x 7 cpy cpy 120 12月 23 16:59 game_manager 0 drwxrwxr-x 4 cpy cpy 28 12月 9 19:12 go 4 drwxrwxr-x 10 cpy cpy 4096 11月 26 12:25 perfCCpp 0 drwxrw---- 3 cpy cpy 19 12月 9 19:12 .pki 0 drwxrwxr-x 5 cpy cpy 176 12月 14 11:53 soft 0 drwx------ 2 cpy cpy 25 11月 25 12:21 .ssh [cpy@public ~]$
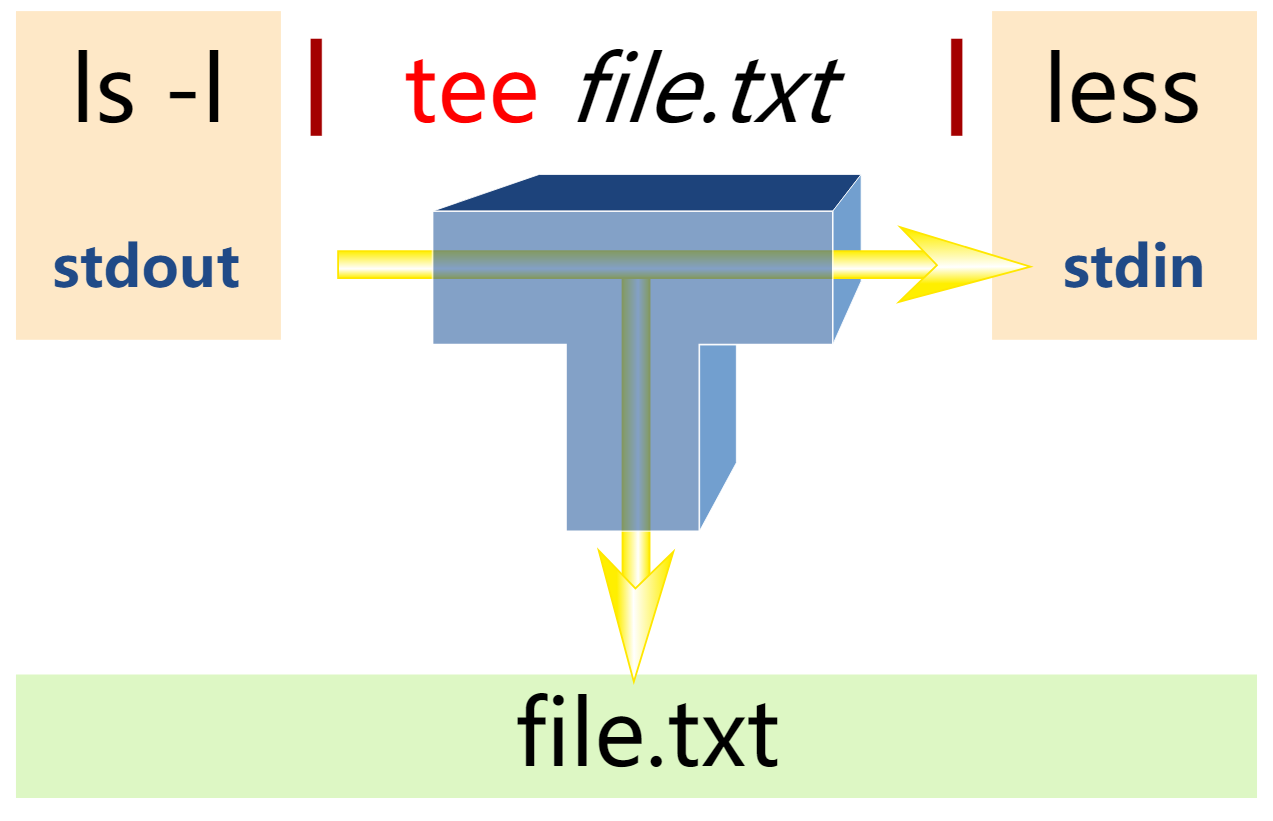
In computing, tee is a command in command-line interpreters (shells) using standard streams which reads standard input and writes it to both standard output and one or more files, effectively duplicating its input.[1] It is primarily used in conjunction with pipes and filters. The command is named after the T-splitter used in plumbing.[2]
The tee command is normally used to split the output of a program so that it can be both displayed and saved in a file. The command can be used to capture intermediate output before the data is altered by another command or program. The tee command reads standard input, then writes its content to standard output. It simultaneously copies the result into the specified file(s) or variables. The syntax differs depending on the command's implementation.
io/multi.go
// MultiWriter creates a writer that duplicates its writes to all the
// provided writers, similar to the Unix tee(1) command.
//
// Each write is written to each listed writer, one at a time.
// If a listed writer returns an error, that overall write operation
// stops and returns the error; it does not continue down the list.
func MultiWriter(writers ...Writer) Writer {
allWriters := make([]Writer, 0, len(writers))
for _, w := range writers {
if mw, ok := w.(*multiWriter); ok {
allWriters = append(allWriters, mw.writers...)
} else {
allWriters = append(allWriters, w)
}
}
return &multiWriter{allWriters}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号