Apache ShardingSphere
Apache ShardingSphere https://shardingsphere.apache.org/
背景
传统的将数据集中存储至单一节点的解决方案,在性能、可用性和运维成本这三方面已经难于满足海量数据的场景。
从性能方面来说,由于关系型数据库大多采用 B+ 树类型的索引,在数据量超过阈值的情况下,索引深度的增加也将使得磁盘访问的 IO 次数增加,进而导致查询性能的下降; 同时,高并发访问请求也使得集中式数据库成为系统的最大瓶颈。
从可用性的方面来讲,服务化的无状态性,能够达到较小成本的随意扩容,这必然导致系统的最终压力都落在数据库之上。 而单一的数据节点,或者简单的主从架构,已经越来越难以承担。数据库的可用性,已成为整个系统的关键。
从运维成本方面考虑,当一个数据库实例中的数据达到阈值以上,对于 DBA 的运维压力就会增大。 数据备份和恢复的时间成本都将随着数据量的大小而愈发不可控。一般来讲,单一数据库实例的数据的阈值在 1TB 之内,是比较合理的范围。
在传统的关系型数据库无法满足互联网场景需要的情况下,将数据存储至原生支持分布式的 NoSQL 的尝试越来越多。 但 NoSQL 对 SQL 的不兼容性以及生态圈的不完善,使得它们在与关系型数据库的博弈中始终无法完成致命一击,而关系型数据库的地位却依然不可撼动。
数据分片指按照某个维度将存放在单一数据库中的数据分散地存放至多个数据库或表中以达到提升性能瓶颈以及可用性的效果。 数据分片的有效手段是对关系型数据库进行分库和分表。分库和分表均可以有效的避免由数据量超过可承受阈值而产生的查询瓶颈。 除此之外,分库还能够用于有效的分散对数据库单点的访问量;分表虽然无法缓解数据库压力,但却能够提供尽量将分布式事务转化为本地事务的可能,一旦涉及到跨库的更新操作,分布式事务往往会使问题变得复杂。 使用多主多从的分片方式,可以有效的避免数据单点,从而提升数据架构的可用性。
通过分库和分表进行数据的拆分来使得各个表的数据量保持在阈值以下,以及对流量进行疏导应对高访问量,是应对高并发和海量数据系统的有效手段。 数据分片的拆分方式又分为垂直分片和水平分片。
垂直分片
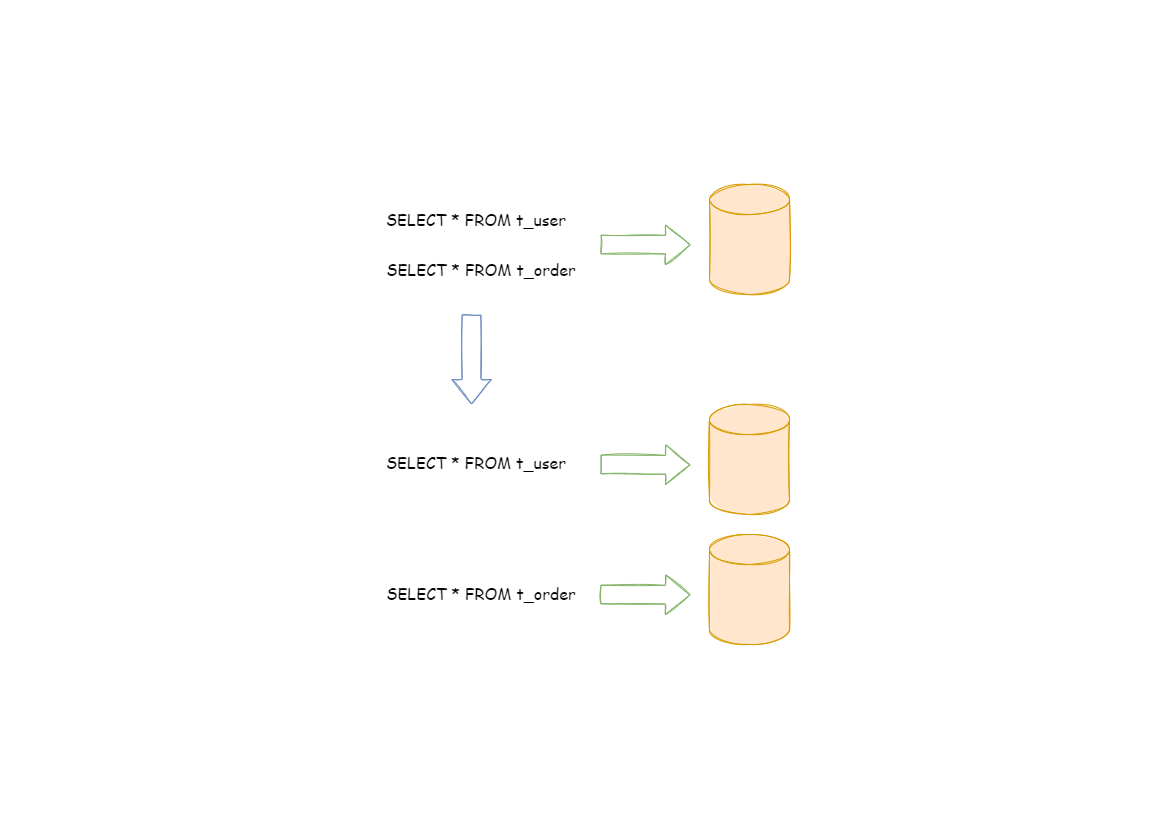
按照业务拆分的方式称为垂直分片,又称为纵向拆分,它的核心理念是专库专用。 在拆分之前,一个数据库由多个数据表构成,每个表对应着不同的业务。而拆分之后,则是按照业务将表进行归类,分布到不同的数据库中,从而将压力分散至不同的数据库。 下图展示了根据业务需要,将用户表和订单表垂直分片到不同的数据库的方案。
垂直分片往往需要对架构和设计进行调整。通常来讲,是来不及应对互联网业务需求快速变化的;而且,它也并无法真正的解决单点瓶颈。 垂直拆分可以缓解数据量和访问量带来的问题,但无法根治。如果垂直拆分之后,表中的数据量依然超过单节点所能承载的阈值,则需要水平分片来进一步处理。
水平分片
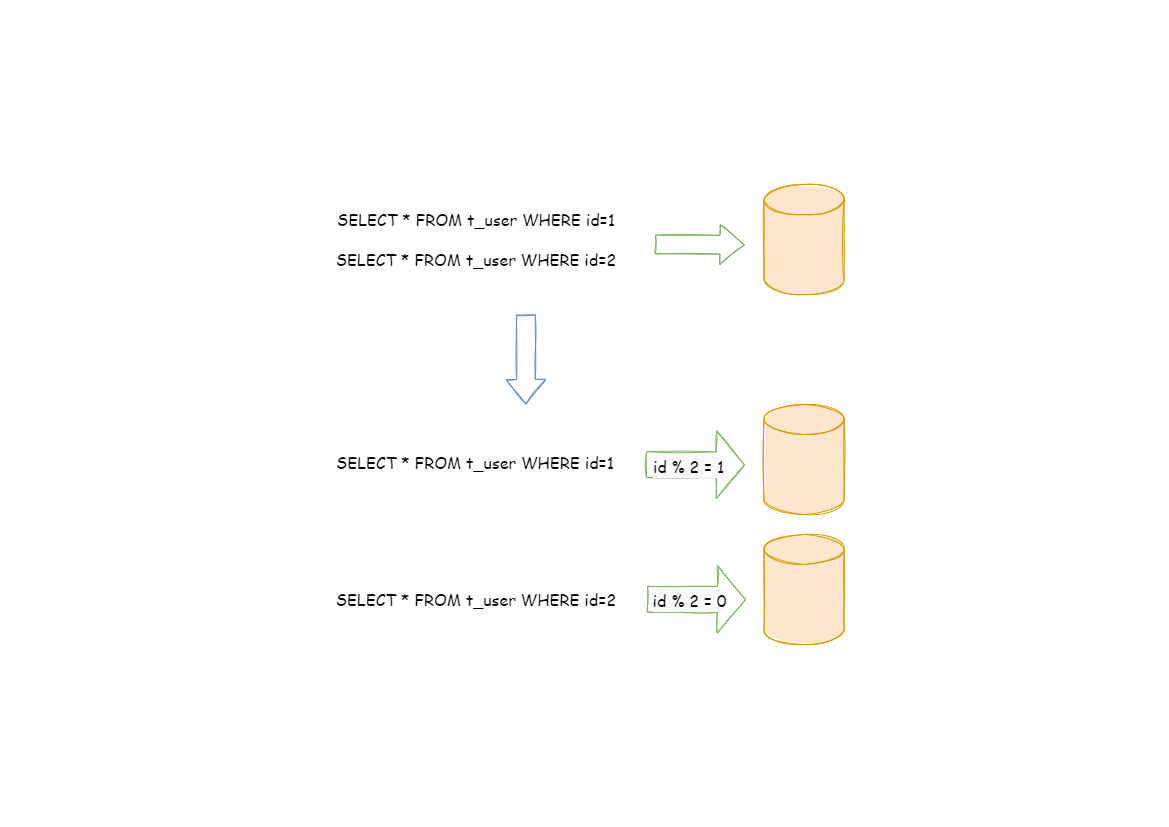
水平分片又称为横向拆分。 相对于垂直分片,它不再将数据根据业务逻辑分类,而是通过某个字段(或某几个字段),根据某种规则将数据分散至多个库或表中,每个分片仅包含数据的一部分。 例如:根据主键分片,偶数主键的记录放入 0 库(或表),奇数主键的记录放入 1 库(或表),如下图所示。
水平分片从理论上突破了单机数据量处理的瓶颈,并且扩展相对自由,是数据分片的标准解决方案。
挑战
虽然数据分片解决了性能、可用性以及单点备份恢复等问题,但分布式的架构在获得了收益的同时,也引入了新的问题。
面对如此散乱的分片之后的数据,应用开发工程师和数据库管理员对数据库的操作变得异常繁重就是其中的重要挑战之一。 他们需要知道数据需要从哪个具体的数据库的子表中获取。
另一个挑战则是,能够正确的运行在单节点数据库中的 SQL,在分片之后的数据库中并不一定能够正确运行。 例如,分表导致表名称的修改,或者分页、排序、聚合分组等操作的不正确处理。
跨库事务也是分布式的数据库集群要面对的棘手事情。 合理采用分表,可以在降低单表数据量的情况下,尽量使用本地事务,善于使用同库不同表可有效避免分布式事务带来的麻烦。 在不能避免跨库事务的场景,有些业务仍然需要保持事务的一致性。 而基于 XA 的分布式事务由于在并发度高的场景中性能无法满足需要,并未被互联网巨头大规模使用,他们大多采用最终一致性的柔性事务代替强一致事务。
目标
尽量透明化分库分表所带来的影响,让使用方尽量像使用一个数据库一样使用水平分片之后的数据库集群,是 Apache ShardingSphere 数据分片模块的主要设计目标。
应用场景
海量数据高并发的 OLTP 场景
由于关系型数据库大多采用 B+ 树类型的索引,在数据量超过阈值的情况下,索引深度的增加也将使得磁盘访问的 IO 次数增加,进而导致查询性能的下降。通过 ShardingSphere 数据分片,按照某个业务维度,将存放在单一数据库中的数据分散地存放至多个数据库或表中,可以达到提升性能的效果。通过使用 ShardingSphere-JDBC 接入端,可以满足高并发的 OLTP 场景下的性能要求。
海量数据实时分析 OLAP 场景
在传统的数据库架构中,如果用户想要进行数据分析,需要先使用 ETL 工具,将数据同步至数据平台中,然后再进行数据分析,使用 ETL 工具会导致数据分析的实效性大打折扣。ShardingSphere-Proxy 提供静态入口以及异构语言的支持,独立于应用程序部署,适用于实时分析的 OLAP 场景。
相关参考
核心概念
表
表是透明化数据分片的关键概念。 Apache ShardingSphere 通过提供多样化的表类型,适配不同场景下的数据分片需求。
逻辑表
相同结构的水平拆分数据库(表)的逻辑名称,是 SQL 中表的逻辑标识。 例:订单数据根据主键尾数拆分为 10 张表,分别是 t_order_0 到 t_order_9,他们的逻辑表名为 t_order。
真实表
在水平拆分的数据库中真实存在的物理表。 即上个示例中的 t_order_0 到 t_order_9。
绑定表
指分片规则一致的一组分片表。 使用绑定表进行多表关联查询时,必须使用分片键进行关联,否则会出现笛卡尔积关联或跨库关联,从而影响查询效率。 例如:t_order 表和 t_order_item 表,均按照 order_id 分片,并且使用 order_id 进行关联,则此两张表互为绑定表关系。 绑定表之间的多表关联查询不会出现笛卡尔积关联,关联查询效率将大大提升。 举例说明,如果 SQL 为:
SELECT i.* FROM t_order o JOIN t_order_item i ON o.order_id=i.order_id WHERE o.order_id in (10, 11);
在不配置绑定表关系时,假设分片键 order_id 将数值 10 路由至第 0 片,将数值 11 路由至第 1 片,那么路由后的 SQL 应该为 4 条,它们呈现为笛卡尔积:
SELECT i.* FROM t_order_0 o JOIN t_order_item_0 i ON o.order_id=i.order_id WHERE o.order_id in (10, 11);
SELECT i.* FROM t_order_0 o JOIN t_order_item_1 i ON o.order_id=i.order_id WHERE o.order_id in (10, 11);
SELECT i.* FROM t_order_1 o JOIN t_order_item_0 i ON o.order_id=i.order_id WHERE o.order_id in (10, 11);
SELECT i.* FROM t_order_1 o JOIN t_order_item_1 i ON o.order_id=i.order_id WHERE o.order_id in (10, 11);
在配置绑定表关系,并且使用 order_id 进行关联后,路由的 SQL 应该为 2 条:
SELECT i.* FROM t_order_0 o JOIN t_order_item_0 i ON o.order_id=i.order_id WHERE o.order_id in (10, 11);
SELECT i.* FROM t_order_1 o JOIN t_order_item_1 i ON o.order_id=i.order_id WHERE o.order_id in (10, 11);
其中 t_order 表由于指定了分片条件,ShardingSphere 将会以它作为整个绑定表的主表。 所有路由计算将会只使用主表的策略,那么 t_order_item 表的分片计算将会使用 t_order 的条件。
注意:绑定表中的多个分片规则,需要按照逻辑表前缀组合分片后缀的方式进行配置,例如:
rules:
- !SHARDING
tables:
t_order:
actualDataNodes: ds_${0..1}.t_order_${0..1}
t_order_item:
actualDataNodes: ds_${0..1}.t_order_item_${0..1}
广播表
指所有的数据源中都存在的表,表结构及其数据在每个数据库中均完全一致。 适用于数据量不大且需要与海量数据的表进行关联查询的场景,例如:字典表。
单表
指所有的分片数据源中仅唯一存在的表。 适用于数据量不大且无需分片的表。
注意:符合以下条件的单表会被自动加载:
- 数据加密、数据脱敏等规则中显示配置的单表
- 用户通过 ShardingSphere 执行 DDL 语句创建的单表
其余不符合上述条件的单表,ShardingSphere 不会自动加载,用户可根据需要配置单表规则进行管理。
数据节点
数据分片的最小单元,由数据源名称和真实表组成。 例:ds_0.t_order_0。 逻辑表与真实表的映射关系,可分为均匀分布和自定义分布两种形式。
均匀分布
指数据表在每个数据源内呈现均匀分布的态势, 例如:
db0
├── t_order0
└── t_order1
db1
├── t_order0
└── t_order1
数据节点的配置如下:
db0.t_order0, db0.t_order1, db1.t_order0, db1.t_order1
自定义分布
指数据表呈现有特定规则的分布, 例如:
db0
├── t_order0
└── t_order1
db1
├── t_order2
├── t_order3
└── t_order4
数据节点的配置如下:
db0.t_order0, db0.t_order1, db1.t_order2, db1.t_order3, db1.t_order4
分片
分片键
用于将数据库(表)水平拆分的数据库字段。 例:将订单表中的订单主键的尾数取模分片,则订单主键为分片字段。 SQL 中如果无分片字段,将执行全路由,性能较差。 除了对单分片字段的支持,Apache ShardingSphere 也支持根据多个字段进行分片。
分片算法
用于将数据分片的算法,支持 =、>=、<=、>、<、BETWEEN 和 IN 进行分片。 分片算法可由开发者自行实现,也可使用 Apache ShardingSphere 内置的分片算法语法糖,灵活度非常高。
自动化分片算法
分片算法语法糖,用于便捷的托管所有数据节点,使用者无需关注真实表的物理分布。 包括取模、哈希、范围、时间等常用分片算法的实现。
自定义分片算法
提供接口让应用开发者自行实现与业务实现紧密相关的分片算法,并允许使用者自行管理真实表的物理分布。 自定义分片算法又分为:
- 标准分片算法
用于处理使用单一键作为分片键的 =、IN、BETWEEN AND、>、<、>=、<= 进行分片的场景。
- 复合分片算法
用于处理使用多键作为分片键进行分片的场景,包含多个分片键的逻辑较复杂,需要应用开发者自行处理其中的复杂度。
- Hint 分片算法
用于处理使用 Hint 行分片的场景。
分片策略
包含分片键和分片算法,由于分片算法的独立性,将其独立抽离。 真正可用于分片操作的是分片键 + 分片算法,也就是分片策略。
强制分片路由
对于分片字段并非由 SQL 而是其他外置条件决定的场景,可使用 SQL Hint 注入分片值。 例:按照员工登录主键分库,而数据库中并无此字段。 SQL Hint 支持通过 Java API 和 SQL 注释两种方式使用。 详情请参见强制分片路由。
行表达式
行表达式是为了解决配置的简化与一体化这两个主要问题。在繁琐的数据分片规则配置中,随着数据节点的增多,大量的重复配置使得配置本身不易被维护。 通过行表达式可以有效地简化数据节点配置工作量。
对于常见的分片算法,使用 Java 代码实现并不有助于配置的统一管理。 通过行表达式书写分片算法,可以有效地将规则配置一同存放,更加易于浏览与存储。
行表达式作为字符串由两部分组成,分别是字符串开头的对应 SPI 实现的 Type Name 部分和表达式部分。 以 <GROOVY>t_order_${1..3} 为例,字符 串<GROOVY> 部分的子字符串 GROOVY 为此行表达式使用的对应 SPI 实现的 Type Name,其被 <> 符号包裹来识别。而字符串 t_order_${1..3} 为此行表达式的表达式部分。当行表达式不指定 Type Name 时,例如 t_order_${1..3},行表示式默认将使用 InlineExpressionParser SPI 的 GROOVY 实现来解析表达式。
以下部分介绍 GROOVY 实现的语法规则。
行表达式的使用非常直观,只需要在配置中使用 ${ expression } 或 $->{ expression } 标识行表达式即可。 目前支持数据节点和分片算法这两个部分的配置。 行表达式的内容使用的是 Groovy 的语法,Groovy 能够支持的所有操作,行表达式均能够支持。 例如:
${begin..end} 表示范围区间 ${[unit1, unit2, unit_x]} 表示枚举值
行表达式中如果出现连续多个 ${ expression } 或 $->{ expression } 表达式,整个表达式最终的结果将会根据每个子表达式的结果进行笛卡尔组合。
例如,以下行表达式:
${['online', 'offline']}_table${1..3}
最终会解析为:
online_table1, online_table2, online_table3, offline_table1, offline_table2, offline_table3
分布式主键
传统数据库软件开发中,主键自动生成技术是基本需求。而各个数据库对于该需求也提供了相应的支持,比如 MySQL 的自增键,Oracle 的自增序列等。 数据分片后,不同数据节点生成全局唯一主键是非常棘手的问题。同一个逻辑表内的不同实际表之间的自增键由于无法互相感知而产生重复主键。 虽然可通过约束自增主键初始值和步长的方式避免碰撞,但需引入额外的运维规则,使解决方案缺乏完整性和可扩展性。
目前有许多第三方解决方案可以完美解决这个问题,如 UUID 等依靠特定算法自生成不重复键,或者通过引入主键生成服务等。为了方便用户使用、满足不同用户不同使用场景的需求, Apache ShardingSphere 不仅提供了内置的分布式主键生成器,例如 UUID、SNOWFLAKE,还抽离出分布式主键生成器的接口,方便用户自行实现自定义的自增主键生成器。
Background
The traditional solution that stores all the data in one concentrated node has hardly satisfied the requirement of massive data scenario in three aspects, performance, availability and operation cost.
In performance, the relational database mostly uses B+ tree index. When the data amount exceeds the threshold, deeper index will increase the disk IO access number, and thereby, weaken the performance of query. In the same time, high concurrency requests also make the centralized database to be the greatest limitation of the system.
In availability, capacity can be expanded at a relatively low cost and any extent with stateless service, which can make all the pressure, at last, fall on the database. But the single data node or simple primary-replica structure has been harder and harder to take these pressures. Therefore, database availability has become the key to the whole system.
From the aspect of operation costs, when the data in a database instance has reached above the threshold, DBA’s operation pressure will also increase. The time cost of data backup and data recovery will be more uncontrollable with increasing amount of data. Generally, it is a relatively reasonable range for the data in single database case to be within 1TB.
Under the circumstance that traditional relational databases cannot satisfy the requirement of the Internet, there are more and more attempts to store the data in native distributed NoSQL. But its incompatibility with SQL and imperfection in ecosystem block it from defeating the relational database in the competition, so the relational database still holds an unshakable position.
Sharding refers to splitting the data in one database and storing them in multiple tables and databases according to some certain standard, so that the performance and availability can be improved. Both methods can effectively avoid the query limitation caused by data exceeding affordable threshold. What’s more, database sharding can also effectively disperse TPS. Table sharding, though cannot ease the database pressure, can provide possibilities to transfer distributed transactions to local transactions, since cross-database upgrades are once involved, distributed transactions can turn pretty tricky sometimes. The use of multiple primary-replica sharding method can effectively avoid the data concentrating on one node and increase the architecture availability.
Splitting data through database sharding and table sharding is an effective method to deal with high TPS and mass amount data system, because it can keep the data amount lower than the threshold and evacuate the traffic. Sharding method can be divided into vertical sharding and horizontal sharding.
Vertical Sharding
According to business sharding method, it is called vertical sharding, or longitudinal sharding, the core concept of which is to specialize databases for different uses. Before sharding, a database consists of many tables corresponding to different businesses. But after sharding, tables are categorized into different databases according to business, and the pressure is also separated into different databases. The diagram below has presented the solution to assign user tables and order tables to different databases by vertical sharding according to business need.
Vertical sharding requires to adjust the architecture and design from time to time. Generally speaking, it is not soon enough to deal with fast changing needs from Internet business and not able to really solve the single-node problem. it can ease problems brought by the high data amount and concurrency amount, but cannot solve them completely. After vertical sharding, if the data amount in the table still exceeds the single node threshold, it should be further processed by horizontal sharding.
Horizontal Sharding
Horizontal sharding is also called transverse sharding. Compared with the categorization method according to business logic of vertical sharding, horizontal sharding categorizes data to multiple databases or tables according to some certain rules through certain fields, with each sharding containing only part of the data. For example, according to primary key sharding, even primary keys are put into the 0 database (or table) and odd primary keys are put into the 1 database (or table), which is illustrated as the following diagram.
Theoretically, horizontal sharding has overcome the limitation of data processing volume in single machine and can be extended relatively freely, so it can be taken as a standard solution to database sharding and table sharding.
Challenges
Although data sharding solves problems regarding performance, availability, and backup recovery of single points, the distributed architecture has introduced new problems while gaining benefits.
One of the major challenges is that application development engineers and database administrators become extremely overwhelmed with all these operations after such a scattered way of data sharding. They need to know from which specific sub-table can they fetch the data needed.
Another challenge is that SQL that works correctly in one single-node database does not necessarily work correctly in a sharded database. For example, table splitting results in table name changes, or incorrect handling of operations such as paging, sorting, and aggregate grouping.
Cross-library transactions are also tricky for a distributed database cluster. Reasonable use of table splitting can minimize the use of local transactions while reducing the amount of data in a single table, and appropriate use of different tables in the same database can effectively avoid the trouble caused by distributed transactions. In scenarios where cross-library transactions cannot be avoided, some businesses might still be in the need to maintain transaction consistency. The XA-based distributed transactions are not used by Internet giants on a large scale because their performance cannot meet the needs in scenarios with high concurrency, and most of them use flexible transactions with ultimate consistency instead of strong consistent transactions.
Goal
The main design goal of the data sharding modular of Apache ShardingSphere is to try to reduce the influence of sharding, in order to let users use horizontal sharding database group like one database.
Application Scenarios
Mass data high concurrency in OLTP scenarios
Most relational databases use B+ tree indexes, but when the amount of data exceeds the threshold, the increase in index depth will also increase the number of I/O in accessing the disk, which will lower the query performance. Data sharding through ShardingSphere enables data stored in a single database to be dispersed into multiple databases or tables according to a business dimension, which improves performance. The ShardingSphere-JDBC access port can meet the performance requirements of high concurrency in OLTP scenarios.
Mass data real-time analysis in OLAP scenarios
In traditional database architecture, if users want to analyze data, they need to use ETL tools first, synchronize the data to the data platform, and then perform data analysis. However, ETL tools will greatly reduce the effectiveness of data analysis. ShardingSphere-Proxy provides support for static entry and heterogeneous languages, independent of application deployment, which is suitable for real-time analysis in OLAP scenarios.
Related References


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号