数据宽度和存储容量的单位 数据在内存中的存放顺序 字节顺序 大端 小端 对齐 网络传输一般采用大端序 BigEndian ByteOrder
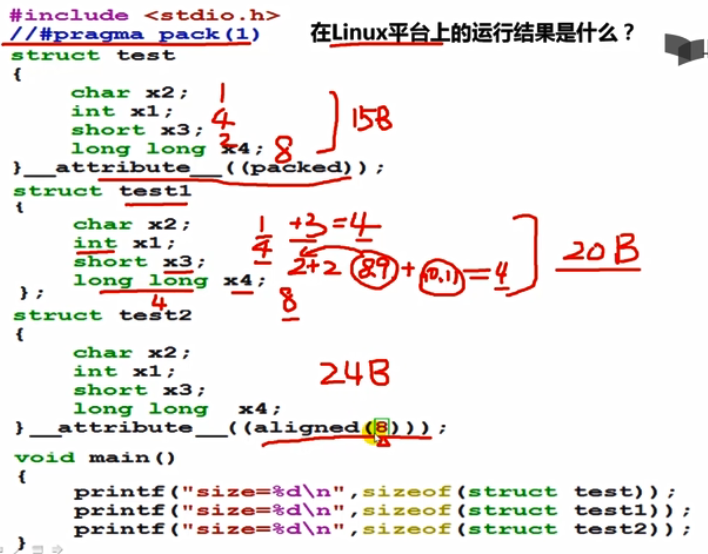
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 | char x2; int x1; short x3; long long x4;1,4,2,8struct test{ char x2; int x1; short x3; long long x4;} __attribute__((packed));struct test1{ char x2; int x1; short x3; long long x4;};struct test2{ char x2; int x1; short x3; long long x4;} __attribute__((aligned(4)));struct test3{ char x2; int x1; short x3; long long x4;} __attribute__((aligned(8)));struct test4{ char x2; int x1; short x3; long long x4;} __attribute__((aligned(16)));Linux short char 2字节对齐,其他4字节对齐 当cpu字长64位=8byte1,4,2,8#pragma pack()1,4,2,8=151,4,2,8=0-0,4-7,8-9,16-23=241,4,2,8=0-0,4-7,8-9,12-19=20->241,4,2,8=0-0,4-7,8-9,12-19=20->241,4,2,8=0-0,4-7,8-9,12-19=20->32# pragma pack(1)1,4,2,8=151,4,2,8=151,4,2,8=15->161,4,2,8=15->161,4,2,8=15->16# pragma pack(2)1,4,2,8=151,4,2,8=0-0,2-5,6-7,8-15=161,4,2,8=0-0,2-5,6-7,8-15=161,4,2,8=0-0,2-5,6-7,8-15=161,4,2,8=0-0,2-5,6-7,8-15=16# pragma pack(4)1,4,2,8=151,4,2,8=0-0,4-7,8-9,12-19=201,4,2,8=0-0,4-7,8-9,12-19=201,4,2,8=0-0,4-7,8-9,12-19=20->241,4,2,8=0-0,4-7,8-9,12-19=20->32 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 | #include <stdio.h>#pragma pack()struct test{ char x2; int x1; short x3; long long x4;} __attribute__((packed));struct test1{ char x2; int x1; short x3; long long x4;};struct test2{ char x2; int x1; short x3; long long x4;} __attribute__((aligned(4)));struct test3{ char x2; int x1; short x3; long long x4;} __attribute__((aligned(8)));struct test4{ char x2; int x1; short x3; long long x4;} __attribute__((aligned(16)));void main(){ printf("%lu \n", sizeof(struct test)); printf("%lu \n", sizeof(struct test1)); printf("%lu \n", sizeof(struct test2)); printf("%lu \n", sizeof(struct test3)); printf("%lu \n", sizeof(struct test4));} 1 .file "alignment_pragma_pack.c" 2 .text 3 .section .rodata 4 .LC0: 5 .string "%lu \n" 6 .text 7 .globl main 8 .type main, @function 9 main: 10 .LFB0: 11 .cfi_startproc 12 endbr64 13 pushq %rbp 14 .cfi_def_cfa_offset 16 15 .cfi_offset 6, -16 16 movq %rsp, %rbp 17 .cfi_def_cfa_register 6 18 movl $15, %esi 19 leaq .LC0(%rip), %rax 20 movq %rax, %rdi 21 movl $0, %eax 22 call printf@PLT 23 movl $24, %esi 24 leaq .LC0(%rip), %rax 25 movq %rax, %rdi 26 movl $0, %eax 27 call printf@PLT 28 movl $24, %esi 29 leaq .LC0(%rip), %rax 30 movq %rax, %rdi 31 movl $0, %eax 32 call printf@PLT 33 movl $24, %esi 34 leaq .LC0(%rip), %rax 35 movq %rax, %rdi 36 movl $0, %eax 37 call printf@PLT 38 movl $32, %esi 39 leaq .LC0(%rip), %rax 40 movq %rax, %rdi 41 movl $0, %eax 42 call printf@PLT 43 nop 44 popq %rbp 45 .cfi_def_cfa 7, 8 46 ret 47 .cfi_endproc 48 .LFE0: 49 .size main, .-main 50 .ident "GCC: (Ubuntu 11.2.0-19ubuntu1) 11.2.0" 51 .section .note.GNU-stack,"",@progbits 52 .section .note.gnu.property,"a" 53 .align 8 54 .long 1f - 0f 55 .long 4f - 1f 56 .long 5 57 0: 58 .string "GNU" 59 1: 60 .align 8 61 .long 0xc0000002 62 .long 3f - 2f 63 2: 64 .long 0x3 65 3: 66 .align 8 67 4:1524242432processor : 0vendor_id : GenuineIntelcpu family : 6model : 142model name : Intel(R) Core(TM) i3-10110U CPU @ 2.10GHzstepping : 12cpu MHz : 2592.000cache size : 4096 KBphysical id : 0siblings : 1core id : 0cpu cores : 1apicid : 0initial apicid : 0fpu : yesfpu_exception : yescpuid level : 22wp : yesflags : fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush mmx fxsr sse sse2 ht syscall nx rdtscp lm constant_tsc rep_good nopl xtopology nonstop_tsc cpuid tsc_known_freq pni pclmulqdq monitor ssse3 cx16 pcid sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic movbe popcnt aes xsave avx rdrand hypervisor lahf_lm abm 3dnowprefetch invpcid_single fsgsbase avx2 invpcid rdseed clflushopt md_clear flush_l1d arch_capabilitiesbugs : spectre_v1 spectre_v2 spec_store_bypass swapgs itlb_multihit srbds mmio_stale_data retbleedbogomips : 5184.00clflush size : 64cache_alignment : 64address sizes : 39 bits physical, 48 bits virtualpower management: |


对齐方式设定
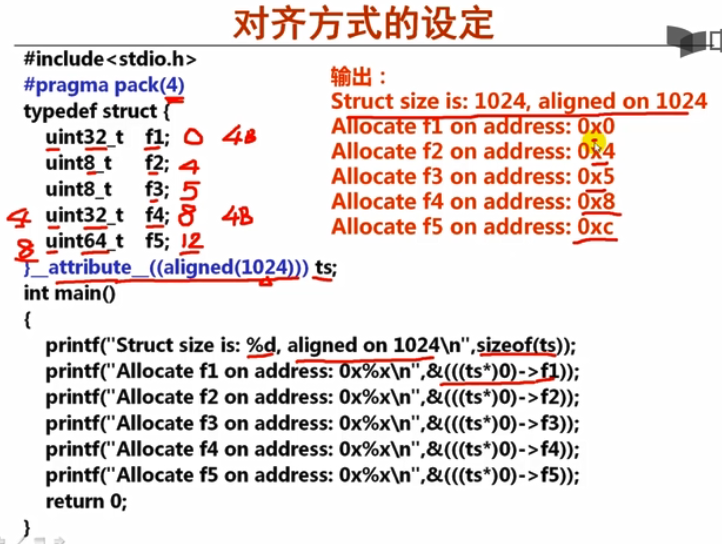
f5 自然边界8,比4大,按4边界对齐,12是4倍数满足。
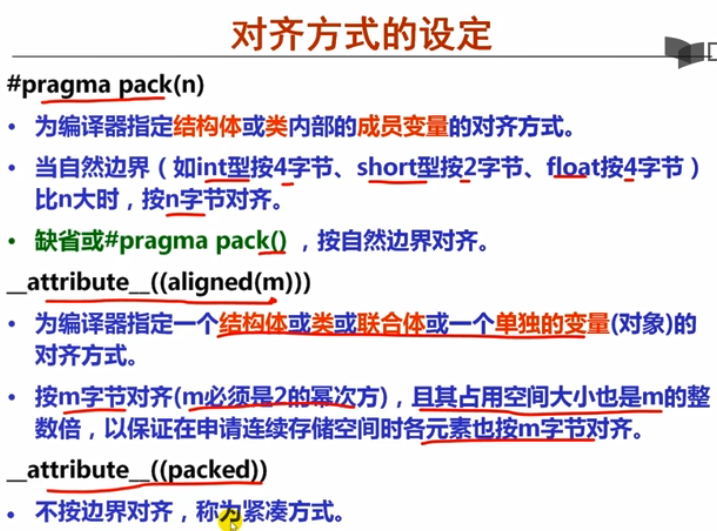
# pragma_pack(n)
自然边界比n大,按n字节对齐;反之按自然边界对齐。
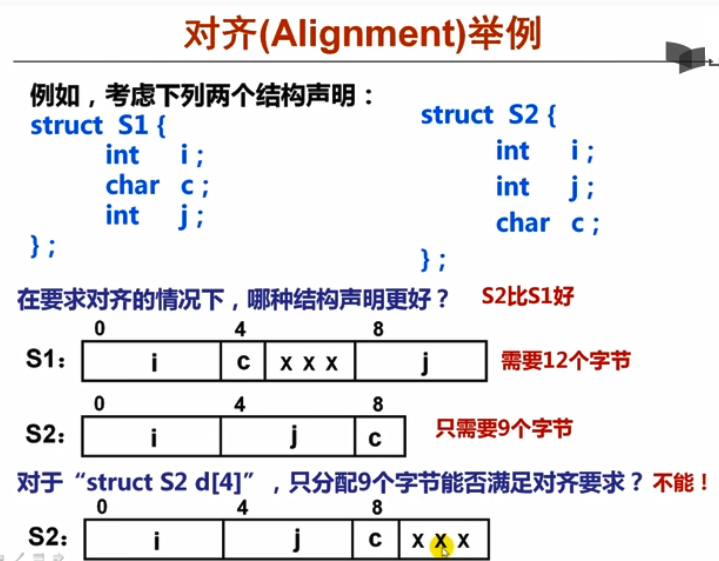
减少插空: 结构体成员的顺序
计算机系统基础(一):程序的表示、转换与链接-模块八 第3讲 数据的对齐存放(1)-网易公开课 https://open.163.com/newview/movie/free?pid=WFVPGEQSL&mid=YFVPGFBSQ
结构数组变量最后可能需要插空,以使每个元素都边界对齐

Linux short char 2字节对齐,其他4字节对齐
对齐 alignment 可能需要插空 用空间换时间
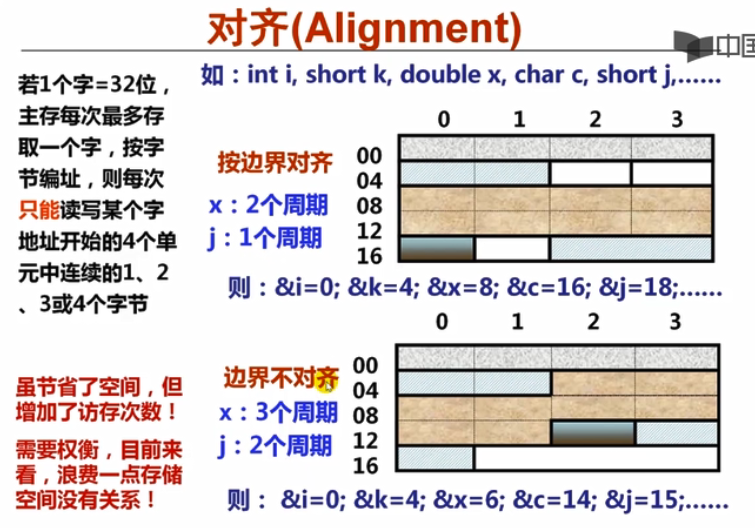

传送单位 不是 1字节;传送按字长的整数倍数;存储按字节; 字长16位(历史)、32位、64位;
主存按照一个存储单位进行存取
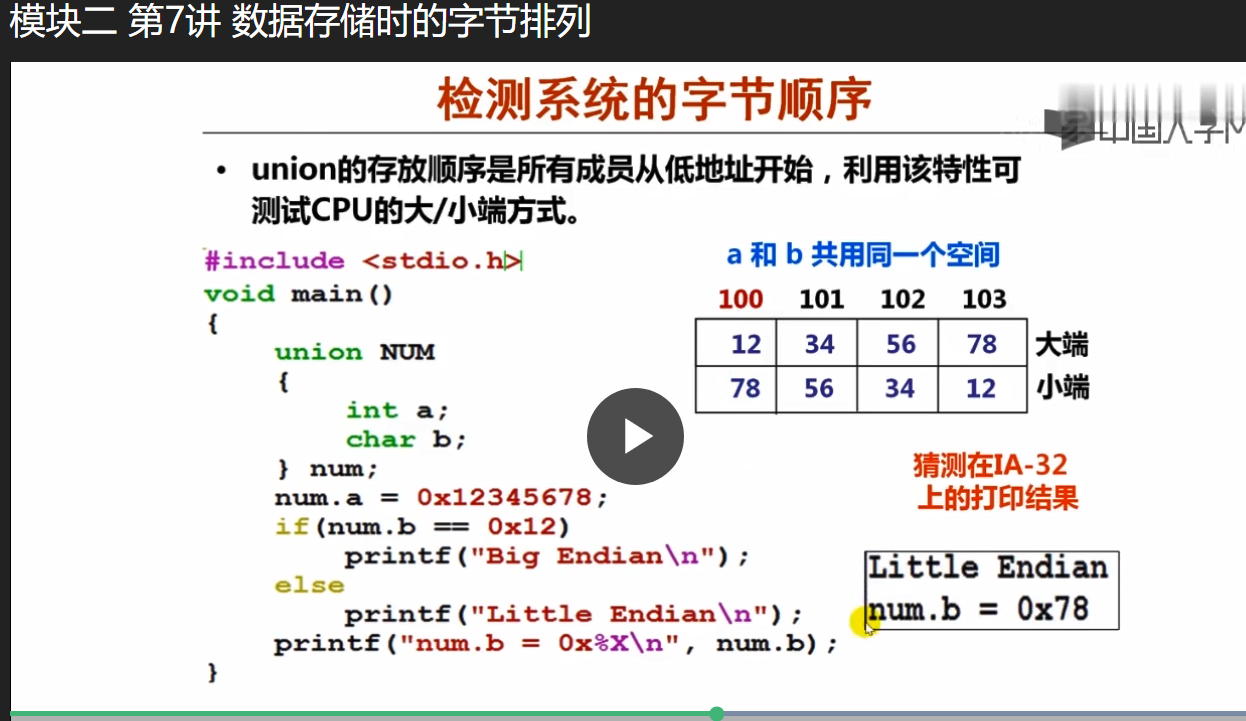
检测系统的字节顺序
联合体
union的存放顺序是所有成员从低地址开始,利用该
特性可以测试CPU的大/小端方式。
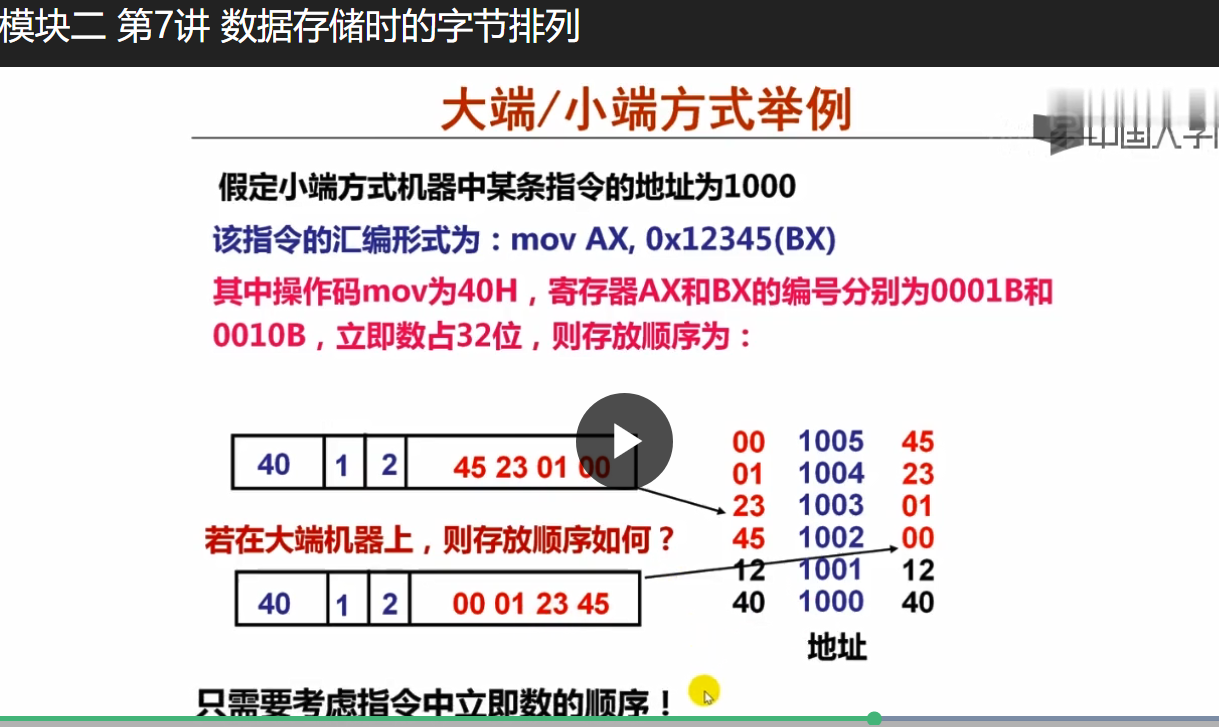
指令地址 指令汇编形式
计算机系统基础(一):程序的表示、转换与链接-模块二 第7讲 数据存储时的字节排列-网易公开课 https://open.163.com/newview/movie/free?pid=WFVPGEQSL&mid=AFVPGF0JI
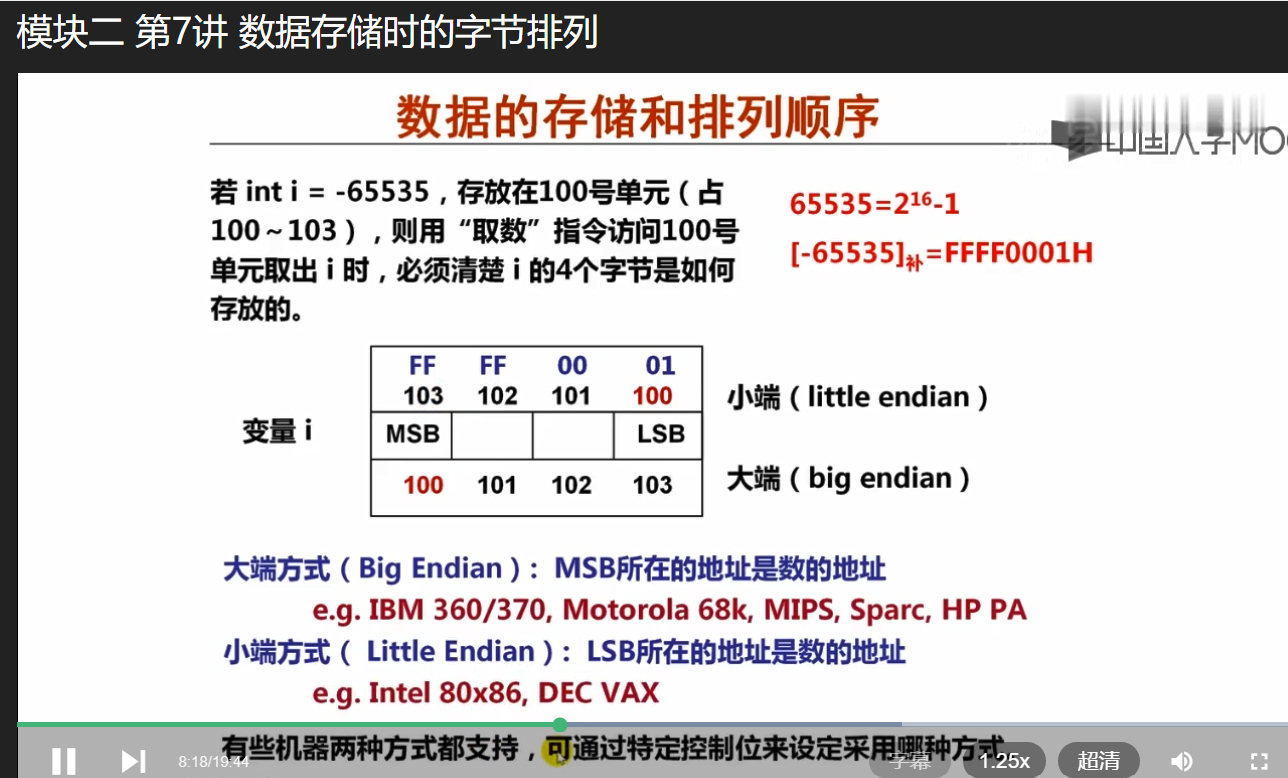
数的地址:存储单元中第一个字节的编号
例如:int i=-65535,存储时占4个字节, 存放在 100-103 4个存储单元;
100存储单元为该数的地址;
在100放第1个字节,则为小端
在100放第4个字节,则为大端
计算机系统基础(一):程序的表示、转换与链接-模块二 第6讲 数据宽度和存储容量的单位-网易公开课 https://open.163.com/newview/movie/free?pid=WFVPGEQSL&mid=PFVPGF0BI
存储器按照字节编址,一个字节为一个存储单位,一个数据,可能占多个字节,怎么排序呢?

LSB 最低有效字节 ,在低位则小端
MSB 高





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(六):基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类