Spring IoC 中的(Singleton)单例对象创建过程探索
前言
之前将spring framework 源码导入了idea,后来折腾调试了一下,于是研究了一下最简单的singleton对象在spring中是如何创建的。这里所谓的简单,就是指无属性注入,无复杂构造函数的对象。
测试代码
spring配置:
<bean id="userService" class="UserService" scope="singleton"></bean>
测试类:
public class UserService {
private final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
public UserService(){
logger.info("UserService created");
id = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
}
private String id;
public String getId(){
return id;
}
public String getUserName(){
return "xiaopanzi";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
context.start();
testNormalSingleton(context);
}
private static void testCircleSingleton(ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context){
SingletonAService aService = context.getBean("aService",SingletonAService.class);
SingletonBService bService = context.getBean("bService",SingletonBService.class);
aService.getbService().print();
bService.getaService().print();
}
调试详情
首先在ApplicationContext 初始化过程,在 refresh 方法中会调用 finishBeanFactoryInitialization 方法,注释上也写的很明白:Instantiate all remaining (not-lazy-init) signletons。(初始化剩余的非懒加载的单例对象)。那么这里就是入口点。
然后在调用 beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons().
后续调用链如下:
DefaultListBeanFactory.getBean(beanName)
AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean(name,requiredType,args,typeCheckOnly)
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.createBean(String beanName,RootBeanDefinition mbd,Object[] args)
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean(String beanName,RootBeanDefinition mbd,Object[] args)
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.instantiateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd)
getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, parent); (this.instantiationStrategy=CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy)
SimpleInstantiationStrategy.instantiate(RootBeanDefinition bd, String beanName, BeanFactory owner)
BeanUtils.instantiateClass(Constructor<T> ctor, Object... args)
通过上述代码调用链我们可以看出,最终的示例创建是由 BeanUtils.instantiateClass 方法完成的,也就是这个方法:
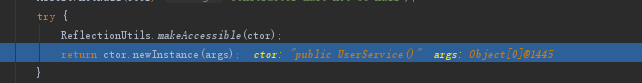
public static <T> T instantiateClass(Constructor<T> ctor, Object... args) throws BeanInstantiationException {
Assert.notNull(ctor, "Constructor must not be null");
try {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(ctor);
return ctor.newInstance(args);
}
catch (InstantiationException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Is it an abstract class?", ex);
}
catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Is the constructor accessible?", ex);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Illegal arguments for constructor", ex);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Constructor threw exception", ex.getTargetException());
}
}
到此为止单例就创建完毕了。但是创建完成之后,还有后续的处理。
DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.addSingletonFactory(String beanName,ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory);
也就是将该示例放入到 singletonObjects 中,作为缓存方便后续取值。
this.singletonObjects.put(beanName, (singletonObject != null ? singletonObject : NULL_OBJECT));
当我们在次调用getBean的时候,那么在 DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.getSingleton 方法中直接从 singletonObjects 中获取即可。
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
return (singletonObject != NULL_OBJECT ? singletonObject : null);
}
总结
上述内容记录的很少,基本就是一个轮廓的记录,要真正理解详情内容,还得自己去慢慢调试啊!!!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号