今天我们一起来探讨下安卓中BroadcastReceiver组件以及详细分析下它的两种注册方式。
BroadcastReceiver也就是“广播接收者”的意思,顾名思义,它就是用来接收来自系统和应用中的广播。在Android系统中,广播体现在方方面面,例如当开机完成后系统会产生一条广播,接收到这条广播就能实现开机启动服务的功能;当网络状态改变时系统会产生一条广播,接收到这条广播就能及时地做出提示和保存数据等操作;当电池电量改变时,系统会产生一条广播,接收到这条广播就能在电量低时告知用户及时保存进度等等。Android中的广播机制设计的非常出色,很多事情原本需要开发者亲自操作的,现在只需等待广播告知自己就可以了,大大减少了开发的工作量和开发周期。而作为应用开发者,就需要数练掌握Android系统提供的一个开发利器,那就是BroadcastReceiver。
在我们详细分析创建BroadcastReceiver的两种注册方式前,我们先罗列本次分析的大纲:
(1)对静态和动态两种注册方式进行概念阐述以及演示实现步骤
(2)简述两种BroadcastReceiver的类型(为后续注册方式的对比做准备)
(3)在默认广播类型下设置优先级和无优先级情况下两种注册方式的比较
(4)在有序广播类型下两种注册方式的比较
(5)通过接受打电话的广播,在程序(Activity)运行时和终止运行时,对两种注册方式的比较
(6)总结两种方式的特点
第一步:静态和动态注册方式基本概念以及实现步骤
构建Intent,使用sendBroadcast方法发出广播定义一个广播接收器,该广播接收器继承BroadcastReceiver,并且覆盖onReceive()方法来响应事件注册该广播接收器,我们可以在代码中注册(动态注册),也可以AndroidManifest.xml配置文件中注册(静态注册)。
动态注册:
效果如下图:

这里就不演示点击按钮布局的实现了,MainActivity.java中实现代码如下:
1 import android.content.BroadcastReceiver; 2 import android.content.Context; 3 import android.content.Intent; 4 import android.content.IntentFilter; 5 import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity; 6 import android.os.Bundle; 7 import android.view.Gravity; 8 import android.view.View; 9 import android.widget.Toast; 10 11 public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { 12 DynamicReceiver dynamicReceiver; 13 @Override 14 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 15 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 16 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); 17 //实例化IntentFilter对象 18 IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter(); 19 filter.addAction("panhouye"); 20 dynamicReceiver = new DynamicReceiver(); 21 //注册广播接收 22 registerReceiver(dynamicReceiver,filter); 23 } 24 //按钮点击事件 25 public void send2(View v){ 26 Intent intent = new Intent(); 27 intent.setAction("panhouye"); 28 intent.putExtra("sele","潘侯爷"); 29 sendBroadcast(intent); 30 } 31 /*动态注册需在Acticity生命周期onPause通过 32 *unregisterReceiver()方法移除广播接收器, 33 * 优化内存空间,避免内存溢出 34 */ 35 @Override 36 protected void onPause() { 37 super.onPause(); 38 unregisterReceiver(new MyReceiver()); 39 } 40 //通过继承 BroadcastReceiver建立动态广播接收器 41 class DynamicReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver{ 42 @Override 43 public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { 44 //通过土司验证接收到广播 45 Toast t = Toast.makeText(context,"动态广播:"+ intent.getStringExtra("sele"), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT); 46 t.setGravity(Gravity.TOP,0,0);//方便录屏,将土司设置在屏幕顶端 47 t.show(); 48 } 49 } 50 }
建立方法代码中做了详细注释,有不明白的地方请留言讨论。
静态注册:
效果如下:

静态注册建立第一步,新建BroadcastReceiver,见下图:
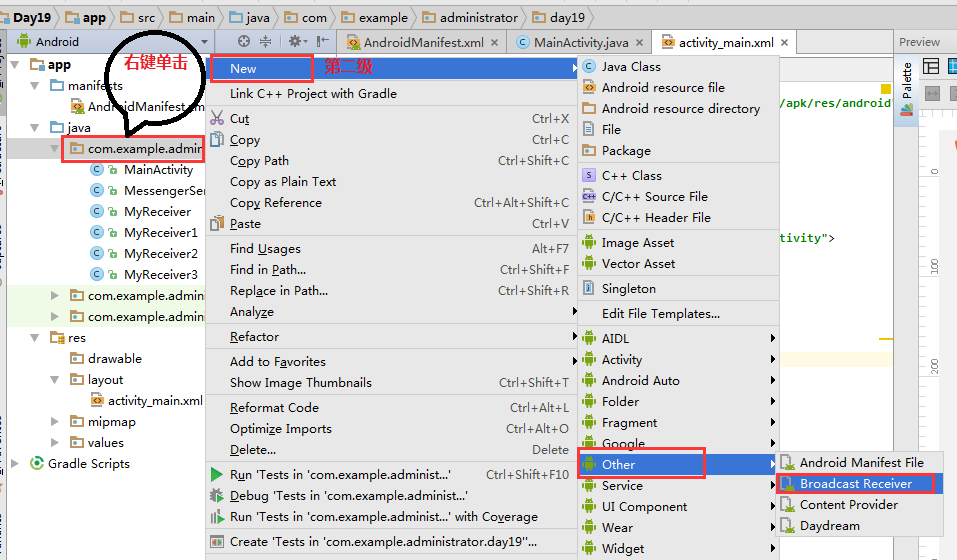
通过以上步骤,生成MyReceiver.java文件:
1 import android.content.BroadcastReceiver; 2 import android.content.Context; 3 import android.content.Intent; 4 import android.view.Gravity; 5 import android.widget.Toast; 6 7 public class MyReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver { 8 public MyReceiver() { 9 } 10 @Override 11 public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { 12 Toast t = Toast.makeText(context,"静态广播:"+intent.getStringExtra("info"), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT); 13 t.setGravity(Gravity.TOP,0,0); 14 t.show(); 15 } 16 }
生成MyReceiver.java的同时,修改AndroidMainfest.xml配置文件中的代码:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 package="com.example.administrator.day19"> 4 <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.PROCESS_OUTGOING_CALLS"/> 5 <application 6 android:allowBackup="true" 7 android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" 8 android:label="@string/app_name" 9 android:supportsRtl="true" 10 android:theme="@style/AppTheme"> 11 <activity android:name=".MainActivity"> 12 <intent-filter> 13 <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> 14 15 <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> 16 </intent-filter> 17 </activity> 18 //生成的receiver配置文件 19 <receiver 20 android:name=".MyReceiver" 21 android:enabled="true" 22 android:exported="true"> 23 <intent-filter> 24 //自定义Action 25 <action android:name="MLY" /> 26 </intent-filter> 27 </receiver> 28 </application> 29 </manifest>
最后在MainActivity.java文件中添加按钮点击事件,如下:
1 import android.content.BroadcastReceiver; 2 import android.content.Context; 3 import android.content.Intent; 4 import android.content.IntentFilter; 5 import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity; 6 import android.os.Bundle; 7 import android.view.Gravity; 8 import android.view.View; 9 import android.widget.Toast; 10 11 public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { 12 DynamicReceiver dynamicReceiver; 13 @Override 14 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 15 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 16 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); 17 } 18 //静态广播点击 19 public void send(View v){ 20 Intent intent = new Intent(); 21 intent.setAction("MLY"); 22 intent.putExtra("info","panhouye"); 23 sendBroadcast(intent); 24 } 25 }
至此,两种注册方式的实现代码演示完毕,欢迎探讨。
第二步:为方便后续分析,这里插入BroadcastReceiver的两种常用类型
(1)Normalbroadcasts:默认广播
发送一个默认广播使用Context.sendBroadcast()方法,普通广播对于多个接收者来说是完全异步的,通常每个接收者都无需等待即可以接收到广播,接收者相互之间不会有影响。对于这种广播,接收者无法终止广播,即无法阻止其他接收者的接收动作。
(2)orderedbroadcasts:有序广播
发送一个有序广播使用Context.sendorderedBroadcast()方法,有序广播比较特殊,它每次只发送到优先级较高的接收者那里,然后由优先级高的接受者再传播到优先级低的接收者那里,优先级高的接收者有能力终止这个广播。
发送有序广播:sendorderedBroadCast()
在注册广播中的<intent-filter>中使用android:priority属性。这个属性的范围在-1000到1000,数值越大,优先级越高。在广播接收器中使用setResultExtras方法将一个Bundle对象设置为结果集对象,传递到下一个接收者那里,这样优先级低的接收者可以用getResuttExtras获取到最新的经过处理的信息集合。使用sendorderedBroadcast方法发送有序广播时,需要一个权限参数,如果为null则表示不要求接收者声明指定的权限,如果不为null则表示接收者若要接收此广播,需声明指定权限。这样做是从安全角度考虑的,例如系统的短信就是有序广播的形式,一个应用可能是具有拦截垃圾短信的功能,当短信到来时它可以先接受到短信广播,必要时终止广播传递,这样的软件就必须声明接收短信的权限。
第三步:在默认广播下两种注册方式的比较
(1)两种注册方式均不设置优先级
这里将动态与静态两种注册的广播触发集中在一个按钮上,显示效果如下(未设置优先级的情况下,先动态后静态):

这里同样不演示按钮布局文件,以及静态注册涉及AndroidMainfest.xml和MyReceiver.java文件。直接展示MainActicity.java的实现代码:
1 import android.content.BroadcastReceiver; 2 import android.content.Context; 3 import android.content.Intent; 4 import android.content.IntentFilter; 5 import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity; 6 import android.os.Bundle; 7 import android.view.Gravity; 8 import android.view.View; 9 import android.widget.Toast; 10 11 public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { 12 DynamicReceiver dynamicReceiver; 13 @Override 14 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 15 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 16 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); 17 IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter(); 18 filter.addAction("panhouye"); 19 dynamicReceiver = new DynamicReceiver(); 20 registerReceiver(dynamicReceiver,filter); 21 } 22 //静态广播点击 23 public void send(View v){ 24 Intent intent = new Intent(); 25 //设置与动态相同的Action,方便同时触发静态与动态 26 intent.setAction("panhouye"); 27 intent.putExtra("info","潘侯爷"); 28 sendBroadcast(intent);//默认广播 29 } 30 @Override 31 protected void onPause() { 32 super.onPause(); 33 unregisterReceiver(new MyReceiver()); 34 } 35 class DynamicReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver{ 36 @Override 37 public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { 38 Toast t = Toast.makeText(context,"动态广播:"+ intent.getStringExtra("info"), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT); 39 t.setGravity(Gravity.TOP,0,0); 40 t.show(); 41 } 42 } 43 }
(2)将动态优先级设置为最低-1000,静态优先级设置为最高1000
显示效果如下(动态仍先于静态被接收到):

MainActivity中动态优先级设置如下:
1 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 2 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 3 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); 4 IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter(); 5 filter.addAction("panhouye"); 6 filter.setPriority(-1000);//设置动态优先级 7 dynamicReceiver = new DynamicReceiver(); 8 registerReceiver(dynamicReceiver,filter); 9 }
AndroidMainfest.xml中静态优先级设置如下:
1 <receiver 2 android:name=".MyReceiver" 3 android:enabled="true" 4 android:exported="true"> 5 //设置静态优先级 6 <intent-filter android:priority="1000"> 7 <action android:name="panhouye" /> 8 </intent-filter> 9 </receiver>
第四步:在有序广播下两种注册方式比较
静态广播1(优先级为200),静态广播2(优先级为300),静态广播3(优先级为400),静态广播优先级为(-100),动态广播优先级为0。显示效果如下:

出现顺序由优先级决定,由高到低分别为静态3-静态2-静态1-动-静态。(这里参照前文代码)
第五步:接受打电话的广播,比较程序运行中与结束运行时,两种注册方式的比较
本次比较采用比对Log的方式对两种注册方式进行比较,在MainActivity.java中会插入Activity全部生命周期用于检测Log分析。
AndroidMainfest.xml配置文件代码如下:
1 <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 2 package="com.example.administrator.test19"> 3 //添加拨打电话权限 4 <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.PROCESS_OUTGOING_CALLS"/> 5 <application 6 android:allowBackup="true" 7 android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" 8 android:label="@string/app_name" 9 android:supportsRtl="true" 10 android:theme="@style/AppTheme"> 11 <activity android:name=".MainActivity"> 12 <intent-filter> 13 <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> 14 15 <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> 16 </intent-filter> 17 </activity> 18 <receiver 19 android:name=".StaticReceiver" 20 android:enabled="true" 21 android:exported="true"> 22 <intent-filter> 23 //设置打电话对应的action 24 <action android:name="android.intent.action.NEW_OUTGOING_CALL" /> 25 </intent-filter> 26 </receiver> 27 </application> 28 </manifest>
MainActivity.java中实现代码(动态注册将解除注册放在onDestory方法内是因为在真机测试过程中拨打电话,需要返回主页面,而此操作会造成Activity处于onStop状态,若放在onPause中,将无法在程序运行时启用动态注册接受广播。真实环境下建议在onpause下解除注册,尽早释放内存,避免内存溢出):
1 import android.content.BroadcastReceiver; 2 import android.content.Context; 3 import android.content.Intent; 4 import android.content.IntentFilter; 5 import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity; 6 import android.os.Bundle; 7 import android.util.Log; 8 9 public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { 10 DynamicReceiver dynamicReceiver;//声明动态注册广播接收 11 @Override 12 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 13 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 14 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); 15 IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter(); 16 filter.addAction("android.intent.action.NEW_OUTGOING_CALL"); 17 dynamicReceiver = new DynamicReceiver(); 18 registerReceiver(dynamicReceiver,filter); 19 Log.i("Tag","Activity-onCreate"); 20 } 21 @Override 22 protected void onStart() { 23 super.onStart(); 24 Log.i("Tag","Activity-onStart"); 25 } 26 @Override 27 protected void onResume() { 28 super.onResume(); 29 Log.i("Tag","Activity-onResume"); 30 } 31 @Override 32 protected void onPause() { 33 super.onPause(); 34 Log.i("Tag","Activity-onPause"); 35 } 36 @Override 37 protected void onStop() { 38 super.onPause(); 39 Log.i("Tag","Activity-onStop"); 40 } 41 @Override 42 protected void onDestroy() { 43 super.onDestroy(); 44 Log.i("Tag","Activity-onDestroy"); 45 unregisterReceiver(dynamicReceiver); 46 } 47 class DynamicReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver{ 48 @Override 49 public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { 50 Log.i("Tag","动态注册广播接收到您正在拨打电话"+getResultData()); 51 } 52 } 53 }
StaticReceiver.java中实现代码:
1 import android.content.BroadcastReceiver; 2 import android.content.Context; 3 import android.content.Intent; 4 import android.util.Log; 5 public class StaticReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver { 6 public StaticReceiver() { 7 } 8 @Override 9 public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { 10 Log.i("Tag","静态注册广播接收到您正在拨打电话"+getResultData()); 11 } 12 }
(1)在未退出Activity时,拨打电话,Log如下:

由Log可知在未退出Activity是,两种方式均可接受到广播。
(2)在退出Activity时,拨打电话,Log如下(即便不解除注册,动态仍无法接受到广播):

在退出程序(Activity)时,只有静态注册方式可以接受到广播。
第六步:总结两种注册方式特点
广播接收器注册一共有两种形式:静态注册和动态注册.
两者及其接收广播的区别:
(1)动态注册广播不是常驻型广播,也就是说广播跟随Activity的生命周期。注意在Activity结束前,移除广播接收器。
静态注册是常驻型,也就是说当应用程序关闭后,如果有信息广播来,程序也会被系统调用自动运行。
(2)当广播为有序广播时:优先级高的先接收(不分静态和动态)。同优先级的广播接收器,动态优先于静态
(3)同优先级的同类广播接收器,静态:先扫描的优先于后扫描的,动态:先注册的优先于后注册的。
(4)当广播为默认广播时:无视优先级,动态广播接收器优先于静态广播接收器。同优先级的同类广播接收器,静态:先扫描的优先于后扫描的,动态:先注册的优先于后册的。



