A timer based on timerfd and epoll
源码获取
HighPrecisionTimer
This is a millisecond-level timer implemented with timerfd+epoll on Linux, and the demo is developed using Qt.
how to use
- I need to create a timer that runs periodically with millisecond precision. The timer supports setting the running period and a callback function for timeout. Additionally, the timer provides interfaces for starting the timer, stopping the timer, and setting the timer interval.
- follow this step
HighPrecisionTimer timer;
/// mill second: 40
timer.setInterval(40);
/// ... replace your call back func
timer.setCallback(...);
/// start timer
/// true - the timer timeout function execution is located in a separate thread
/// false - the timer timeout function execution is not in a separate thread.
timer.start(true);
/// do something
...
/// stop timer
timer.stop();
dmeo
- you can get the demo from
TDDMUserheader file and source file.
example
- results on
Manjaro
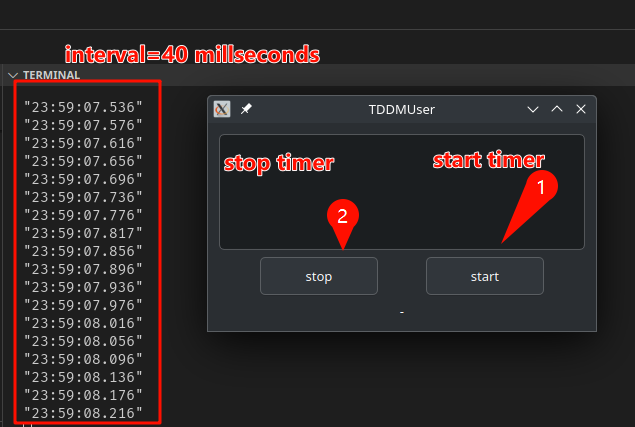
enjoy the soure
#pragma once
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <sys/timerfd.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <thread>
#include <functional>
#include <atomic>
#include <chrono>
#include <mutex>
class HighPrecisionTimer
{
enum
{
MAXNUM = 20,
};
public:
using Callback = std::function<void()>;
HighPrecisionTimer() : m_running(false), m_interval(1000)
{
epoll_fd = epoll_create(1);
timer_fd = timerfd_create(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, 0);
fcntl(timer_fd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
}
~HighPrecisionTimer()
{
stop();
close(timer_fd);
close(epoll_fd);
}
void setInterval(uint64_t ms)
{
m_interval = ms;
}
void start(bool isInThread)
{
if(true == m_running)
{
return;
}
m_running = true;
if (true == isInThread)
{
m_workerThread = new std::thread(&HighPrecisionTimer::run, this);
return;
}
run();
}
void stop()
{
m_running = false;
if (m_workerThread)
{
if (m_workerThread->joinable())
{
m_workerThread->join();
}
delete m_workerThread;
}
m_workerThread= nullptr;
}
/// uevi
void setCallback(Callback cb)
{
m_onTimeoutFunc = std::move(cb);
}
private:
void run()
{
struct itimerspec new_value;
new_value.it_value.tv_sec = m_interval / 1000;
new_value.it_value.tv_nsec = (m_interval % 1000) * 1000000;
new_value.it_interval.tv_sec = m_interval / 1000;
new_value.it_interval.tv_nsec = (m_interval % 1000) * 1000000;
timerfd_settime(timer_fd, 0, &new_value, nullptr);
struct epoll_event ev;
struct epoll_event events[MAXNUM];
ev.data.fd = timer_fd;
ev.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET;
epoll_ctl(epoll_fd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, timer_fd, &ev); // 添加到epoll事件集合
uint64_t exp = 0;
ssize_t s = 0;
while (m_running)
{
int num = epoll_wait(epoll_fd, events, MAXNUM, -1);
assert(num >= 0);
for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i)
{
if (events[i].events & EPOLLIN)
{
if (events[i].data.fd == timer_fd)
{
s = read(events[i].data.fd, &exp, sizeof(uint64_t)); // 需要读出uint64_t大小, 不然会发生错误
assert(s == sizeof(uint64_t));
if (m_onTimeoutFunc)
{
m_onTimeoutFunc();
}
}
}
}
}
epoll_ctl(epoll_fd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, timer_fd, &ev);
// 停止定时器
stopTimer();
}
void stopTimer()
{
struct itimerspec new_value;
memset(&new_value, 0, sizeof(new_value)); // 设置it_value为0
timerfd_settime(timer_fd, 0, &new_value, nullptr); // 这将停止定时器
}
int epoll_fd{0};
int timer_fd{0};
std::thread* m_workerThread{nullptr};
Callback m_onTimeoutFunc{nullptr};
std::atomic<bool> m_running{false};
///
uint64_t m_interval{40};
};


