Qt5使用QSqlQuery读写sqlite3数据库
概述
- 本文将介绍使用 Qt5使用QSqlQuery读写sqlite3。
- 设计初衷: 项目需要使用配置文件,配置文件使用的是sqlite3 , 这是V1.0.0, 后期增加其他功能。
- 需要C++11支持(可删除代码中的c++11代码),不过后期可能会增加更多基于C++11代码
- Qt creator 的.pro文件需要加入: QT += sql
- 本文的项目是基于Qt creator的qmake编译的,非CMake.
- 本文涉及的Qt version: Qt5.14 (好像Qt5.9要是已经支持C++11, 具体的,大家可以google一下 )
- 本文使用的sqlite3可视化软件是:sqlite studio
功能
- 执行sql语句: 增加、删除、修改、查询
使用顺序
- 1.先调用函数 init_, 传入数据库文件
- 2.【1】返回0,再调用函数【get_record_】 或者 【exec_sql_】函数操作
- 3.可显示调用函数【uninit_】
sqlite_assistant.h
#ifndef SQLITE_ASSISTANT_H
#define SQLITE_ASSISTANT_H
#include <QObject>
#include <QSqlDatabase>
#include <QSqlQuery>
namespace oct_db
{
/// 读写sqlite3
class sqlite_assistant : public QObject
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit sqlite_assistant(QObject *parent = nullptr);
~sqlite_assistant();
/// 这些都需要屏蔽
sqlite_assistant(const sqlite_assistant& instance) = delete;
sqlite_assistant(const sqlite_assistant&& instance) = delete;
sqlite_assistant& operator = (const sqlite_assistant& instance) = delete;
sqlite_assistant& operator = (const sqlite_assistant&& instance) = delete;
/// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/// @brief: 初始化,str_db_file是数据库文件,例如: C:/demo/hello_sqlite.db3
/// @str_db_file - sqlite3数据库文件: 例如: C:/demo/demo.db3
/// @return - int
/// 0 - 成功
/// -2 - 失败, 参数【str_db_file】为空
/// -3 - 失败, 参数【str_db_file】文件不存在
/// -5 - 失败, 打开参数【str_db_file】的数据库失败
/// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
int init_(const QString& str_db_file) noexcept;
/// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/// @brief: 查询表的数据, 如果没有调用函数 init_, 也将返回 nullptr
/// @str_table_name - 【str_table_name】表的名字
/// @return - QSqlQuery*
/// nullptr - 失败, 【str_table_name】为空、【数据库没有打开】、执行【SELECT* FROM table_name】语句失败 中的一种
/// 否则,成功
/// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
QSqlQuery* get_record_(const QString& str_table_name);
/// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/// @brief: 执行sql语句,这里主要用作: 修改、删除、增加,查询用函数【get_record_】
/// @str_sql - sql语句
/// @return - int
/// 0 - 成功
/// -2 - 失败,参数【str_sql】为空
/// -3 - 失败,数据库没有打开,应该先调用函数 【init_】
/// -5 - 失败,执行sql语句失败,检查sql语句
/// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
int exec_sql_(const QString& str_sql);
/// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/// @brief: 返回当前连接的数据库文件
/// @return - QString
/// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
QString get_db_file();
/// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/// @brief: release the space at first, 可显示调用
/// @return - void
/// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void uninit_();
private:
/// 当前使用的数据库文件
QString str_db_file_;
/// 连接字符串
QString str_connection_;
///
QSqlDatabase sql_database_;
///
QSqlQuery *psqlquery_ = nullptr;
};
}
#endif // SQLITE_ASSISTANT_H
sqlite_assistant.cc
#include "sqlite_assistant.h"
#include <QFile>
namespace oct_db
{
sqlite_assistant::sqlite_assistant(QObject *parent) : QObject(parent)
{
str_connection_ = QString("sqlite_assistant");
}
sqlite_assistant::~sqlite_assistant()
{
uninit_();
}
int sqlite_assistant::init_(const QString &str_db_file) noexcept
{
/// 1. 字符串为空
if ((str_db_file.isNull()) || (str_db_file.isEmpty()) )
return -2;
/// 2..文件不存在
QFile db_file(str_db_file);
if (!db_file.exists())
return -3;
/// 保存文件名
str_db_file_ = str_db_file;
/// 2.5 断开先前的连接
uninit_();
/// 3. 连接数据库
if (QSqlDatabase::contains(str_connection_))
sql_database_ = QSqlDatabase::database(str_connection_);
else
sql_database_ = QSqlDatabase::addDatabase("QSQLITE", str_connection_);
/// 4.设置数据库名
sql_database_.setDatabaseName(str_db_file_);
/// 打开数据库
if (!sql_database_.open())
return -5;
if (nullptr != psqlquery_)
{
delete psqlquery_;
psqlquery_ = nullptr;
}
if (nullptr == psqlquery_)
psqlquery_ = new QSqlQuery(sql_database_);
/// 打开成功
return 0;
}
QSqlQuery *sqlite_assistant::get_record_(const QString& str_table_name)
{
/// 1. 字符串为空
if ((str_table_name.isNull()) || (str_table_name.isEmpty()) )
{
// str_err = QString("the parameter [str_table_name] is null");
return nullptr;
}
/// 2. 数据库没有打开
if (!sql_database_.isOpen())
{
// str_err = QString("failure, the database didn't open");
return nullptr;
}
if (nullptr == psqlquery_)
{
// str_err = QString("failure, db file is openned, but the /*QSqlQuery*/ object created failure");
return nullptr;
}
/// 3.构建sql语句、执行,并返回结果
QString str_sql = QString("SELECT * FROM ") + str_table_name;
bool flag = psqlquery_->prepare(str_sql);
if (!psqlquery_->exec())
{
// str_err = QString("failure, the error is from executing sql");
return nullptr;
}
return psqlquery_;
}
int sqlite_assistant::exec_sql_(const QString &str_sql)
{
/// 1. 字符串为空
if ((str_sql.isNull()) || (str_sql.isEmpty()) )
return -2;
if (!sql_database_.isOpen())
return -3;
if (nullptr == psqlquery_)
return -5;
psqlquery_->prepare(str_sql);
bool is_success = psqlquery_->exec();
return ( (true == is_success) ? 0 : -6);
}
void sqlite_assistant::uninit_()
{
try
{
if (nullptr != psqlquery_)
{
psqlquery_->clear();
delete psqlquery_;
psqlquery_ = nullptr;
}
if (sql_database_.isOpen())
sql_database_.close();
}
catch(...)
{
/// take the exception and do not expand
}
}
QString sqlite_assistant::get_db_file()
{
return str_db_file_;
}
}
调用示例
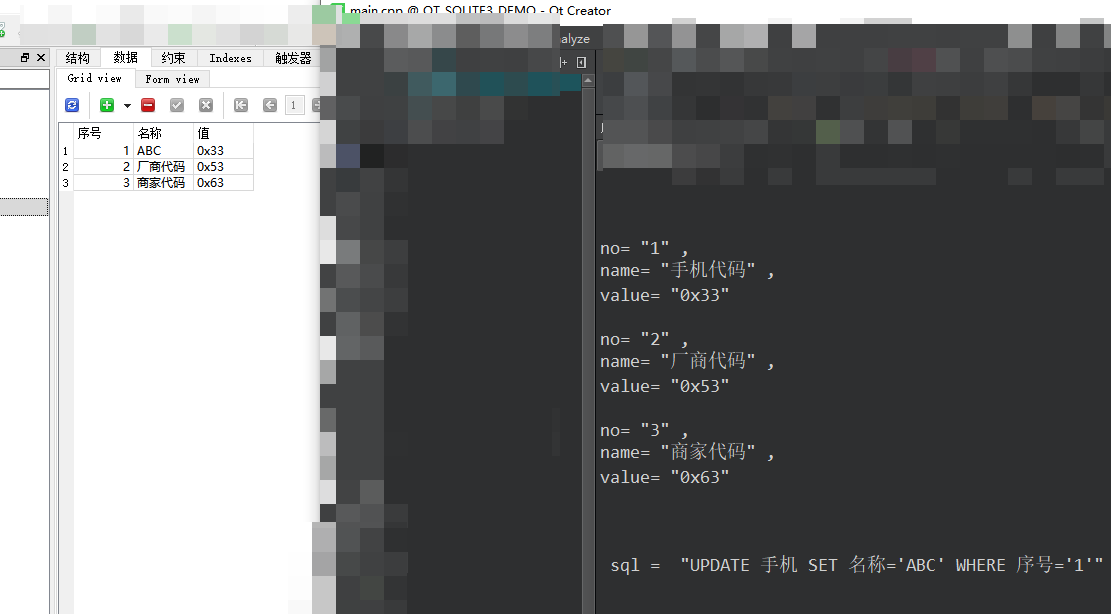
准备了一张表,内容如下;

包含头文件
#include <QApplication>
#include "sqlite_assistant.h"
using namespace oct_db;
#include <QDebug>
#include <QSqlQuery>
#include <QStringLiteral>
调用代码
/// 1.创建数据据访问对象
sqlite_assistant* psq = new sqlite_assistant;
if (nullptr == psq)
return a.exec();
/// 2.准备数据库文件
QString str_db_file = QApplication::applicationDirPath() + QString("/cmd_makeup.db3");
qDebug() << "\n\n 33333 rstr_db_fileet=" << str_db_file << "\n\n\n";
/// 3.调用初始化数据库操作
int ret = psq->init_(str_db_file);
qDebug() << "\n\n AAA ret=" << ret << "\n\n\n";
/// 4.查询【手机】表中的内容
QSqlQuery* pquery = psq->get_record_(QStringLiteral("手机"));
if (nullptr == pquery)
{
qDebug() << "\n\n error pquery is null \n\n";
}
else
{
/// 读取测试
while(pquery->next())
{
/// 读取并显示一行数据, 与数据库中的对应
qDebug() << "no=" << pquery->value(QStringLiteral("序号")).toString() << ", ";
qDebug() << "name=" << pquery->value(QStringLiteral("名称")).toString() << ", ";
qDebug() << "value=" << pquery->value(QStringLiteral("值")).toString() << "\n";
}
}
/// 5. 执行sql语句测试
QString str_sql = QStringLiteral("UPDATE 手机 SET 名称='ABC' WHERE 序号='1'");
qDebug() << "\n\n sql = " << str_sql << "\n\n";
qDebug () << "\n\n ret = " << psq->exec_sql_(str_sql) << "\n\n";
/// 6.下面这句可显示调用,也可以不用调用,因为析构函数中已经做了调用
psq->uninit_();
执行结果:
完整演示代码
#include "dialog.h"
#include <QApplication>
#include "sqlite_assistant.h"
using namespace oct_db;
#include <QDebug>
#include <QSqlQuery>
#include <QStringLiteral>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QApplication a(argc, argv);
Dialog w;
w.show();
/// 1.创建数据据访问对象
sqlite_assistant* psq = new sqlite_assistant;
if (nullptr == psq)
return a.exec();
/// 2.准备数据库文件
QString str_db_file = QApplication::applicationDirPath() + QString("/cmd_makeup.db3");
qDebug() << "\n\n 33333 rstr_db_fileet=" << str_db_file << "\n\n\n";
/// 3.调用初始化数据库操作
int ret = psq->init_(str_db_file);
qDebug() << "\n\n AAA ret=" << ret << "\n\n\n";
/// 4.查询【手机】表中的内容
QSqlQuery* pquery = psq->get_record_(QStringLiteral("手机"));
if (nullptr == pquery)
{
qDebug() << "\n\n error pquery is null \n\n";
}
else
{
/// 读取测试
while(pquery->next())
{
/// 读取并显示一行数据, 与数据库中的对应
qDebug() << "no=" << pquery->value(QStringLiteral("序号")).toString() << ", ";
qDebug() << "name=" << pquery->value(QStringLiteral("名称")).toString() << ", ";
qDebug() << "value=" << pquery->value(QStringLiteral("值")).toString() << "\n";
}
}
/// 5. 执行sql语句测试
QString str_sql = QStringLiteral("UPDATE 手机 SET 名称='ABC' WHERE 序号='1'");
qDebug() << "\n\n sql = " << str_sql << "\n\n";
qDebug () << "\n\n ret = " << psq->exec_sql_(str_sql) << "\n\n";
/// 6.下面这句可显示调用,也可以不用调用,因为析构函数中已经做了调用
psq->uninit_();
return a.exec();
}


