c++11之find 和 find_if 和 find_if_not 用法
时刻提醒自己
Note: vector的释放
0.头文件
#include <algorithm>
1.区别
返回范围 [first, last) 中满足特定判别标准的首个元素:
| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| find | 搜索等于 value 的元素 |
| find_if | 根据指定的查找规则,在指定区域内查找第一个符合该函数要求(使函数返回 true)的元素 |
| find_if_not | 如果查找成功,该迭代器指向的是查找到的那个元素;反之,如果查找失败,该迭代器的指向和 last 迭代器相同 |
2.原型
2.1 find 原型
template< class InputIt, class T >
InputIt find( InputIt first, InputIt last, const T& value );
(C++20 前)
template< class InputIt, class T >
constexpr InputIt find( InputIt first, InputIt last, const T& value );
(C++20 起)
template< class ExecutionPolicy, class ForwardIt, class T >
ForwardIt find( ExecutionPolicy&& policy, ForwardIt first, ForwardIt last, const T& value );
2.2 find_if 原型
template< class InputIt, class UnaryPredicate >
InputIt find_if( InputIt first, InputIt last,
UnaryPredicate p ); (C++20 前)
template< class InputIt, class UnaryPredicate >
constexpr InputIt find_if( InputIt first, InputIt last,
UnaryPredicate p ); (C++20 起)
template< class ExecutionPolicy, class ForwardIt, class UnaryPredicate >
ForwardIt find_if( ExecutionPolicy&& policy, ForwardIt first, ForwardIt last,
UnaryPredicate p );
2.3 find_if_not 原型
template< class InputIt, class UnaryPredicate >
InputIt find_if_not( InputIt first, InputIt last,
UnaryPredicate q ); (C++11 起)
(C++20 前)
template< class InputIt, class UnaryPredicate >
constexpr InputIt find_if_not( InputIt first, InputIt last,
UnaryPredicate q ); (C++20 起)
template< class ExecutionPolicy, class ForwardIt, class UnaryPredicate >
ForwardIt find_if_not( ExecutionPolicy&& policy, ForwardIt first, ForwardIt last,
UnaryPredicate q );
3.参数
| 参数 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| first, last | 要检验的元素范围 |
| value | 要与元素比较的值 |
| p | 若为要求的元素则返回 true 的一元谓词。对每个(可为 const 的) VT 类型参数 v ,其中 VT 是 InputIt 的值类型,表达式 p(v) 必须可转换为 bool ,无关乎值类别,而且必须不修改 v 。从而不允许 VT& 类型参数,亦不允许 VT ,除非对 VT 而言移动等价于复制 (C++11 起)。 |
| q | 若为要求的元素则返回 false 的一元谓词。对每个(可为 const 的) VT 类型参数 v ,其中 VT 是 InputIt 的值类型,表达式 q(v) 必须可转换为 bool ,无关乎值类别,而且必须不修改 v 。从而不允许 VT& 类型参数,亦不允许 VT ,除非对 VT 而言移动等价于复制 (C++11 起)。 |
4.异常
A. 若作为算法一部分调用的函数的执行抛出异常,且 ExecutionPolicy 为标准策略之一,则调用 std::terminate 。对于任何其他 ExecutionPolicy ,行为是实现定义的。
B. 若算法无法分配内存,则抛出 std::bad_alloc
5.find用法
5.1 代码
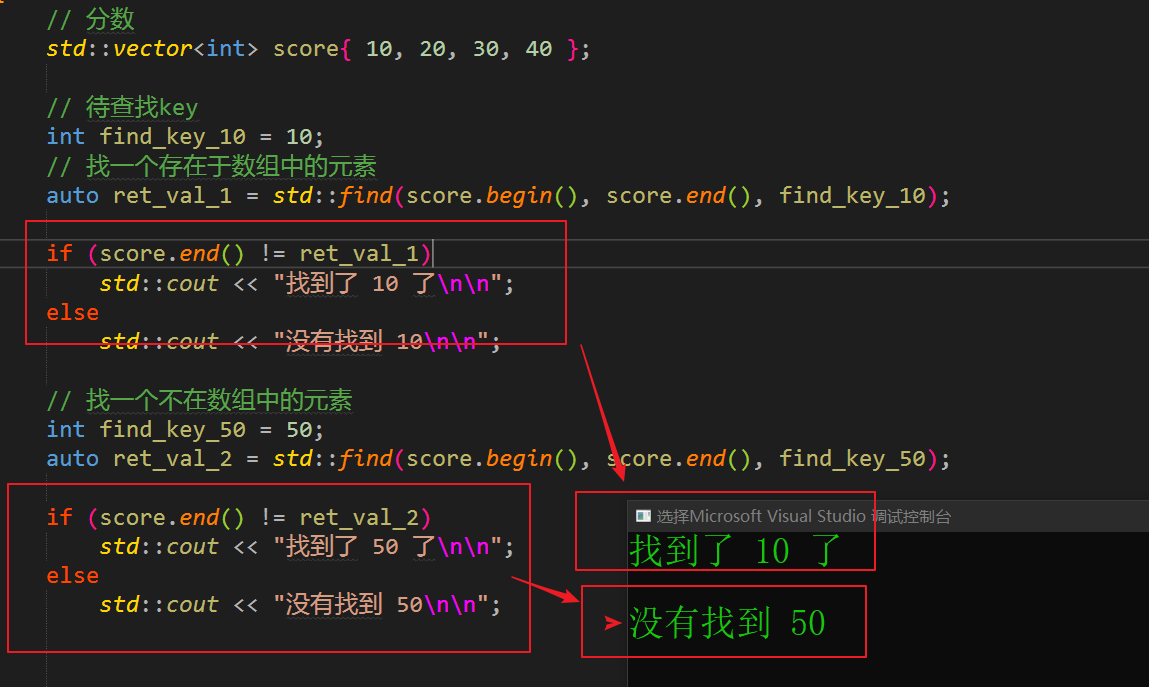
// 分数
std::vector<int> score{ 10, 20, 30, 40 };
// 待查找key
int find_key_10 = 10;
// 找一个存在于数组中的元素
auto ret_val_1 = std::find(score.begin(), score.end(), find_key_10);
if (score.end() != ret_val_1)
std::cout << "找到了 10 了\n\n";
else
std::cout << "没有找到 10\n\n";
// 找一个不在数组中的元素
int find_key_50 = 50;
auto ret_val_2 = std::find(score.begin(), score.end(), find_key_50);
if (score.end() != ret_val_2)
std::cout << "找到了 50 了\n\n";
else
std::cout << "没有找到 50\n\n";
5.2 输出
6.find_if 用法
6.1 代码
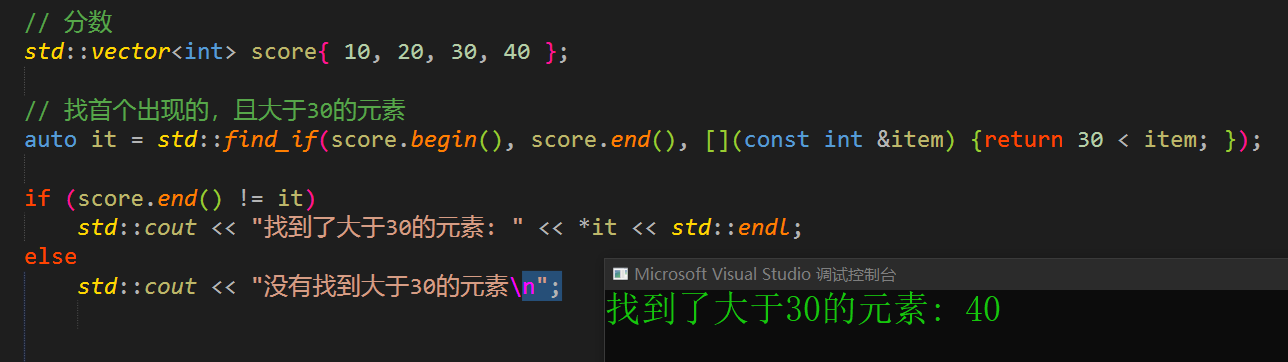
// 分数
std::vector<int> score{ 10, 20, 30, 40 };
// 找首个出现的,且大于30的元素
auto it = std::find_if(score.begin(), score.end(), [](const int &item) {return 30 < item; });
if (score.end() != it)
std::cout << "找到了大于30的元素: " << *it << std::endl;
else
std::cout << "没有找到大于30的元素\n";
6.2 输出
7.find_if_not 用法
7.1 代码
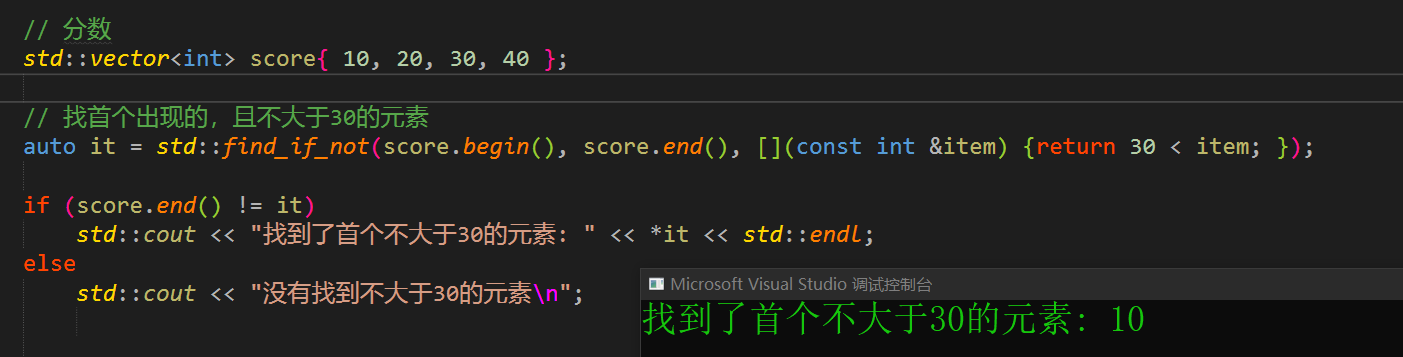
// 分数
std::vector<int> score{ 10, 20, 30, 40 };
// 找首个出现的,且不大于30的元素
auto it = std::find_if_not(score.begin(), score.end(), [](const int &item) {return 30 < item; });
if (score.end() != it)
std::cout << "找到了首个不大于30的元素: " << *it << std::endl;
else
std::cout << "没有找到不大于30的元素\n";
7.2 输出