再谈多线程模型之生产者消费者(单一生产者和单一消费者)(c++11实现)
0.关于
为缩短篇幅,本系列记录如下:
再谈多线程模型之生产者消费者(基础概念)(c++11实现)
再谈多线程模型之生产者消费者(单一生产者和单一消费者)(c++11实现)【本文】
再谈多线程模型之生产者消费者(单一生产者和多消费者)(c++11实现)
再谈多线程模型之生产者消费者(多生产者和单一消费者 )(c++11实现)
再谈多线程模型之生产者消费者(多生产者和多消费者 )(c++11实现)
再谈多线程模型之生产者消费者(总结)(c++11实现)
本文涉及到的代码演示环境: VS2017
欢迎留言指正
1.单一生产者 & 单一消费者
- 1.1 因为只有单一的生产者和消费者,所以,同步的也只有他们俩,互斥仅仅存在消费者和生产者之间,生产者(消费者)之间不存在互斥?一个对象怎么谈互斥?自己与自己互斥? 显然,这是一个假命题。所以,这个模型中,互斥只存在生产者与消费者。
- 1.2 一个结构帮你了解,
struct repo_
{
// 用作互斥访问缓冲区
std::mutex _mtx_queue;
// 缓冲区最大size
unsigned int _count_max_queue_10 = 10;
// 缓冲区
std::queue<int> _queue;
// 缓冲区没有满,通知生产者继续生产
std::condition_variable _cv_queue_not_full;
// 缓冲区不为空,通知消费者继续消费
std::condition_variable _cv_queue_not_empty;
repo_(const unsigned int count_max_queue = 10) :_count_max_queue_10(count_max_queue) {}
};
- 1.3 生产者流程: 1.等待缓冲区没有满信号,2.生产数据放入缓冲区,3.通知消费者可以取数据。
template <typename T>
void thread_produce_item(const int &thread_index, repo<T>& param_repo, const T& repo_item)
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(param_repo._mtx_queue);
// 1. 生产者只要发现缓冲区没有满, 就继续生产
param_repo._cv_queue_not_full.wait(lock, [&] { return param_repo._queue.size() < param_repo._count_max_queue_10; });
// 2. 将生产好的商品放入缓冲区
param_repo._queue.push(repo_item);
// log to console
std::cout << "生产者" << thread_index << "生产数据:" << repo_item << "\n";
// 3. 通知消费者可以消费了
param_repo._cv_queue_not_empty.notify_one();
}
- 1.4 消费者流程: 1.等待缓冲区不为空信号,2.从缓冲区中消费数据,3.通知生产者继续生产数据。
template <typename T>
T thread_consume_item(const int thread_index, repo<T>& param_repo)
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(param_repo._mtx_queue);
// 1. 消费者需要等待【缓冲区不为空】的信号
param_repo._cv_queue_not_empty.wait(lock, [&] {return !param_repo._queue.empty(); });
// 2. 拿出数据
T item;
item = param_repo._queue.front();
param_repo._queue.pop();
std::cout << "消费者" << thread_index << "从缓冲区中拿出一组数据:" << item << std::endl;
// 3. 通知生产者,继续生产
param_repo._cv_queue_not_full.notify_one();
return item;
}
- 1.5 完整源码
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
std::mutex _mtx;
std::condition_variable _cv_not_full;
std::condition_variable _cv_not_empty;
const int max_queue_size_10 = 10;
template<typename T>
struct repo_
{
// 用作互斥访问缓冲区
std::mutex _mtx_queue;
// 缓冲区最大size
unsigned int _count_max_queue_10 = 10;
// 缓冲区
std::queue<T> _queue;
// 缓冲区没有满,通知生产者继续生产
std::condition_variable _cv_queue_not_full;
// 缓冲区不为空,通知消费者继续消费
std::condition_variable _cv_queue_not_empty;
repo_(const unsigned int count_max_queue = 10) :_count_max_queue_10(count_max_queue) {}
};
template <typename T>
using repo = repo_<T>;
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 生产者生产数据
template <typename T>
void thread_produce_item(const int &thread_index, repo<T>& param_repo, const T& repo_item)
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(param_repo._mtx_queue);
// 1. 生产者只要发现缓冲区没有满, 就继续生产
param_repo._cv_queue_not_full.wait(lock, [&] { return param_repo._queue.size() < param_repo._count_max_queue_10; });
// 2. 将生产好的商品放入缓冲区
param_repo._queue.push(repo_item);
// log to console
std::cout << "生产者" << thread_index << "生产数据:" << repo_item << "\n";
// 3. 通知消费者可以消费了
param_repo._cv_queue_not_empty.notify_one();
}
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 消费者消费数据
template <typename T>
T thread_consume_item(const int thread_index, repo<T>& param_repo)
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(param_repo._mtx_queue);
// 1. 消费者需要等待【缓冲区不为空】的信号
param_repo._cv_queue_not_empty.wait(lock, [&] {return !param_repo._queue.empty(); });
// 2. 拿出数据
T item;
item = param_repo._queue.front();
param_repo._queue.pop();
std::cout << "消费者" << thread_index << "从缓冲区中拿出一组数据:" << item << std::endl;
// 3. 通知生产者,继续生产
param_repo._cv_queue_not_full.notify_one();
return item;
}
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* @ brief: 生产者线程
* @ thread_index - 线程标识,区分是哪一个线程
* @ count_max_produce - 最大生产次数
* @ param_repo - 缓冲区
* @ return - void
*/
template< typename T >
void thread_pro(const int thread_index, const int count_max_produce, repo<T>* param_repo)
{
for (int item = 0; item < count_max_produce; ++item)
{
thread_produce_item<T>(thread_index, *param_repo, item);
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::microseconds(16));
}
}
/**
* @ brief: 消费者线程
* @ thread_index - 线程标识,区分线程
* @ param_repo - 缓冲区
* @ return - void
*/
template< typename T >
void thread_con(const int thread_index, repo<T>* param_repo)
{
while (true)
{
T item;
item = thread_consume_item<T>(thread_index, *param_repo);
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::microseconds(16));
if ((param_repo->_count_max_queue_10 - 1) == item)
break;
}
}
// 入口函数
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
int main(int argc, char *argv[], char *env[])
{
// 缓冲区
repo<int> repository;
// 线程池
std::vector<std::thread> vec_thread;
// 生产者
vec_thread.push_back(std::thread(thread_pro<int>, 1, 10, &repository));
// 消费者
vec_thread.push_back(std::thread(thread_con<int>, 1, &repository));
for (auto &item : vec_thread)
{
item.join();
}
return 0;
}
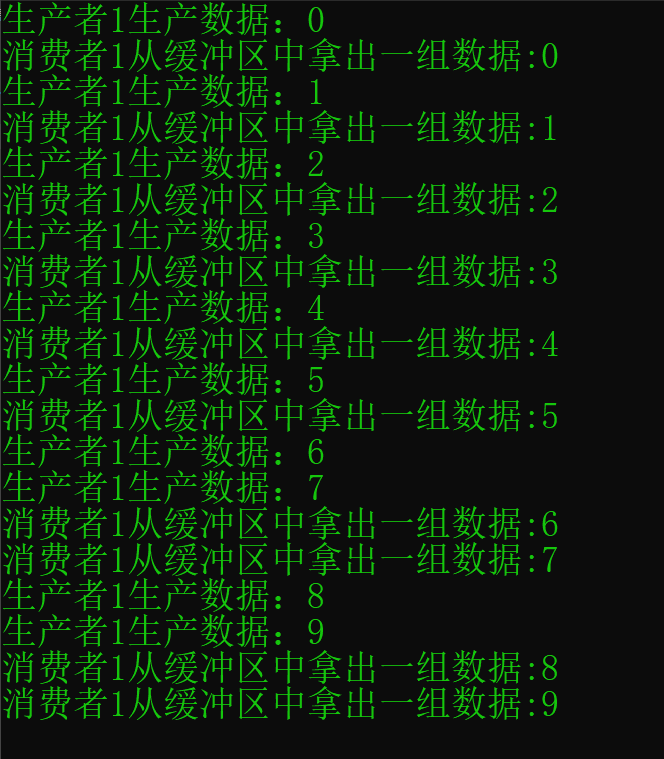
- 1.6 可能输出结果