软工作业3:词频统计
2018-10-09 16:46 潘博 阅读(260) 评论(0) 收藏 举报一、程序分析
1、读取文件到缓冲区
1 def process_file(): # 读文件到缓冲区
2 try: # 打开文件
3 f = open("C:\\Users\\panbo\\Desktop\\A_Tale_of_Two_Cities.txt", "r")
4 except IOError as e:
5 print (e)
6 return None
7 try: # 读文件到缓冲区
8 bvffer = f.read()
9 except:
10 print ("Read File Error!")
11 return None
12 f.close() #关闭文件
13 return bvffer
2、缓冲区字符串分割成带有词频的字典
1 def process_buffer(bvffer):
2 if bvffer:
3 word_freq = {}
4 # 下面添加处理缓冲区 bvffer代码,统计每个单词的频率,存放在字典word_freq
5 #文本字符串前期处理
6 strl_ist = bvffer.replace(punctuation, '').lower().split(' ')
7 #如果单词在字典里,则字典值加1,不在则添加该单词到字典里
8 for str in strl_ist:
9 if str in word_freq.keys():
10 word_freq[str] = word_freq[str] + 1
11 else:
12 word_freq[str] = 1
13 return word_freq
3、将字典按词频排序并输出排名前十的键值对
1 def output_result(word_freq):
2 if word_freq:
3 sorted_word_freq = sorted(word_freq.items(), key=lambda v: v[1], reverse=True)
4 for item in sorted_word_freq[:10]: # 输出 Top 10 的单词
5 print (item)
4、主程序输出前十结果和分析结果
1 if __name__ == "__main__":
2 bvffer = process_file()
3 word_freq = process_buffer(bvffer)
4 output_result(word_freq)
5 import cProfile
6 import pstats;
7 p=pstats.Stats('word_freq.out');
8 #输出调用此处排前十的函数
9 p.sort_stats('calls').print_stats(10)
10 #输出按照运行时间排名前十的函数
11 p.strip_dirs().sort_stats("cumulative", "name").print_stats(10)
12 #p.print_callers(0.5, "sre_parse.py")
13 #查看每个函数分别调用了哪些函数
14 p.print_callees("process_file")
15 p.print_callees("process_buffer")
16 p.print_callees("output_result")
17 #查看有哪些函数调用了builtins.print
18 p.print_callers(0.5, "builtins.print")
19 p.print_callers(0.5, "builtins.exec")
20 #p.strip_dirs().sort_stats("name").print_stats(3)
21 #p.strip_dirs().sort_stats("cumulative", "name").print_stats(0.5)
22 #p.print_callers(0.5, "built-in")
二、代码风格说明
1、python3与python2在print函数的使用上有着细微的区别,在python3中print函数要加上(),如上第一段代码的第五行。
2、使用4个空格进行缩进(即一个tab键),并且缩进符相同的代码属于同一个级别
3、模块级函数和类定义之间空两行。
4、类成员函数之间空一行。
5、不要使用太多的连续空行来区分代码的逻辑块。
三、程序运行结果截图
本程序,运行命令全都写在程序中,而非通过dos窗口执行。
1、A_Tale_of_Two_Cities文本词频统计结果
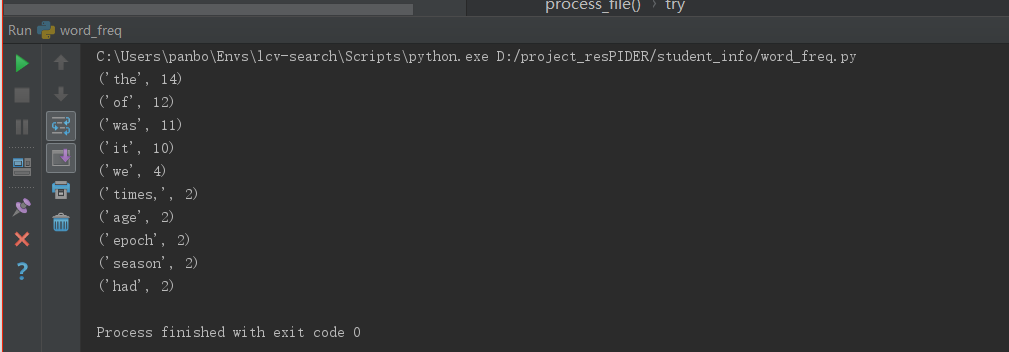
2、Gone_with_the_wind文本词频统计结果
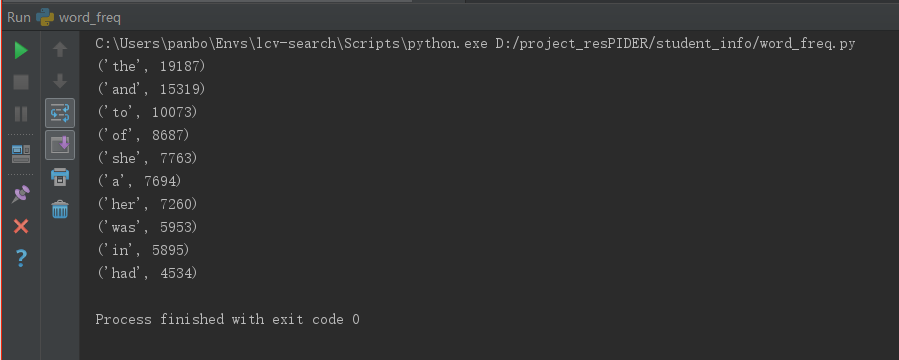
四、性能分析及改进
1、性能分析
1.1、模块耗用时间可视化操作
- 需要安装:graphviz , "pip install graphviz"; 参考使用cProfile分析Python程序性能:链接
-
下载转换 dot 的 python 代码gprof2dot 官方下载,下载完了,解压缩,将『gprof2dot.py』 copy 到当前分析文件的路径,或者你系统 PATH 环境变量设置过的路径。
- 执行下述步骤
1. 性能分析:``` python -m cProfile -o result.out -s cumulative word_freq.py Gone_with_the_wind.txt``` ;分析结果保存到 result.out 文件; 2. 转换为图形;gprof2dot 将 result.out 转换为 dot 格式;再由 graphvix 转换为 png 图形格式。 命令:```python gprof2dot.py -f pstats result.out | dot -Tpng -o result.png```
转换得到图如下:
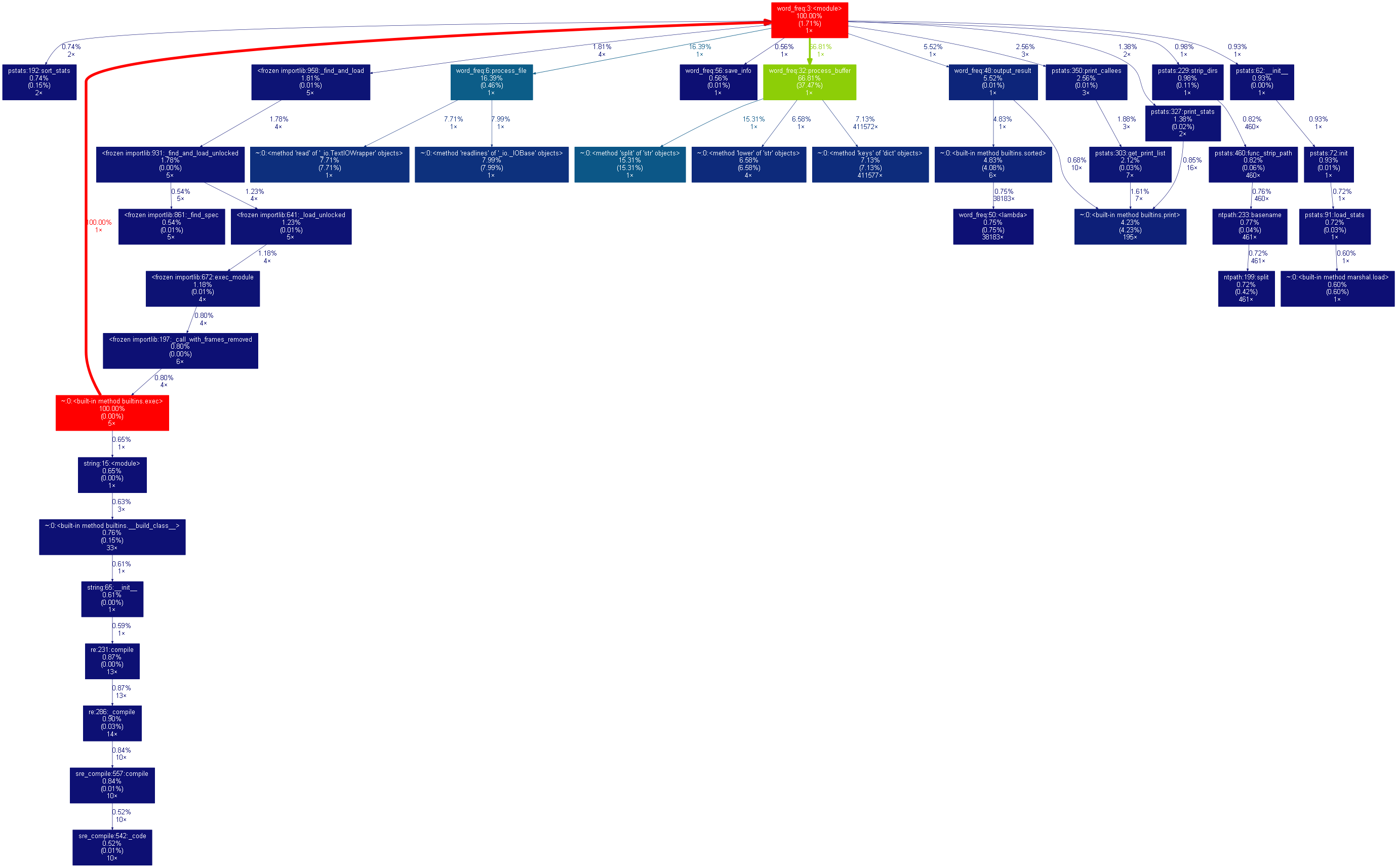
从分析图中我们可以看出process_buffer函数中的split方法耗时占用比例最大,为15%。
1.2、执行时间最多的部分代码
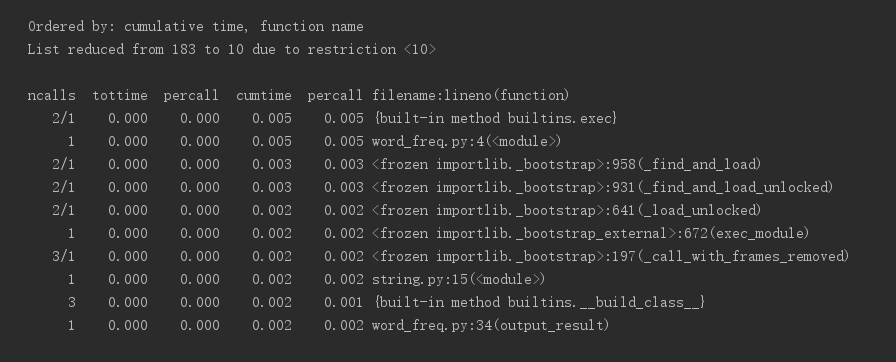
1.3、执行次数最多的部分代码
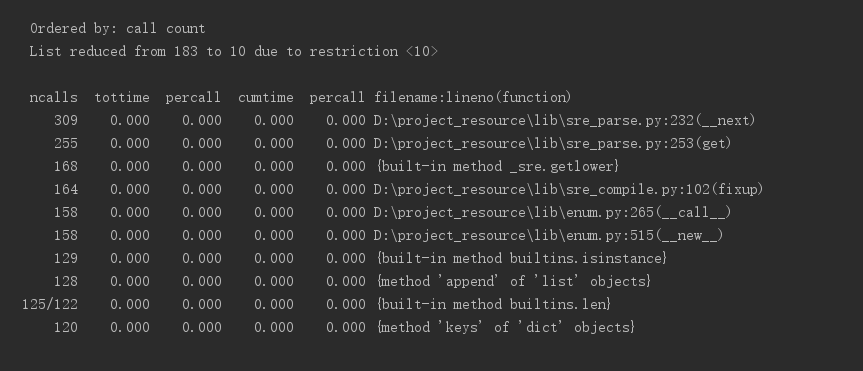
1.4、找到耗时最多的调用函数为
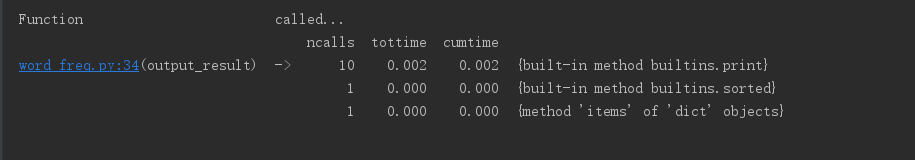
即为: 1 sorted_word_freq = sorted(word_freq.items(), key=lambda v: v[1], reverse=True)
至此,我们从分别按照调用次数和耗时排序的图片来看,程序消耗最大为0.05秒,可以说相当短,并且调用的函数也比较底层,
我们无从下手对程序进行修改。不妨扩大范围,查看每个模块分别调用了哪些方法,并且耗时为多少,如图所示:
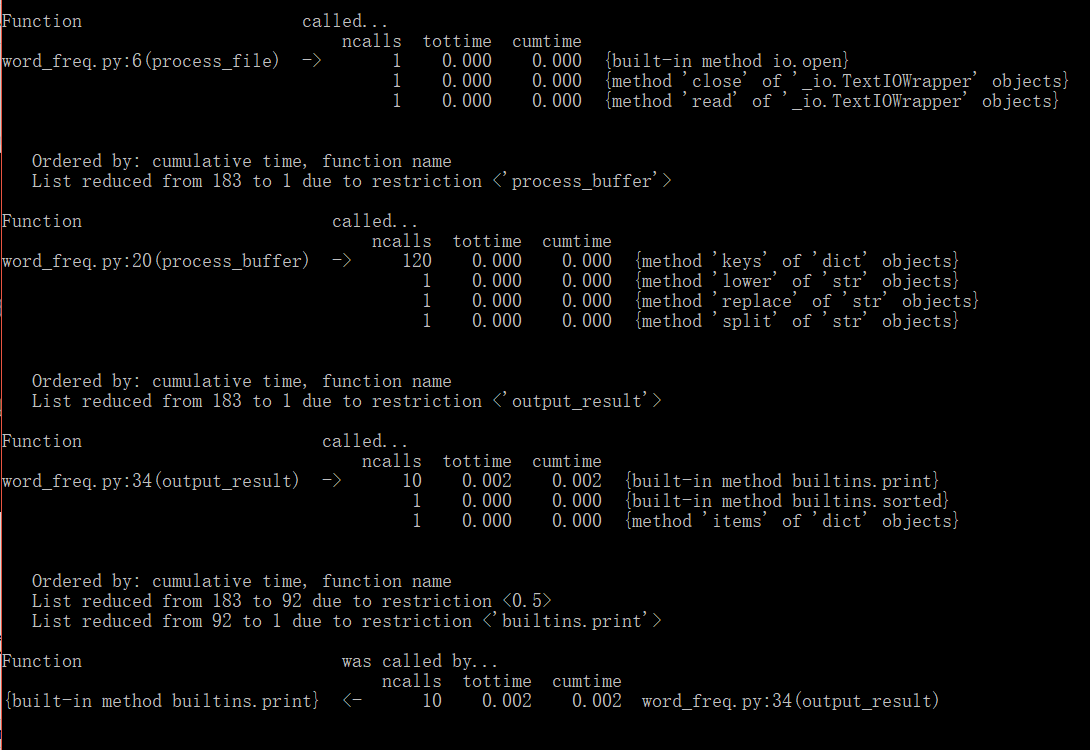
可以看出耗时最多的还是output_result模块所调用的built-in方法。
2、尝试改进程序代码
最终,与其他同学作业比较发现,自己的代码编写优良,不存在把循环内的某条代码提到外面减少运行时间的问题。
并且,本程序时间复杂度与空间复杂度相对较小,程序总运行时间只用0.005秒,再强行修改某过于自找麻烦。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号