Mybatis中<resultMap>用法(主要用于一对多去重)
一、创建部门表和员工表:
创建部门信息表`t_department`,其中包括`id`, `name`
CREATE TABLE t_department (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(20) UNIQUE NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(id)
) DEFAULT CHARSET=UTF8;
往部门表中插入数据:
INSERT INTO t_department (name) VALUES
('UI'), ('RD'), ('TEST');
创建员工信息表t_user
CREATE TABLE t_user(
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
username VARCHAR(20) ,
password VARCHAR(20) ,
age int ,
phone VARCHAR(20) ,
email VARCHAR(20) ,
is_Delete int
)DEFAULT CHARSET=UTF8;
往员工表中插入数据:
INSERT INTO t_user VALUES(null,'张三','123456',23,'110','11111@qq.com',1),(null,'历史','123456',23,'110','11111@qq.com',1),(null,'孙悟空','123456',23,'110','11111@qq.com',2),(null,'李白','123456',23,'110','11111@qq.com',2),(null,'八戒','123456',23,'110','11111@qq.com',2);
插入数据错误:
https://www.cnblogs.com/package-java/p/10494380.html
在查询时,`<select>`节点必须指定结果的类型,可以通过`resultType`属性来指定,也可以通过`resultMap`属性来指定。
当有直接对应的查询结果时,可以使用`resultType`,取值一般是实体类的类型,或VO类的类型。
某些查询可能需要将查询结果进行特殊的封装,例如查询时存在1对多、多对多、多对1等关系,则需要使用`resultMap`来配置封装的方式。
二、创建实体类:
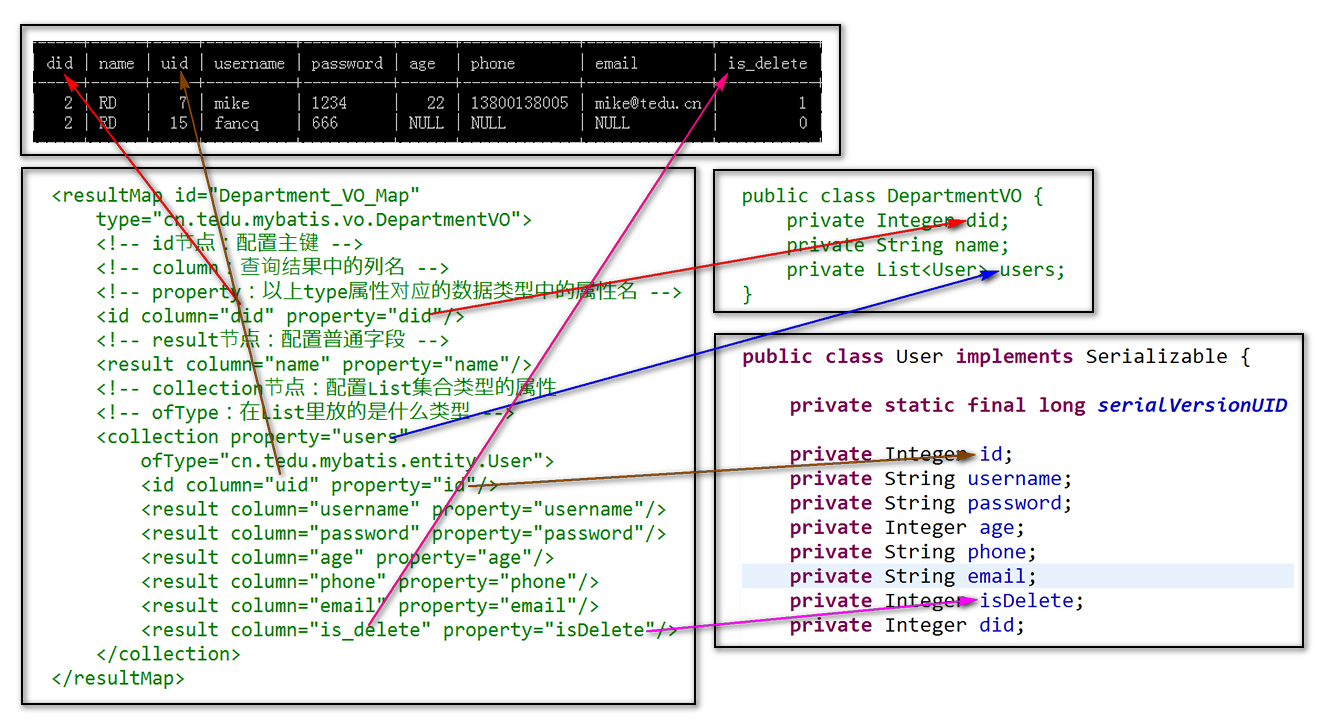
1、Vo类的实体类,因为部门只有三个,三个部门里面可能有很多员工,所以把员工封装到List集合中,由于将多条信息明细存储到了list中,因此查询后将不再出现重复数据,达到了去重的效果
package cn.tedu.mybatis.vo; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.List; import cn.tedu.mybatis.entity.User; public class DepartmentVO implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -6442405812964981459L; private Integer did; private String name; private List<User> users; public Integer getDid() { return did; } public void setDid(Integer did) { this.did = did; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public List<User> getUsers() { return users; } public void setUsers(List<User> users) { this.users = users; } @Override public String toString() { return "DepartmentVO [did=" + did + ", name=" + name + ", users=" + users + "]"; } }
2、员工类:
package cn.tedu.mybatis.entity; import java.io.Serializable; public class User implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 7323921614984096421L; private Integer id; private String username; private String password; private Integer age; private String phone; private String email; private Integer isDelete; private Integer did; public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public String getPhone() { return phone; } public void setPhone(String phone) { this.phone = phone; } public String getEmail() { return email; } public void setEmail(String email) { this.email = email; } public Integer getIsDelete() { return isDelete; } public void setIsDelete(Integer isDelete) { this.isDelete = isDelete; } public Integer getDid() { return did; } public void setDid(Integer did) { this.did = did; } @Override public String toString() { return "User [id=" + id + ", username=" + username + ", password=" + password + ", age=" + age + ", phone=" + phone + ", email=" + email + ", isDelete=" + isDelete + ", did=" + did + "]"; } }
三、创建接口和抽象方法:
package cn.tedu.mybatis.mapper; import cn.tedu.mybatis.vo.DepartmentVO; public interface DepartmentMapper { DepartmentVO findById(Integer id); }
四、SQL语句的映射:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//ibatis.apache.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://ibatis.apache.org/dtd/ibatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="cn.tedu.mybatis.mapper.DepartmentMapper"> <!-- namespace:抽象类绝对路径 --> <resultMap id="Department_VO_Map" type="cn.tedu.mybatis.vo.DepartmentVO">
<!-- id节点:配置主键 --> <!-- type:实体类绝对路径 --> <!-- column:查询结果中的列名 --> <!-- property:以上type属性对应的数据类型中的属性名(类里面的属性) --> <id column="did" property="did"/> <!-- result节点:配置普通字段 --> <result column="name" property="name"/> <!-- collection节点:配置List集合类型的属性,用于1对多的查询 --> <!-- ofType:在List里放的是什么类型 --> <collection property="users" ofType="cn.tedu.mybatis.entity.User"> <id column="uid" property="id"/> <result column="username" property="username"/> <result column="password" property="password"/> <result column="age" property="age"/> <result column="phone" property="phone"/> <result column="email" property="email"/> <result column="isDelete" property="isDelete"/> </collection> </resultMap> <select id="findById" resultMap="Department_VO_Map"> SELECT t_department.id AS did, name, t_user.id AS uid, username, password, age, phone, email, is_delete FROM t_department INNER JOIN t_user ON t_user.did=t_department.id WHERE t_department.id=#{id} </select> </mapper>
> 以上代码中,自定义别名是因为需要区分查询结果中的列的名称,并不是因为需要与数据类型中的属性对应,关于查询结果的列名与数据类型的属性名的对应,可以通过`<resultMap>`中的配置来完成!
五、测试:
package cn.tedu.mybatis.mapper; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import cn.tedu.mybatis.vo.DepartmentVO; public class DepartmentMapperTestCase { AbstractApplicationContext ac; DepartmentMapper mapper; @Before public void doBefore() { ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-dao.xml"); mapper = ac.getBean("departmentMapper", DepartmentMapper.class); } @After public void doAfter() { ac.close(); } @Test public void findById() { Integer id = 2; DepartmentVO data = mapper.findById(id); System.out.println(data); } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号