设计模式之行为型模式-访问者模式
访问者模式(Visitor Pattern)
一、 介绍
模式定义:封装一些作用于某种数据结构中的各元素的操作,它可以在不改变数据结构的前提下定义作用于这些元素的新的操作。
意图:主要将数据结构与数据操作分离。
主要解决:稳定的数据结构和易变的操作耦合问题。(被处理的数据元素相对稳定而访问方式多种多样)
何时使用:
- 一个对象结构包含多个类型的对象,希望对这些对象实施一些依赖其具体类型的操作
- 需要对一个对象结构中的对象进行很多不同的并且不相关的操作,而需要避免让这些操作"污染"这些对象的类,也不希望在增加新操作时修改这些类,可以使用访问者模式将这些封装到类中。
- 对象结构中对象对应的类很少改变,但经常需要在此对象结构上定义新的操作。
如何解决:在被访问的类里面加一个对外提供接待访问者的接口。
关键代码:在数据基础类里面有一个方法接受访问者,将自身引用传入访问者。
应用实例:JDK 对于文件树的遍历(不变:文件树的遍历,变:文件的具体操作 如 打印文件名、计算文件数),ASM 修改字节码
优点:
- 符合单一职责原则。(访问者模式把相关的行为封装在一起,构成一个访问者,使每一个访问者的功能都比较单一。)
2.更强的扩展性。(能够在不修改对象结构中的元素的情况下,为对象结构中的元素添加新的功能。)
3.可维护性(复用性好)。(可以通过访问者来定义整个对象结构通用的功能,从而提高系统的复用程度。)
4.灵活性。(访问者模式将数据结构与用作于结构上的操作解耦,使得操作集合可相对自由地演化而不影响系统的数据结构。)
缺点: 1、具体元素对访问者公布细节,违反了迪米特原则。 2、具体元素(被访问者的)变更比较困难。 3、违反了依赖倒置原则,依赖了具体类,没有依赖抽象。4、类结构变得复杂。(不是简单的调用关系,而是多个类之间的继承和组合关系)
使用场景: 1、对象结构中对象对应的类很少改变,但经常需要在此对象结构上定义新的操作。 2、需要对一个对象结构中的对象进行很多不同的并且不相关的操作,而需要避免让这些操作"污染"这些对象的类,也不希望在增加新操作时修改这些类。(不想直接被改变但又想扩展功能)
注意事项:访问者可以对功能进行统一,可以做报表、UI、拦截器与过滤器。
二、详细
举例:您在朋友家做客,您是访问者,朋友接受您的访问,您通过朋友的描述,然后对朋友的描述做出一个判断,这就是访问者模式。
设计模式的本质是找出不变的东西,再找出变化的东西,然后找到合适的数据结构(设计模式)去承载这种变化。
访问者模式,重点在于访问二字,从字面上的意思理解:其实就相当于被访问者(如某个公众人物)把访问者(如 记者)当成了外人,不想你随便动。你想要什么,我弄好之后给你(调用你的方法)。访问者模式其实就是要把不变的东西固定起来,变化的开放出去。

三、结构
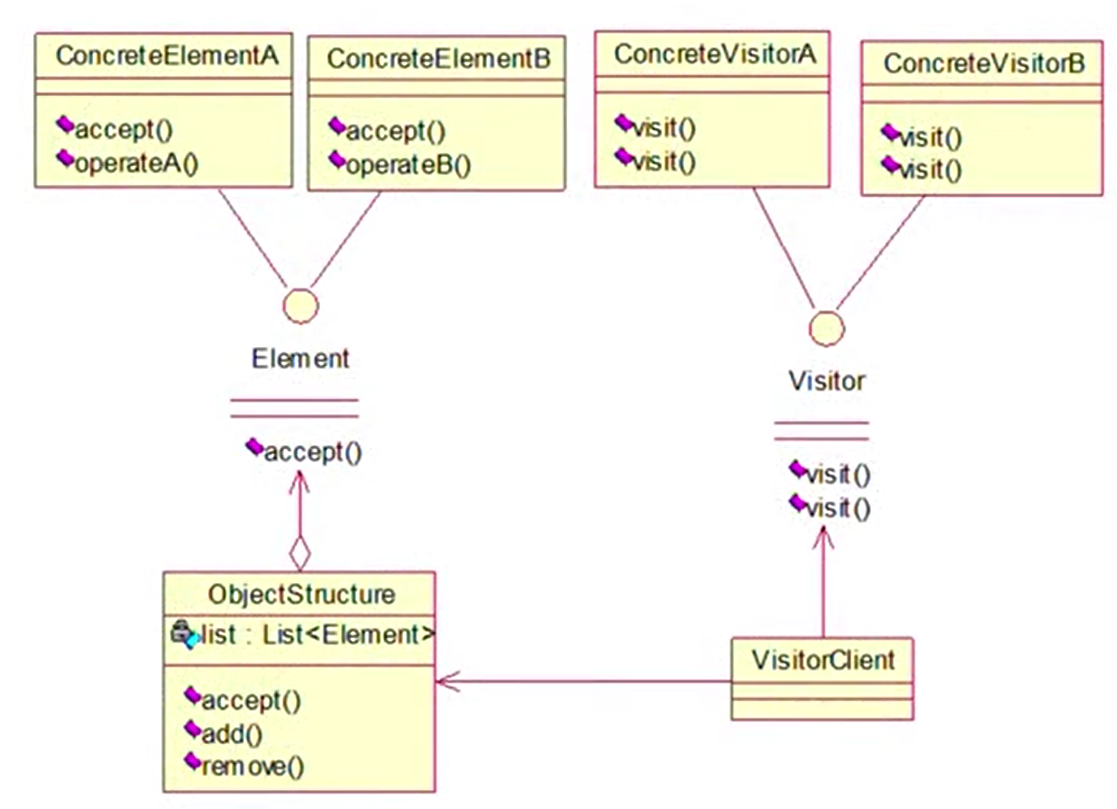
访问者(Visitor) 模式实现的关键是如何将作用于元素的操作分离出来封装成独立的类,其主要角色如下:
- 抽象访问者(Visitor)角色:定义一个访问具体元素的接口,为每个具体元素类对应一个访问操作visit(),该操作中的参数类型表示了被访问的具体元素。
- 具体访问者(Concrete Visitor)角色:实现抽象访问者角色中声明的各个访问操作,确定访问者访问一个元素时该做什么。
- 抽象元素(Element)角色:声明一个包含接受操作accept()操作,其方法体通常都是visitor.visit(this),另外具体元素中可能还包含业务本身逻辑的相关操作。
- 具体元素(Concrete Element)角色:实现抽象元素角色提供的accept()操作,其方法体通常都是visitor.visit(this),另外具体元素中可能还包含本身业务逻辑的相关操作。
- 对象结构(Object Structure)角色:是一个包含元素角色的容器,提供让访问者对象遍历容器中的所有元素的方法,通常由List、Set、Map等聚合类实现。
- 双重分派机制
(1)调用具体元素类的accept(Visitor visitor)方法,并将Visitor子类对象作为其参数
(2)在具体元素类accept(Visitor visitor)方法内部调用传入的Visitor对象的visit(方法,例如visit(ConcreteElementA elementA) ,将当前具体
元素类对象(this)作为参数,例如visitor.visit(this)
(3)执行Visitor对象的visit(方法,在其中还可以调用具体元素对象的业务方法
结构图如下:
简单样例1(访问者类有多个方法)
/**
* 抽象访问者
*/
interface Visitor{
void visit(ConcreteElementA element);
void visit(ConcreteElementB element);
}
/**
* 具体访问者A类
*/
class ConcreteVisitorA implements Visitor{
@Override
public void visit(ConcreteElementA element) {
System.out.println("具体访问者A访问->" + element.operationA());
}
@Override
public void visit(ConcreteElementB element) {
System.out.println("具体访问者A访问->" + element.operationB());
}
}
/**
* 具体访问者B类
*/
class ConcreteVisitorB implements Visitor{
@Override
public void visit(ConcreteElementA element) {
System.out.println("具体访问者B访问->" + element.operationA());
}
@Override
public void visit(ConcreteElementB element) {
System.out.println("具体访问者B访问->" + element.operationB());
}
}
/**
* 抽象元素类
*/
interface Element{
void accept(Visitor visitor);
}
/**
* 具体元素A类
*/
class ConcreteElementA implements Element{
@Override
public void accept(Visitor visitor) {
visitor.visit(this);
}
public String operationA(){
return "具体元素A的操作";
}
}
/**
* 具体元素B类
*/
class ConcreteElementB implements Element{
@Override
public void accept(Visitor visitor) {
visitor.visit(this);
}
public String operationB(){
return "具体元素B的操作";
}
}
/**
* 对象结构角色
*/
class ObjectStructure{
private List<Element> list = new ArrayList<Element>();//泛型
public void accept(Visitor visitor){
Iterator<Element> i = list.iterator();
while(i.hasNext()){
i.next().accept(visitor);
}
}
public void add(Element element){//增加
list.add(element);
}
public void remove(Element element){//删除
list.remove(element);
}
}
public class VisitorPatternSimpleTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
ObjectStructure objectStructure = new ObjectStructure();
objectStructure.add(new ConcreteElementA());
objectStructure.add(new ConcreteElementB());
Visitor visitorA = new ConcreteVisitorA();
objectStructure.accept(visitorA);
System.out.println("------------------------------");
Visitor visitorB = new ConcreteVisitorB();
objectStructure.accept(visitorB);
}
}
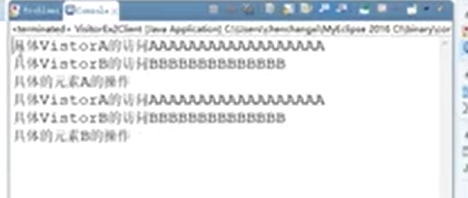
执行:

简单样例2(访问者类只有1个方法)
/**
* 抽象访问者
*/
interface Visitor{
void visit(Element element);
}
/**
* 具体访问者A类
*/
class ConcreteVisitorA implements Visitor{
@Override
public void visit(Element element) {
System.out.println("具体访问者A访问AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA");
}
}
/**
* 具体访问者B类
*/
class ConcreteVisitorB implements Visitor{
@Override
public void visit(Element element) {
System.out.println("具体VisitorB的访问BBBBBBBBBBBBB");
}
}
/**
* 抽象元素类
*/
interface Element{
void accept(Visitor visitor);
}
/**
* 具体元素A类
*/
class ConcreteElementA implements Element{
@Override
public void accept(Visitor visitor) {
visitor.visit(this);
}
public String operation(){
return "具体元素A的操作";
}
}
/**
* 具体元素B类
*/
class ConcreteElementB implements Element{
@Override
public void accept(Visitor visitor) {
visitor.visit(this);
}
public String operation(){
return "具体元素B的操作";
}
}
/**
* 对象结构角色
*/
class ObjectStructure{
private List<Element> list = new ArrayList<Element>();//泛型
public void accept(Visitor visitor){
Iterator<Element> i = list.iterator();
while(i.hasNext()){
i.next().accept(visitor);
}
}
public void add(Element element){//增加
list.add(element);
}
public void remove(Element element){//删除
list.remove(element);
}
}
/**
* 客户端
*/
public class VisitorTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args){
ObjectStructure os = new ObjectStructure();
String[] strs = ("ConcreteElementA", "ConcreteElenentB");
String[] strs1= ("ConcreteVisitorA", "ConcreteVisitorB" );
String pn = VisitorTest2.class.getPackage().getName();
for (String str : strs) {
try {
Element element = (Element) Class.forName(pn +" ."+str).newInstance();
Visitor visitor = null;
for(String str1 : strs1) {
visitor= (Visitor)Class.forName(pn+"."+str1).newInstance() ;
element.accept(visitor);
}
System.out.println(element.operate());
}catch (InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
执行:
三、案例
引进示例1:迭代器打印集合(可pass)
PrintAggregate
public class PrintAggregate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] x={2,3,4,5,10,9,8};
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
for(int i=0;i < x.length;i++){
collection.add(x[i]);
}
print(collection);
}
public static void print(Collection collection) {
Iterator it = collection.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next().toString());
}
}
}
执行:

PrintAggregate2
public class PrintAggregate2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] a="Tianjin is one of the most beautiful city in China".aplit(" ");
/* Arrays.asList方法生成的1ist是List是使用的是类内部的构建ArrayList类,而不是我们常用的Java.util.ArrayList
它的内部类根本就没有写List的add方法,而是调用的java.util.AbstractList.add的add方法
而AbstractList的add方法会直接报出UnsupportedOperationException异常 */
Collection co = new ArrayList();
System.out.println(co.getClass());
Collection co2 = new ArrayList();
co2.add("1");
co2.add("2");
co.addAll(co2);
print(co);
}
public static void print(Collection collection) {
Iterator it= collectlon.iterator ();
while(it.hasNext()){
Object o=it.next();
if(o instanceof Collection){
print((Collection)o);
}else{
System.out.println(o.toString());
}
}
}
}

PrintAggregate3(强耦合,不推荐)
public class PrintAggregate2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] a="Tianjin is one of the most beautiful city in China".aplit(" ");
Collection co = new ArrayList();
Collection co2 = new ArrayList();
co2.add("1");
co2.add("2");
co2.add(3);
co2.add(4.0);
co2.add(5.6f);
co.addAll(co2);
print(co);
}
public static void print(Collection collection) {
Iterator it= collectlon.iterator ();
while(it.hasNext()){
Object o=it.next();
if(o instanceof Collection){
print((Collection)o);
}else if(o instanceof String){
System.out.println(" "+o.toString()+" ");
}else if(o instanceof Double){
System.out.println(o.toString()+"D");
}else if(o instanceof Float){
System.out.println(o.toString()+"f");
}else{
System.out.println(o.toString());
}
访问者模式实例
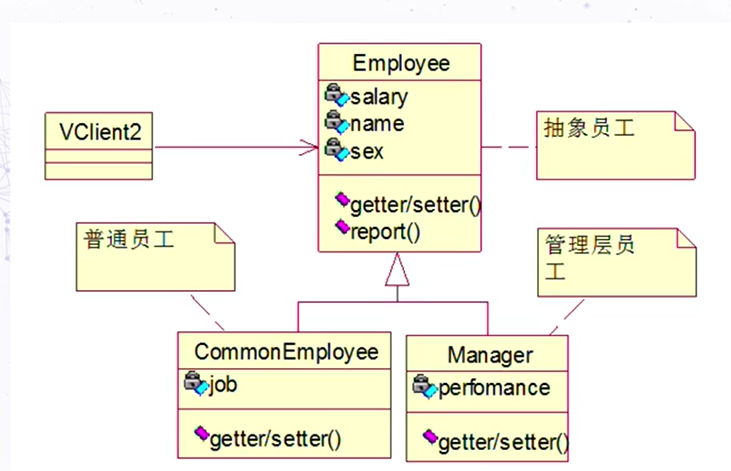
不用访问者模式
public abstract class Employee{
public final static int MALE=0;
public final static int FEMALE=1;
private String name;
private int salary;
private int sex;
public String getNane(){
return name;
}
public void setName (String name) (
this.name = name;
}
public int getSalary(){
return salary:
}
public void setSalary(int salary) {
this.salary=salary;
}
public int getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(int sex) {
this.sex=sex;
}
public final void report() {
String info ="姓名: "+this.name+"\t";
info= info+"性别: "+ (this.sex== FEMALE?"女":"男")+"\t";
info= into+"薪水:" + this.salary+"\t";
info= info+ this.getOtberInfo();
System.out.println (info);
}
protected abstract String getOtherInfo();
}
/*
*普通员工
*/
public class CommonEmployee extends Employee {
private String job;
public String getJob(){
return job;
}
public void setJob(String job) {
this.job = Job;
}
@Override
protected String getOtherInfo() {
return "工作: "+ this.job + "\t";
}
}
/*
*管理者
*/
public class Manager extends Employee {
private String perfomance;
public String getPerfomance(){
return perfomance;
}
public void setPerfomance(String perfomance) {
this.perfomance = perfomance;
}
@Override
protected String getOtherInfo() {
return "表现: "+ this.perfomance + "\t";
}
}
/*
* 客户端
*/
public calss VClient{
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (Employee emp:mockEmployee()){
emp.report();
}
}
private static List<Employee> mockEmployee(){
List<Employee> list =new ArrayList<Employee>;
CommonEmployee zhangsan = new CommonEmployee();
zhangsan.setJob("编写程序,是一个码农");
zhangsan.setName("张三");
zhangsan.setSalary(4500);
zhangsan.setSex(Employee.MALE);
list.add(zhangsan);
CommonEmployee lisi = bew CommonEmployee();
lisi.setJob("美工,审美素质极高!");
lisi.setName("李四");
lisi.setSalary(4000);
lisi.setSex(Employee.FEMALE);
list.add(lisi);
Manager manager = new Manager();
wangwu.setJob("中层管理人员,任劳任怨");
wangwu.setName("王五");
wangwu.setSalary(8000);
wangwu.setSex(Employee.MALE);
list.add(wangwu);
return list;
}
}
使用访问者模式
/*
* 被访问者
*/
public abstract class Employee{
public final static int MALE=0;
public final static int FEMALE=1;
private String name;
private int salary;
private int sex;
public String getNane(){
return name;
}
public void setName (String name) (
this.name = name;
}
public int getSalary(){
return salary:
}
public void setSalary(int salary) {
this.salary=salary;
}
public int getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(int sex) {
this.sex=sex;
}
public abstract void accept(IVisitor visitor);//抽象方法接受访问者
}
/*
*普通员工
*/
public class CommonEmployee extends Employee {
private String job;
public String getJob(){
return job;
}
public void setJob(String job) {
this.job = Job;
}
@Override
public void accept(IVisitor visitor) {
visitor.visit(this);//接受访问者的访问
}
}
/*
*管理者
*/
public class Manager extends Employee {
private String perfomance;
public String getPerfomance(){
return perfomance;
}
public void setPerfomance(String perfomance) {
this.perfomance = perfomance;
}
@Override
public void accept(IVisitor visitor) {
visitor.visit(this);//接受访问者的访问
}
}
/**
* 抽象访问者
*/
interface IVisitor{
void visit(CommonEmployee commonEmp);
void visit(Manager managerEmp);
}
/**
* 具体访问者
*/
class Visitor implements IVisitor{
@Override
public void visit(CommonEmployee commonEmp) {
System.out.println(this.getCommonEmployee(commonEmp));
}
@Override
public void visit(Manager managerEmp) {
System.out.println(this.getManager(managerEmp));
}
private String getManager(Manager managerEmp){
String info =this.getBasicInfo(managerEmp);
String otherInfo ="表现:"+managerEmp.getPerfomance()+"\t";
return info+otherInfo;
}
private String getBasicInfo(Employee emp){
String info ="姓名:"+emp.getName()+"\t";
info =info+"性别:"+(emp.getSex()==Employee.FEMALE?"女":"男")+"\t";
info=info+"薪水:"+emp.getSalary()+"\t";
return info;
}
private String getCommonEmployee (CommonEmployee commonEmp) {
String info= this.getBasicInto (commonEmp);
String otherInfo=" 工作:"+commonEmp.getJob()+"\t";
return infot+otherInto;
}
}
/*
* 客户端
*/
public calss VClient2{
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (Employee emp:mockEmployee()){
emp.accept(new Visitor());
}
}
private static List<Employee> mockEmployee(){
List<Employee> list =new ArrayList<Employee>;
CommonEmployee zhangsan = new CommonEmployee();
zhangsan.setJob("编写程序,是一个码农");
zhangsan.setName("张三");
zhangsan.setSalary(4500);
zhangsan.setSex(Employee.MALE);
list.add(zhangsan);
CommonEmployee lisi = bew CommonEmployee();
lisi.setJob("美工,审美素质极高!");
lisi.setName("李四");
lisi.setSalary(4000);
lisi.setSex(Employee.FEMALE);
list.add(lisi);
Manager manager = new Manager();
wangwu.setJob("中层管理人员,任劳任怨");
wangwu.setName("王五");
wangwu.setSalary(8000);
wangwu.setSex(Employee.MALE);
list.add(wangwu);
return list;
}
}
两者差异:如果要进行薪水汇总操作
访问者模式变更
/**
* 抽象访问者
*/
public interface IVisitor{
void visit(CommonEmployee commonEmp);
void visit(Manager managerEmp);
public int getTotalSalary();//新增操作——薪资汇总
}
/**
* 具体访问者
*/
public class Visitor implements IVisitor{
private final static int MANAGER_COFFICIENT=5;//工资系数
private int COMMENEMPLYEE_COFFICIENT=2;
private int CommonTotalSalary=0;
private int ManagerTotalSalary=0;
@Override
public void visit(CommonEmployee commonEmp) {
System.out.println(this.getCommonEmployee(commonEmp));
}
@Override
public void visit(Manager managerEmp) {
System.out.println(this.getManager(managerEmp));
}
private String getManager(Manager managerEmp){
calManagerSalary(managerEmp);
String info =this.getBasicInfo(managerEmp);
String otherInfo ="表现:"+managerEmp.getPerfomance()+"\t";
return info+otherInfo;
}
private String getBasicInfo(Employee emp){
String info ="姓名:"+emp.getName()+"\t";
info =info+"性别:"+(emp.getSex()==Employee.FEMALE?"女":"男")+"\t";
info=info+"薪水:"+emp.getSalary()+"\t";
return info;
}
private String getCommonEmployee (CommonEmployee commonEmp) {
calManagerSalary(managerEmp);
String info= this.getBasicInto (commonEmp);
String otherInfo=" 工作:"+commonEmp.getJob()+"\t";
return infot+otherInto;
}
private void calManagerSalary(Manager managerEmp){
this.managerTotalSalary=this.managerTotalSalary+managerEmp.getSalary()*MANAGER_COFFICIENT;
}
private void calCommonSalary(CommonEmployee commonEmp){
this.commonTotalSalary=this.commonTotalSalary+commonEmp.getSalary()*COMMENEMPLYEE_COFFICIENT;
}
}
/*
* 客户端
*/
public calss VClient3{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Visitor visitor=new Visitor();
for (Employee emp:mockEmployee()){
emp.accept(new Visitor());
}
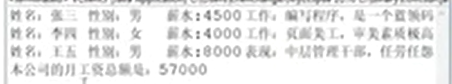
System.out.println("本公司的月工资总额是:"+visitor.getTotalSalary());
}
private static List<Employee> mockEmployee(){
List<Employee> list =new ArrayList<Employee>;
CommonEmployee zhangsan = new CommonEmployee();
zhangsan.setJob("编写程序,是一个码农");
zhangsan.setName("张三");
zhangsan.setSalary(4500);
zhangsan.setSex(Employee.MALE);
list.add(zhangsan);
CommonEmployee lisi = bew CommonEmployee();
lisi.setJob("美工,审美素质极高!");
lisi.setName("李四");
lisi.setSalary(4000);
lisi.setSex(Employee.FEMALE);
list.add(lisi);
Manager manager = new Manager();
wangwu.setJob("中层管理人员,任劳任怨");
wangwu.setName("王五");
wangwu.setSalary(8000);
wangwu.setSex(Employee.MALE);
list.add(wangwu);
return list;
}
}