sort.Sort() interface in GoLang
原文:https://medium.com/@kdnotes/sort-sort-interface-in-golang-1d263d96956d
package main
import (
"fmt"
"sort"
//"unicode/utf8"
)
type P struct {
name string
age int
}
type nameSortedPs []P
func (a nameSortedPs) Len() int {
return len(a)
}
func (a nameSortedPs) Less(i, j int) bool {
//iRune, _ := utf8.DecodeRuneInString(a[i].name)
//jRune, _ := utf8.DecodeRuneInString(a[j].name)
//return int32(iRune) < int32(jRune)
return a[i].age > a[j].age
}
func (a nameSortedPs) Swap(i, j int) {
a[i], a[j] = a[j], a[i]
}
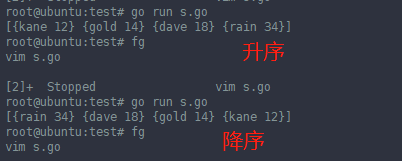
func main() {
groupA := []P{
{"gold", 14}, {"dave", 18}, {"kane", 12}, {"rain", 34},
}
sort.Sort(nameSortedPs(groupA))
fmt.Println(groupA)
}
------------------------------
Sorting is one of those tasks that comes up from time to time in software project, it important to get just the right algorithm. With the sort package from Go, the Sort interface provides an abstraction on top of commonly used sorting algorithm. That makes it very efficient and for most arbitrary sorting task.
This article briefly explores some sorting methods then explores the GoLang Sort interface in details.
Sorting in Go
sort.Ints
sort.Float64s
sort.Strings
These simple methods can be used to sot a slice of ints, float64 or strings
names := []string{“jane”, “dave”, “mike”, “kane”, “rain”}
sort.Strings(names)
fmt.Println(names)
We can also sort using a common comparative using the sort.Slice method, using the less (i,j) comparative function.
group := []struct {
name string
age int
}{
{“Gold”, 14}, {“dave”, 18}, {“kane”, 12}, {“rain”, 34},
}sort.Slice(group, func(i, j int) bool {
return group[i].age < group[j].age
})fmt.Println(group)
The Sort interface
type Interface interface{
Len() int
Less (i , j) bool
Swap(i , j int)
}
Any collection that implements this interface can be easily sorted. Len returns the length of the collection, Less receives two integers that will serve as indices from the collection, Swap implements the needed change after the Less method is called.
import (
"fmt"
"sort"
"unicode/utf8"
)type P struct {
name string
age int
}type nameSortedPs []Pfunc (a nameSortedPs) Len() int {
return len(a)
}func (a nameSortedPs) Less(i, j int) bool {
iRune, _ := utf8.DecodeRuneInString(a[i].name)
jRune, _ := utf8.DecodeRuneInString(a[j].name)
return int32(iRune) < int32(jRune)
}func (a nameSortedPs) Swap(i, j int) {
a[i], a[j] = a[j], a[i]
}func main() {
groupA := []P{
{"gold", 14}, {"dave", 18}, {"kane", 12}, {"rain", 34},
}
sort.Sort(nameSortedPs(groupA))fmt.Println(groupA)
}
The user can implement any logic they wish in regards to what the sort will use to sort on.
By offering the underlying algorithm and defining the sort.Interface the programming language helps us build powerful sorting programs without enforcing a single opinion on what the algorithm should do but rather how to do it.



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号