新手的spring的学习笔记
1.简单的步骤:
创建web项目,导入spring的包
- 导入4个核心的包(core、beans、context、expression)和1个依赖包(common-logging.jar)
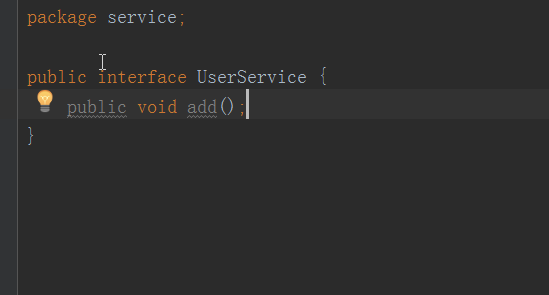
- 写个简单的service
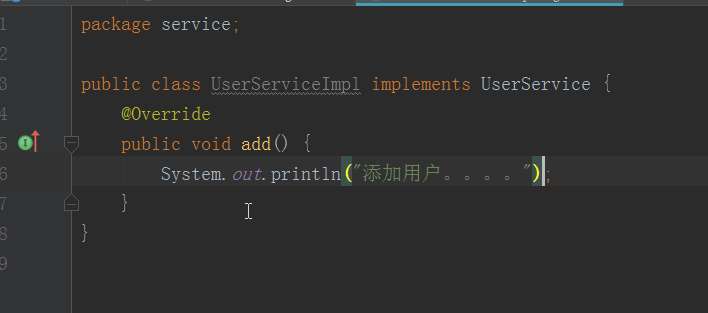
- 配置Beans.xml文件(在src目录下)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 配置一个bean--> <bean id="userService" class="service.UserServiceImpl"> </bean> </beans>
- 创建一个test的类:
package test; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import service.UserService; public class Demo01 { @Test public void test1(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService"); userService.add(); } }
运行结果
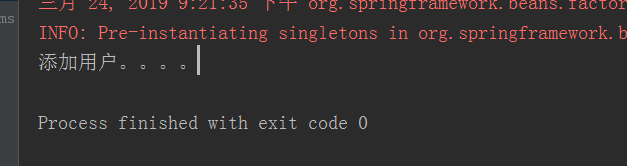
在之前的学习中,我们可能在test类里面实例化一个UserService,然后调用add()方法,这里涉及到了IoC(Inverse of Control)反转控制的概念,也就是说原先在程序中手动创建Userservice的控制权,这里交由Spring框架管理,也就是创建UserService对象控制权被反转到了Spring框架
2.依赖注入(Dependency Injection):在Spring框架负责创建Bean对象时,动态的将依赖对象注入到Bean组件。
例子:
package service; public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { //提供一个属性,要有get/set方法 private String name; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public void add() { System.out.println("添加用户。。。。"); } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 配置一个bean--> <bean id="userService" class="service.UserServiceImpl"> <property name="name" value="oyb"></property> </bean> </beans>
测试结果:
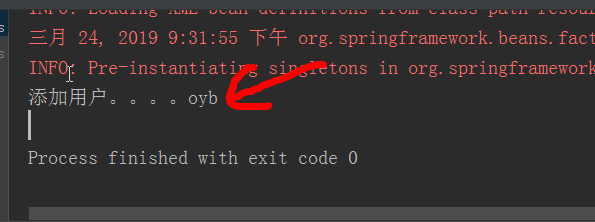
3.Bean的作用域
|
类别 |
说明 |
|
singleton |
在Spring IoC容器中仅存在一个Bean实例,Bean以单例方式存在,默认值 |
|
prototype |
每次从容器中调用Bean时,都返回一个新的实例,即每次调用getBean()时 ,相当于执行new XxxBean() |
|
request |
每次HTTP请求都会创建一个新的Bean,该作用域仅适用于WebApplicationContext环境 |
|
session |
同一个HTTP Session 共享一个Bean,不同Session使用不同Bean,仅适用于WebApplicationContext 环境 |
|
globalSession |
一般用于Portlet应用环境,该作用域仅适用于WebApplicationContext 环境 |
4.Bean的生命周期
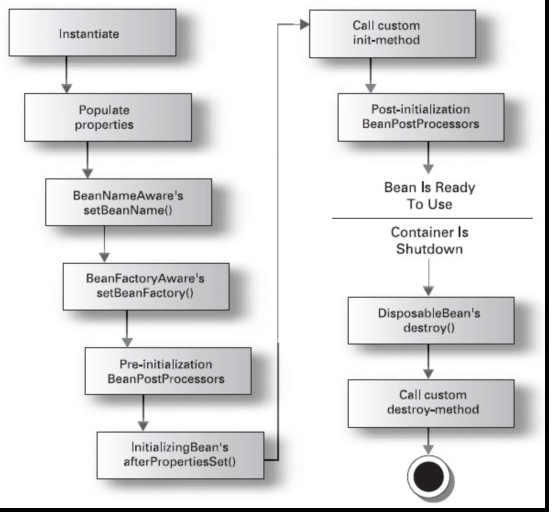
1.instantiate bean对象实例化
2.populate properties 封装属性
3.如果Bean实现BeanNameAware 执行 setBeanName
4.如果Bean实现BeanFactoryAware 执行setBeanFactory ,获取Spring容器
5.如果存在类实现 BeanPostProcessor(后处理Bean) ,执行postProcessBeforeInitialization
6.如果Bean实现InitializingBean 执行 afterPropertiesSet
7.调用<bean init-method="init"> 指定初始化方法 init
8.如果存在类实现 BeanPostProcessor(处理Bean) ,执行postProcessAfterInitialization
执行业务处理
9.如果Bean实现 DisposableBean 执行 destroy
101.调用<bean destroy-method="customerDestroy"> 指定销毁方法 customerDestroy
5.依赖注入Bean属性:
5.1构造方法注入
创建实体类:
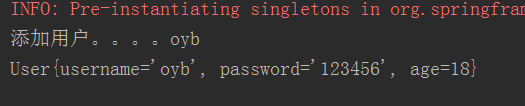
package domain; public class User { private String username; private String password; private Integer age; public User(String username, String password, Integer age) { this.username = username; this.password = password; this.age = age; } public User() { } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "username='" + username + '\'' + ", password='" + password + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } }
配置一个bean
<bean id="user" class="domain.User"> <property name="username" value="oyb"></property> <property name="password" value="123456"></property> <property name="age" value="18"></property> </bean>
还有一种时候通过set方法注入,上面已经讲到了,这里就不讲了。
测试结果
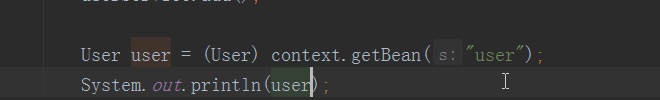
5.2集合注入
集合的注入都是给<property>添加子标签
数组:<array>
List:<list>
Set:<set>
Map:<map> ,map存放k/v 键值对,使用<entry>描述
Properties:<props> <prop key=""></prop> 【】
普通数据:<value>
引用数据:<ref>
例子:
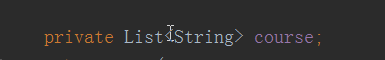
在User这个类中添加一条集合属性course,同样的我们要提供set方法,才能够在bean文件中注入
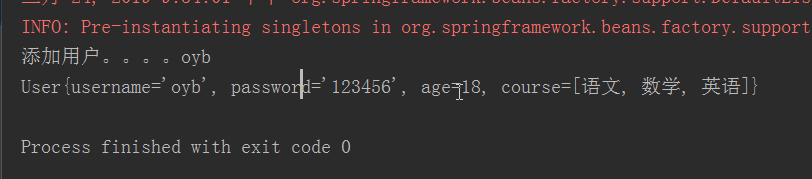
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 配置一个bean--> <bean id="userService" class="service.UserServiceImpl" scope="singleton"> <property name="name" value="oyb"></property> </bean> <bean id="user" class="domain.User"> <property name="username" value="oyb"></property> <property name="password" value="123456"></property> <property name="age" value="18"></property> <property name="course"> <list> <value>语文</value> <value>数学</value> <value>英语</value> </list> </property> </bean> </beans>
测试结果:
关于注解的内容下一篇博文将会介绍


