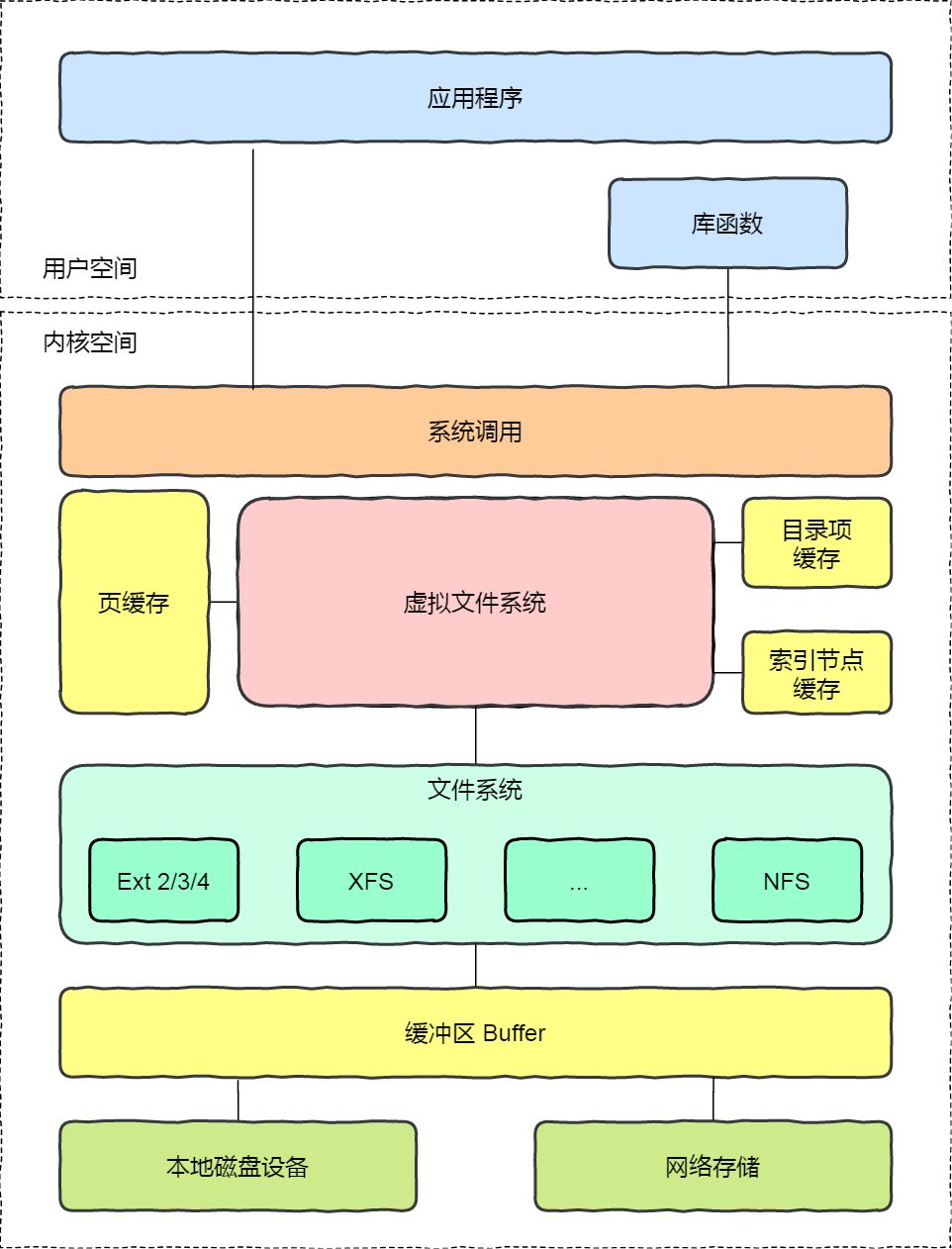
Linux文件系统
在Linux文件系统中的总体结构图
相关数据结构
1. file_system_type
这个结构来描述一种文件系统类型,一般具体文件系统会定义这个结构,然后注册到系统中;定义了具体文件系统的挂载和卸载方法,文件系统挂载时调用其挂载方法构建超级块、跟dentry等实例。

1 struct file_system_type { 2 const char *name; 3 int fs_flags; 4 /* 5 struct super_block *(struct file_system_type *, int, 6 const char *, void *); 7 */ 8 struct dentry *(*mount) (struct file_system_type *, int, 9 const char *, void *); 10 void (*kill_sb) (struct super_block *); 11 12 struct module *owner; 13 struct file_system_type * next; 14 struct hlist_head fs_supers; 15 };
2. inode
索引节点,用来记录文件的元信息,比如 inode 编号、文件大小、访问权限、创建时间、修改时间、数据在磁盘的位置等等。索引节点是文件的唯一标识,它们之间一一对应,也同样都会被存储在硬盘中,所以索引节点同样占用磁盘空间。

1 struct inode { 2 umode_t i_mode; 3 unsigned short i_opflags; 4 kuid_t i_uid; 5 kgid_t i_gid; 6 unsigned int i_flags; 7 8 #ifdef CONFIG_FS_POSIX_ACL 9 struct posix_acl *i_acl; 10 struct posix_acl *i_default_acl; 11 #endif 12 13 const struct inode_operations *i_op; 14 struct super_block *i_sb; 15 struct address_space *i_mapping; 16 17 #ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY 18 void *i_security; 19 #endif 20 21 /* Stat data, not accessed from path walking */ 22 unsigned long i_ino; 23 /* 24 * Filesystems may only read i_nlink directly. They shall use the 25 * following functions for modification: 26 * 27 * (set|clear|inc|drop)_nlink 28 * inode_(inc|dec)_link_count 29 */ 30 union { 31 const unsigned int i_nlink; 32 unsigned int __i_nlink; 33 }; 34 dev_t i_rdev; 35 loff_t i_size; 36 struct timespec64 i_atime; 37 struct timespec64 i_mtime; 38 struct timespec64 i_ctime; 39 spinlock_t i_lock; /* i_blocks, i_bytes, maybe i_size */ 40 unsigned short i_bytes; 41 u8 i_blkbits; 42 u8 i_write_hint; 43 blkcnt_t i_blocks; 44 45 #ifdef __NEED_I_SIZE_ORDERED 46 seqcount_t i_size_seqcount; 47 #endif 48 49 /* Misc */ 50 unsigned long i_state; 51 struct rw_semaphore i_rwsem; 52 53 unsigned long dirtied_when; /* jiffies of first dirtying */ 54 unsigned long dirtied_time_when; 55 56 struct hlist_node i_hash; 57 struct list_head i_io_list; /* backing dev IO list */ 58 #ifdef CONFIG_CGROUP_WRITEBACK 59 struct bdi_writeback *i_wb; /* the associated cgroup wb */ 60 61 /* foreign inode detection, see wbc_detach_inode() */ 62 int i_wb_frn_winner; 63 u16 i_wb_frn_avg_time; 64 u16 i_wb_frn_history; 65 #endif 66 struct list_head i_lru; /* inode LRU list */ 67 struct list_head i_sb_list; 68 struct list_head i_wb_list; /* backing dev writeback list */ 69 union { 70 struct hlist_head i_dentry; 71 struct rcu_head i_rcu; 72 }; 73 atomic64_t i_version; 74 atomic64_t i_sequence; /* see futex */ 75 atomic_t i_count; 76 atomic_t i_dio_count; 77 atomic_t i_writecount; 78 #ifdef CONFIG_IMA 79 atomic_t i_readcount; /* struct files open RO */ 80 #endif 81 const struct file_operations *i_fop; /* former ->i_op->default_file_ops */ 82 struct file_lock_context *i_flctx; 83 struct address_space i_data; 84 struct list_head i_devices; 85 union { 86 struct pipe_inode_info *i_pipe; 87 struct block_device *i_bdev; 88 struct cdev *i_cdev; 89 char *i_link; 90 unsigned i_dir_seq; 91 }; 92 93 __u32 i_generation; 94 95 #ifdef CONFIG_FSNOTIFY 96 __u32 i_fsnotify_mask; /* all events this inode cares about */ 97 struct fsnotify_mark_connector __rcu *i_fsnotify_marks; 98 #endif 99 100 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_FS_ENCRYPTION) 101 struct fscrypt_info *i_crypt_info; 102 #endif 103 104 void *i_private; /* fs or device private pointer */ 105 } __randomize_layout;
3. dentry
目录项,用来记录文件的名字、索引节点指针以及与其他目录项的层级关联关系。多个目录项关联起来,就会形成目录结构,但它与索引节点不同的是,目录项是由内核维护的一个数据结构,不存放于磁盘,而是缓存在内存。

1 struct dentry { 2 /* RCU lookup touched fields */ 3 unsigned int d_flags; /* protected by d_lock */ 4 seqcount_t d_seq; /* per dentry seqlock */ 5 struct hlist_bl_node d_hash; /* lookup hash list */ 6 struct dentry *d_parent; /* parent directory */ 7 struct qstr d_name; 8 struct inode *d_inode; /* Where the name belongs to - NULL is 9 * negative */ 10 unsigned char d_iname[DNAME_INLINE_LEN]; /* small names */ 11 12 /* Ref lookup also touches following */ 13 struct lockref d_lockref; /* per-dentry lock and refcount */ 14 const struct dentry_operations *d_op; 15 struct super_block *d_sb; /* The root of the dentry tree */ 16 unsigned long d_time; /* used by d_revalidate */ 17 void *d_fsdata; /* fs-specific data */ 18 19 union { 20 struct list_head d_lru; /* LRU list */ 21 wait_queue_head_t *d_wait; /* in-lookup ones only */ 22 }; 23 struct list_head d_child; /* child of parent list */ 24 struct list_head d_subdirs; /* our children */ 25 /* 26 * d_alias and d_rcu can share memory 27 */ 28 union { 29 struct hlist_node d_alias; /* inode alias list */ 30 struct hlist_bl_node d_in_lookup_hash; /* only for in-lookup ones */ 31 struct rcu_head d_rcu; 32 } d_u; 33 } __randomize_layout;



