一:orm新增,删除,创建表
1 orm的创建
(1) 创建完django 项目后,设置对settingsj进行设置

DATABASES = { 'default': { 'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql', 'HOST': '127.0.0.1', 'PORT': 3306, 'USER': 'root', 'PASSWORD': 'admin', 'NAME': 'day72', } }
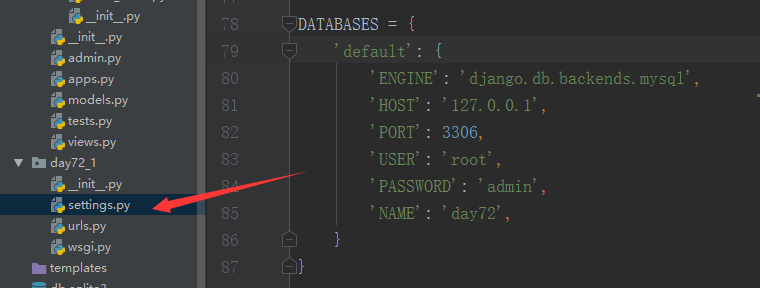
(2)对app下面的__init__进行设置

import pymysql pymysql.install_as_MySQLdb()

(3) tools--->Run manage.py Task
python3 manage.py makemigrations
只需要敲命令:makemigrations(记录数据库的修改记录)
python3 manage.py migrate
只需要敲命令:migrate(把数据同步到数据库)
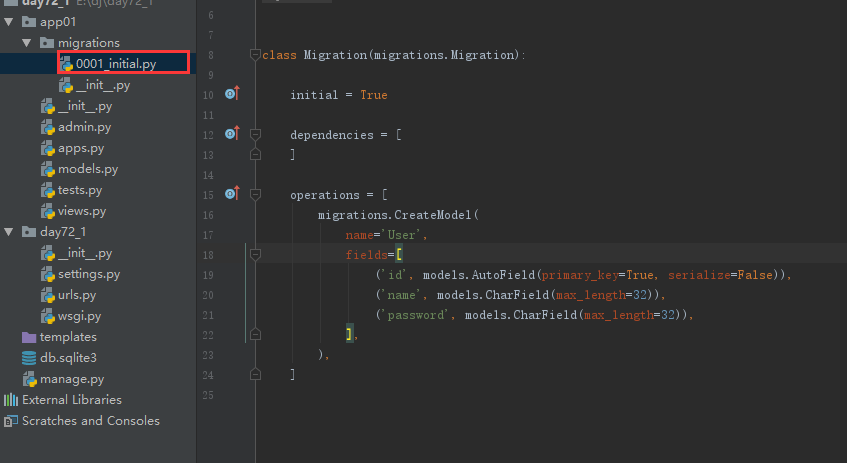
(4)就会看到下面的代码,不能删任何东西
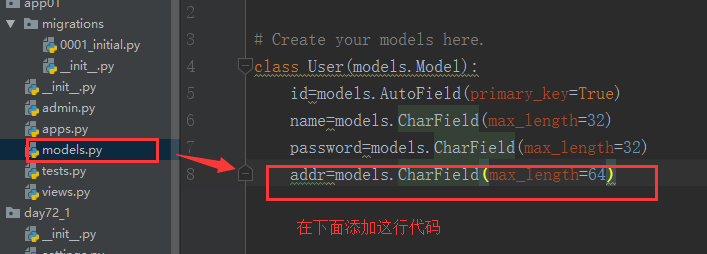
2 orm的新增
addr=models.CharField(max_length=64)
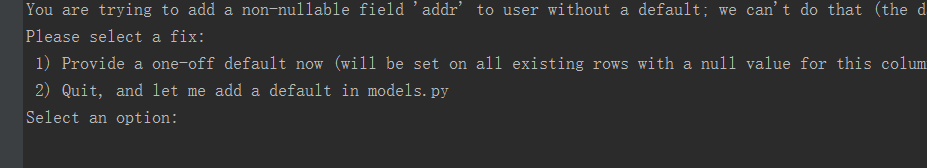
先敲python3 manage.py makemigrations
会出现这种情况(1 给默认值,传一个字符串))
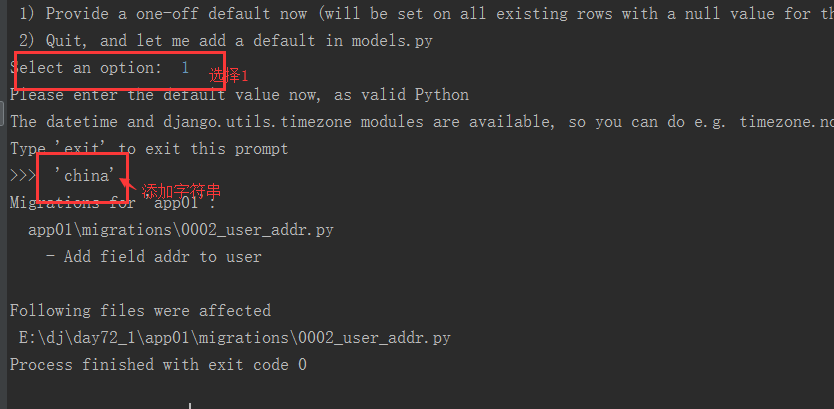
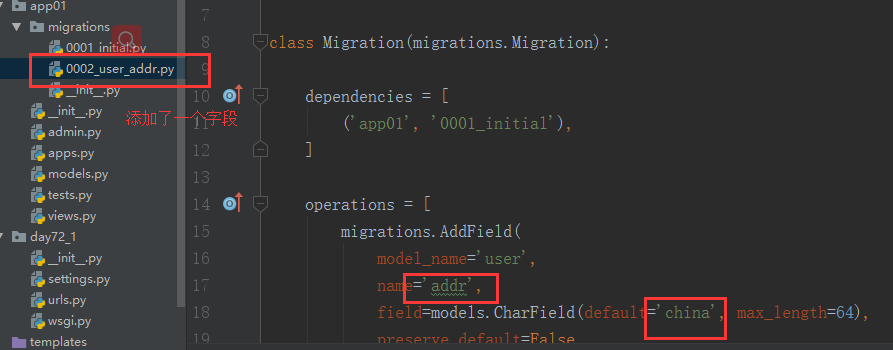
再敲python3 manage.py migrate

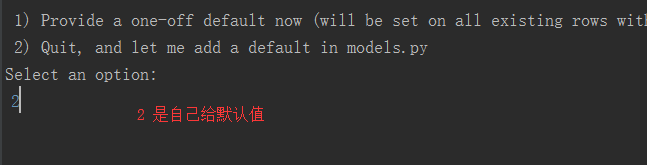
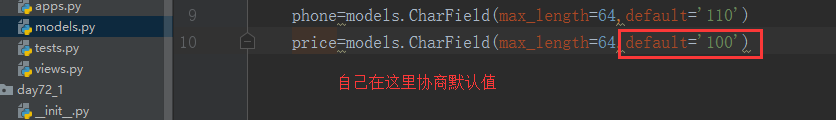
再敲python3 manage.py migrate
3 orm字段的删除

python3 manage.py migrate
二::django请求的生命周期
先访问url --> 查数据库--->拿模板 ,查询出来的数据库结果渲染到模板上,返回回去
web服务器 --> 实现这个协议的socket(把数据进行封装)-->web应用程序,进入了路由层的视图函数-->从数据库拿数据,进行数据的处理-->模板层拿模板,用数据渲染到模板上,最后原路返回到浏览器
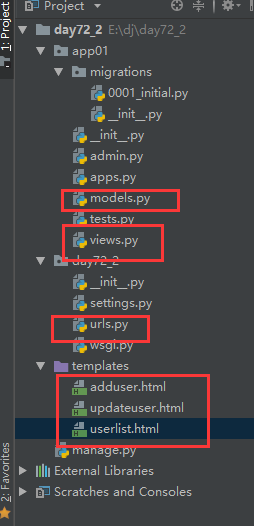
三:实现用户的增删查改
小项目总目录

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Generated by Django 1.11.9 on 2018-11-06 12:09 from __future__ import unicode_literals from django.db import migrations, models class Migration(migrations.Migration): initial = True dependencies = [ ] operations = [ migrations.CreateModel( name='User', fields=[ ('id', models.AutoField(primary_key=True, serialize=False)), ('name', models.CharField(max_length=32)), ('sex', models.CharField(max_length=32)), ('age', models.CharField(max_length=32)), ], ), ]

import pymysql pymsql.install_as_MySQLdb()

from django.db import models # Create your models here. class User(models.Model): id=models.AutoField(primary_key=True) name=models.CharField(max_length=32) sex=models.CharField(max_length=32) age=models.CharField(max_length=32)

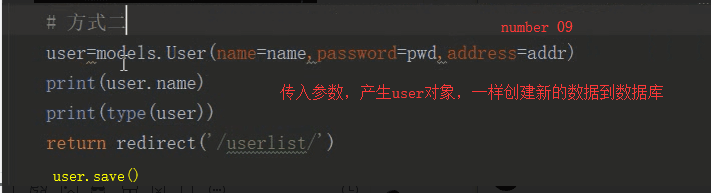
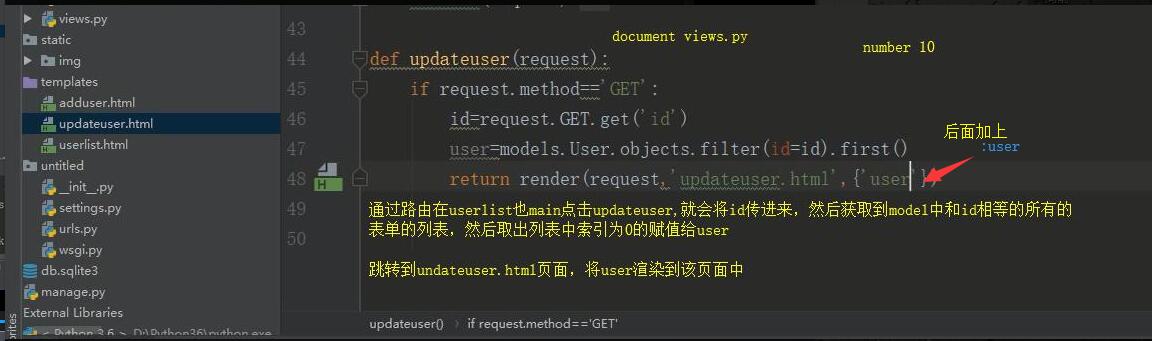
from django.shortcuts import render,redirect from app01 import models # Create your views here. def userlist(request): if request.method=='GET': ret= models.User.objects.all() return render(request,'userlist.html',{'user_list':ret}) def deleteuser(request): if request.method == 'GET': id = request.GET.get('id') # 删除数据 ret = models.User.objects.filter(id=id).delete() return redirect('/userlist/') def adduser(request): if request.method == 'GET': return render(request,'adduser.html') elif request.method=='POST': name=request.POST.get('name') sex=request.POST.get('sex') age=request.POST.get('age') user=models.User(name=name,sex=sex,age=age) user.save() return redirect('/userlist/') def updateuser(request): if request.method == 'GET': id = request.GET.get('id') user = models.User.objects.filter(id=id).first() return render(request, 'updateuser.html', {'user': user}) # 将user传给updateuser当作参数 elif request.method == 'POST': id=request.GET.get('id') print(id) name = request.POST.get("name") sex = request.POST.get("sex") age = request.POST.get("age") user=models.User.objects.filter(id=id).update(name=name,sex=sex,age=age) return redirect('/userlist/')

""" Django settings for day72_2 project. Generated by 'django-admin startproject' using Django 1.11.9. For more information on this file, see https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.11/topics/settings/ For the full list of settings and their values, see https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.11/ref/settings/ """ import os # Build paths inside the project like this: os.path.join(BASE_DIR, ...) BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))) # Quick-start development settings - unsuitable for production # See https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.11/howto/deployment/checklist/ # SECURITY WARNING: keep the secret key used in production secret! SECRET_KEY = 'j+dzo(f#+gv13_tac67$^&5g963h-wxr8_dcoj40!egwzxk6$2' # SECURITY WARNING: don't run with debug turned on in production! DEBUG = True ALLOWED_HOSTS = [] # Application definition INSTALLED_APPS = [ 'django.contrib.admin', 'django.contrib.auth', 'django.contrib.contenttypes', 'django.contrib.sessions', 'django.contrib.messages', 'django.contrib.staticfiles', 'app01.apps.App01Config', ] MIDDLEWARE = [ 'django.middleware.security.SecurityMiddleware', 'django.contrib.sessions.middleware.SessionMiddleware', 'django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware', # 'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware', 'django.contrib.auth.middleware.AuthenticationMiddleware', 'django.contrib.messages.middleware.MessageMiddleware', 'django.middleware.clickjacking.XFrameOptionsMiddleware', ] ROOT_URLCONF = 'day72_2.urls' TEMPLATES = [ { 'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates', 'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates')] , 'APP_DIRS': True, 'OPTIONS': { 'context_processors': [ 'django.template.context_processors.debug', 'django.template.context_processors.request', 'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth', 'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages', ], }, }, ] WSGI_APPLICATION = 'day72_2.wsgi.application' # Database # https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.11/ref/settings/#databases DATABASES = { 'default': { 'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql', 'HOST': '127.0.0.1', 'PORT': 3306, 'USER': 'root', 'PASSWORD': 'admin', 'NAME': 'day72_2', } } # Password validation # https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.11/ref/settings/#auth-password-validators AUTH_PASSWORD_VALIDATORS = [ { 'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.UserAttributeSimilarityValidator', }, { 'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.MinimumLengthValidator', }, { 'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.CommonPasswordValidator', }, { 'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.NumericPasswordValidator', }, ] # Internationalization # https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.11/topics/i18n/ LANGUAGE_CODE = 'en-us' TIME_ZONE = 'UTC' USE_I18N = True USE_L10N = True USE_TZ = True # Static files (CSS, JavaScript, Images) # https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.11/howto/static-files/ STATIC_URL = '/static/'

"""day72_2 URL Configuration The `urlpatterns` list routes URLs to views. For more information please see: https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.11/topics/http/urls/ Examples: Function views 1. Add an import: from my_app import views 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: url(r'^$', views.home, name='home') Class-based views 1. Add an import: from other_app.views import Home 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: url(r'^$', Home.as_view(), name='home') Including another URLconf 1. Import the include() function: from django.conf.urls import url, include 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: url(r'^blog/', include('blog.urls')) """ from django.conf.urls import url from django.contrib import admin from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls), url(r'^userlist/', views.userlist), url(r'^deleteuser/', views.deleteuser), url(r'^adduser/', views.adduser), url(r'^updateuser/', views.updateuser), ]

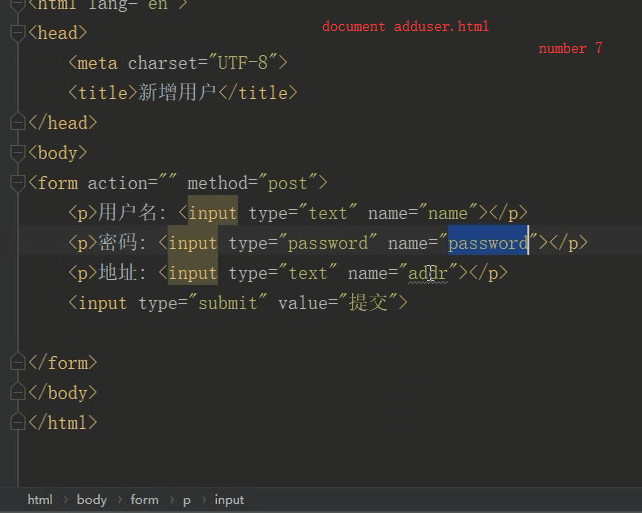
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>添加作者</title> </head> <body> <div> <form action="" method="post"> <p>用户名:<input type="text" name="name"></p> <p>性别:<input type="text" name="sex"></p> <p>年龄:<input type="text" name="age"></p> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </form> </div> </body> </html>

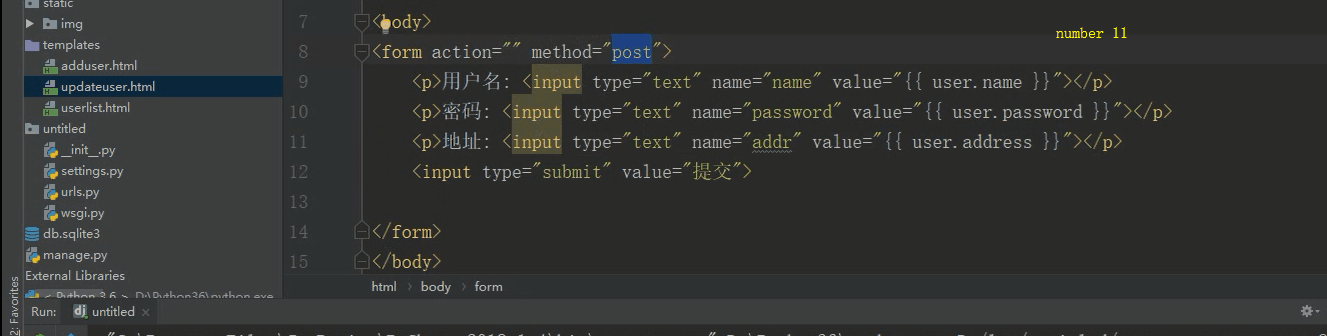
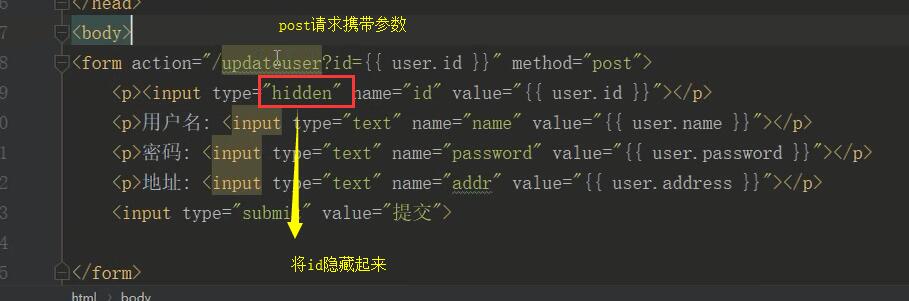
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>更改数据</title> </head> <body> <form action="" method="post"> <h2>更改数据</h2> <p><input type="hidden" name="id" value="{{ user.id }}"></p> <p>作者名:<input type="text" name="name" value="{{ user.name }}"></p> <p>性别:<input type="text" name="sex" value="{{ user.sex }}"></p> <p>年龄:<input type="text" name="age" value="{{ user.age }}"></p> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </form> </body> </html>

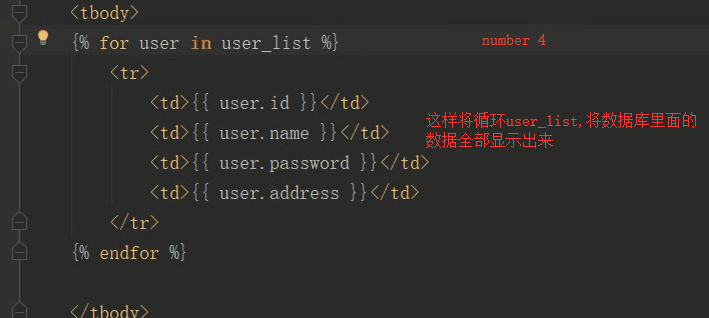
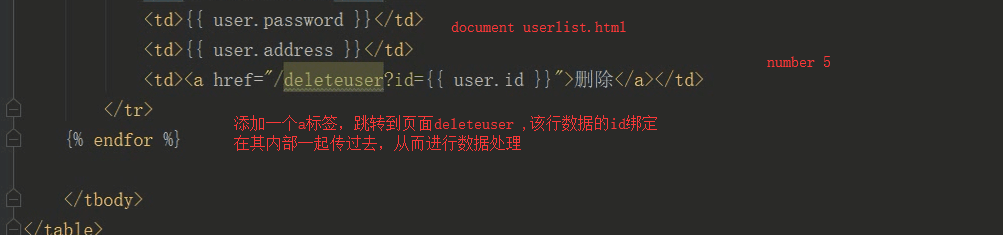
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>显示页面</title> <style> table{ text-align: center; font: normal 20px/40px "STSong"; margin: auto; } </style> </head> <body > <table border="1"> <thead > <tr > <td>id</td> <td>name</td> <td>sex</td> <td>age</td> </tr> </thead> <tbody> {% for user in user_list %} <tr> <td>{{ user.id }}</td> <td>{{ user.name }}</td> <td>{{ user.sex }}</td> <td>{{ user.age }}</td> <td><a href="/deleteuser?id={{ user.id }}">删除</a></td> <td><a href="/updateuser?id={{ user.id }}">改变</a></td> </tr> {% endfor %} <a href="/adduser/" style="width:100%;line-height:40px;margin-left:50%">添加作者</a> </tbody> </table> </body> </html>
==========具体的实现方法及其讲解=============






不管请求方式是get还是post,只要携带数据的,都通过GET取值

总结
1 orm 创建表,新增字段,修改,删除字段,不能创建数据库 -字段属性phone=models.CharField(max_length=64,null=True) -null=True 代表该列可以为空 2 数据的增删改查 -增(1):User.objects.create(address='') -增(2):实例化产生一个user对象,user对象的save方法 -删:User.objects.filter(id=1,name='lqz').first().delete() -删:User.objects.filter(id=1,name='lqz').delete() -改:User.objects.filter(id=1,name='lqz').update() -查:User.objects.all() user=User.objects.filter(name='lqz') user.name 3 前后台交互 -id=1&name='lqz'& <form action="/updateuser/?id={{ user.id }}" method="post"> <p><input type="hidden" name="id" value="{{ user.id }}"></p> <p>用户名: <input type="text" name="name" value="{{ user.name }}"></p> <p>密码: <input type="text" name="password" value="{{ user.password }}"></p> <p>地址: <input type="text" name="addr" value="{{ user.address }}"></p> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </form> 4 django生命周期 5 一对多,多对多 -publish_id -publish=models.ForeignKey(to='Publish', to_field='id') book.publish_id book.publish 多对多:(自动创建第三张表) authors = models.ManyToManyField(to='Author')


