JDK1.8源码(六)——java.util.ArrayList类
一、概述
1、介绍
ArrayList元素是有序的,可重复。线程不安全的。底层维护一个 Object 数组。
JDK1.7:ArrayList像饿汉式,默认初始长度直接创建一个容量为 10 的数组。
JDK1.8:ArrayList像懒汉式,默认一开始创建一个长度为 0 的数组,当添加第一个元素时再创建一个始容量为10的数组。
默认情况扩容都为原来数组的 1.5 倍。
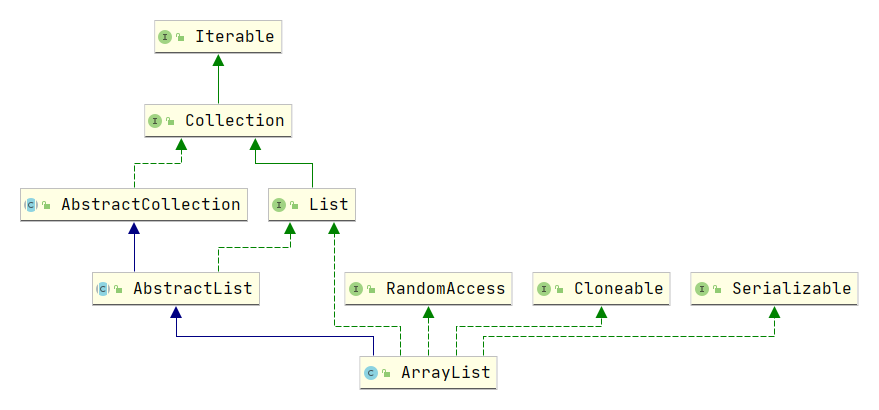
继承关系:
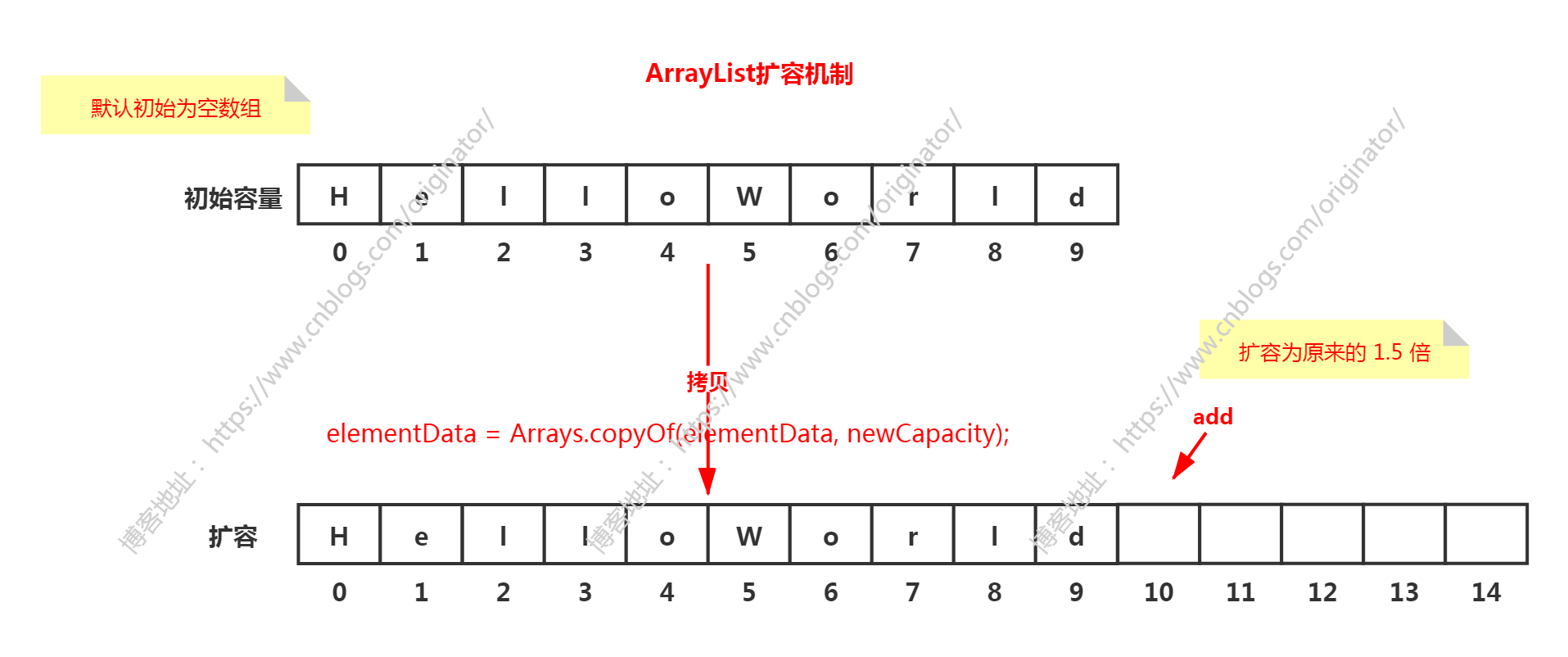
扩容原理:
2、遍历方式
①随机访问
由于实现了 RandomAccess 接口,它支持通过索引值去随机访问元素。
1 ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); 2 list.add("1"); 3 list.add("3"); 4 list.add("2"); 5 for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { 6 System.out.println(list.get(i)); 7 }
②增强forEach,底层还是使用的迭代器
1 ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); 2 list.add("1"); 3 list.add("3"); 4 list.add("2"); 5 for (String s : list) { 6 System.out.println(s); 7 }
这种语法可以看成是 JDK 的一种语法糖,通过反编译 class 文件,可以看到生成的 java 文件,还是通过调用 Iterator 迭代器来遍历的。
1 for (Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator(); iterator.hasNext(); ) { 2 iterator.next(); 3 }
③迭代器 iterator
1 ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); 2 list.add("1"); 3 list.add("3"); 4 list.add("2"); 5 6 final Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator(); 7 while (iterator.hasNext()) { 8 System.out.println(iterator.next()); 9 }
④迭代器 ListIterator
1 ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); 2 list.add("1"); 3 list.add("3"); 4 list.add("2"); 5 6 final ListIterator<String> iterator = list.listIterator(); 7 // 向后遍历 8 while (iterator.hasNext()) { 9 System.out.println(iterator.next()); // 1 3 2 10 } 11 12 // 向前遍历.此时由于上面进行了向后遍历,游标指向了最后一个元素,所以此处向前遍历能有值 13 while (iterator.hasPrevious()) { 14 System.out.println(iterator.previous()); // 2 3 1 15 }
二、类源码
1、类声明
源码示例:
1 * @author Josh Bloch 2 * @author Neal Gafter 3 * @see Collection 4 * @see List 5 * @see LinkedList 6 * @see Vector 7 * @since 1.2 8 */ 9 10 public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> 11 implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable 12 {}
继承了AbstractList:AbstractList提供List接口的骨干实现,以最大限度地减少"随机访问"数据存储(如ArrayList)实现Llist所需的工作。
实现了 List 接口:定义了实现该接口的类都必须要实现的一组方法,实现了所有可选列表操作。
实现了 RandmoAccess 接口:表明ArrayList支持快速(通常是固定时间)随机访问。此接口的主要目的是允许一般的算法更改其行为,从而在将其应用到随机或连续访问列表时能提供良好的性能。比如在工具类 Collections 中,应用二分查找方法时判断是否实现了 RandomAccess 接口:
1 // Collections类 2 public static <T> 3 int binarySearch(List<? extends Comparable<? super T>> list, T key) { 4 if (list instanceof RandomAccess || list.size()<BINARYSEARCH_THRESHOLD) 5 return Collections.indexedBinarySearch(list, key); 6 else 7 return Collections.iteratorBinarySearch(list, key); 8 }
实现了 Cloneable 接口:一个标记接口,接口内无任何方法体和常量的声明。需要复写Object.clone()函数,表示它可以被克隆。
实现了 Serializable 接口:一个标记接口,标识该类可序列化。
2、类属性
源码示例:读一下源码中的英文注释。
1 private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L; 2 3 // 默认的初始化容量(大小) 4 /** 5 * Default initial capacity. 6 */ 7 private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; 8 9 // 空的数组实例 10 /** 11 * Shared empty array instance used for empty instances. 12 */ 13 private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; 14 15 // 也是一个空的数组实例.个人觉得和上一个属性没啥区别 16 private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; 17 18 // 任何一个空的 elementData 就是 DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 19 // 当它第一次 add 元素的时候会被扩展到DEFAULT_CAPACITY,也就是 10 20 /** 21 * The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored. 22 * The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any 23 * empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 24 * will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added. 25 */ 26 transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access 27 28 // 容器的实际元素个数 29 private int size; 30 31 private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
3、类构造器
源码示例:三个重载(重要)
ArrayList list = new ArrayList(); // 集合长度初始化是0,而不是 10,JDK7才是10。
1 public ArrayList() { 2 // 很清楚的看到,初始化的是一个空数组 3 this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; 4 }
ArrayList list = new ArrayList(7); // 指定大小时,初始多大就是多大。
1 // 不写注释也能看懂的代码 2 public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { 3 if (initialCapacity > 0) { 4 // 大于 0 时, new 的数组大小就是多少 5 this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; 6 } else if (initialCapacity == 0) { 7 // 等于 0 时, 初始化的是一个空数组 8 this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; 9 } else { 10 // 否则,参数异常 11 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ 12 initialCapacity); 13 } 14 }
传入一个集合。
1 public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { 2 elementData = c.toArray(); 3 if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) { 4 // c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652) 5 if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) 6 // 数组拷贝 7 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); 8 } else { 9 // 否则,就初始化一个空数组 10 // replace with empty array. 11 this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; 12 } 13 }
4、add()方法
源码示例:扩容原理
1 public boolean add(E e) { 2 // 判断是否需要扩容 3 ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! 4 elementData[size++] = e; 5 return true; 6 } 7 8 private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { 9 // 如果是第一次初始化的空数组 10 if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { 11 // minCapacity = max(10,1) 体现出第一次 add 时,才初始化长度 10 的数组 12 minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); 13 } 14 15 ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); 16 } 17 18 private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { 19 // 修改次数+1.用于集合的快速失败机制 20 modCount++; 21 22 // 需要扩容 23 // overflow-conscious code 24 if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) 25 grow(minCapacity); 26 }
源码示例:真正扩容的方法
1 private void grow(int minCapacity) { 2 // overflow-conscious code 3 int oldCapacity = elementData.length; 4 5 // 体现出扩容为原来的 1.5 倍 6 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); 7 8 // 当新数组长度仍然比minCapacity小,则为保证最小长度,新数组等于minCapacity 9 if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) 10 newCapacity = minCapacity; 11 12 // MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8 = 2147483639 13 if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) 14 newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); 15 16 // 将原数组拷贝到一个大小为 newCapacity 的新数组(注意是拷贝引用) 17 // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: 18 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); 19 } 20 21 // 用于判断容量是否超过最大值 22 private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { 23 if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow 24 throw new OutOfMemoryError(); 25 return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? 26 Integer.MAX_VALUE : 27 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; 28 }
说明:
modCount给ArrayList的迭代器使用的,在并发修改时,提供快速失败行为,保证modCount在迭代期间不变,否则抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常。
ArrayList 的扩容,核心方法就是调用 Arrays.copyOf 方法,创建一个更大的数组,然后将原数组元素拷贝过去。
总结:
①当通过 ArrayList() 构造一个空集合,初始长度是为0的,第1次添加元素,会创建一个长度为10的数组,并将该元素赋值到数组的第一个位置。
②第2次添加元素,集合不为空,由于集合大小size + 1 < 数组的长度 10,所以直接添加元素到数组的第二个位置,不用扩容。
③第 11 次添加元素,此时 size+1 = 11 > 数组长度10。这时候创建一个长度为10+10*0.5 = 15 的数组(扩容1.5倍),然后将原数组元素引用拷贝到新数组。并将第 11 次添加的元素赋值到新数组下标为10的位置。
④第 Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8 = 2147483639,然后 2147483639%1.5=1431655759(这个数是要进行扩容)次添加元素,为了防止溢出,此时会直接创建一个 1431655759 + 1 大小的数组,这样一直,每次添加一个元素,都只扩大一个范围。
⑤第 Integer.MAX_VALUE - 7 次添加元素时,创建一个大小为 Integer.MAX_VALUE 的数组,在进行元素添加。
⑥第 Integer.MAX_VALUE + 1 次添加元素时,抛出 OutOfMemoryError 异常。
5、remove()方法
源码示例:
1 // 根据索引删除 2 public E remove(int index) { 3 // 检查索引 index 是否越界 4 rangeCheck(index); 5 6 modCount++; 7 // 获取索引处的元素 8 E oldValue = elementData(index); 9 10 int numMoved = size - index - 1; 11 // 表示 0 <= index < (size-1),即索引不是最后一个元素 12 if (numMoved > 0) 13 // 将数组elementData的下标index+1之后长度为numMoved的元素拷贝到从index开始的位置 14 System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, 15 numMoved); 16 // 将数组最后一个元素置为 null, 便于垃圾回收 17 elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work 18 19 return oldValue; 20 } 21 22 // 删除指定元素 23 public boolean remove(Object o) { 24 // 如果 o 为null 25 if (o == null) { 26 for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) 27 if (elementData[index] == null) { 28 fastRemove(index); 29 return true; 30 } 31 } else { 32 // 如果o不是null,则循环查找.删除第一次出现的该元素 33 for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) 34 if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { 35 fastRemove(index); 36 return true; 37 } 38 } 39 return false; 40 } 41 private void fastRemove(int index) { 42 modCount++; 43 int numMoved = size - index - 1; 44 if (numMoved > 0) 45 // 通过System.arraycopy进行数组自身拷贝。 46 System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, 47 numMoved); 48 elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work 49 }
6、set()方法
源码示例:将指定索引index处的元素修改。
1 public E set(int index, E element) { 2 rangeCheck(index); 3 4 // 获取索引处的元素 5 E oldValue = elementData(index); 6 // 将index处元素修改为element 7 elementData[index] = element; 8 return oldValue; 9 } 10 11 // 很简单.就是检查索引合法性 12 private void rangeCheck(int index) { 13 if (index >= size) 14 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); 15 }
7、get()方法
源码示例:
1 public E get(int index) { 2 rangeCheck(index); 3 // 通过索引下标返回数组中的元素 4 return elementData(index); 5 }
源码示例:很简单,略
indexOf(Object o):返回集合中第一次出现该元素的下标,没有则返回 -1。
lastIndexOf(Object o):返回集合中最后一次出现该元素的下标。没有则返回 -1。
8、SubList()
返回从 [fromIndex, toIndex) 的一个子串。但是注意,这里只是原集合的一个视图。
1 public class Main { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); 4 list.add("1"); 5 list.add("3"); 6 list.add("2"); 7 8 List<String> subList = list.subList(0, 1); 9 System.out.println(subList); // [1] 10 11 subList.add("k"); 12 System.out.println(subList); // [1, k] 13 14 // 对子串的添加影响了原集合 15 System.out.println(list); // [1, k, 3, 2] 16 } 17 }
想要独立出来一个集合,解决办法如下:
1 List<String> sub = new ArrayList<>(list.subList(0, 1));
9、Size()
1 public int size() { 2 // 返回集合的大小 3 return size; 4 }
10、isEmpty()
1 public boolean isEmpty() { 2 // 集合是否为空 3 return size == 0; 4 }
11、trimToSize()
1 public void trimToSize() { 2 modCount++; 3 if (size < elementData.length) { 4 // 如果集合大小为 0 ,则数组为空 5 elementData = (size == 0) 6 ? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 7 8 // 否则,按集合实际大小拷贝一份数组 9 : Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); 10 } 11 }
该方法用于回收多余的内存。可以在确定集合不在添加多余的元素之后,调用 trimToSize() 方法会将数组大小调整为集合元素的大小。
注意:该方法会花时间来复制数组元素,所以应该在确定不会添加元素之后在调用。
三、迭代器
1、iterator
源码示例:

1 // 返回一个 Itr 对象.这个类是 ArrayList 的内部类。 2 public Iterator<E> iterator() { 3 return new Itr(); 4 } 5 6 private class Itr implements Iterator<E> { 7 // 游标.下一个要返回的元素的索引 8 int cursor; // index of next element to return 9 // 返回最后一个元素的索引; 如果没有返回-1. 10 int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such 11 int expectedModCount = modCount; 12 13 // 通过 cursor != size 判断是否还有下一个元素 14 public boolean hasNext() { 15 return cursor != size; 16 } 17 18 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 19 public E next() { 20 // 迭代器进行元素迭代时同时进行增加和删除操作,会抛出异常 21 checkForComodification(); 22 int i = cursor; 23 if (i >= size) 24 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 25 Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; 26 if (i >= elementData.length) 27 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 28 // 游标向后移动一位 29 cursor = i + 1; 30 // 返回索引为 i 处的元素,并将lastRet赋值为i 31 return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; 32 } 33 34 public void remove() { 35 if (lastRet < 0) 36 throw new IllegalStateException(); 37 checkForComodification(); 38 39 try { 40 // 调用ArrayList的remove方法删除元素 41 ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet); 42 // 游标指向删除元素的位置,本来是lastRet+1的,这里删除一个元素,然后游标就不变了 43 cursor = lastRet; 44 // 恢复默认值-1 45 lastRet = -1; 46 //expectedModCount值和modCount同步,因为进行add和remove操作,modCount会加1 47 expectedModCount = modCount; 48 } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { 49 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 50 } 51 } 52 53 @Override 54 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 55 public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) { 56 Objects.requireNonNull(consumer); 57 final int size = ArrayList.this.size; 58 int i = cursor; 59 if (i >= size) { 60 return; 61 } 62 final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; 63 if (i >= elementData.length) { 64 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 65 } 66 while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) { 67 consumer.accept((E) elementData[i++]); 68 } 69 // update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic 70 cursor = i; 71 lastRet = i - 1; 72 checkForComodification(); 73 } 74 75 76 // 在新增元素add() 和 删除元素 remove() 时, modCount++。修改set() 是没有的 77 // 也就是说不能在迭代器进行元素迭代时进行增加和删除操作,否则抛出异常 78 final void checkForComodification() { 79 if (modCount != expectedModCount) 80 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 81 } 82 }
注意:在进行 next() 方法调用的时候,会进行 checkForComodification() 调用,该方法表示迭代器进行元素迭代时,如果同时进行增加和删除操作,会抛出 ConcurrentModificationException 异常。比如:
1 ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); 2 list.add("1"); 3 list.add("3"); 4 list.add("2"); 5 6 final Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator(); 7 while (iterator.hasNext()) { 8 final String next = iterator.next(); 9 10 // Exception in thread "main" java.util.ConcurrentModificationException 11 // list.remove(next); 12 list.set(0, "k"); 13 14 // 正确方式是调用迭代器的 remove 方法 15 iterator.remove(); 16 }
注意:迭代器只能向后遍历,不能向前遍历,能够删除元素,但是不能新增元素。
2、listIterator
这是 list 集合特有的迭代器。可以一边遍历,一边新增或删除。
1 public class Main { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); 4 list.add("1"); 5 list.add("3"); 6 list.add("2"); 7 8 final ListIterator<String> iterator = list.listIterator(); 9 // 向后遍历 10 while (iterator.hasNext()) { 11 System.out.print(iterator.next() + " "); // 1 3 2 12 13 iterator.add("K"); 14 } 15 16 // [1, K, 3, K, 2, K] 17 System.out.println("\n" + list); 18 19 // 向前遍历 20 while (iterator.hasPrevious()) { 21 System.out.print(iterator.previous() + " "); // K 2 K 3 K 1 22 } 23 } 24 }
相比于 Iterator 迭代器, listIterator 多出了能向前迭代,以及新增元素的功能。
源码示例:

1 public interface ListIterator<E> extends Iterator<E> { 2 // 正向迭代.是否有下一个 3 boolean hasNext(); 4 // 取下一个 5 E next(); 6 // 反向迭代.是否有上一个 7 boolean hasPrevious(); 8 // 取上一个 9 E previous(); 10 int nextIndex(); 11 int previousIndex(); 12 // 删除元素 13 void remove(); 14 void set(E e); 15 // 添加元素 16 void add(E e); 17 }
在ArrayList类中,对上述接口的实现。
1 public ListIterator<E> listIterator() { 2 return new ListItr(0); 3 } 4 5 // 一个内部类 6 private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> { 7 // 进行游标初始化.默认是 0 8 ListItr(int index) { 9 super(); 10 cursor = index; 11 } 12 // 是否有上一个元素 13 public boolean hasPrevious() { 14 return cursor != 0; 15 } 16 // 返回下一个元素的索引 17 public int nextIndex() { 18 return cursor; 19 } 20 // 返回上一个元素的索引 21 public int previousIndex() { 22 return cursor - 1; 23 } 24 25 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 26 public E previous() { 27 // 迭代器进行元素迭代时同时进行增加和删除操作,会抛出异常 28 checkForComodification(); 29 int i = cursor - 1; 30 if (i < 0) 31 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 32 Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; 33 if (i >= elementData.length) 34 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 35 // 游标指向上一个元素 36 cursor = i; 37 // 返回上一个元素的值 38 return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; 39 } 40 41 public void set(E e) { 42 if (lastRet < 0) 43 throw new IllegalStateException(); 44 checkForComodification(); 45 46 try { 47 ArrayList.this.set(lastRet, e); 48 } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { 49 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 50 } 51 } 52 53 public void add(E e) { 54 checkForComodification(); 55 56 try { 57 int i = cursor; 58 ArrayList.this.add(i, e); 59 cursor = i + 1; 60 lastRet = -1; 61 expectedModCount = modCount; 62 } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { 63 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 64 } 65 } 66 }
参考文档:https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/ArrayList.html#
作者:Craftsman-L
本博客所有文章仅用于学习、研究和交流目的,版权归作者所有,欢迎非商业性质转载。
如果本篇博客给您带来帮助,请作者喝杯咖啡吧!点击下面打赏,您的支持是我最大的动力!




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号