数据结构与算法(六)——二叉树
一、排序二叉树(二叉查找树、二叉搜索树)
1、介绍
排序二叉树(Binary Sort Tree),性质:左孩子 < 根结点 < 右孩子。在一般情况下,查询效率比链表要高。
按照中序遍历可以得到一个从小到大的有序序列。
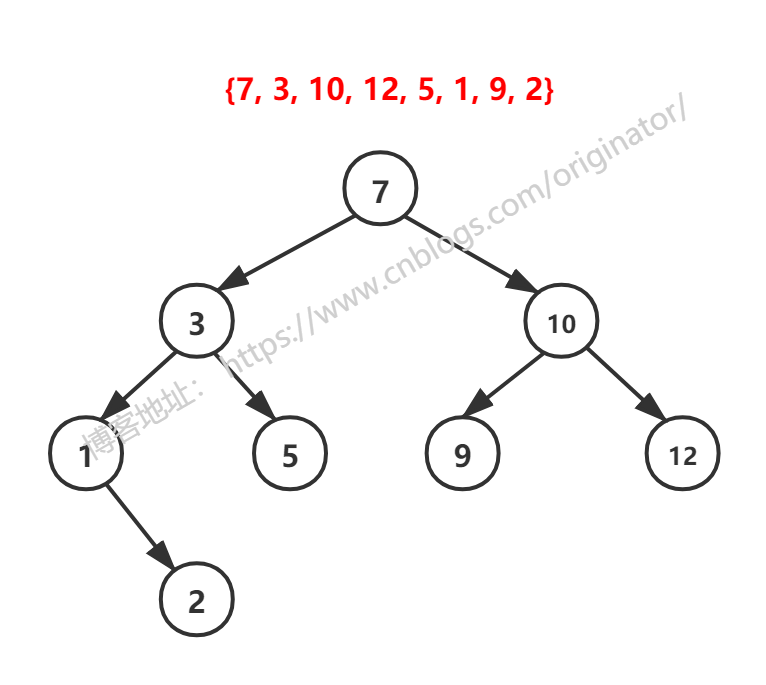
2、创建、添加、删除
创建和添加简单,删除情况比较复杂,有三种情况考虑:
①删除叶子结点(度为0),比如:2,5,9,12。
②删除只有左(右)孩子的结点(度为1),比如:1。
③删除有左(右)孩子的结点(度为2),比如:7,3,10。
删除度为2的结点,方法:取右子树的最小值替换它,且删除这个最小值。比如:删除7,用 7 的右子树最小值 9 替换7。且删除9。
代码示例:排序二叉树创建、添加、删除

1 // 二叉树 2 public class BinaryTree { 3 // 根结点 4 protected TreeNode root; 5 6 /** 7 * 获取树的高度 8 * 9 * @return 10 */ 11 public int getHeight() { 12 return this.getHeight(root); 13 } 14 15 protected int getHeight(TreeNode root) { 16 if (root == null) { 17 return 0; 18 } 19 20 final int left = this.getHeight(root.left); 21 final int right = this.getHeight(root.right); 22 23 return Math.max(left, right) + 1; 24 } 25 26 /** 27 * 获取树的结点数 28 * 29 * @return 30 */ 31 public int getSize() { 32 return this.getSize(root); 33 } 34 35 private int getSize(TreeNode root) { 36 if (root == null) { 37 return 0; 38 } 39 40 final int left = this.getSize(root.left); 41 final int right = this.getSize(root.right); 42 43 return left + right + 1; 44 } 45 46 // 中序遍历 47 public void infixOrder() { 48 this.infixOrder(root); 49 } 50 51 private void infixOrder(TreeNode root) { 52 if (root != null) { 53 this.infixOrder(root.left); 54 System.out.print("-->" + root.value); 55 this.infixOrder(root.right); 56 } 57 } 58 59 /** 60 * 树结点结构 61 */ 62 protected static class TreeNode { 63 public int value; 64 public TreeNode left; 65 public TreeNode right; 66 67 public TreeNode(int value) { 68 this.value = value; 69 } 70 71 // 返回结点的度 72 public int getDegree() { 73 if (this.left == null && this.right == null) { 74 return 0; 75 } 76 77 if ((this.left != null && this.right == null) || (this.left == null && this.right != null)) { 78 return 1; 79 } 80 81 return 2; 82 } 83 84 @Override 85 public String toString() { 86 return "TreeNode{" + 87 "value=" + value + 88 '}'; 89 } 90 } 91 92 }

1 public class BinarySortTree extends BinaryTree { 2 3 public BinarySortTree() { 4 5 } 6 7 // arr = {7, 3, 10, 12, 5, 1, 9}; 8 public BinarySortTree(int[] arr) { 9 if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) { 10 return; 11 } 12 13 for (int i : arr) { 14 this.add(i); 15 } 16 } 17 18 /** 19 * 添加结点 20 * 21 * @param value 22 */ 23 public void add(int value) { 24 TreeNode node = new TreeNode(value); 25 26 if (root == null) { 27 root = node; 28 return; 29 } 30 31 this.add(root, node); 32 } 33 34 private void add(TreeNode root, TreeNode node) { 35 if (node.value <= root.value) { 36 if (root.left == null) { 37 root.left = node; 38 } else { 39 this.add(root.left, node); 40 } 41 } else { 42 if (root.right == null) { 43 root.right = node; 44 } else { 45 this.add(root.right, node); 46 } 47 } 48 } 49 50 /** 51 * 删除结点 52 * 53 * @param value 54 */ 55 public void delNode(int value) { 56 if (this.checkRoot(value)) { 57 return; 58 } 59 60 // 1.查找要删除的结点 61 final TreeNode targetNode = this.search(value); 62 if (targetNode == null) { 63 return; 64 } 65 66 this.delNode(targetNode); 67 } 68 69 private void delNode(TreeNode targetNode) { 70 // 2.查找 targetNode 的父结点 71 final int value = targetNode.value; 72 final TreeNode parent = this.searchParent(value); 73 74 // 度为0 75 if (targetNode.getDegree() == 0) { 76 if (parent.left != null && parent.left.value == value) { 77 parent.left = null; 78 } else if (parent.right != null && parent.right.value == value) { 79 parent.right = null; 80 } 81 } 82 // 度为1 83 else if (targetNode.getDegree() == 1) { 84 // 是左子结点 85 if (targetNode.left != null) { 86 if (parent.left.value == value) { 87 parent.left = targetNode.left; 88 } else { 89 parent.right = targetNode.left; 90 } 91 } else { 92 if (parent.left.value == value) { 93 parent.left = targetNode.right; 94 } else { 95 parent.right = targetNode.right; 96 } 97 } 98 } 99 // 度为2 100 else { 101 targetNode.value = this.delRightTreeMin(targetNode.right); 102 } 103 104 } 105 106 // 单独处理根结点 107 private boolean checkRoot(int value) { 108 if (root == null) { 109 return true; 110 } 111 112 if (root.value == value) { 113 if (root.getDegree() == 0) { 114 root = null; 115 return true; 116 } 117 118 if (root.getDegree() == 1) { 119 if (root.left != null) { 120 root = root.left; 121 } else { 122 root = root.right; 123 } 124 return true; 125 } 126 } 127 128 return false; 129 } 130 131 private int delRightTreeMin(TreeNode node) { 132 TreeNode temp = node; 133 134 while (temp.left != null) { 135 temp = temp.left; 136 } 137 138 this.delNode(temp); 139 140 return temp.value; 141 } 142 143 /** 144 * 查找指定结点 value 145 * 146 * @param value 147 * @return 148 */ 149 private TreeNode search(int value) { 150 return this.search(root, value); 151 } 152 153 private TreeNode search(TreeNode root, int value) { 154 if (root != null) { 155 if (value == root.value) { 156 return root; 157 } 158 159 // 递归左孩子 160 if (value < root.value) { 161 return this.search(root.left, value); 162 } else { 163 // 递归右孩子 164 return this.search(root.right, value); 165 } 166 } 167 168 return null; 169 } 170 171 /** 172 * 查找指定结点 value 的父结点 173 * 174 * @param value 175 * @return 176 */ 177 private TreeNode searchParent(int value) { 178 return this.searchParent(root, value); 179 } 180 181 private TreeNode searchParent(TreeNode root, int value) { 182 if (root != null) { 183 if ((root.left != null && root.left.value == value) || 184 (root.right != null && root.right.value == value)) { 185 return root; 186 } 187 188 // 递归左子树 189 if (value < root.value) { 190 return this.searchParent(root.left, value); 191 } else { 192 // 递归右子树 193 return this.searchParent(root.right, value); 194 } 195 } 196 197 return null; 198 } 199 200 }
代码示例:测试类

1 public class Main { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 // 1.创建 5 int[] arr = {7, 3, 10, 12, 5, 1, 9}; 6 BinarySortTree sortTree = new BinarySortTree(arr); 7 8 // 2.中序遍历 9 sortTree.infixOrder(); 10 System.out.println(""); 11 12 // 3.添加 13 sortTree.add(2); 14 sortTree.infixOrder(); 15 System.out.println(""); 16 17 // 4.删除 18 sortTree.delNode(10); 19 sortTree.delNode(3); 20 sortTree.delNode(9); 21 sortTree.delNode(12); 22 sortTree.delNode(1); 23 sortTree.delNode(2); 24 sortTree.delNode(5); 25 //sortTree.delNode(7); 26 sortTree.infixOrder(); 27 } 28 } 29 30 // 结果 31 -->1-->3-->5-->7-->9-->10-->12 32 -->1-->2-->3-->5-->7-->9-->10-->12 33 -->7
二、平衡二叉树(Self-balancing binary search tree ,AVL树)
1、介绍
给定一个数列,{1,2,3,4,5},构建排序二叉树为:
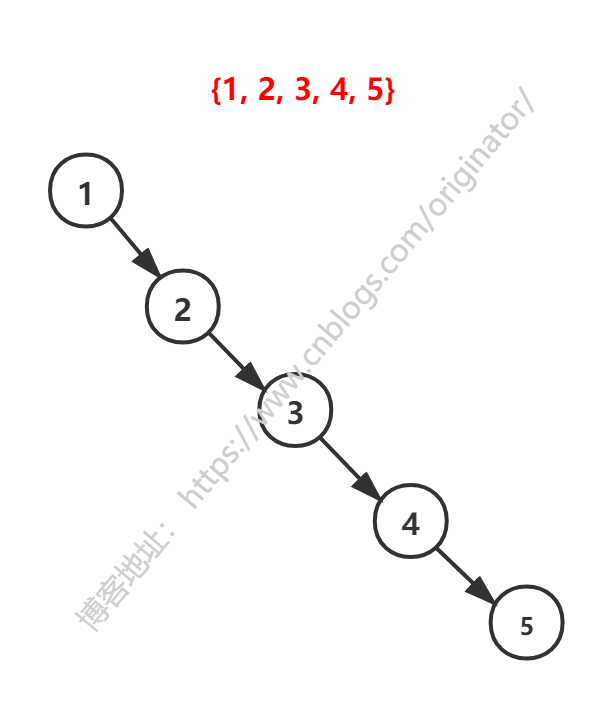
排序二叉树存在的问题:左子树都为空,从形式上看,像一个单链表;插入速度没有影响,查询速度明显降低(因为每次需要比较左子树),比单链表还慢。
解决:引入平衡二叉树。
定义:自平衡的排序二叉树。性质:左右两个子树的高度差绝对值不超过1,且左右子树也是平衡二叉树。
在平衡二叉树中插入结点要随时保证插入后整棵二叉树是平衡的,所以可能需要通过一次或多次旋转来重新平衡这个树。可以保证查询效率较高。
平衡二叉树是在排序二叉树的基础上定义的,所以,平衡二叉树是一颗排序二叉树。
2、左旋
右高,左旋
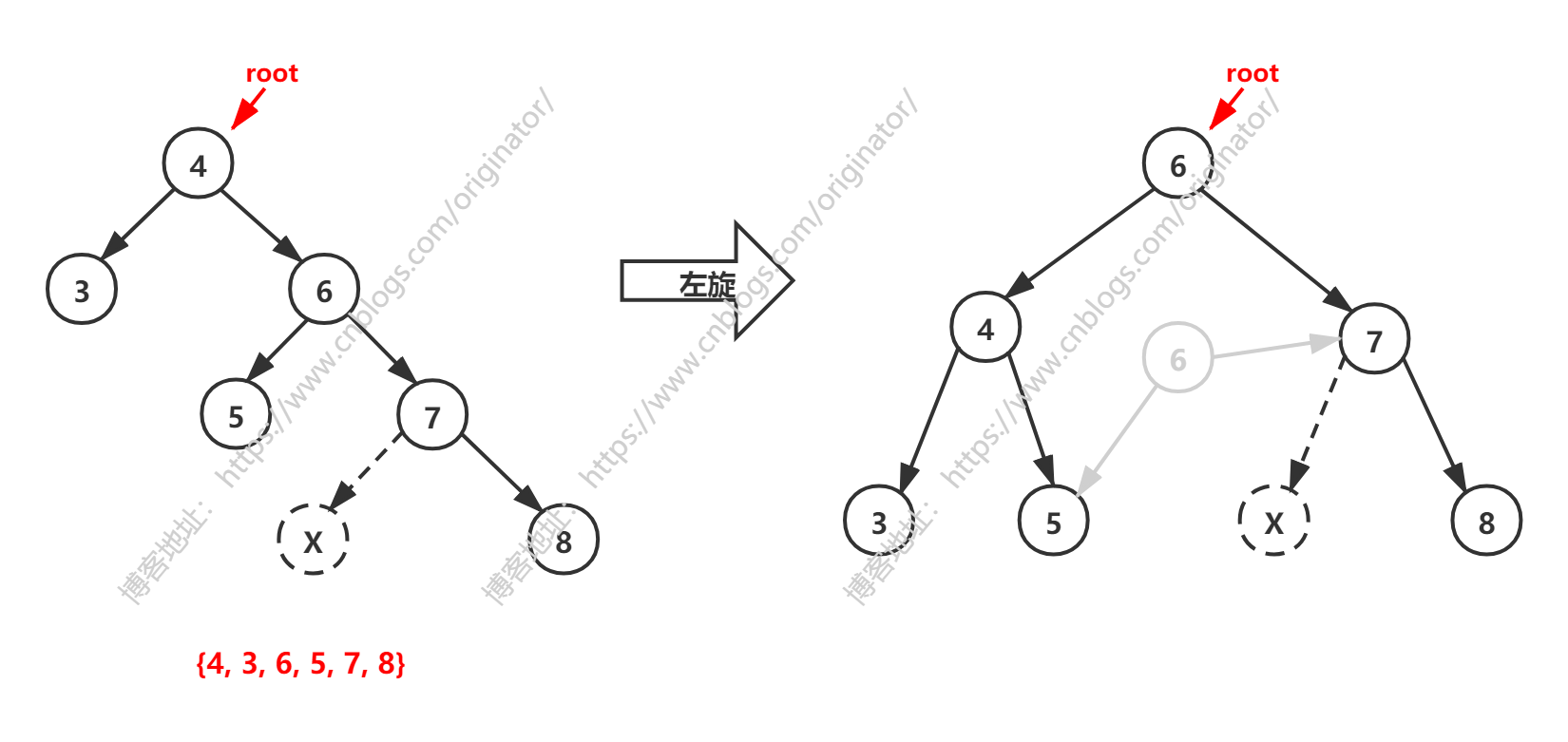
代码示例:对 root 左旋
1 // 左旋 2 private void leftRotate(TreeNode root) { 3 TreeNode newNode = new TreeNode(root.value); 4 newNode.left = root.left; 5 newNode.right = root.right.left; 6 7 root.value = root.right.value; 8 root.left = newNode; 9 root.right = root.right.right; 10 }
说明:root 的右子树高度 - 左子树高度 > 1,那么进行左旋。图示:X 结点,可能是 7 的左孩子或者右孩子。按上述方法左旋,都可以达到平衡。但是,如果 X 结点是 5 的左孩子或者右孩子,按上述方法就不能平衡,后面会介绍。
旋转后,原来的结点 6(灰色)其实还在,只是没有引用指向它,它会JVM视为垃圾回收掉。
3、右旋
左高,右旋
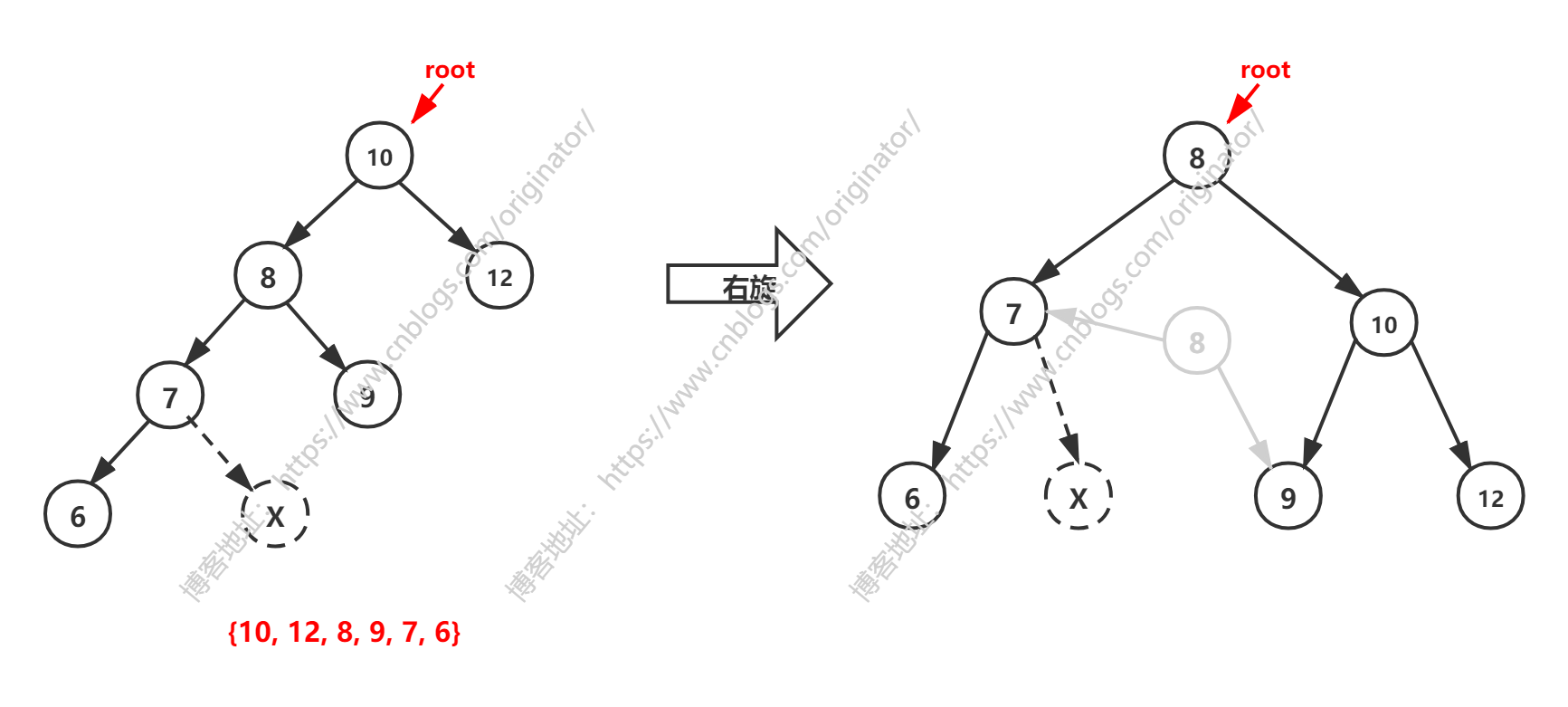
代码示例:对 root 右旋
1 // 右旋 2 private void rightRotate(TreeNode root) { 3 TreeNode newNode = new TreeNode(root.value); 4 newNode.left = root.left.right; 5 newNode.right = root.right; 6 7 root.value = root.left.value; 8 root.left = root.left.left; 9 root.right = newNode; 10 }
说明:与左旋同理。
4、双旋
左旋问题:
上面提到,"如果 X 结点是 5 的左孩子或者右孩子,按上述方法就不能平衡。",如图所示:
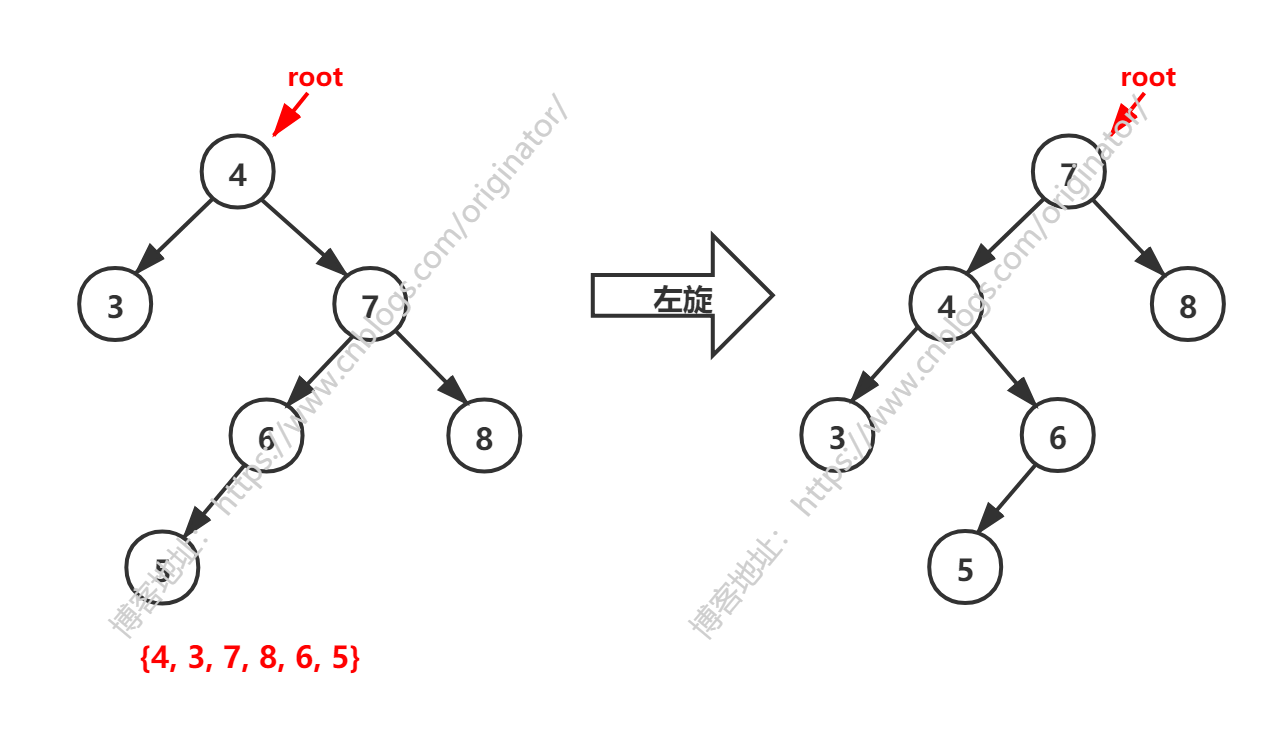
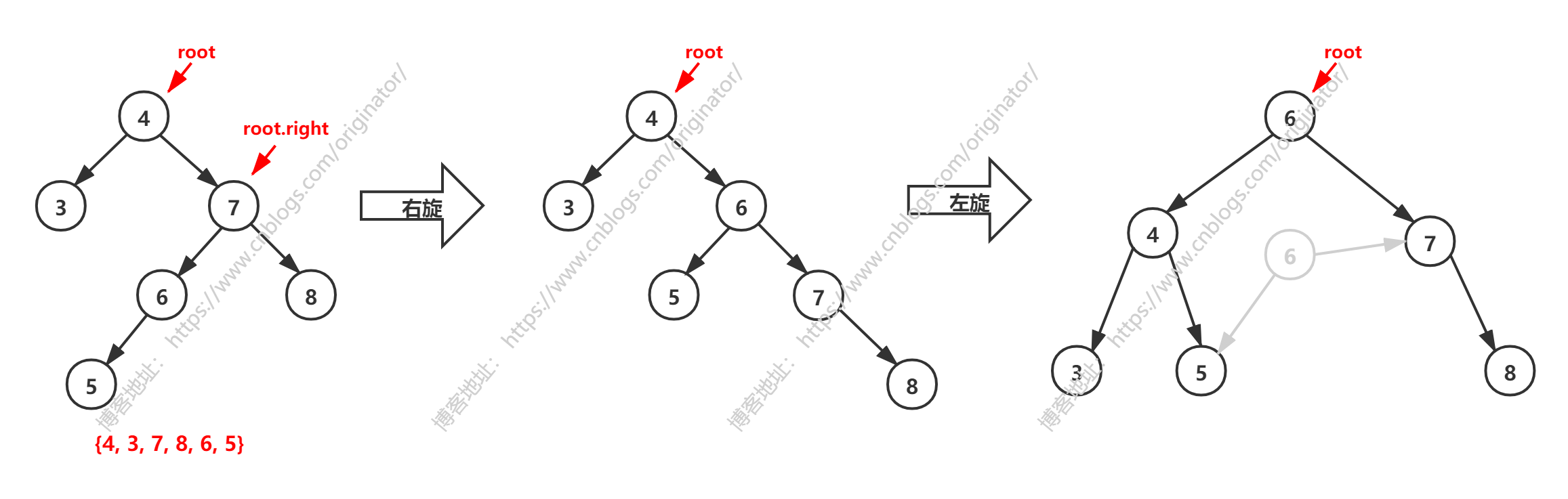
经过左旋后,发现树并没有平衡。解决办法:
①先 root.right 右旋(因为对于root.right是左子树高度 > 右子树)。
②再对 root 左旋。
右旋问题:
同理:
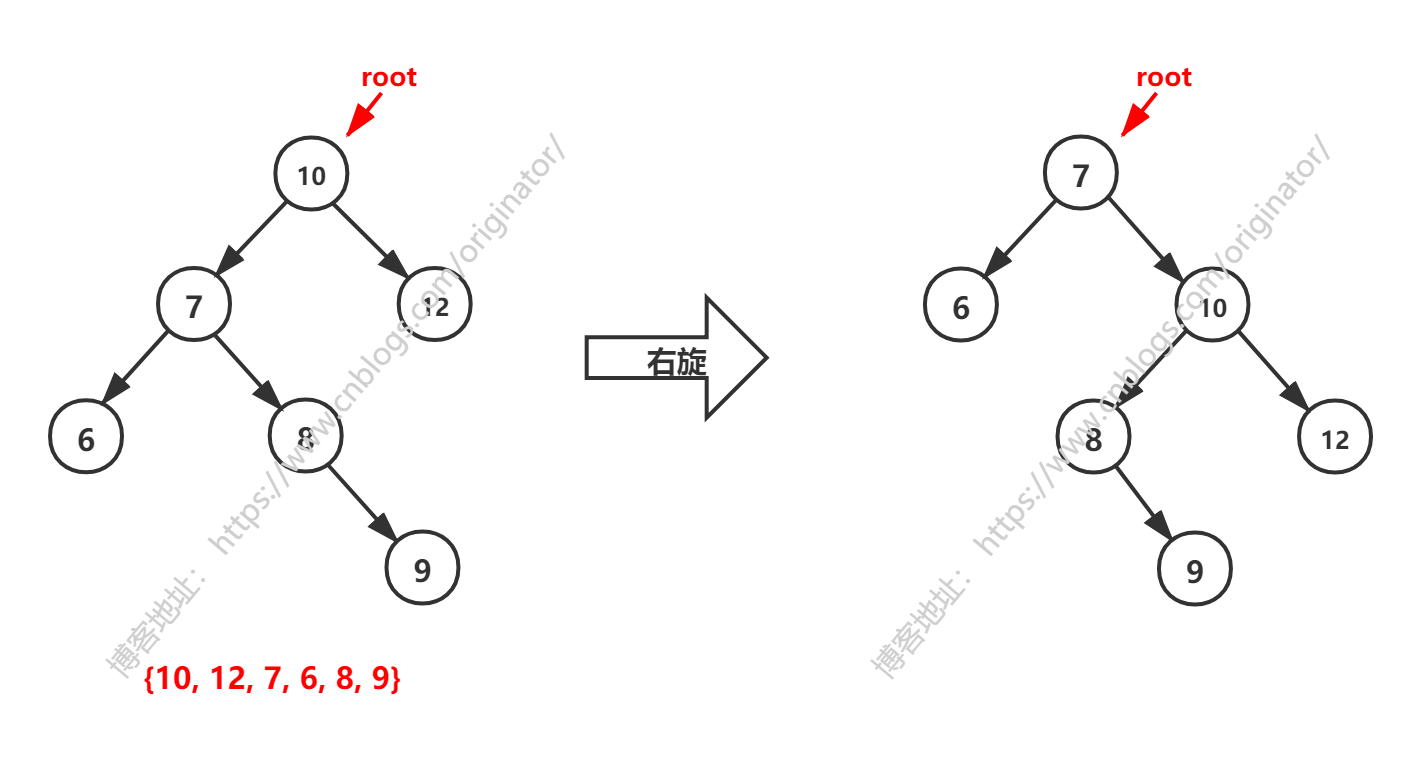
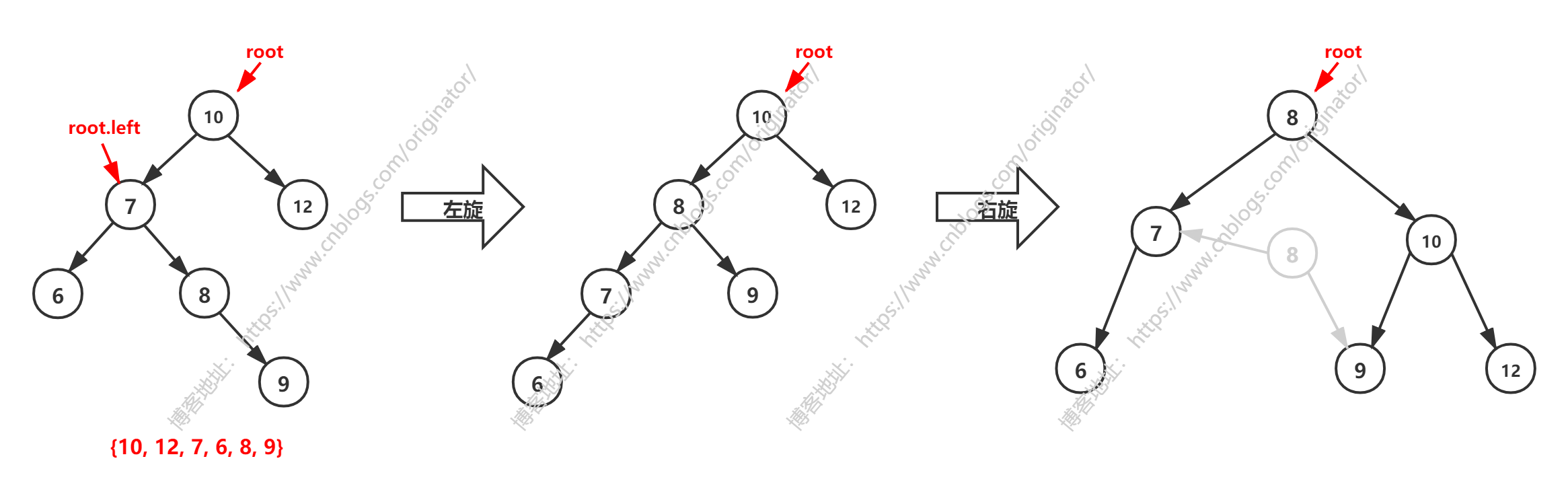
经过右旋后,发现树并没有平衡。解决办法:
①先 root.left 左旋(因为对于root.left是右子树高度 > 左子树)。
②再对 root 右旋。
5、代码实现
代码示例:平衡二叉树

1 public class AVLTree extends BinarySortTree { 2 3 public AVLTree() { 4 } 5 6 public AVLTree(int[] arr) { 7 super(arr); 8 } 9 10 /** 11 * 复写add方法,在排序二叉树性质上,需要调整树的平衡 12 * 13 * @param value 14 */ 15 @Override 16 public void add(int value) { 17 // 1.添加结点 18 super.add(value); 19 20 // 2.检查是否平衡.如果(右子树高度 - 左子树 > 1),左旋 21 if (this.getHeight(root.right) - this.getHeight(root.left) > 1) { 22 // 右.左子树高度 > 右.右子树 23 if (this.getHeight(root.right.left) > this.getHeight(root.right.right)) { 24 // 右子树->右旋 25 rightRotate(root.right); 26 } 27 28 leftRotate(root); 29 } 30 31 // 2.检查是否平衡.如果(左子树高度 - 右子树 > 1),右旋 32 if (this.getHeight(root.left) - this.getHeight(root.right) > 1) { 33 // 左.右子树高度 > 左.左子树 34 if (this.getHeight(root.left.right) > this.getHeight(root.left.left)) { 35 // 左子树->左旋 36 leftRotate(root.left); 37 } 38 39 rightRotate(root); 40 } 41 } 42 43 // 左旋 44 private void leftRotate(TreeNode root) { 45 TreeNode newNode = new TreeNode(root.value); 46 newNode.left = root.left; 47 newNode.right = root.right.left; 48 49 root.value = root.right.value; 50 root.left = newNode; 51 root.right = root.right.right; 52 } 53 54 // 右旋 55 private void rightRotate(TreeNode root) { 56 TreeNode newNode = new TreeNode(root.value); 57 newNode.left = root.left.right; 58 newNode.right = root.right; 59 60 root.value = root.left.value; 61 root.left = root.left.left; 62 root.right = newNode; 63 } 64 65 }
代码示例:测试类

1 public class Main { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 // int[] arr = {4, 3, 6, 5, 7, 8}; 4 // int[] arr = {10, 12, 8, 9, 7, 6}; 5 // int[] arr = {4, 3, 7, 8, 6, 5}; 6 int[] arr = {10, 12, 7, 6, 8, 9}; 7 8 AVLTree avlTree = new AVLTree(arr); 9 10 avlTree.infixOrder(); 11 } 12 }
三、多路查找树(multi-way search tree)
1、介绍
二叉树的问题,二叉树需要加载到内存,如果结点少,没有什么问题,但是如果二叉树的结点很多(比如1亿),就存在如下问题:
问题1:在构建二叉树时,需要多次进行I/O操作(海量数据存在数据库或文件中),结点海量,构建二叉树时,速度有影响。
问题2:结点海量,也会造成二叉树的高度很大,降低操作速度。
2、2-3树
在二叉树中,每个结点有数据项,最多有两个子结点。如果允许每个结点可以有更多的数据项和更多的子结点,就是多叉树(multiway tree)。2-3树,2-3-4树就是多叉树,多叉树通过重新组织结点,减少树的高度,能对二叉树进行优化。如图:
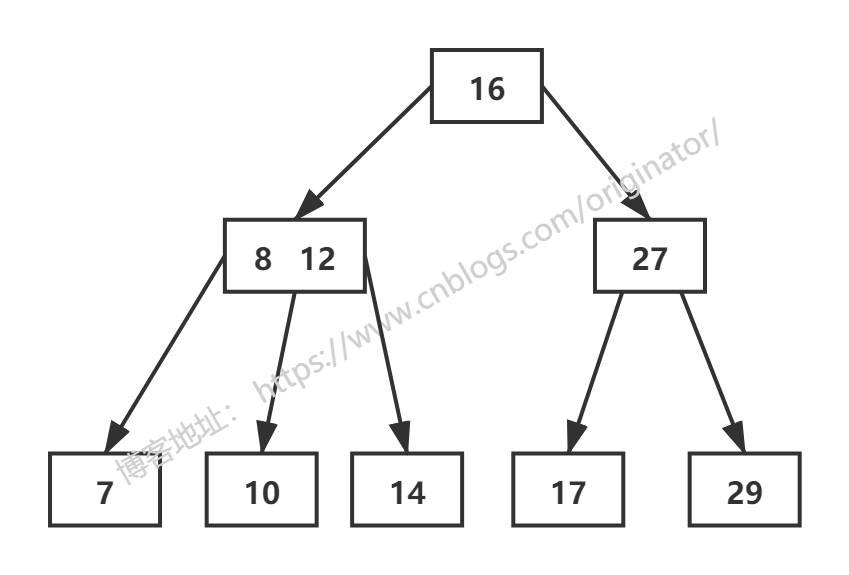
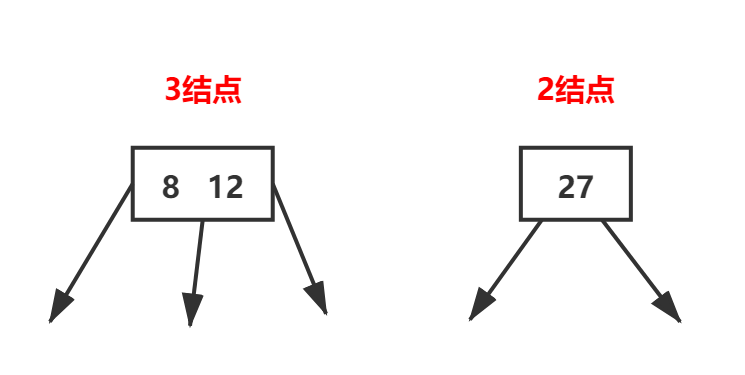
多路查找树中的每一个结点都具有两个孩子或者三个孩子,我们称之为2-3树。是一种平衡的多路查找树。2-3树,2-3-4树是B树的一个特例,属于B树。2-3树,高度平衡。
一个结点拥有两个孩子和一个元素称之为2结点,它跟二叉排序树类似,左子树包含的元素小于结点的元素,小于右子树包含的元素。
不同的是,这个2结点要么没有孩子,要么有两个孩子。不能只有一个孩子。
2-3树所有叶子都在同一层次。
3、2-3-4树
概念和2-3树类似,也是一种B树。
四、B树(B-树)
1、介绍
B树通过重新组织结点,降低树的高度,减少I/O读写次数来提升效率。文件系统及数据库系统的设计者利用了磁盘预读原理,将一个结点的大小设为等于一页(页得大小通常为4k),这样每个结点只需要一次I/O就可以完全载入。
将树的度M设置为1024,在600亿个元素中最多只需要4次I/O操作就可以读取到想要的元素,B树(B+)广泛应用于文件存储系统以及数据库系统中。
所有叶子结点都在同一层。
2、结构
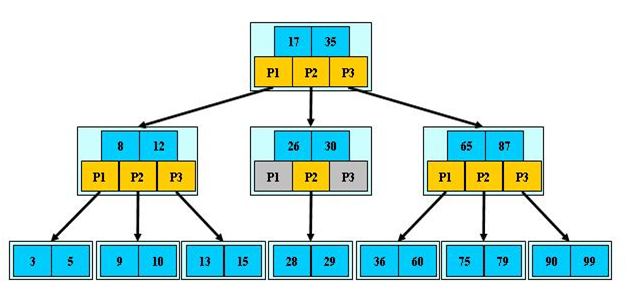
B树的阶:节点的最多子节点个数。比如2-3树的阶是3,2-3-4树的阶是4
B树的搜索:从根结点开始,对结点内的关键字(有序)序列进行二分查找,如果命中则结束,否则进入查询关键字所属范围的儿子结点;重复,直到所对应的儿子指针为空,或已经是叶子结点。关键字集合分布在整颗树中,即叶子节点和非叶子节点都存放数据。搜索有可能在非叶子结点结束。其搜索性能等价于在关键字全集内做一次二分查找。
B树的插入算法中,通过结点的向上"分裂",代替了专门的平衡调整。
五、B+树
1、介绍
B+树是B树的变体,也是一种多路搜索树。
2、结构
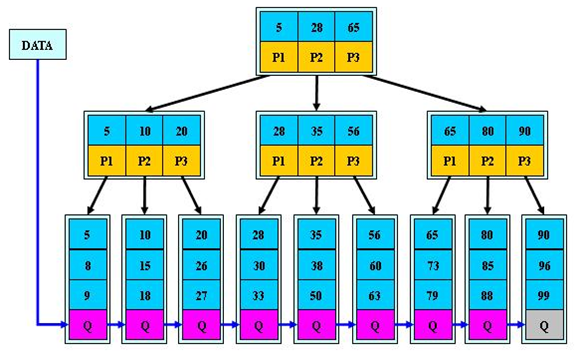
B+树的搜索:与B树基本相同,区别是B+树只有达到叶子结点才命中(B树可以在非叶子结点命中),其性能也等价于在关键字全集做一次二分查找。所有关键字都出现在叶子结点的链表中(即数据只能在叶子节点【也叫稠密索引】),且链表中的关键字恰好是有序的。
不可能在非叶子结点命中。
非叶子结点相当于是叶子结点的索引(稀疏索引),叶子结点相当于是存储(关键字)数据的数据层。
更适合文件索引系统。
B树和B+树各有自己的应用场景,不能说B+树完全比B树好,反之亦然。
六、B*树
1、介绍
B*树是B+树的变体,在B+树的非根和非叶子结点再增加指向兄弟的指针。
2、结构
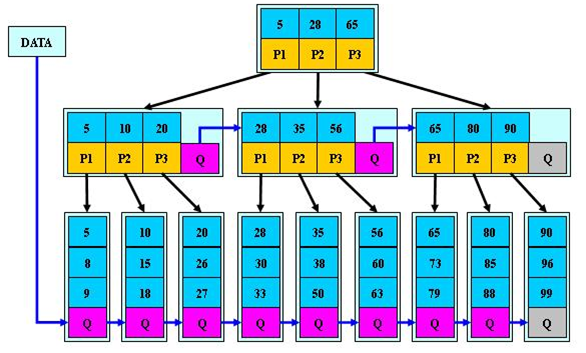
B*树定义了非叶子结点关键字个数至少为(2/3)*M,即块的最低使用率为2/3,而B+树的块的最低使用率为B+树的1/2。
B*树分配新结点的概率比B+树要低,空间使用率更高。
作者:Craftsman-L
本博客所有文章仅用于学习、研究和交流目的,版权归作者所有,欢迎非商业性质转载。
如果本篇博客给您带来帮助,请作者喝杯咖啡吧!点击下面打赏,您的支持是我最大的动力!




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号