数据结构与算法(四)——队列
二、队列
1、介绍
队列是一种先进先出的线性表,它只允许在一端(队尾)进行插入操作,在另一端(队头)进行删除操作。可以用数组或链表来实现,一般用链表来实现,简称为链队列,建立在内存的动态区。
2、队列的顺序存储实现
顾名思义,用顺序表的方法实现,通常用数组。队列的顺序储存结构:

下面用数组实现队列:
思想:队列出队入队动态图:
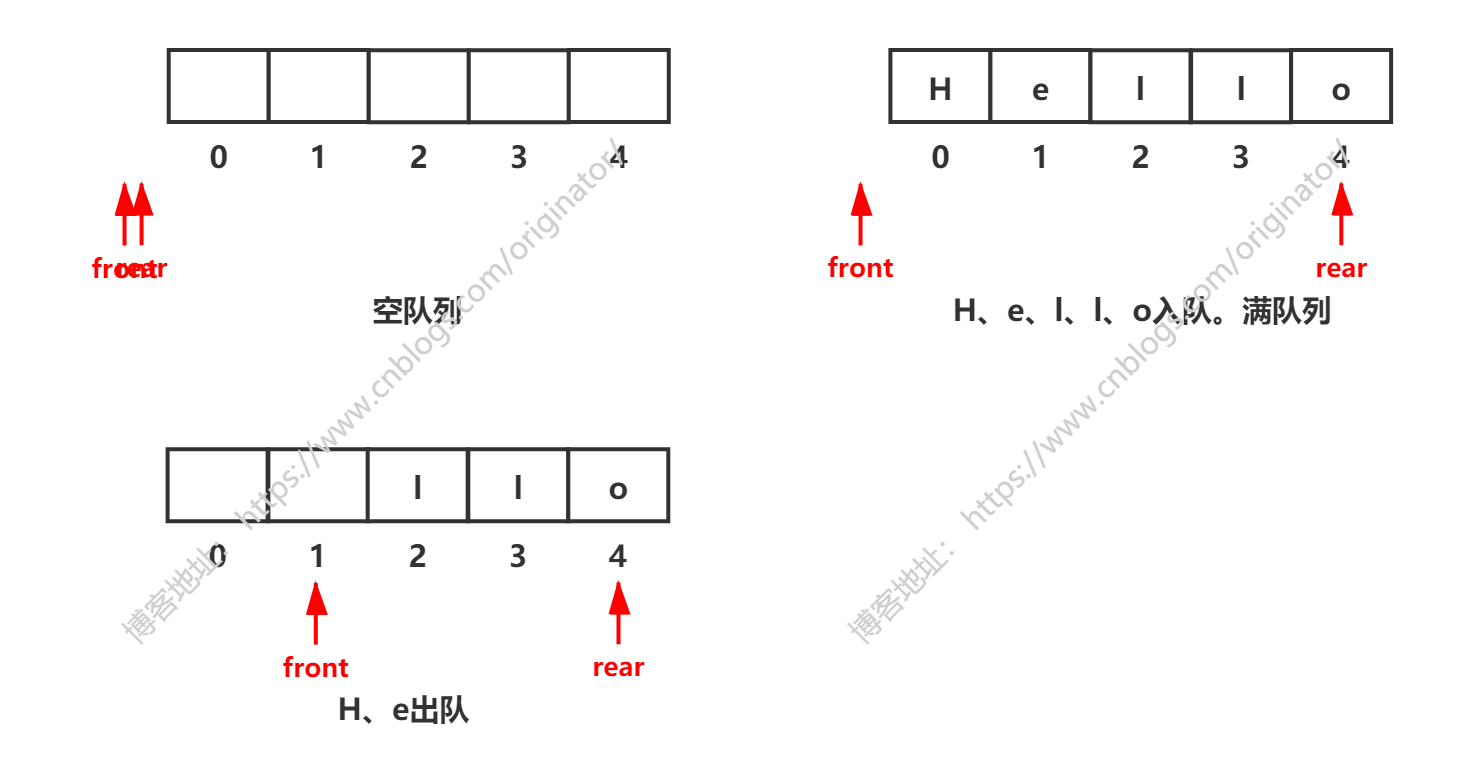
队列的特性:队尾插入,队头删除。那么,一个元素入队列,rear++;一个元素出队列,front++。
结论:看图可知
判空:起始状态,front == rear == -1,则空队列判定,front == rear。
判满:一个元素入队列,rear++,则满队列判定,rear == length() - 1。
代码示例:数组实现队列

1 // 用数组模拟队列 2 public class MyQueue<T> { 3 private T[] elementData; 4 private int front; 5 private int rear; 6 7 public MyQueue(int initialCapacity) { 8 if (initialCapacity > 0) { 9 this.elementData = (T[]) new Object[initialCapacity]; 10 } else if (initialCapacity == 0) { 11 this.elementData = (T[]) new Object[]{}; 12 } else { 13 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: " + 14 initialCapacity); 15 } 16 17 front = -1; 18 rear = -1; 19 } 20 21 // 入队 22 public boolean offer(T e) { 23 if (isFull()) { 24 System.out.println("队列满,不能添加~"); 25 return false; 26 } 27 rear++; 28 elementData[rear] = e; 29 return true; 30 } 31 32 // 出队 33 public T poll() { 34 if (isEmpty()) { 35 throw new RuntimeException("队空,没有任何数据~"); 36 } 37 front++; 38 return elementData[front]; 39 } 40 41 // 读取队头 42 public T peek() { 43 if (isEmpty()) { 44 throw new RuntimeException("队空,没有任何数据~"); 45 } 46 return elementData[front + 1]; 47 } 48 49 // 判空 50 public boolean isEmpty() { 51 return front == rear; 52 } 53 54 // 判满 55 private boolean isFull() { 56 return rear == elementData.length - 1; 57 } 58 59 // 获取队列元素的个数 60 public int size() { 61 return rear - front; 62 } 63 64 @Override 65 public String toString() { 66 if (isEmpty()) { 67 return "[]"; 68 } 69 70 StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); 71 builder.append("["); 72 for (int i = front + 1; i < rear + 1; i++) { 73 builder.append(elementData[i]) 74 .append(","); 75 } 76 // 去掉最后一个, 77 builder.deleteCharAt(builder.length() - 1); 78 builder.append("]"); 79 80 return builder.toString(); 81 } 82 }
代码示例:测试类

1 // 测试类 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 MyQueue<Integer> myQueue = new MyQueue<>(5); 4 myQueue.offer(1); 5 myQueue.offer(10); 6 myQueue.offer(5); 7 myQueue.offer(9); 8 myQueue.offer(90); 9 myQueue.offer(900); 10 11 // 1 10 5 9 90 12 System.out.println(myQueue); 13 System.out.println("size:" + myQueue.size()); 14 15 System.out.println(myQueue.poll()); 16 System.out.println(myQueue.poll()); 17 System.out.println(myQueue.poll()); 18 System.out.println(myQueue.poll()); 19 System.out.println(myQueue); 20 System.out.println("size:" + myQueue.size()); 21 22 myQueue.offer(900); 23 } 24 25 // 结果 26 堆满,不能添加~ 27 [1,10,5,9,90] 28 size:5 29 1 30 10 31 5 32 9 33 [90] 34 size:1 35 堆满,不能添加~
问题:看图可知
假溢出:这样实现的队列,在H、e出队后,继续入队列,会出现"堆满,不能添加元素"或"数组越界"的情况。但事实上,数组索引 0 和 1 的位置已经空了,这叫假溢出。
那么,如何解决这个问题呢?
很自然的想到,如果此时继续入队列,就将元素放在索引 0 的位置。这就是循环队列。
循环队列:
为解决假溢出,将数组的首尾相接,模拟出来的逻辑上的循环,容量是固定的。循环队列出队入队动态图:
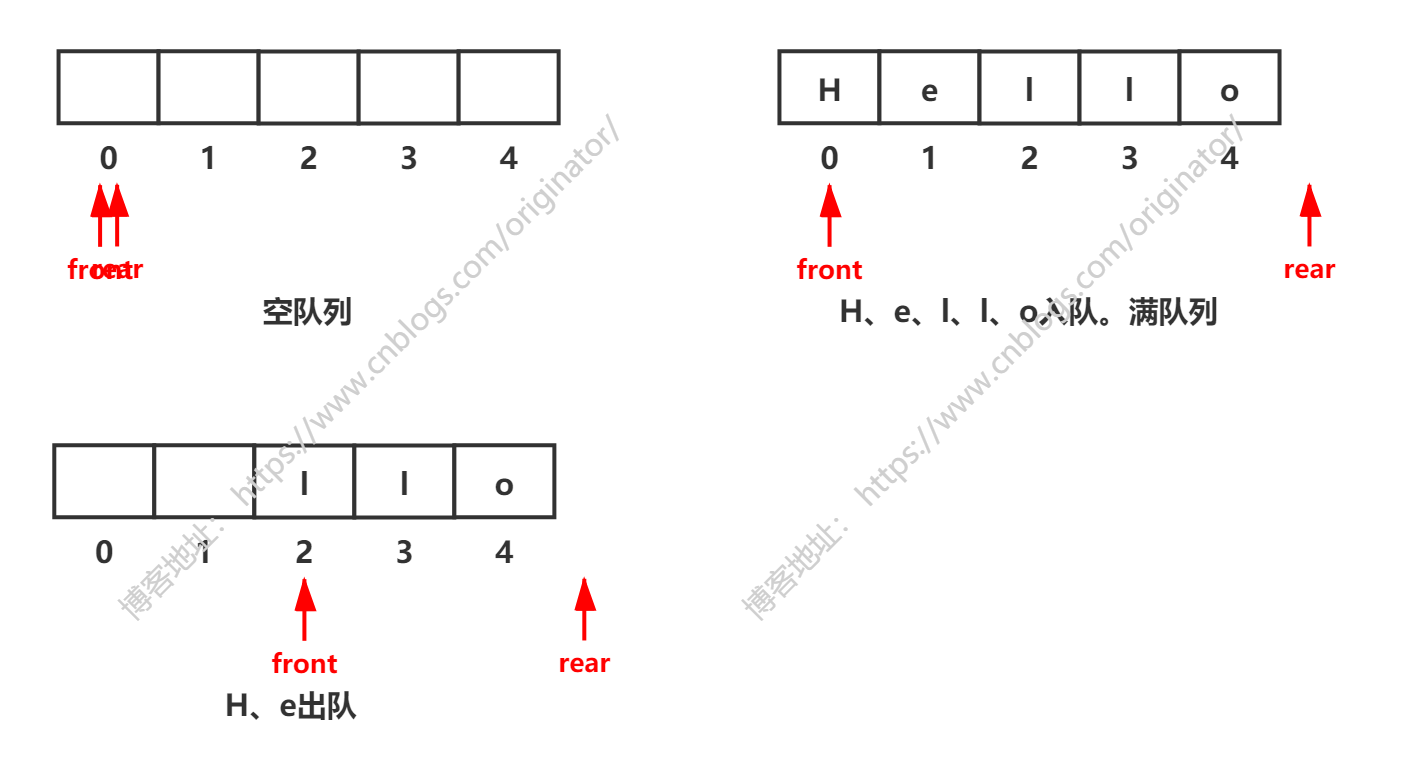
特别注意:①这里修改了front、rear的含义,起始状态,front == rear == 0。②上图是一个循环队列,请脑补一下,将他们首尾相接。所以上图,后两图rear == 0。
为了让小伙伴方便看的清楚,下面给出一个上图首尾相接的图。
思想:
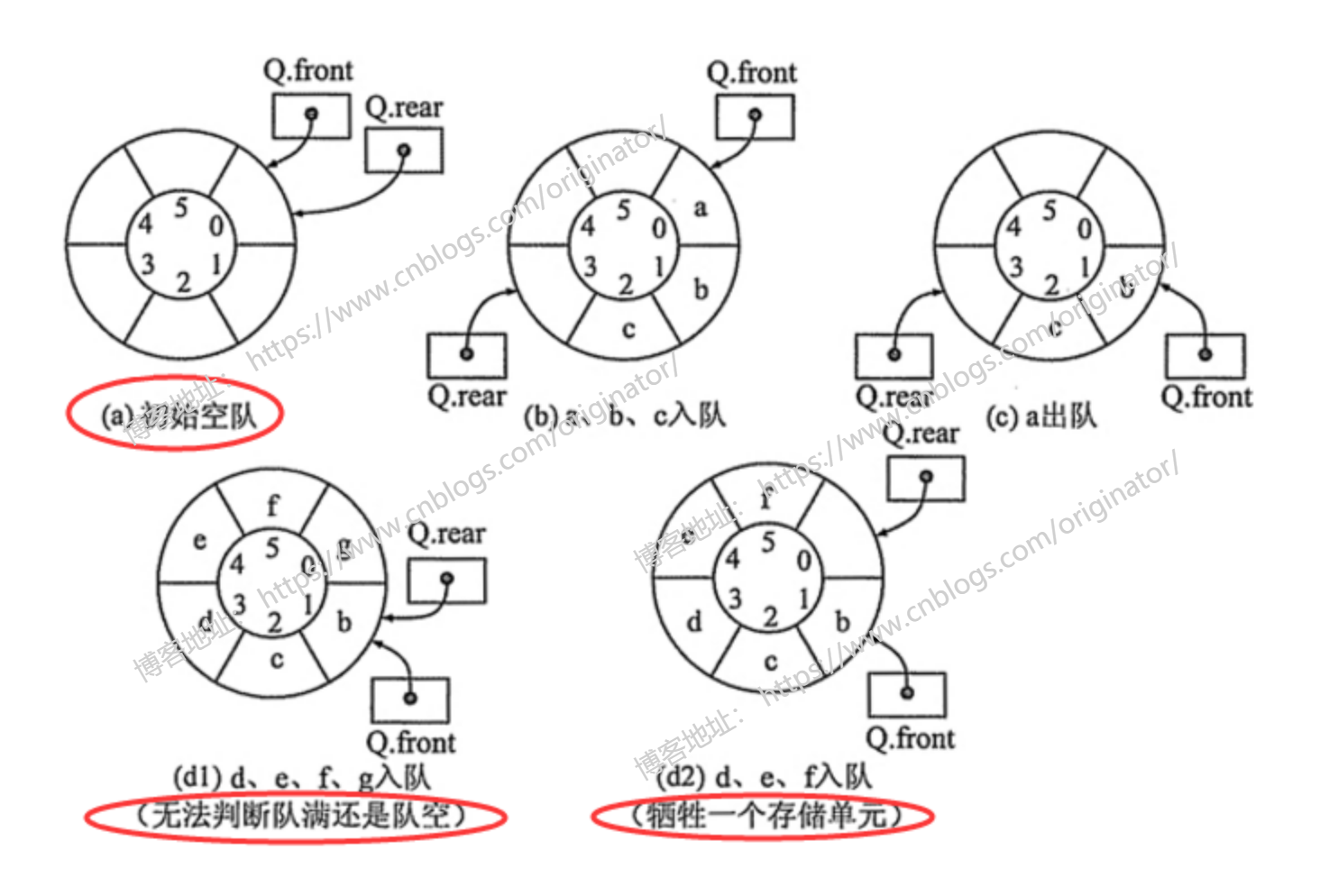
由队列的特性:队尾插入,队头删除。那么,一个元素入队列,rear++;一个元素出队列,front++。
问题:队空(图a):front == rear == 0。队满(图d1):front == rear。那么,队空和队满就无法判断。
解决方案:牺牲一个存储单元(图d2),即队列最后一个存储单元不用。
结论:看图可知
判空:起始状态,front == rear == 0,则空队列判定,front == rear。
判满:一个元素入队列,rear++,则满队列判定,(rear + 1) % length() == front。
队列长度:队列元素的个数,(rear - front + length()) % length()。
代码示例:数组实现循环队列

1 // 用数组模拟循环队列 2 public class MyCircleQueue<T> { 3 private T[] elementData; 4 private int front; 5 private int rear; 6 7 public MyCircleQueue(int initialCapacity) { 8 if (initialCapacity > 0) { 9 this.elementData = (T[]) new Object[initialCapacity]; 10 } else if (initialCapacity == 0) { 11 this.elementData = (T[]) new Object[]{}; 12 } else { 13 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: " + 14 initialCapacity); 15 } 16 17 front = 0; 18 rear = 0; 19 } 20 21 // 入队 22 public boolean offer(T e) { 23 if (isFull()) { 24 System.out.println("队列满,不能添加~"); 25 return false; 26 } 27 elementData[rear] = e; 28 rear = (rear + 1) % elementData.length; 29 return true; 30 } 31 32 // 出队 33 public T poll() { 34 if (isEmpty()) { 35 throw new RuntimeException("队空,没有任何数据~"); 36 } 37 final T t = elementData[front]; 38 front = (front + 1) % elementData.length; 39 40 return t; 41 } 42 43 // 读取队头 44 public T peek() { 45 if (isEmpty()) { 46 throw new RuntimeException("队空,没有任何数据~"); 47 } 48 return elementData[front]; 49 } 50 51 // 判空 52 public boolean isEmpty() { 53 return front == rear; 54 } 55 56 // 判满 57 private boolean isFull() { 58 return (rear + 1) % elementData.length == front; 59 } 60 61 // 获取队列元素的个数 62 public int size() { 63 return (rear - front + elementData.length) % elementData.length; 64 } 65 66 @Override 67 public String toString() { 68 if (isEmpty()) { 69 return "[]"; 70 } 71 72 StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); 73 builder.append("["); 74 // 从front开始遍历,遍历 size() 个元素 75 for (int i = front; i < front + size(); i++) { 76 builder.append(elementData[i % elementData.length]) 77 .append(","); 78 } 79 // 去掉最后一个, 80 builder.deleteCharAt(builder.length() - 1); 81 builder.append("]"); 82 83 return builder.toString(); 84 } 85 }
代码示例:测试类

1 // 测试类 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 MyCircleQueue<Integer> myQueue = new MyCircleQueue<>(6); 4 myQueue.offer(1); 5 myQueue.offer(10); 6 myQueue.offer(5); 7 myQueue.offer(9); 8 myQueue.offer(90); 9 10 // 1 10 5 9 90 11 System.out.println(myQueue); 12 System.out.println("size:" + myQueue.size()); 13 myQueue.offer(900); 14 15 System.out.println(myQueue.poll()); 16 System.out.println(myQueue.poll()); 17 System.out.println(myQueue.poll()); 18 System.out.println(myQueue.poll()); 19 System.out.println(myQueue); 20 System.out.println("size:" + myQueue.size()); 21 22 // 可以继续入队数据 23 myQueue.offer(900); 24 System.out.println(myQueue); 25 } 26 27 // 结果 28 [1,10,5,9,90] 29 size:5 30 队列满,不能添加~ 31 1 32 10 33 5 34 9 35 [90] 36 size:1 37 [90,900]
3、队列的链式存储实现
顾名思义,用链表的方法实现,通常用单链表。队列的链式储存结构:
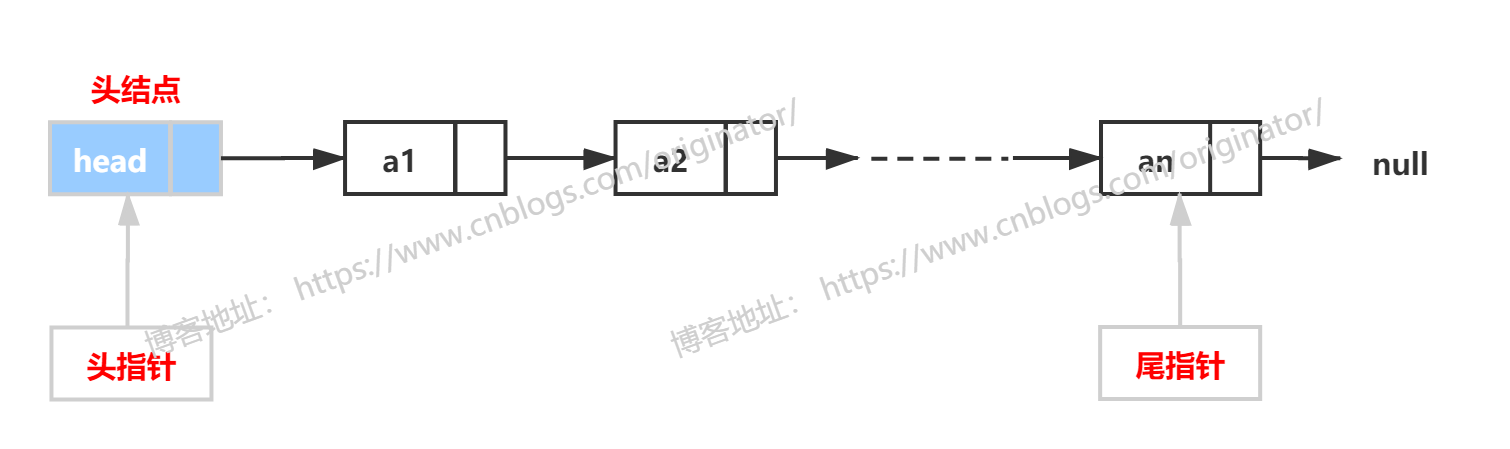
下面用链表实现队列:
代码示例:带头结点的链表实现队列

1 public class MyLinkedQueue<E> { 2 // 头指针.不变 3 private final Node<E> front; 4 5 // 尾指针 6 private Node<E> rear; 7 8 public MyLinkedQueue() { 9 // 初始化头结点 10 front = new Node<>(null); 11 rear = front; 12 } 13 14 // 入队 15 public boolean offer(E e) { 16 Node<E> node = new Node<>(e); 17 18 rear.next = node; 19 rear = node; 20 21 return true; 22 } 23 24 // 出队 25 public E poll() { 26 Node<E> temp = front.next; 27 28 if (temp == null) { 29 return null; 30 } 31 32 // 出队.删除队头元素 33 front.next = front.next.next; 34 if (isEmpty()) { 35 rear = front; 36 } 37 38 return temp.item; 39 } 40 41 // 获取.队头 42 public E peek() { 43 Node<E> temp = front.next; 44 45 if (temp != null) { 46 return temp.item; 47 } 48 return null; 49 } 50 51 // 空队列时,front和rear都指向头结点. 52 public boolean isEmpty() { 53 return front.next == null; 54 } 55 56 /** 57 * 打印队列 58 */ 59 @Override 60 public String toString() { 61 StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); 62 63 Node<E> temp = front.next; 64 65 while (temp != null) { 66 builder.append(temp.item) 67 .append(","); 68 temp = temp.next; 69 } 70 71 if (builder.length() == 0) { 72 return "[]"; 73 } 74 75 builder.insert(0, "["); 76 // 去掉最后一个, 77 builder.deleteCharAt(builder.length() - 1); 78 builder.append("]"); 79 80 return builder.toString(); 81 } 82 83 /** 84 * 队列的结点 85 */ 86 private static class Node<E> { 87 public E item; 88 public Node<E> next; 89 90 public Node(E item) { 91 this.item = item; 92 } 93 } 94 95 }
代码示例:测试类

1 // 测试类 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 MyLinkedQueue<Integer> queue = new MyLinkedQueue<>(); 4 5 // 添加.入队 6 queue.offer(9); 7 queue.offer(5); 8 queue.offer(2); 9 queue.offer(7); 10 System.out.println(queue); 11 12 // 出队 13 final Integer poll = queue.poll(); 14 System.out.println(poll); 15 System.out.println(queue); 16 17 // 获取.队头 18 final Integer peek = queue.peek(); 19 System.out.println(peek); 20 System.out.println(queue); 21 } 22 23 // 结果 24 [9,5,2,7] 25 9 26 [5,2,7] 27 5 28 [5,2,7]
作者:Craftsman-L
本博客所有文章仅用于学习、研究和交流目的,版权归作者所有,欢迎非商业性质转载。
如果本篇博客给您带来帮助,请作者喝杯咖啡吧!点击下面打赏,您的支持是我最大的动力!




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号