linux SVN 安装配置
1、设置Yum存储库
首先,我们需要在我们的系统上配置yum存储库。创建一个新的repo文件/etc/yum.repos.d/wandisco-svn.repo并根据您的操作系统版本添加以下内容。
vim /etc/yum.repos.d/wandisco-svn.repo
添加以下内容:
[WandiscoSVN] name=Wandisco SVN Repo baseurl=http://opensource.wandisco.com/centos/$releasever/svn-1.8/RPMS/$basearch/ enabled=1 gpgcheck=0
或:
[Subversion] name=Wandisco SVN Repo baseurl=http://opensource.wandisco.com/centos/$releasever/svn-1.9/RPMS/$basearch/ enabled=1 gpgcheck=0
*注:由于我们这里安装的是SVN1.9,在repo文件里配置的是svn-1.9,如果要安装SVN1.8,可以改为svn-1.8
2、安装Subversion包
在安装最新软件包之前,从系统中删除现有的subversion软件包以消除冲突。
yum remove subversion*
现在使用yum命令行包管理器实用程序安装最新的可用Subversion包。
yum clean all yum install subversion
3、验证SVN版本
在此阶段,您已在系统上成功安装Subversion客户端。让我们使用以下命令来验证svn客户端的版本。
svn --version
显示以下内容:
svn, version 1.8.19 (r1800620) compiled Aug 11 2017, 09:34:52 on x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu Copyright (C) 2017 The Apache Software Foundation. This software consists of contributions made by many people; see the NOTICE file for more information. Subversion is open source software, see http://subversion.apache.org/ The following repository access (RA) modules are available: * ra_svn : Module for accessing a repository using the svn network protocol. - with Cyrus SASL authentication - handles 'svn' scheme * ra_local : Module for accessing a repository on local disk. - handles 'file' scheme * ra_serf : Module for accessing a repository via WebDAV protocol using serf. - using serf 1.3.7 - handles 'http' scheme - handles 'https' scheme
4、创建运行SVN服务器所需的用户svn
groupadd svn
useradd -g svn svn
这里之所以要创建svn用户启动SVN服务器,而不使用root用户启动SVN服务器,是因为如果使用root用户启动SVN服务器,通过SVN客户端使用非root账户访问SVN服务器时,会出现
"xxxxxxxx db/txn-current-lock:permission denied"错误。
将svn用户加入sudoers用户中,执行命令:
visudo
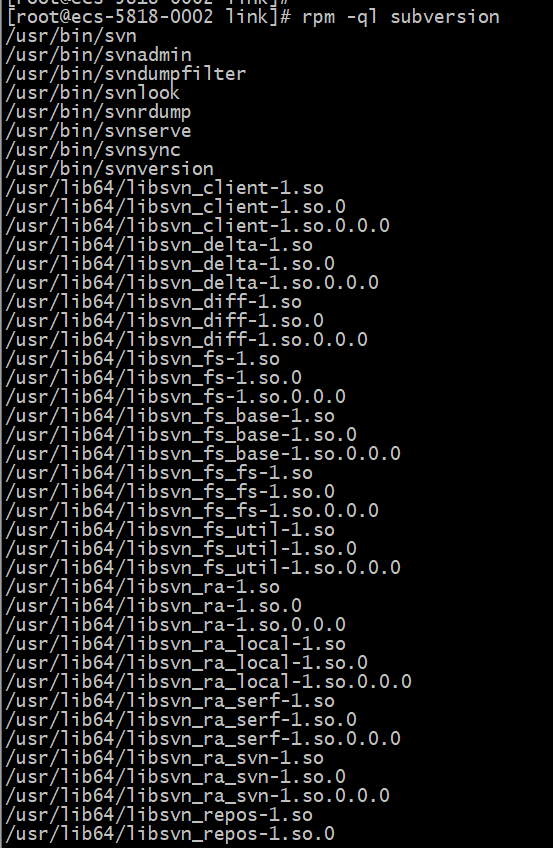
5、执行rpm -ql subversion查看安装位置
rpm -ql subversion
6、创建svn版本库目录
mkdir -p /opt/svnRepos
切换到svn用户,为svn用户添加这个文件夹的访问权限
chmod -R o+rw /opt/svnRepos su - svn cd /opt/svnRepos

7、创建版本库
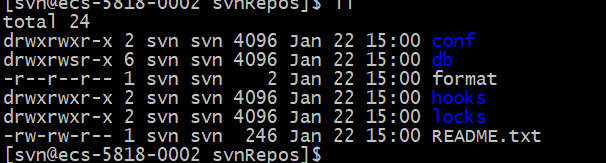
svnadmin create /opt/svnRepos
执行命令后/opt/svnRepos文件夹下新增了一些文件夹
8、删除版本库
rm -rf /opt/svnRepos
9、添加用户密码和访问权限
进入conf目录,可以看到以下文件
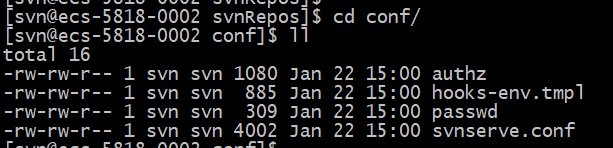
authz 文件是权限控制文件
passwd 是帐号密码文件
svnserve.conf 是SVN服务配置文件
10、设置帐号密码
修改passwd文件,在[users]段添加用户svnuser1和访问密码
在[users]块中添加用户和密码,格式:帐号=密码,如svnuser = linktech
vim passwd
内容如下:
### This file is an example password file for svnserve. ### Its format is similar to that of svnserve.conf. As shown in the ### example below it contains one section labelled [users]. ### The name and password for each user follow, one account per line. [users] # harry = harryssecret # sally = sallyssecret svnuser = linktech
11、设置权限
修改authz文件,在文件最后为svnuser用户添加svn根目录访问权限
vim authz
在末尾添加如下代码:
[/]
svnuser = rw
内容如下:
### This file is an example authorization file for svnserve. ### Its format is identical to that of mod_authz_svn authorization ### files. ### As shown below each section defines authorizations for the path and ### (optional) repository specified by the section name. ### The authorizations follow. An authorization line can refer to: ### - a single user, ### - a group of users defined in a special [groups] section, ### - an alias defined in a special [aliases] section, ### - all authenticated users, using the '$authenticated' token, ### - only anonymous users, using the '$anonymous' token, ### - anyone, using the '*' wildcard. ### ### A match can be inverted by prefixing the rule with '~'. Rules can ### grant read ('r') access, read-write ('rw') access, or no access ### (''). [aliases] # joe = /C=XZ/ST=Dessert/L=Snake City/O=Snake Oil, Ltd./OU=Research Institute/CN=Joe Average [groups] # harry_and_sally = harry,sally # harry_sally_and_joe = harry,sally,&joe # [/foo/bar] # harry = rw # &joe = r # * = # [repository:/baz/fuz] # @harry_and_sally = rw # * = r [/] svnuser = rw
*注:这里[/]表示是svn根目录,svnuser=rw说明svnuser用户对根目录有读写权限。如果要限制某些用户对某些文件夹的读写权限, 这里的[/]可以改为具体的文件夹目录,再添加具体的用户权限,这里不再赘述。
12、修改svn配置文件
修改svnserve.conf文件
打开以下几项的注释(图中以红色圈标注)
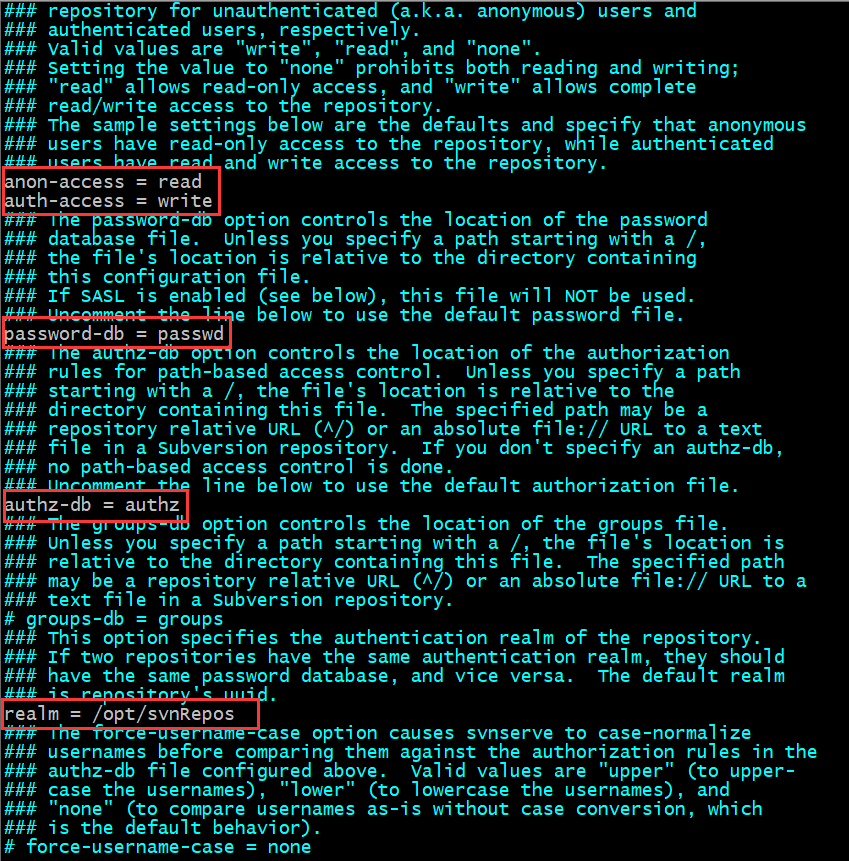
vim svnserve.conf
打开下面的几个注释:
anon-access = read #匿名用户可读 auth-access = write #授权用户可写 password-db = passwd #使用哪个文件作为账号文件 authz-db = authz #使用哪个文件作为权限文件 realm = /opt/svnRepos # 认证空间名,版本库所在目录
*注:需要把 anon-access = read 配置修改为 anon-access = none ,如下所示:
[general] anon-access = none #控制非鉴权用户访问版本库的权限 auth-access = write #控制鉴权用户访问版本库的权限 password-db = passwd #指定用户名口令文件名 authz-db = authz #指定权限配置文件名 realm = somnus #指定版本库的认证域,即在登录时提示的认证域名称
13、启动SVN服务器
执行以下命令
svnserve -d -r /opt/svnRepos --config-file=/opt/svnRepos/conf/svnserve.conf
这条指令的参数-d表示以守护进程形式运行Svn服务器,-r表示Svn服务器的根目录,后接SVN的根目录。
--config-file 是Svn服务器启动所引用的配置文件,后接配置文件路径。
svnserve 指令的更多参数可以参考此文
https://linux.die.net/man/8/svnserve
-------------------------------------------------------分割线--------------------------------------------------------------
svnserve [ 选项 ]
描述
svnserve允许使用svn网络协议访问Subversion存储库。它既可以作为独立的服务器进程运行,也可以用完inetd。启动svnserve时必须选择一种操作模式。可识别以下选项:
-d, - damon 使svnserve以守护进程模式运行。svnserve背景本身并接受并提供svn端口上的TCP / IP连接(默认情况下为3690)。 --listen-port = port 原因Svnserve的上监听端口在守护进程模式时。 --listen-host = host 使svnserve侦听host指定的接口,该接口可以是主机名或IP地址。 - 前景 与-d一起使用时,此选项会使svnserve保持在前台。此选项主要用于调试。 -i, - intd 使svnserve使用stdin / stdout文件描述符,因为它适用于运行inetd的守护进程。 -h, - help 显示使用情况摘要并退出。 -version 打印svnserve的版本和特定svnserve支持的存储库文件系统后端。 -r root,--root = 根 设置svnserve提供的存储库的虚拟根目录。客户端提供的URL中的路径名将相对于此根进行解释,并且不允许转义此根。 -R --read-only 强制禁止通过此svnserve实例执行所有写入操作,从而覆盖所有其他访问策略配置。不要使用此选项来设置常规存储库访问策略 - 这就是conf / svnserve.conf存储库配置文件的用途。此选项应仅用于通过调用svnserve的某种方法来限制访问- 例如,允许通过SSH进行写访问,而不是通过svnserve守护进程进行写访问,或者创建仅能够读访问的受限SSH密钥。 -t, -tunnel 导致svnserve以隧道模式运行,这就像inetd操作模式(通过stdin / stdout提供一个连接),除了连接被认为是使用当前uid的用户名进行预身份验证。客户端在通过隧道代理程序运行时选择此标志。 --tunnel-user = username 与--tunnel结合使用时,使用提供的用户名覆盖预先验证的用户名。这与ssh authorized_key文件的“command”指令结合使用非常有用,它允许多个提交者使用单个系统帐户,每个提交者都具有不同的ssh标识。 -T, --threads 在守护程序模式下运行时,会导致svnserve为每个连接生成一个线程而不是一个进程。该svnserve的过程中仍然背景本身在启动时。 --config-file = filename 指定时,svnserve在程序启动时读取文件名一次,并缓存svnserve配置以及从filename引用的任何密码和授权配置。使用此选项时,svnserve不会读取任何每个存储库的conf / svnserve.conf文件。有关此选项的文件格式的详细信息。 --pid-file = filename 指定后,svnserve会将其进程ID写入filename。 -X,- 生活一次 使svnserve接受svn端口上的一个连接,提供它并退出。此选项主要用于调试。
除非--config文件选项是在命令行上指定,一旦客户端通过传递URL选择了一个仓库,svnserve的 读取文件名为CONF / svnserve.conf的存储库中的目录,以确定库特定的设置,例如什么要使用的身份验证数据库以及要应用的授权策略。
repository-path /conf/svnserve.conf
svnserve.conf基于每个存储库控制svnserve守护程序的行为。它位于存储库的conf子目录中。
文件的整体结构与Subversion用户配置文件的结构相同。在顶层是部分,由方括号中的单词指定; 每个部分内部都是“variable = value”形式的变量定义。以“#”开头的行将被忽略。 svnserve.conf目前只使用一个名为“general”的节,并支持以下变量:
anon-access = none | 读 | 写 确定未经身份验证的用户的访问级别。write访问允许所有存储库操作。读访问允许除提交和更改修订版属性之外的所有操作。无访问权限不允许访问。读取默认级别。 auth-access = none | 读 | 写 使用与上述相同的访问级别确定经过身份验证的用户的访问级别。写入默认级别。 password-db = filename 设置密码数据库的位置。filename可能与存储库conf目录相关。没有默认值。密码数据库与此文件具有相同的总体格式。它只使用一个部分“用户”; 该部分中的每个变量都是用户名,每个值都是密码。 authz-db = filename authz-db选项控制基于路径的访问控制的授权规则的位置。filename可能与存储库conf目录相关。没有默认值。如果未指定authz-db,则不会执行基于路径的访问控制。 realm = 领域名称 设置存储库的身份验证领域。如果两个存储库具有相同的密码数据库,则它们应具有相同的域,反之亦然; 此关联允许客户端为多个存储库使用单个缓存密码。默认领域值是存储库的uuid。 例 以下示例svnserve.conf允许对经过身份验证的用户进行读访问,不允许匿名用户访问,指向同一目录中的passwd数据库,并定义域名。 [一般] anon-access = none auth-access =读取 password-db = passwd realm =我的第一个存储库 文件“passwd”看起来像: [用户] joeuser = joepassword jayrandom = randomjay
-------------------------------------------------------分割线--------------------------------------------------------------
启动后可以查看到svnserve进程已经启动
ps -ef|grep svnserve

SVN默认的打开端口是3690
可以通过下面的命令查看:
netstat -antp | grep svn
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3690 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 442/svnserve
14、在防火墙上开放SVN服务器端口
SVN服务器默认端口是3690,如果要修改默认端口,可以在运行svnserve命令时添加 --listen-port 参数,后接需要指定的端口号。
执行以下命令在CentOS7系统防火墙上开放SVN服务器端口
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=3690/tcp firewall-cmd --reload #重启防火墙(正常不需要重启,只需要reload) systemctl restart firewalld.service
15、在windows上测试
在客户端安装Tortoise SVN 1.9.7,安装完成后新建一个文件夹,在文件夹中右击,在弹出右键菜单中选择[Repo-brower]菜单,在弹出的地址对话框中输入SVN://IP(我们这里是svn://49.4.78.56),再在验证对话框中输入用户名rick和密码,即可以访问SVN根目录,我们使用svnuser用户登录SVN,如下图所示

输入刚才在passwd文件中定义的用户名和密码
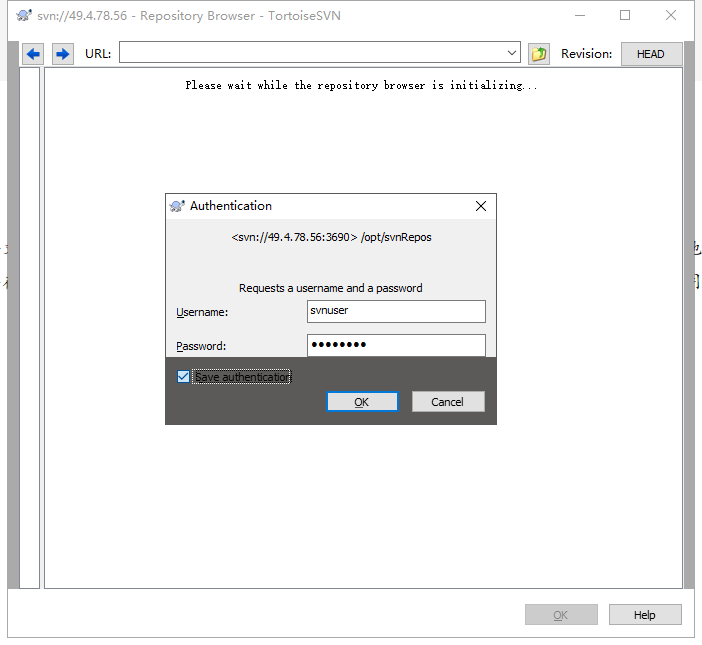
我们使用svnuser用户在根目录下新建trunk,tags和branches三个文件夹

16、将SVN服务器设置为开机启动服务
网上有相关文件通过修改/etc/rc.local文件设置SVN服务器开机启动,这种做法在CentOS 7环境下已经过时,我们使用CentOS 7正常添加服务的方式。
我们切换到/usr/lib/systemd/system目录下,创建名为svnserver.service的文件,添加以下内容
cd /usr/lib/systemd/system
vim svnserver.service
添加以下内容
[Unit] Description=SVN Server service After=network.target [Service] Type=forking ExecStart= /usr/bin/svnserve -d -r /opt/svnRepos --config-file=/opt/svnRepos/conf/svnserve.conf ExecStop= /home/svn/stopSVN.sh User=svn Restart=on-abort [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
这里启动SVN服务器直接使用命令,我试过写一个.sh文件替换,但启动后出现code=exited,status=203/EXEC错误,改用现在这种形式。
stopSVN.sh是用于关闭SVN服务的脚本文件,内容如下:
#!/bin/sh #查找是否有svnserve对应的进程,有的话关闭进程 ps -ef|grep svnserve |grep -v grep if [ $? -ne 0 ] then echo "the svn server does not start" else killall -9 sh svnserve fi
保存svnserver.service文件后,执行以下命令
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable svnserver.service
systemctl start svnserver.service
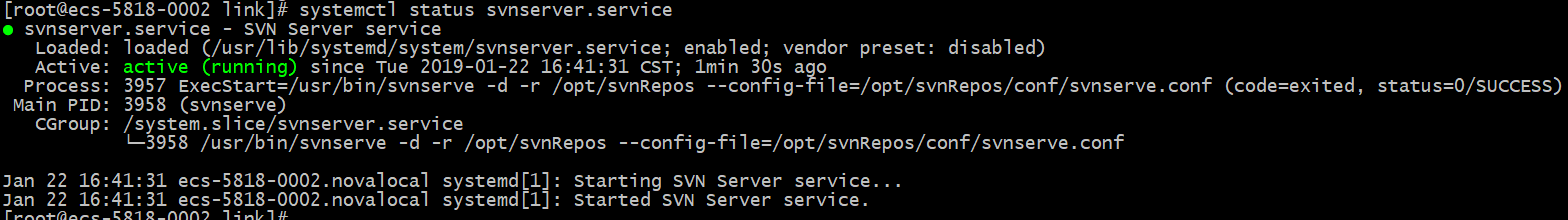
如果shell窗口没有出现错误信息,表示启动已成功,我们可以执行以下命令检查启动状态
systemctl status svnserver.service
运行以下命令停止服务
systemctl stop svnserver.service
我们这时再运行systemctl stop svnserver.service,可以看到服务已经被停掉
至此SVN服务器在Linux服务器安装成功,再次启动CentOS系统后SVN服务器会开机启动。
17、补充
补充一点,CentOS自带的SELinux默认是Enforcing,处于打开状态,对于自启动的SVN服务,会导致客户端访问SVN服务器时出现Permisson Denied的错误,我们需要手动关闭它,修改/etc/selinux/config文件
vim /etc/selinux/config # This file controls the state of SELinux on the system. # SELINUX= can take one of these three values: # enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced. # permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing. # disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded. SELINUX=disabled # SELINUXTYPE= can take one of three two values: # targeted - Targeted processes are protected, # minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected. # mls - Multi Level Security protection. SELINUXTYPE=targeted
把SELINUX从enforcing改为disabled,重启系统,SVN服务自启动后,从客户端访问不再出现Permssion Denied错误。
临时关闭:
setenforce 0

