SQL锁机制 - 基础概念+示例分析
锁机制: 解决因资源共享而出现的并发控制问题
🔒锁机制主要包含两个部分【锁类型 - 对数据集合操作的权力】和【锁粒度 - 操作数据集合的大小】
锁机制的基本概念
示例:买最后一件衣服X A: X 买 : X加锁 ->试衣服...下单..付款..打包 ->X解锁 B: X 买:发现X已被加锁,等待X解锁, X已售空 分类: 🥚操作类型(锁类型): a.读锁(共享锁): 对同一个数据(衣服),多个读操作可以同时进行,互不干扰。 b.写锁(排他锁): 如果当前写操作没有完毕(买衣服的一系列操作),则无法进行其他的读操作、写操作 🥚操作范围(锁粒度\范围): a.表锁 :一次性对一张表整体加锁。如MyISAM存储引擎使用表锁,开销小、加锁快、并发能力小;无死锁;但锁的范围大,容易发生锁冲突、并发度低。 b.行锁 :一次性对一条数据加锁。如InnoDB存储引擎使用行锁,开销大,加锁慢、并发能力大;容易出现死锁;锁的范围较小,不易发生锁冲突,并发度高(很小概率 发生高并发问题:脏读、幻读、不可重复度、丢失更新等问题)。 c.页锁
表锁: -- 自增操作 MySQL/SqlServer支持; oracle需要借助于序列来实现自增
【数据准备】
create table tablelock ( id int primary key auto_increment , name varchar(20) )engine myisam; insert into tablelock(name) values('a1'); insert into tablelock(name) values('a2'); insert into tablelock(name) values('a3'); insert into tablelock(name) values('a4'); insert into tablelock(name) values('a5'); commit; -- 🥗增加锁 lock table 表1 read/write ,表2 read/write ,... mysql> lock table tablelock read; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) -- 🥗查看加锁表 mysql> SHOW OPEN TABLES; +--------------------+----------------------------------------------+--------+-------------+ | Database | Table | In_use | Name_locked | +--------------------+----------------------------------------------+--------+-------------+ | mysql | time_zone_transition_type | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | events_waits_summary_global_by_event_name | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | setup_timers | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | events_waits_history_long | 0 | 0 | | mysql | time_zone_transition | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | mutex_instances | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | events_waits_summary_by_instance | 0 | 0 | | mysql | tables_priv | 0 | 0 | | mysql | procs_priv | 0 | 0 | | mysql | func | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | events_waits_history | 0 | 0 | | mysql | time_zone_name | 0 | 0 | | mysql | user | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | setup_consumers | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | file_instances | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | cond_instances | 0 | 0 | | mysql | plugin | 0 | 0 | | mysql | db | 0 | 0 | | mysql | proxies_priv | 0 | 0 | | mysql | time_zone | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | rwlock_instances | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | events_waits_current | 0 | 0 | | mysql | event | 0 | 0 | | mysql | columns_priv | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | performance_timers | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | threads | 0 | 0 | | mysql | host | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | events_waits_summary_by_thread_by_event_name | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | file_summary_by_event_name | 0 | 0 | | mysql | time_zone_leap_second | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | file_summary_by_instance | 0 | 0 | | learn_demo | tablelock | 1 | 0 | -- ☺ | mysql | servers | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | setup_instruments | 0 | 0 | +--------------------+----------------------------------------------+--------+-------------+ 34 rows in set (0.00 sec)
会话:session :每一个访问数据的dos命令行、数据库客户端工具 都是一个会话
🍎 加读锁🔒
-- 会话1: lock table tablelock read; select * from tablelock; -- 读(查) 可以 delete from tablelock where id = 1; -- 写(增删改) 不可以 select * from emp; -- 读 不可以 delete from emp where id = 1; --- 写(增删改) 不可以 -- 🥐如果一个会话对一个表施加了读锁,则该会话只能对该表进行读的操作不能进行写操作而且也不能对其他的表进行读或写。 -- 会话2: select * from tablelock; -- 读(查) 可以 delete from tablelock where id = 1; -- 写,📌会等待会话1将锁释放 select * from emp; -- 读(查) 可以 delete from emp where id = 1; -- 写 可以 -- 🥐如果某一个会话对A表加了读锁则其他的会话可以对A表进行读的操作但写需要等待A表上的锁释放,其他会话对其他表的读写没有影响。
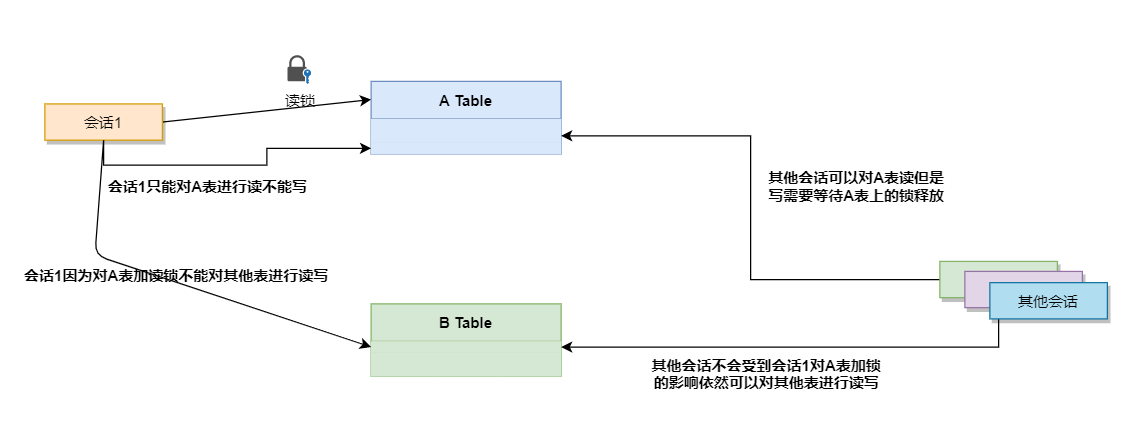
释放锁: UNLOCK TABLES
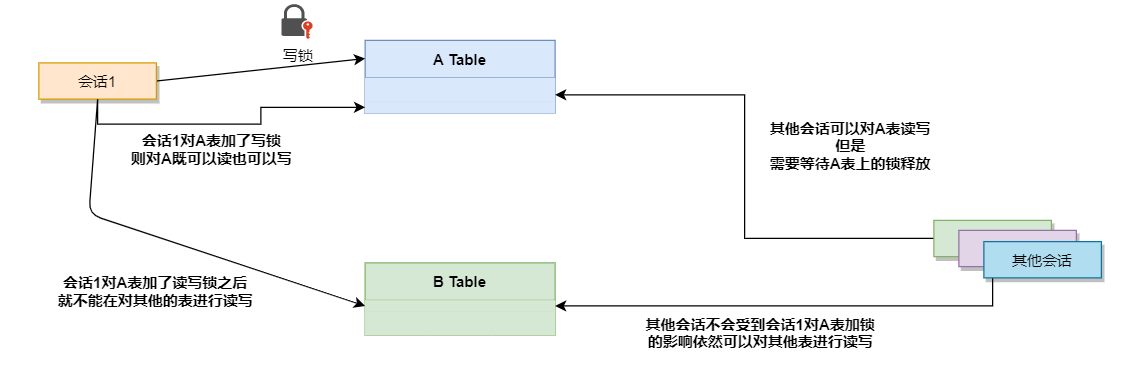
🍎 加写锁🔒
【数据准备】
mysql> LOCK TABLE tablelock WRITE; -- Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> SHOW OPEN TABLES; +--------------------+----------------------------------------------+--------+-------------+ | Database | Table | In_use | Name_locked | +--------------------+----------------------------------------------+--------+-------------+ | mysql | time_zone_transition_type | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | events_waits_summary_global_by_event_name | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | setup_timers | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | events_waits_history_long | 0 | 0 | | mysql | time_zone_transition | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | mutex_instances | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | events_waits_summary_by_instance | 0 | 0 | | mysql | tables_priv | 0 | 0 | | mysql | procs_priv | 0 | 0 | | mysql | func | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | events_waits_history | 0 | 0 | | mysql | time_zone_name | 0 | 0 | | mysql | user | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | setup_consumers | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | file_instances | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | cond_instances | 0 | 0 | | mysql | plugin | 0 | 0 | | mysql | db | 0 | 0 | | mysql | proxies_priv | 0 | 0 | | mysql | time_zone | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | rwlock_instances | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | events_waits_current | 0 | 0 | | mysql | event | 0 | 0 | | mysql | columns_priv | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | performance_timers | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | threads | 0 | 0 | | mysql | host | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | events_waits_summary_by_thread_by_event_name | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | file_summary_by_event_name | 0 | 0 | | mysql | time_zone_leap_second | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | file_summary_by_instance | 0 | 0 | | learn_demo | tablelock | 1 | 0 | | mysql | servers | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | setup_instruments | 0 | 0 | +--------------------+----------------------------------------------+--------+-------------+ 34 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> SELECT * -> FROM tablelock; +----+------+ | id | name | +----+------+ | 1 | a1 | | 2 | a2 | | 3 | a3 | | 4 | a4 | | 5 | a5 | | 6 | wyt | +----+------+ 6 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> UPDATE tablelock -> SET name = "wzz" -> WHERE id = 5; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.03 sec) Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0 mysql> SELECT * -> FROM tablelock; +----+------+ | id | name | +----+------+ | 1 | a1 | | 2 | a2 | | 3 | a3 | | 4 | a4 | | 5 | wzz | | 6 | wyt | +----+------+ 6 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> unlock tables; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) -- 如果一个会话对A表加了写锁,则该会话可以对A表进行读写(增删改查), 其他会话对A表进行读写的前提是A表上的锁释放
👔MySQL表级锁的锁模式
MyISAM在执行查询语句(SELECT)前,会自动给涉及的所有表加读锁,
在执行更新操作(DML)前,会自动给涉及的表加写锁。
所以对MyISAM表进行操作,会有以下情况:
a、对MyISAM表的读操作(加读锁),不会阻塞其他进程(会话)对同一表的读请求,
但会阻塞对同一表的写请求。只有当读锁释放后,才会执行其它进程的写操作。
b、对MyISAM表的写操作(加写锁),会阻塞其他进程(会话)对同一表的读和写操作,
只有当写锁释放后,才会执行其它进程的读写操作。
在执行更新操作(DML)前,会自动给涉及的表加写锁。
所以对MyISAM表进行操作,会有以下情况:
a、对MyISAM表的读操作(加读锁),不会阻塞其他进程(会话)对同一表的读请求,
但会阻塞对同一表的写请求。只有当读锁释放后,才会执行其它进程的写操作。
b、对MyISAM表的写操作(加写锁),会阻塞其他进程(会话)对同一表的读和写操作,
只有当写锁释放后,才会执行其它进程的读写操作。
对表级锁的分析
分析表锁定: 查看哪些表加了锁: show open tables ; 1代表被加了锁 分析表锁定的严重程度: show status like 'table%' ; mysql> SHOW STATUS LIKE "table%"; +-----------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +-----------------------+-------+ | Table_locks_immediate | 49 | | Table_locks_waited | 0 | +-----------------------+-------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) Table_locks_immediate :即可能获取到的锁数 Table_locks_waited:需要等待的表锁数(如果该值越大,说明存在越大的锁竞争) 一般建议: Table_locks_immediate/Table_locks_waited > 5000, 建议采用InnoDB引擎,否则MyISAM引擎
行锁 - InnoDB的锁粒度
【数据准备】
mysql> create table linelock( -> id int(5) primary key auto_increment, -> name varchar(20) -> )engine=innodb ; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) mysql> insert into linelock(name) values('1') ; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.02 sec) mysql> insert into linelock(name) values('2') ; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> insert into linelock(name) values('3') ; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> insert into linelock(name) values('4') ; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> insert into linelock(name) values('5') ; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> SELECT * -> FROM linelock; +----+------+ | id | name | +----+------+ | 1 | 1 | | 2 | 2 | | 3 | 3 | | 4 | 4 | | 5 | 5 | +----+------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
为了研究行级锁,暂时将自动的commit关闭;
SET AUTOCOMMIT = 0; 研究之后需要commit
-- 【行锁 - 操作同一条记录 eg: id = 6】 -- 会话1: 写操作 mysql> INSERT INTO linelock VALUES(6, 'a6');; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> commit; -- 如果一直不commit即结束此事务则造成其他会话无法对该行数据进行读写 -- ★ 💎表锁 是通过unlock tables,也可以通过事务解锁 ; 行锁 是通过事务解锁💎 -- 会话2: 写操作同样的数据 mysql> update linelock set name='ax' where id = 6; -- 总结: 如果会话x对某条数据a进行 DML操作(研究时:关闭了自动commit的情况下),则其他会话必须等待会话x结束事务(commit/rollback)后 才能对数据a进行操作。 -- 【行锁 - 操作不同记录 eg: name = ax 】 会话1: 写操作 insert into linelock values(8,'a8') ; 会话2: 写操作, 不同的数据 update linelock set name='ax' where id = 5; 行锁,一次锁一行数据;因此 如果操作的是不同数据,则不干扰。
🔴 如果没有索引,则行锁会转为表锁
【按理来说,两个会话操作不同的记录相互之间不会发送阻塞的现象但下面的情况发生了阻塞】 会话0: 写操作 update linelock set name = 'ai' where name = '3' ; 会话1: 写操作, 不同的数据 update linelock set name = 'aiX' where name = '4' ; commit -- 📛📛📛 原因:如果索引类 发生了类型转换,则索引失效。 因此 此次操作,会从行锁转为表锁。
行锁的一种特殊情况: 间隙锁
b.行锁的一种特殊情况:间隙锁:值在范围内,但却不存在 --此时linelock表中 没有id=7的数据 update linelock set name ='x' where id >1 and id<9 ; --即在此where范围中,没有id=7的数据,则id=7的数据成为间隙。 间隙:Mysql会自动给 间隙 加索 ->间隙锁。即 本题 会自动给id=7的数据加 间隙锁(行锁)。 行锁:如果有where,则实际加索的范围 就是where后面的范围(不是实际的值) 如何仅仅是查询数据,能否加锁? 可以 for update 研究学习时,将自动提交关闭: set autocommit =0 ; start transaction ; begin ; select * from linelock where id =2 for update ; 通过for update对query语句进行加锁。
👔MySQL行级锁的锁模式
InnoDB默认采用行锁;
缺点: 比表锁性能损耗大。
优点:并发能力强,效率高。
因此建议,高并发用InnoDB,否则用MyISAM。
缺点: 比表锁性能损耗大。
优点:并发能力强,效率高。
因此建议,高并发用InnoDB,否则用MyISAM。
行锁分析:
show status like '%innodb_row_lock%' ; Innodb_row_lock_current_waits :当前正在等待锁的数量 Innodb_row_lock_time:等待总时长。从系统启到现在 一共等待的时间 Innodb_row_lock_time_avg :平均等待时长。从系统启到现在平均等待的时间 Innodb_row_lock_time_max :最大等待时长。从系统启到现在最大一次等待的时间 Innodb_row_lock_waits :等待次数。从系统启到现在一共等待的次数
学而不思则罔,思而不学则殆!





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 写一个简单的SQL生成工具