JUnit-单元测试框架基本使用
参考内容:
单元测试概念
单元测试: 隔离程序部件验证单个部件的正确性(以程序模块为单位比较输出结果和预期结果是否一致)
过程式编程中一个单元:单个程序、函数以及过程。
面向对象编程中一个单元:父类、子类、抽象类中的方法。为了保证程序的正确性每次代码的修改都要执行对应的单元测试以发现程序中错误并进行定位和修复。
Usage and Idioms(用法和风格)
Assertions(断言)
JUnit provide overloaded assertion methods for all primitive types and Objects and arrays
The parameter order is eexpected value followed by actual value.
Optinally the first parameter can be a String message that is output on failure.
*AssertTests.class public class AssertTests { @Test public void testAssertArrayEquals(){ byte[] expected = "trial".getBytes(); byte[] actual = "trail".getBytes(); // 测试两个数组包含的内容是否相同(第一个参数是在不同的情况下即failure时输出的内容) assertArrayEquals("failure - byte arrays not same", expected, actual); } @Test public void testAssertEquals(){ // 测试两个字符串是否相同 assertEquals("failure - strings are not equal", "Java", "Python"); } @Test public void testAssertFalse(){ // 测试是否为false, 如果是false测试成功否则输出测试失败信息 // assertFalse("failure - should be false", true); java.lang.AssertionError: failure - should be false assertFalse("failure - shoudl be false", false); // assertTrue("error: msg", boolean val); 测试是否为true } @Test public void testAssertNotNull(){ assertNotNull("should not be null", null); // java.lang.AssertionError: should not be null // assertNotNull("should not be null", new Object()); } @Test public void testAssertNotSame(){ // assertNotSame("should be the same object", new Object(), new Object()); } @Test public void testAssertSame(){ Integer aNumber = Integer.valueOf(768); assertSame("should be same", aNumber, 123); // java.lang.AssertionError: should be same expected same:<768> was not:<123> } @Test public void testAssertThatBothContainsString(){ // JUnit Matchers assertThat assertThat("username: wangzz", both(containsString("username")).and(containsString("wangzz"))); } @Test public void testAssertThatHasItems(){ assertThat(Arrays.asList("one", "two", "three"), hasItems("one", "three")); } @Test public void testAssertThatEveryItemContainsString(){ assertThat(Arrays.asList(new String[]{"fun", "ban", "net"}), everyItem(containsString("n"))); } // Core Hamcrest Matchers with assertThat @Test public void testAssertThatHamcrestCoreMatchers(){ assertThat("good", allOf(equalTo("good"), startsWith("good"))); }
@RunWith annotation
When a class is annotated with
@RunWithor extends a class annotated with@RunWith, JUnit will invoke the class it references(调用它所引用的类) to run the tests in that class instead of the runner built into JUnit.
* JavaDoc for @RunWith http://junit.org/javadoc/latest/org/junit/runner/RunWith.html
* The default runner is BlockJUnit4ClassRunner which supersedes the older JUnit4ClassRunner.
* Annotating a class with@RunWith(JUnit4.class)will always invoke the deault JUnit 4 runner in the current version of JUnit.
Specialized Runners
Suite[swi:t](套件)
测试套件用于批量运行测试类
Suiteis a standard runner that allows you to mannually build a suite containing tests from many classses.<a href='http:/junit.org/javadoc/latest/org/junit/runners/Suite.html
注意事项
随着项目进度的开展,单元测试类会越来越多,为了实现自动化批量处理,JUnit提供了一种批量运行测试类的方法,叫做测试套件。
每次需要验证系统功能正确性的时候,只执行一个或几个测试套件便可以了。
遵循的规则:
- 创建一个空类作为测试套件的入口。
- 使用注解org.junit.runnerRunWith 和 org.junit.runners.Suite.SuiteClasses修饰这个空类。
- 将org.junit.runners.Suite作为参数传入注解RunWith,以提示JUnit为此类使用套件运行器执行。
- 将需要放入此测试套件的测试类组成数组作为注册SuiteClassess的参数。
- 保证这个空类使用public修饰,而且存在公开的不带有任何参数的构造函数。
Aggregating tests in suites
Using
Suiteas a runner allows you to manually build a suite containing tests from many classes.
To use it, annotate a class with@RunWith(Suite.class)and@SuiteClasses(TestClass1.class, ...). When you run this class, it will run all the tests in all the suite classes.
Example
Note the
@RunWithannotation, with specifies that the JUnit4 test runner to use isorg.junit.runners.Suitefor running this particular test class. This works in conjunction with the@Suite.SuiteClassesannotation, which tells the Suite runner which test classes to include in this suite and in which order.(它告诉套件运行程序在这个套件中包含哪些测试类以及以什么顺序包含。)
* TestFeatureLogin.class public class TestFeatureLogin{ public TestFeatureLogin(){} @Test public void testAssertThatBothContainsUsername(){ assertThat("username: wangzz", both(containsString("username")) .and(containsString("wangzz"))); } } *TestFeatureLogout.class public class TestFeatureLogout{ public TestFeatureLogout(){} @Test public void testAssertEquals(){ assertEquals("退出应用失败!","0","0"); } } *TestFeatureNavigate.class public class TestFeatureNavigate{ public TestFeatureNavigate(){} @Test public void testAssertTrue(){ assertTrue("导航失败!",true); } } *TestFeatureUpdate.class public class TestFeatureUpdate{ public TestFeatureUpdate(){} @Test public void testFeatureUpdate(){ assertNotNull("数据获取失败", new Object()); } } *TestFeatureSuite.class import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.junit.runners.Suite; @RunWith(Suite.class) @Suite.SuiteClasses({ TestFeatureLogin.class, TestFeatureLogout.class, TestFeatureNavigate.class, TestFeatureUpdate.class }) public class TestFeatureSuite { } *TestRunner.class import org.junit.runner.JUnitCore; import org.junit.runner.Result; import org.junit.runner.notification.Failure; public class TestRunner { public static void main(String[] args) { Result result = JUnitCore.runClasses(TestFeatureSuite.class); for(Failure failure : result.getFailures()){ System.out.println(failure.toString()); } System.out.println(result.wasSuccessful()); } } ===》输出 true
Parameterized(参数化)
Parameterizedis a standard runner that implements parameterized tests.When running a parameterized test class, instances are created for the cross-product of the test methods and the test data elements.
Parameterized Tests
Example
*Fibonacci.class public class Fibonacci { public static int compute(int n){ if(n <= 1){ return n; } return n * compute(n - 1); } } *FibonacciTest.class @RunWith(Parameterized.class) public class FibonacciTest { @Parameterized.Parameters public static Collection<Object[]> data(){ return Arrays.asList(new Object[][]{ {0, 0}, {1, 1}, {2, 1}, {3, 2}, {4, 3}, {5, 5}, {6, 8} }); } private int fInput; private int fExpected; public FibonacciTest(int input, int expected){ this.fInput = input; this.fExpected = expected; } @Test public void testAssertEquals(){ assertEquals(fExpected, Fibonacci.compute(fInput)); } } ===》输出 java.lang.AssertionError: Expected :1 Actual :2 <Click to see difference> java.lang.AssertionError: Expected :2 Actual :6 <Click to see difference> java.lang.AssertionError: Expected :3 Actual :24 <Click to see difference> java.lang.AssertionError: Expected :5 Actual :120 <Click to see difference> java.lang.AssertionError: Expected :8 Actual :720 <Click to see difference>
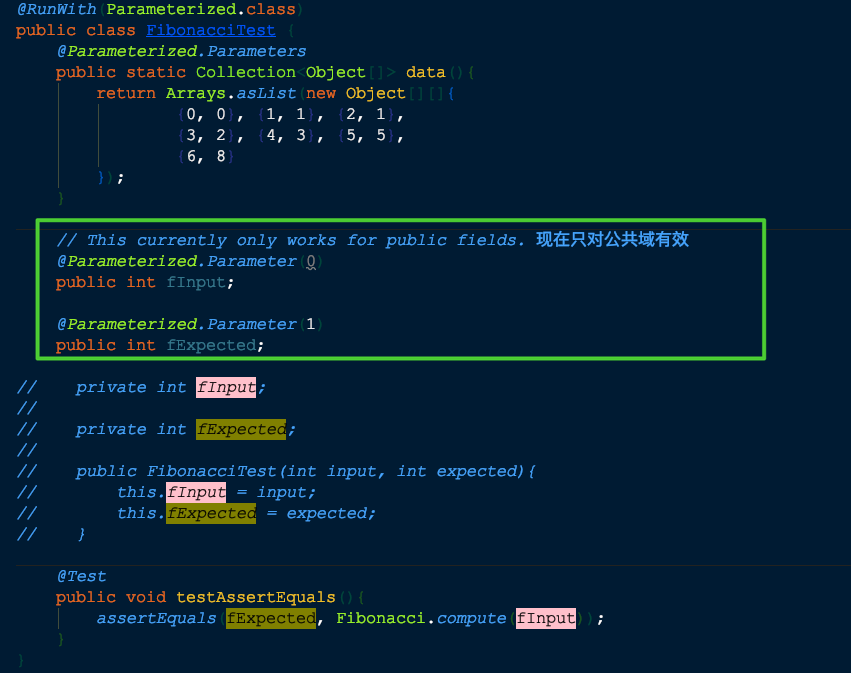
Using @Parameter for Field injection instead of Constructor
It is also possible to inject data values directly into fields without needing a constructor using the @Parameter annotation.
Tests with single parameter (使用单独参数测试)
If your test needs a single parameter only, you do not have to wrap it with an array. Instead you can provide an Iterable or an array of objects.
@Parameters public static Iterable<? extends Object> data(){ return Arrays.asList("first test", "second test"); }
or
@Parameters public static Object[] data(){ return new Object[] {"first test", "second test"}; }
Identify Individual test cases
In order to easily identify the individual test cases in a Parameterized test, you may provide a name using the @Parameters annotation. This name is allowed to contain placeholders that are replaced at runtime: (此名称允许包含在运行时被替换的占位符)
{index}: the current parameter index{0}, {1}, ...: the first, second, and so on, parameter value. NOTE: single quotes`should be escaped as two single quotes''.
Example
@RunWith(Parameterized.class) public class FibonacciTest { @Parameterized.Parameters(name = "{index}: fib({0})={1}") public static Iterable<Object[]> data(){ return Arrays.asList(new Object[][]{ {0, 0}, {1, 1}, {2, 1}, {3, 2}, {4, 3}, {5, 5}, {6, 8} }); } private int input; private int expected; public FibonacciTest(int input, int expected){ this.input = input; this.expected = expected; } @Test public void test(){ assertEquals(expected, Fibonacci.compute(input)); } }





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 写一个简单的SQL生成工具