Javadoc使用
Javadoc工具:一种用于从源代码中的文档注释生成HTML格式的API文档的工具。
Javadoc作用: 用来描述类和方法的作用
Javadoc工具详述
| Title | Desc |
|---|---|
| Javadoc版本 | 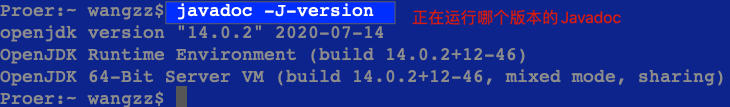 |
| Javadoc工作原理 | Javadoc在Java编译器(Java Compiler)下调用javac的一部分来编译代码,保留声明和doc注释,但放弃实现。它构建一个解析树,然后从中生成HTML。 |
| Javadoc工具用法 | 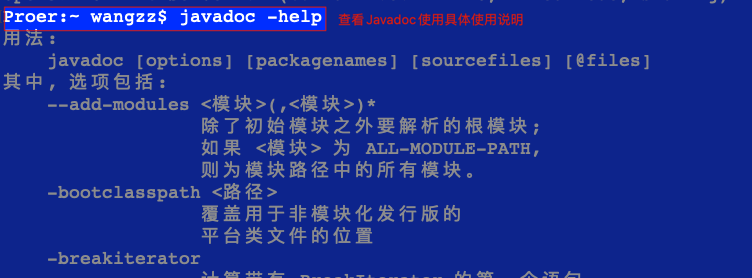 |
Javadoc文档生成
第一种通过Java命令行生成文档
命令: javadoc -d [文档存放目录] -author:[显示作者] -version:[显示版本] [源文件所在文件包以及文件名]
- 源代码
package ink.openmind.base; import java.io.IOException; /** * 测试Javadoc工具使用 * ClassName: HelloWorld * Date: 2020/9/10 3:22 下午 * @author Wangzhuang2 * @version 1.0.1 * @since 1.0 */ public class HelloWorld { /** * 返回用户指定信息 bla bla bla ... * @author wangzhuang2 * @param username 用户名称 * @throws IOException If an input or output exception occurred * @return 返回信息 * @see #submitInfo(String) * @since 1.0 * */ public String getInfo(String username)throws IOException { return "用户名称: " + username; } /** * 提交用户信息 * @author wangzhuang2 * @param username 用户名称 * @since 1.0 * */ public void submitInfo(String username){ } }
- 执行命令
javadoc -d /users/wz/demoapi -header Javadoc测试 -doctitle 文档注释 -version -author HelloWorld.java 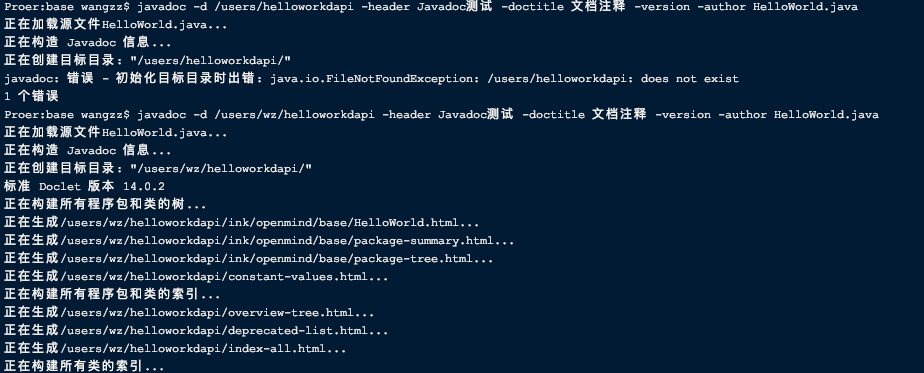
- 执行结果
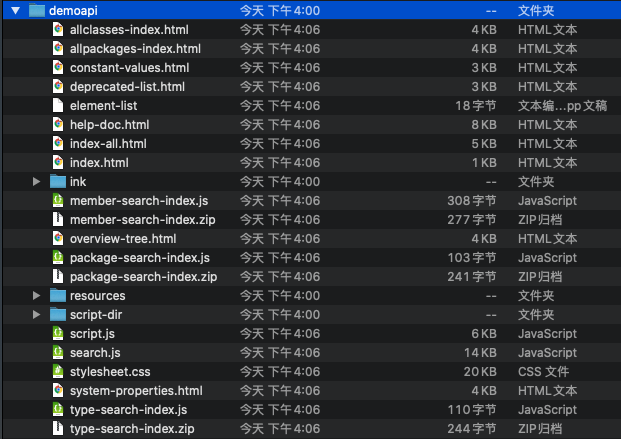
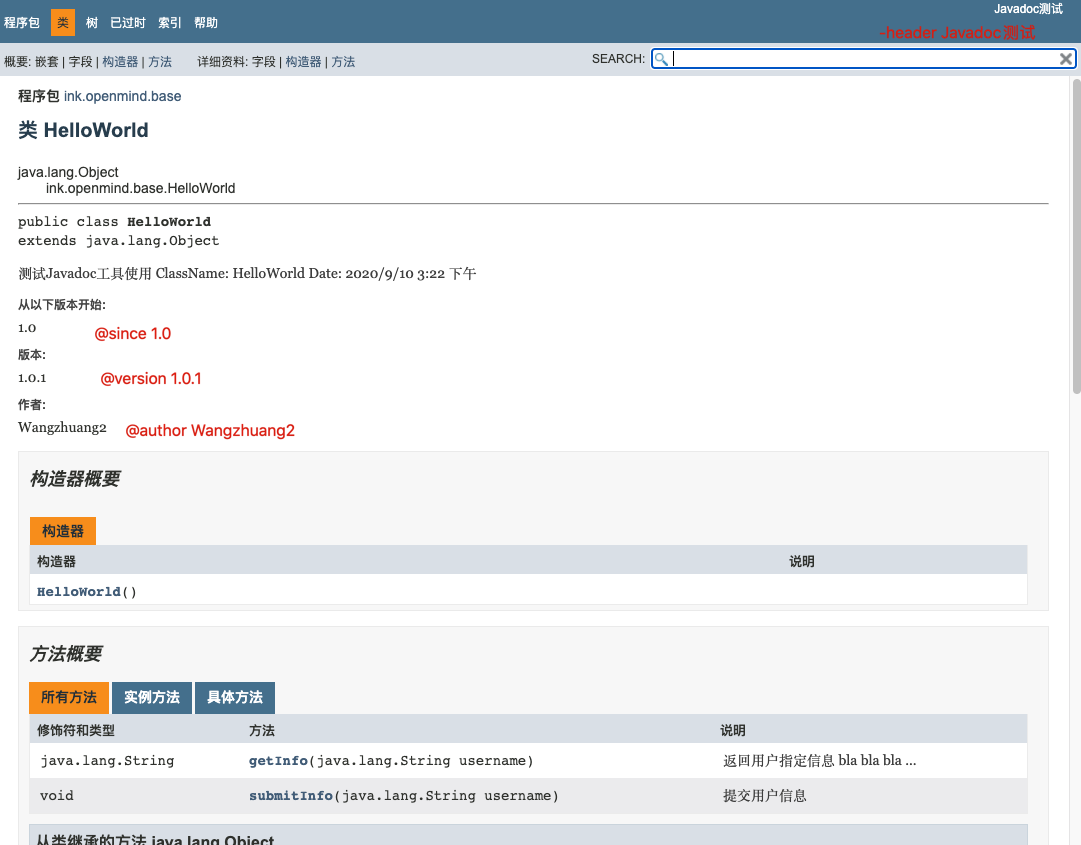
- 文档API展示
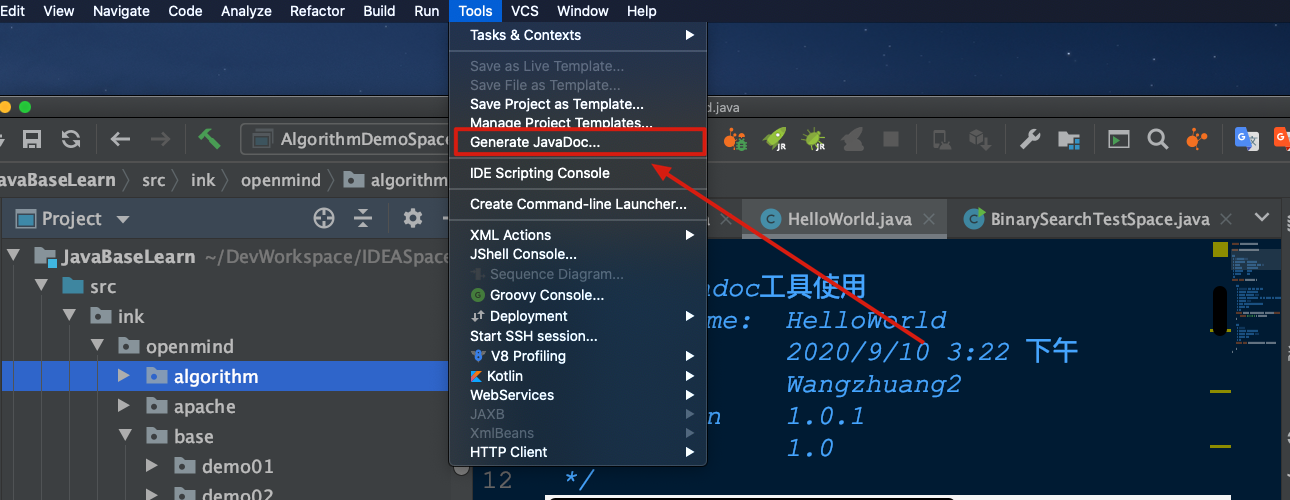
第二种通过IDEA工具生成文档
- Generate Javadoc
- 配置属性

Javadoc文档编写指南
文档编写注意项
1.文档注释 : Java源代码中由/** ....... */分隔符分隔的特殊注释,Javadoc工具处理此种注释内容生成API文档工具
2.文档注释位置:必须在类、字段、构造函数、方法声明之前
3.文档注释组成: 块标记(@param、@return ...) + 描述
4.文档注释开头第一行是注释定界符:
/** * bla bla bla ... */
5.文档注释第一句应为摘要句,包含对API项的简洁但完整的描述。
6.JavaDoc自动重复使用方法注释(使用场景如下)
- 当类中的方法覆盖超类中的方法时(生成一个子标题“ Overrides” m()) - 当接口中的方法覆盖超级接口中的方法时 (生成一个子标题“ Overrides” m()) - 当类中的方法在接口中实现方法时 (“ Specified by” m())
7.对关键字和名称使用<code>...</code>> Eg: Java关键字、包装名称、类名、方法名称、接口名称、参数名称、代码实例
8.为了简洁尽量使用短语而非句子(尤其是初始摘要和@param标记中)
9.使用第三人称描述而不是第一人称
运用第三人称即以第三者的身份来叙述,能比较直接客观地展现丰富多彩的生活,不受时间和空间限制,反映现实比较灵活自由。 1、第一人称:我、我du们。 2、第二人称:你、你们。 3、第三人称:除“我,我们,你,你们”的其他主语, 是指你谈论的不在现场的人称代词 如"他", "她" ,"他们"
10.方法描述以动词短语开头,(方法实现操作 eg: Get the value of the input text)
11.记录默认构造函数,代码中所有构造函数都应该是显式的,显式声明有助于防止类被无意中实例化。> 在创建显式构造函数时,它必须与自动生成的构造函数的声明完全匹配;即使在逻辑上应该保护构造函数,也必须将其公开以匹配自动生成的构造函数的声明,以实现兼容性。然后应提供适当的文档注释。
/** * Sole constructor. (For invocation by subclass * constructors, typically implicit.) */ protected AbstractMap() { }
12.类/接口/字段描述可以省略主题而仅声明对象
private int username; // 用户名 ✅ private int username; // 这个字段是用户名 ❌
13.在API名称之外添加说明最好的API名称是具有“自我描述性”,如果doc注释仅以句子形式重复API名称,则不会提供更多信息。
避免以下
/** * Sets the tool tip text. * * @param text the text of the tool tip */ public void setToolTipText(String text) {
首选以下 (在具体方法功能之上从系统功能层面来阐述该方法的作用 - 宏观角度)
/** * Registers the text to display in a tool tip. The text * displays when the cursor lingers over the component. * * @param text the string to display. If the text is null, * the tool tip is turned off for this component. */ public void setToolTipText(String text) {
14.pre元素可定义预格式化的文本。被包围在pre元素中的文本通常会保留空格和换行符。而文本也会呈现为等宽字体,pre标签的一个常见应用就是用来表示计算机的源代码
15.必要标签每个参数都需要一个@param标记除了构造函数和void类型都需要一个@return标记
使用多个标签的顺序,当标签在文档注释中多次出现,如何排序要参考以下约定
- 按时间顺序列出多个
@author标签,并在顶部列出该类的创建者。 - 多个
@param按照参数声明顺序列出。 - 多个
@throws or @exception按照异常名称中首字母的顺序 - 多个
@see由近到远
@see #field @see #Constructor(Type, Type...) @see #Constructor(Type id, Type id...) @see #method(Type, Type,...) @see #method(Type id, Type, id...) @see Class @see Class#field @see Class#Constructor(Type, Type...) @see Class#Constructor(Type id, Type id) @see Class#method(Type, Type,...) @see Class#method(Type id, Type id,...) @see package.Class @see package.Class#field @see package.Class#Constructor(Type, Type...) @see package.Class#Constructor(Type id, Type id) @see package.Class#method(Type, Type,...) @see package.Class#method(Type id, Type, id) @see package
🏷 标签概要(⚠️遵守以下标签的顺序约定)
| 标签名称 | 标签描述描述 | 标签使用场景 |
|---|---|---|
@author |
作者标识 | 类和接口是必需的 |
@version |
版本号 | 类和接口是必需的 |
@param |
方法参数描述 | 仅方法和构造函数 |
@return |
方法返回值描述 | 仅方法 |
@exception |
方法异常描述 | 和@throws是Javadoc 1.2中同义词 |
@see |
引用其他类 | 通过@see标签链接到其他文档 |
@since |
从下一个版本开始 | 标记文件创建时项目对应组件版本 |
@deprecated |
不推荐使用方法 |
🏷 标签详述
@author 标签一般作用在: 概述、包以及类级别上,仅适用于对设计或实现具有重大实际贡献的成员(如果作者不明可以使用 "unscribed"作为 @author的参数)
// 纯文本作者 @author Wangzhuang2 // 纯文本作者,邮件 @author Wangzhuang2, wz_bepro@163.com // 超链接 纯文本作者 @author <a href="mailto:wz_bepro@163.com">Wangzhuang2</a> // 纯文本邮件 @author wz_bepro@163.com // 纯文本 组织 @author Apache Software Foundation // 超链接组织地址 纯文本组织 @author <a href="https://jakarta.apache.org/turbine"> Apache Jakarta Turbine</a>
@version 标签的参数约定为SCCS字符串 %I%,%G%
@param 标签后跟参数的名称(不是数据类型),后跟上参数描述。参数名称按惯例小写
* 写短语时,请忽大写且不要以句号结尾 @param x the x-coordinate, measured in pixels * 在写一个短语后接一个句子时,不要将其大写,要在句号结尾将其与下一个句子的开头区分开 @param x the x-coordinate. Measured in pixels * 以句子开头,则将其大写并以句号结尾 @param x Specifies the x-coordinate, measured in pixels. * 写多个句子时,遵循正常句子规则 @param x Specifies the x-coordinate. Measured in pixels.
@return 对于返回void的方法和构造函数不要使用,拥有一个明确的@return标记可以使某人更容易快速地找到返回值。尽可能提供特殊情况的返回值(例如,指定提供越界参数时返回的值)。
/** * @return {@code true} if the {@code String} is not {@code null}, its */ public static boolean hasText(@Nullable String str){}
@deprecated描述告诉用户何时不推荐使用API,以及用什么代替,解释为什么不推荐使用它。
- 在为已弃用的API生成描述时,Javadoc工具会将@deprecated文本移到描述之前,将其以斜体显示,并在其前面加粗体警告:“ Deprecated”。 - 对于Javadoc 1.2和更高版本使用<code>@deprecated</code>标签和嵌入式<code>{@link}</code>的正确使用模板 /** * @deprecated As of JDK 1.1, replaced by * {@link #setBounds(int,int,int,int)} */
@since 从以下版本开始,一般用于标记文件创建时项目当时对应的版本,一般后面跟版本号,也可以跟是一个时间,表示文件当前创建的时间
package java.util.stream; /** * @since 1.8 */ public interface Stream<T> extends BaseStream<T, Stream<T>> {} package org.springframework.util; /** * @since 16 April 2001 */ public abstract class StringUtils {}
@throws (@exception是原始标记)
/** * @throws IllegalArgumentException when the given source contains invalid encoded sequences */ public static String uriDecode(String source, Charset charset){}
@value用于标注在常量上,{@value}用于表示常量的值
/** 默认数量 {@value} */ private static final Integer QUANTITY = 1;
@inheritDoc 用于注解在重写方法或子类上,用于继承父类中的JavaDoc
- 基类的文档注释被继承到了子类 - 子类可以再加入自己的注释(特殊化扩展) - @return @param @throws 也会被继承
{@link 包名.类名#方法名(参数类型)} 用于快速链接到相关代码
// 完全限定类名 {@link java.lang.Character} // 省略包名 {@link String} // 省略类名,表示指向当前的某个方法 {@link #length()} // 包名.类名.方法名(参数类型) {@link java.lang.String#getInfo(int)}
{@code text} 将文本标记为code会被解析为 ``` text , 在code内部使用<、>等不会解释成HTML标签
// 类名 {@code HelloWorld} // 方法名 {@code getInfo()}
详细标签: <p> 、<pre>、<a>、<ul>、<i>等标签的使用(其中p标签通常用于详细描述),详细描述和概要描述通常有一个空行来分隔
package org.springframework.util; /** * Miscellaneous {@link String} utility methods. * * <p>Mainly for internal use within the framework; consider * <a href="http://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-lang/">Apache's Commons Lang</a> * for a more comprehensive suite of {@code String} utilities. * * <p>This class delivers some simple functionality that should really be * provided by the core Java {@link String} and {@link StringBuilder} * classes. It also provides easy-to-use methods to convert between * delimited strings, such as CSV strings, and collections and arrays. * */ public abstract class StringUtils {
文档注释示例
/** * Graphics is the abstract base class for all graphics contexts * which allow an application to draw onto components realized on * various devices or onto off-screen images. * A Graphics object encapsulates the state information needed * for the various rendering operations that Java supports. This * state information includes: * <ul> * <li>The Component to draw on * <li>A translation origin for rendering and clipping coordinates * <li>The current clip * <li>The current color * <li>The current font * <li>The current logical pixel operation function (XOR or Paint) * <li>The current XOR alternation color * (see <a href="#setXORMode">setXORMode</a>) * </ul> * <p> * Coordinates are infinitely thin and lie between the pixels of the * output device. * Operations which draw the outline of a figure operate by traversing * along the infinitely thin path with a pixel-sized pen that hangs * down and to the right of the anchor point on the path. * Operations which fill a figure operate by filling the interior * of the infinitely thin path. * Operations which render horizontal text render the ascending * portion of the characters entirely above the baseline coordinate. * <p> * Some important points to consider are that drawing a figure that * covers a given rectangle will occupy one extra row of pixels on * the right and bottom edges compared to filling a figure that is * bounded by that same rectangle. * Also, drawing a horizontal line along the same y coordinate as * the baseline of a line of text will draw the line entirely below * the text except for any descenders. * Both of these properties are due to the pen hanging down and to * the right from the path that it traverses. * <p> * All coordinates which appear as arguments to the methods of this * Graphics object are considered relative to the translation origin * of this Graphics object prior to the invocation of the method. * All rendering operations modify only pixels which lie within the * area bounded by both the current clip of the graphics context * and the extents of the Component used to create the Graphics object. * * @author Sami Shaio * @author Arthur van Hoff * @version %I%, %G% * @since 1.0 */ public abstract class Graphics { /** * Draws as much of the specified image as is currently available * with its northwest corner at the specified coordinate (x, y). * This method will return immediately in all cases, even if the * entire image has not yet been scaled, dithered and converted * for the current output device. * <p> * If the current output representation is not yet complete then * the method will return false and the indicated * {@link ImageObserver} object will be notified as the * conversion process progresses. * * @param img the image to be drawn * @param x the x-coordinate of the northwest corner * of the destination rectangle in pixels * @param y the y-coordinate of the northwest corner * of the destination rectangle in pixels * @param observer the image observer to be notified as more * of the image is converted. May be * <code>null</code> * @return <code>true</code> if the image is completely * loaded and was painted successfully; * <code>false</code> otherwise. * @see Image * @see ImageObserver * @since 1.0 */ public abstract boolean drawImage(Image img, int x, int y, ImageObserver observer); /** * Dispose of the system resources used by this graphics context. * The Graphics context cannot be used after being disposed of. * While the finalization process of the garbage collector will * also dispose of the same system resources, due to the number * of Graphics objects that can be created in short time frames * it is preferable to manually free the associated resources * using this method rather than to rely on a finalization * process which may not happen for a long period of time. * <p> * Graphics objects which are provided as arguments to the paint * and update methods of Components are automatically disposed * by the system when those methods return. Programmers should, * for efficiency, call the dispose method when finished using * a Graphics object only if it was created directly from a * Component or another Graphics object. * * @see #create(int, int, int, int) * @see #finalize() * @see Component#getGraphics() * @see Component#paint(Graphics) * @see Component#update(Graphics) * @since 1.0 */ public abstract void dispose(); /** * Disposes of this graphics context once it is no longer * referenced. * * @see #dispose() * @since 1.0 */ public void finalize() { dispose(); } }
学而不思则罔,思而不学则殆!
分类:
Java





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 写一个简单的SQL生成工具