面向切面的Spring -- 《Spring In Action》
简介
软件系统中像日志、事务以及安全等功能是必不可少,按照传统可以由应用对象主动发起调用但如何每个模块都发起此类共同的调用将带来大量重复性代码且与核心业务逻辑脱离,AOP通过横切关注点模块化让应用对象只关注自己的业务领域问题。
散步在各个业务模块多处的功能(辅助功能)称之为横切关注点(cross-cutting concern)(横切关注点是与应用的业务逻辑相互分离的,但会直接嵌入到应用业务逻辑之中)
AOP解决的问题: 将横切关注点与业务逻辑相分离
什么是面向切面编程
- 切面:实现模块化横切关注点(横切关注点被描述为影响应用多处的功能)
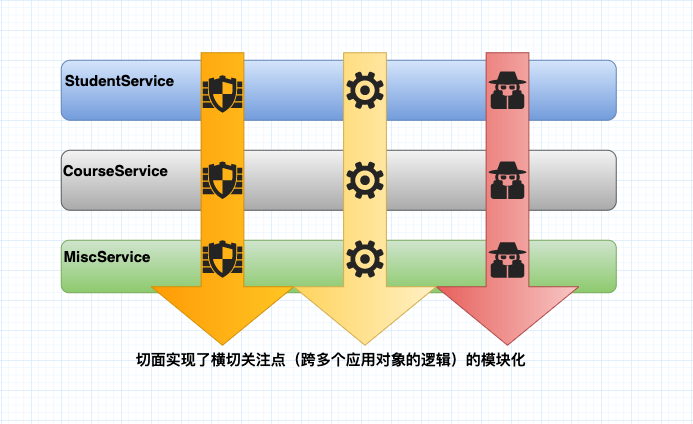
每个模块的核心功能都是为特定业务领域提供服务,但是这些模块中需要提供一些辅助功能(日志、安全、事务管理、缓存)
在OO中,继承(inheritance)和委托(delegation)是实现重用的主要技术,但继承导致脆弱的继承体系;委托导致复杂的对象调用,切面是重用技术实现的另一方案。
AOP中,在一个地方定义通用功能,通过【声明的方式】定义这些功能要以何种方式在何处应用,而无需修改受影响的类。
横切关注点可以被模块化为特殊的类,这些类称之为切面(aspect)
- 面向切面编程的好处:
1. 对于切面来说将关注点统一管理而非散乱到多处代码中。
2. 对于业务模块来说只包含主要关注点代码次要关注点代码集成到切面中。
AOP术语
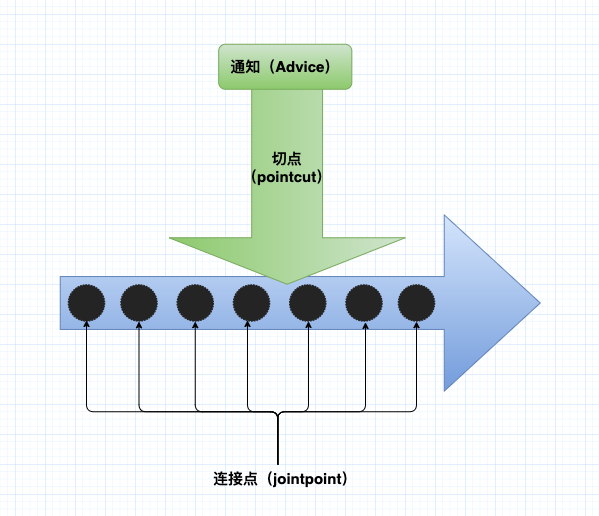
通知(Advice): 通知定义了切面要完成的工作以及何时执行工作
切面的工作应用在某个方法调用之前还是之后还是抛出异常时调用?
- Spring存在5中类型的通知
1.前置通知(Before):目标方法执行之前调用通知
2.后置通知(After):目标方法执行之后调用通知
3.返回通知(After-returning):目标方法成功执行之后调用通知
4.异常通知(After-throwing):目标方法抛出异常后调用通知
5.环绕通知(Around):目标方法执行之前之后调用通知
切入点(pointcut):切点定义了切面要完成的地方
切点的定义会织入一个或多个连接点。通常使用明确的类和方法名称,或是利用正则表达式定义所匹配的类和方法名称来指定切面执行的场所
连接点(joinpoint):连接点是指应用执行过程中能够插入切面的一个点。
连接点可以调用方法时、抛出异常时、甚至修改一个字段时。切面代码利用连接点插入到应用的正常流程之中并添加新的行为
切面(Aspect):是通知(切面是什么和什么时候执行)和切点(切面执行的场所)的结合(切面是模块化横切关注点集成到特殊的类)
切面是通知和切点的结合。通知和切点共同定义了切面的全部内容—— 切面是什么、什么时候执行以及执行的场所。
引入(Introduction):增加切面的工作
引入是向现有的类添加新方法或属性。
织入(Weaving):将切面应用到目标对象的过程
织入是把切面应用到目标对象并创建新的代理对象的过程。切面在指定的连接点织入到目标对象中。
在目标对象的生命周期中有多个点可以进行织入:
- 编译器: 切面在目标类编译时被织入。
- 类加载期:切面在目标类加载到JVM时被织入。在目标类被引入应用之前增强该目标类的字节码。
- 运行期:切面在App运行的某个时刻被织入。在织入切面时,AOP容器会为目标对象动态地创建一个代理对象。
通知包含多个应用对象的横切行为
连接点是程序执行过程中能够应用通知的所有点
切点定义了通知被应用的具体位置(在哪些连接点)
切点定义了哪些连接点会得到通知
Spring对AOP的支持
无论什么支持根本上: 创建切点来定义切面织入的连接点是AOP框架的基本功能;
- Spring存在4类型对AOP支持:
- 基于代理的经典Spring AOP;
- 纯POJO切面;
- @ApsectJ注解驱动的切面;
- 注入式AspectJ切面;
Spring的aop命名空间可以将纯POJO转换为切面
Spring提供更简洁和干净的AOP方式,引入简单的声明式AOP和基于注解的AOP将AOP的实现更加高效
Spring借鉴ApsectJ的切面,以提供注解驱动的AOP
编写Spring通知
- Spring 通知均有标准Java类编写
- 定义通知的切入点是通过注解或Spring配置文件采用XML编写
Spring在运行时通知对象
Spring在运行期把切面织入到Spring管理的bean中*
当代理拦截到方法调用时,在调用目标bean方法之前,会执行切面逻辑。知道应用需要被代理的bean时,Spring才创建代理对象。
Spring只支持方法级别的连接点
Spring基于动态代理,所以Spring只支持方法连接点
通过切点来选择连接点
在Spring AOP中使用AspectJ的切点表达式语言来定义切点。
| AspectJ指示器 | 描述 |
|---|---|
arg() |
限制连接点匹配参数为指定类型的执行方法 |
@args() |
限制连接点匹配参数为指定注解标注的执行方法 |
execution |
用于匹配是连接点的执行方法 |
this() |
匹配AOP代理的bean引用为指定类型的类 |
target |
匹配目标对象为指定类型的类 |
@target |
匹配特定的执行对象,这些对象对应的类具有指定类型的注解 |
within() |
限制连接点匹配指定的类型 |
@within() |
限制连接点匹配指定注解所标注的类型 |
@annotation() |
限定匹配带有指定注解的连接点 |
上述Spring支持的指示器只有execution指示器是实际执行匹配的,而其他的指示器都是用来限制匹配的。
execution指示器是编写切点定义时最主要使用的指示器。
编写切点
定义一个Performance接口
package concert; public interface Performance{ public void perform(); }
Performance代表任何类型的现场表演,如果编写Performance的perform()方法触发的通知

上图使用AspectJ切点表达式来选择Performance的perform()方法作为切点
-> 假设需要配置的切点仅匹配concert包,可以使用within()指示器来限制匹配,使用&&操作符把execution()和within()指示器连接在一起形成“与”关系,使用”||”操作符来标识“或,or”关系,使用“!"操作符来标识非(not)操作

在切点选择bean
Spring引入bean()指示器,bean()使用bean ID或bean名称作为参数来限制切点只匹配特定的bean
-
编织到特定的bean

-
编织到所有bean但排除特定的bean

使用注解创建切面
使用注解来创建切面是AspectJ 5所引入的关键特性,AspectJ面向注解的模型可以通过简单少量的注解将任意类转变为切面
定义切面
假设将观众定义为切面
package ink.openmind.mywebapp.concert; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; /** * ClassName: Audience * Function: * Date: 2020/9/1 7:55 上午 * author Wangzhuang2 * version V1.0 * TODO: */ @Aspect // 表明Audience不仅是一个POJO还是一个切面(Audience类中的方法使用注册来定义切面具体行为) public class Audience { @Before("execution(* ink.openmind.mywebapp.concert.Performance.perform(..))") public void silenceCellPhones(){ System.out.println("在演出开始之前要把手机设置为静音🔇!"); } @Before("execution(* ink.openmind.mywebapp.concert.Performance.perform(..))") public void takeSeats(){ System.out.println("找好座位💺"); } @AfterReturning("execution(* ink.openmind.mywebapp.concert.Performance.perform(..))") public void applause(){ System.out.println("👏👏👏👏👏👏👏"); } @AfterThrowing("execution(* ink.openmind.mywebapp.concert.Performance.perform(..))") public void demandRefund(){ System.out.println("在未能进行表演的情况下,申请退款!!!"); } }
可以看到切点表达式重复了四遍如何解决重复可以通过@Pointcut注解在一个@AspectJ切面内定义可重用的切点。
@Aspect // 表明Audience不仅是一个POJO还是一个切面(Audience类中的方法使用注册来定义切面具体行为) public class Audience { @Pointcut("execution(* ink.openmind.mywebapp.concert.Performance.perform(..))") public void performance(){} @Before("performance()") public void silenceCellPhones(){ System.out.println("在演出开始之前要把手机设置为静音🔇!"); } @Before("performance()") public void takeSeats(){ System.out.println("找好座位💺"); } @AfterReturning("performance()") public void applause(){ System.out.println("👏👏👏👏👏👏👏"); } @AfterThrowing("performance()") public void demandRefund(){ System.out.println("在未能进行表演的情况下,申请退款!!!"); } }
在Audience中,performance()方法使用@Pointcut注解,为@Pointcut注解设置一个切点表达式。通过在performance()方法上添加@Pointcut注解,扩展了切点表达式语言可以在任何切点表达式中使用performance()
如何开启切面注解
第一种通过JavaConfig中启用AspectJ注解的自动代理
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy; /** * 在JavaConfig中启用ApsectJ注解的自动代理 * */ @Configuration @EnableAspectJAutoProxy // 启用AspectJ自动代理 @ComponentScan public class ConcertConfig { @Bean // 声明Audience Bean public Audience audience(){ return new Audience(); } }
第二种使用XML开启AspectJ注解
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="ink.openmind.myWebApp.concert"/> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/> <!-- 启用AspectJ代理 --> <bean class="ink.openmind.myWebApp.concert.Audience"/> <!-- 声明Audience bean --> </beans>
无论是JavaConfig还是XML实现注解,AspectJ都会使用
@Aspect注解的bean创建一个代理,这个代理围绕着所有该切面的切点所匹配的bean,会为Concert bean创建代理,Audience类中的方法根据通知注解的类型在performance()执行之前或后执行
创建环绕通知
环绕通知是最为强大的通知,可以让编写的逻辑将被通知的目标方法完全包装起来。(在一个通知方法中处理前置通知、后置通知、返回通知、异常通知)
@Pointcut("execution(* ink.openmind.mywebapp.concert.Performance.perform(..))") public void performance(){} @Around("performance()") // @Around表明watchPerformance()方法会作为performance()切点的环绕通知 public void watchPerfromance(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){ try{ System.out.println("Silencing cell phones"); System.out.println("Taking seats"); joinPoint.proceed(); // 当要将控制权交给被通知的方法时需要调用ProceedingJoinPoint的proceed()方法 System.out.println("CLAP CLAP CLAP CLAP"); }catch (Throwable throwable){ System.out.println("Demanding a refund!"); } }
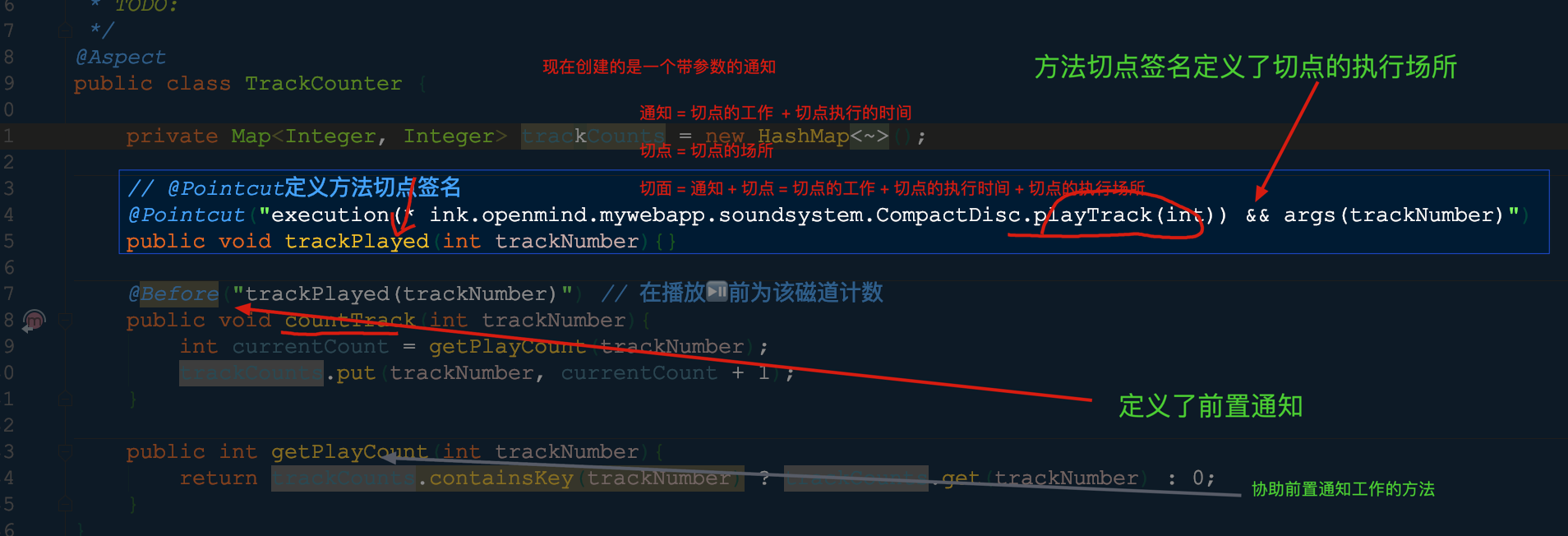
⭐️处理通知参数(创建的通知带有参数)
情景设置: play()方法会循环所有的磁道并调用playTrack()方法,直接在每次调用的时候记录📝磁道的数量,记录磁道的播放次数与播放本身是不同的关注点,因此不应该属于playTrack()方法。
为记录每个磁道所播放的次数将创建TrackCounter类作为一个切面用来通知playTrack()方法
使用参数化的通知定义切面
@Aspect public class TrackCounter { private Map<Integer, Integer> trackCounts = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>(); // @Pointcut定义方法切点签名🌈 @Pointcut("execution(* ink.openmind.mywebapp.soundsystem.CompactDisc.playTrack(int)) && args(trackNumber)") public void trackPlayed(int trackNumber){} @Before("trackPlayed(trackNumber)") // 在播放⏯前为该磁道计数 public void countTrack(int trackNumber){ int currentCount = getPlayCount(trackNumber); trackCounts.put(trackNumber, currentCount + 1); } public int getPlayCount(int trackNumber){ return trackCounts.containsKey(trackNumber) ? trackCounts.get(trackNumber) : 0; } }
execution(* ink.openmind.mywebapp.soundsystem.CompactDisc.playTrack(int)) && args(trackNumber) 在切点表达式中声明参数,这个参数传入到通知方法中
args(trackNumber)限定符,表明传递给playTrack()方法的int类型参数也会传递到通知中去。参数的名称trackNumber与切点方法签名中的参数相互匹配void playTrack(int trackNumber); //CompactDisc中
切点定义中的参数与切点方法中的参数名称是一样的,这样就完成了从命名切点到通知方法的参数转移
- 将TrackCounter切面类交由AspectJ进行代理
/** * 配置TrackCount记录每个磁道播放的次数 */ @Configuration @EnableAspectJAutoProxy // 启用AspectJ自动代理 public class TrackCounterConfig { @Bean // 将切面类交由AspectJ进行代理 public TrackCounter trackCounter(){ return new TrackCounter(); } }
基于注解配置 > 基于Java配置 > 基于XML配置
在XML中声明切面
Spring的aop命名空间提供下列元素来在XML中声明切面
| AOP配置元素 | 用途 |
|---|---|
aop:advisor |
AOP通知器 |
aop:after |
AOP后置通知(不管被通知方法是否执行成功) |
aop:after-returning |
AOP返回通知 |
aop:after-throwing |
AOP异常通知 |
aop:around |
AOP环绕通知 |
aop:aspect |
定义一个切面 |
aop:aspectj-autoproxy |
启用@AspectJ注解驱动的切面(能够自动代理AspectJ注解的通知类) |
aop:before |
定义一个AOP前置通知 |
aop:config |
顶层的AOP配置元素,大多数的aop:*元素必须在aop:config元素内 |
aop:declare-parents |
以透明的方式为被通知的对象引入额外的接口 |
aop:pointcut |
定义一个切点 |
- 一个简单的类Audience没有任何注解,之后将通过一系列注解来将其声明为一个切面类,提供相关通知声明
public class Audience { public void performance(){} public void watchPerfromance(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){ try{ System.out.println("Silencing cell phones"); System.out.println("Taking seats"); joinPoint.proceed(); System.out.println("CLAP CLAP CLAP CLAP"); }catch (Throwable throwable){ System.out.println("Demanding a refund!"); } } public void silenceCellPhones(){ System.out.println("在演出开始之前要把手机设置为静音🔇!"); } public void takeSeats(){ System.out.println("找好座位💺"); } public void applause(){ System.out.println("👏👏👏👏👏👏👏"); } public void demandRefund(){ System.out.println("在未能进行表演的情况下,申请退款!!!"); } }
声明前置通知和后置通知
通过XML将无注解的Audience声明为切面
<aop:config> <!-- 在<aop:config>元素内,可以声明一个或多个通知器、切面或者切点--> <aop:aspect ref="audience"> <!-- 引入audience bean <aop:aspect ref="xxx"> 根据引入的bean定义切面bean--> <aop:before pointcut="execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))" <!-- 表演之前执行--> method="silenceCellPhones"/> <aop:before pointcut="execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))" <!-- 表演之前执行--> method="takeSeats"/> <aop:after-returning pointcut="execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))" <!-- 表演之后执行--> method="applause"/> <aop:after-throwing pointcut="execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))" <!-- 表演失败(异常抛出)执行--> method="demandRefund"/> <!-- pointcut属性定义了通知所应用的切点 --> </aop:aspect> </aop:config>
使用aop:pointcut命名切点
<aop:config> <aop:aspect ref="audience"> <!-- 如果需要将切点应用在多个切面,可以将<aop:pointcut>放在与<aop:aspect>元素同级的水平上!--> <aop:pointcut id="performance" expression="execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))"/> <aop:before pointcut-ref="performance" method="silenceCellPhones"/> <aop:before pointcut-ref="performance" method="takeSeats"/> <aop:after-returning pointcut-ref="performance" method="applause"/> <aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref="performance" method="demandRefund"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config>
声明环绕通知
如果不使用成员变量存储信息的话,在前置通知和后置通知之间共享信息非常麻烦(因为audience是单例的会带来线程安全问题)
使用环绕通知只需要在一个方法内实现,不需要使用成员变量保存状态
// 传统使用注解 @Aspect public class Audience{ @Around("execution("* xx.perform(..)") public void watchPerformance(ProceedingJoinPoint jp){ try{ System.out.println("Silencing cell phones"); // 表演之前 System.out.println("Taking seats"); // 表演之前 jp.proceed(); // 执行被通知的方法 System.out.println("CLAP CLAP CLAP"); // 表演成功之后 }catch(Throwable e){ System.out.println("Demanding a refund"); // 表演失败之后 } } }
在XML中使用aop:around元素声明环绕通知
<aop:config> <aop:aspect ref="audience"> <!-- 定义切点 --> <aop:pointcut id="performance" expression="execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))"/> <!-- 声明环绕通知--> <aop:around pointcut-ref="performance" method="watchPerformance"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config>
XML中为通知传递参数
无注解的TrackCounter(将作为切面)
public class TrackCounter{ private Map<Integer, Integer> trackCounts = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>(); public void countTrack(int trackNumber){ int currentCount = getPlayCount(trackNumber); trackCounts.put(trackNumber, currentCount + 1); } public int getPlayCount(int trackNumber){ return trackCounts.containsKey(trackNumber) ? trackCounts.get(trackNumber) : 0; } }
在XML中将TrackCounter配置为参数化的切面
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <bean id="trackCounter" class="soundsystem.TrackCounter"/> <bean id="cd" class="soundsystem.BlankDisc"> <property name="title" value="xxx"/> <property name="artist" value="xxx"/> <property name="tracks"> <list> <value>xxx</value> <value>xxx</value> <value>xxx</value> </list> </property> </bean> <aop:config> <aop:aspect ref="trackCounter"> <aop:pointcut id="trackPlayed" expression="execution(* soundsystem.CompactDisc.playTrack(int)) and args(trackNumber)"/> <aop:before pointcut-ref="trackPlayed" method="countTrack"/> </aop:config> </beans>
小结
- AOP是面向对象编程的一个强大补充
- 通过AspectJ,可以把之前分散在应用各处的行为放入可重用的模块中,这个模块是模块化的横切关注点即切面
- 当SpringAOP无法满足需求时,可以采用ApsectJ





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 写一个简单的SQL生成工具