循环
循环(loop)是一种控制语句块重复执行的一种结构。
Java提供的三种循环语句:while循环、do-while循环以及for循环
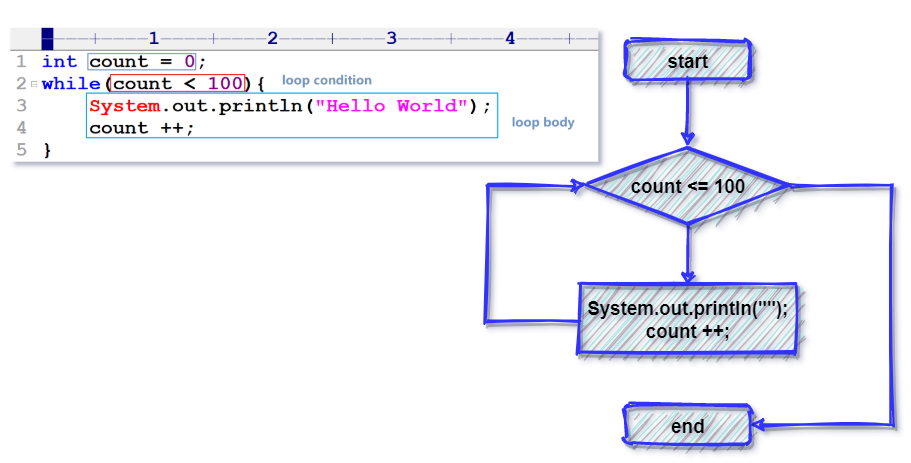
while循环
while循环在条件为真的情况下重复执行语句。
-
语法:
![]()
-
示例01:
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num01 = (int)(Math.random() * 10);
int num02 = (int)(Math.random() * 10);
System.out.println("What is " + num01 + " + " + num02 + " = ? " );
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int answer = scanner.nextInt();
while((num01 + num02) != answer){
System.out.println("Wrong answer, try again! What is "
+ num01 + " + " + num02 + " = ? ");
answer = scanner.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("You got it!");
}
}
// What is 5 + 5 = ?
// 9
// Wrong answer, try again! What is 5 + 5 = ?
// 10
// You got it!
- 示例02:
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
guessNumberWithIfStylePlus();
}
private static void guessNumberWithWhileStyle() {
int randomInteger = generateRandomIntegerBetween0And100();
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int inputInteger = -1;
while (randomInteger != inputInteger) {
System.out.println("Please input a guess number: ");
inputInteger = input.nextInt();
if (inputInteger == randomInteger) {
System.out.println("You guessed");
}
if (inputInteger > randomInteger) {
System.out.println("The guessed integer is too high!");
}
if (inputInteger < randomInteger) {
System.out.println("The guessed integer is too low!");
}
}
}
private static String guessNumberWithIfSytle() {
int randomInteger = generateRandomIntegerBetween0And100();
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please input a guess number: ");
int inputInteger = input.nextInt();
if (randomInteger > inputInteger) {
return "the guess number is too low!";
}
if (randomInteger < inputInteger) {
return "the guess number is too high!";
}
return "You guessed!";
}
private static void guessNumberWithIfStylePlus() {
int randomInteger = generateRandomIntegerBetween0And100();
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.println("Please input a guess number: ");
int inputInteger = input.nextInt();
if (randomInteger == inputInteger) {
System.out.println("You guessed!");
break;
}
if (randomInteger > inputInteger) {
System.out.println("the guess number is too low!");
}
if (randomInteger < inputInteger) {
System.out.println("the guess number is too high!");
}
}
}
/**
* generates a random integer between 0 and 100
*
* @return an random integer
*/
private static int generateRandomIntegerBetween0And100() {
return ((int) (Math.random() * 101));
}
}
示例03
/**
* @Description:
* @Author: Wangzz
* @Version: 1.0.0
* @CreateDate: Created in 2021/2/28 16:28
* @UpdateDate: [dateFormat:YYYY-MM-DD][modifier][description]
*/
public class SubtractionQuizLoop {
// the privatization of constructor method that represents all of methods
// in the class should be prefixed with "public static"
private SubtractionQuizLoop() {
}
// the client of SubtractionQuizLoop
protected static void subtractionQuizLoopClient() {
calculateGradesInSubtractionQuiz02();
}
private static void calculateGradesInSubtractionQuiz01() {
int grades = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
grades = executeSubtraction(grades);
}
System.out.println("The quiz's grades: " + grades);
}
// What is 78 + 32 = ?
// 110
// You correct!
// What is 7 + 93 = ?
// 100
// You correct!
// What is 94 + 51 = ?
// 145
// You correct!
// What is 63 + 30 = ?
// 93
// You correct!
// What is 13 + 89 = ?
// 10
// The quiz's grades: 4
private static void calculateGradesInSubtractionQuiz02() {
int grades = 0;
int i = 0;
while (i < 5) {
grades = executeSubtraction(grades);
i++;
}
System.out.println("The quiz's grades: " + grades);
}
// What is 22 + 49 = ?
// 71
// You correct!
// What is 78 + 60 = ?
// 138
// You correct!
// What is 83 + 64 = ?
// 147
// You correct!
// What is 32 + 32 = ?
// 64
// You correct!
// What is 35 + 60 = ?
// 95
// You correct!
// The quiz's grades: 5
// [refacotring code] - Extract Method
private static int executeSubtraction(int grades) {
int num01 = MathUtil.generateRandomIntegerBetween0And100();
int num02 = MathUtil.generateRandomIntegerBetween0And100();
System.out.println("What is " + num01 + " + " + num02 + " = ? ");
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int answer = input.nextInt();
if (num01 + num02 == answer) {
System.out.println("You correct!");
grades++;
}
return grades;
}
}
使用标记值(sentinel value)来控制循环 - sentinel-controlled loop
public class SentinelControlledLoop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a num: ");
int data = input.nextInt(); // 标记值(sentinel value)
int sum = 0;
while(data != 0){
sum += data;
System.out.println("Enter a num: ");
data = input.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("The sum is : " + sum);
}
}
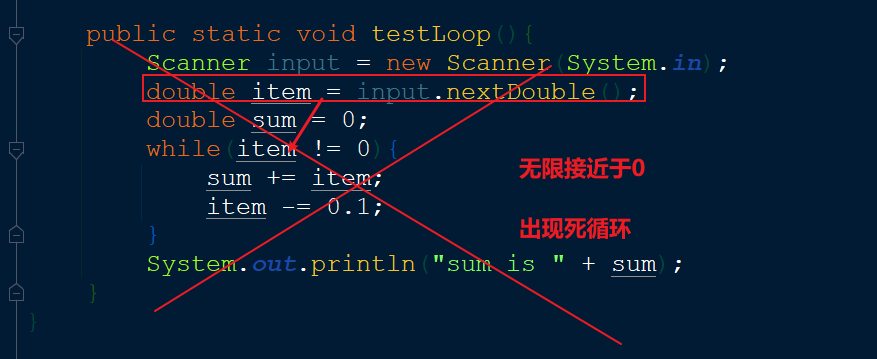
⚠ 在循环控制中,绝对不要使用浮点值来比较值是否相等,因此计算机无法用二进制准确表示浮点值
都是某个值的近似值,使用它们可能导致不精确的循环次数和不准确的结果。
do-while循环
do-while循环至少执行一次然后再判断条件。
do {
loop body;
}while(loop condition);
示例:
int data;
int sum = 0;
do{
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter an integer(the input ends if it is 0: ");
data = input.nextInt();
sum += data;
}while(data != 0);
System.out.println("The sum is : " + sum);
如果执行的语句中至少要执行一次就需要使用
do{}while();循环
for循环
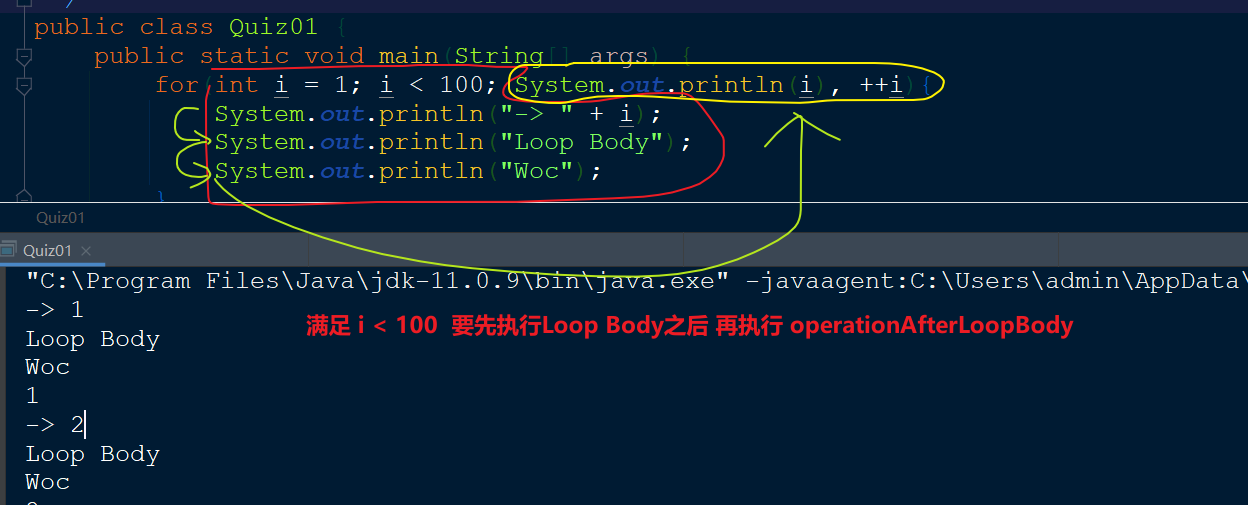
for(initialOperation; loopCondition; operationAfterLoop){
// loop body
}
- 在已经知道要循环的次数前提下 ===》 使用【for循环】
- 当无法确定循环次数 ===》 使用【while循环】
- 当需要实现检验继续条件 ===》 使用【do-while循环】
do-while的循环中不要忘了 【;】
do{
loop body
}while(loop-continuation-condition);
嵌套查询
代码示例:
/**
* @Description:
* @Author: Wangzz
* @Version: 1.0.0
* @CreateDate: Created in 2021/2/28 16:44
* @UpdateDate: [dateFormat:YYYY-MM-DD][modifier][description]
*/
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("\t\tMultiplication Table");
System.out.println("\t1\t2\t3\t4\t5\t6\t7\t8\t9");
System.out.println("\t-----------------------------------");
for(int i = 1; i <= 9; i++){
System.out.print(i + "|\t");
for(int j = 1; j <= 9; j++){
System.out.print((i * j) + "\t");
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}
Multiplication Table
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
---------------------------------------------------------------------
1| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
2| 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18
3| 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27
4| 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36
5| 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45
6| 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 54
7| 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63
8| 8 16 24 32 40 48 56 64 72
9| 9 18 27 36 45 54 63 72 81
嵌套循环是由外层循环和内层循环组成, 外层循环每执行一次都要对内层循环执行其所有次数,依此类推!!!
【示例代码(★)】将十进制数转换为十六进制
private static String executeConversionDecimalToHexadecimal(int num){
String res = "";
while(num != 0){ // 明白十进制转换为十六进制具体操作细节。
int reminder = num % 16;
res = getHexdecimalFromReminder(reminder) + res;
num = num / 16;
}
return res;
}
private static char getHexdecimalFromReminder(int reminder){
return (reminder >= 0 && reminder <= 9) ? (char)(reminder + '0') : (char)(reminder - 10 + 'A');
}
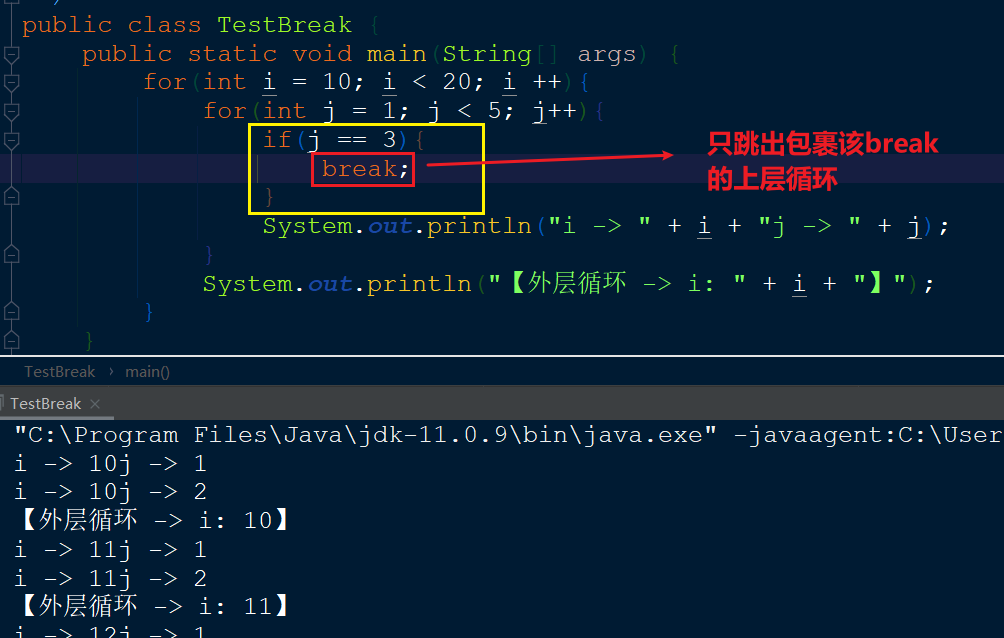
break和continue
break和continue关键字增加开发人员对循环的控制
适当的break和contine可以简化程序设计但过度的使用将降低程序的可读性。
break跳出所有循环
Eg:
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 1;
int number = 0;
while(number <= 20){
number ++;
sum = sum * number;
if(sum >= 100){
System.out.println("【break】 sum : " + sum + " , number: " + number);
// 【break】 sum : 120 , number: 5
break;
}
}
}
}
【示例代码(★)】寻找除了1之外最小因子
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
getSmallestFactor01(15);
getSmallestFactor02(15);
getSmallestFactor03(15);
}
// 求除了1之外的最小因子 [version 1.0.1]
private static void getSmallestFactor01(int num){
// 采用break实现
int factor = 2;
while(factor <= num){
if(num % factor == 0){
break;
}
factor ++;
}
System.out.println("The smallest factor for [ " + num + " ] is " + factor);
}
// 求除了1之外的最小因子 [version 1.0.2]
private static void getSmallestFactor02(int num){
// 采用sentinel
int factor = 2;
boolean found = false; // 当前未找到
while((factor <= num) && (!found)){
if(num % factor == 0){
found = true;
}else{
factor ++;
}
}
System.out.println("The smallest factor for [ " + num + " ] is " + factor);
}
// 求除了1之外的最小因子 [version 1.0.3]
private static void getSmallestFactor03(int num){
// 直接将结果出现的条件写入loop condition中
int factor = 2;
while((factor <= num) && (num % factor != 0)){ // 只要还没有找到该因子就继续循环
factor ++;
}
System.out.println("The smallest factor for [ " + num + " ] is " + factor);
}
}
// The smallest factor for [ 15 ] is 3
// The smallest factor for [ 15 ] is 3
// The smallest factor for [ 15 ] is 3
continue跳出当前循环
Eg:
int sum = 0;
int num = 0;
while(num < 20){
num ++;
if((num == 10) | (num == 11)){
continue;
}
sum += num;
}
System.out.println("The sum is " + sum);
判断回文串
private static void judgePalindrome01(String str){
int low = 0;
int high = str.length() - 1;
boolean isPalindrome = true;
while(low < high){
if(str.charAt(low) != str.charAt(high)){
isPalindrome = false;
break;
}
low++;
high--;
}
if(isPalindrome){
System.out.println(str + " is a palindrome!");
}else{
System.out.println(str + " is not a palindrome!");
}
}
显示素数
public class PrimeJudgement {
public static void main(String [] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a num: ");
System.out.println(judgeResult(input.nextInt()));
}
private static String judgeResult(int num){
if(judgePrime(num)){
return num + " is a Prime!";
}else{
return num + " is not a Prime!";
}
}
private static boolean judgePrime(int num){
boolean res = true;
int high = num - 1;
for(int low = 2; low < high; low++){
if(num % low == 0){
res = false;
}
}
return res;
}
}
关键术语
| -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| break statement | input redirection 输入重定向 | continue statementcontinue 语句 | iteration 迭代 | infinite loop 无限循环 | nested loop 嵌套循环 |
| off-by-one error 差一错误 | pretest loop 前测循环 | posttest loop 后测循环 | while loop | sentinel value 标志值 | loop body 循环体 |
总结
- 循环语句类型: 【while循环】、【do...while循环】、【for循环】
- 循环体:循环中包含重复执行的语句的部分。
- 一次迭代:循环体执行一次。
- 无限循环:循环语句被无限次执行。
- 在设计循环的时候既要考虑循环控制结构也要考虑循环体。
- while和do-while循环用于【循环次数不确定】的情况。
- 【sentinel value - 标记值】用来标记循环的结束。
- for循环用于【循环次数确定】的情况。
- for循环结构组成: for(初始操作 - initial operation; 循环继续条件 - circulating condition; 迭代后完成的操作 - operation after per circulation)
- while、for循环为前测循环
- do-while循环为后测循环
- 在循环中可以使用【continue】和【break】两个关键字
- break用于跳出包含它的这一层循环。
![]()
学而不思则罔,思而不学则殆!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号