Django模板之模板标签
标签比变量更加复杂:一些在输出中创建文本,一些通过循环或逻辑来控制流程,一些加载其后的变量将使用到的额外信息到模版中。
一些标签需要开始和结束标签 (例如:{% tag %} ...标签 内容 ... {% endtag %}),有些标签不需要结束{% tag %}
快捷键:输入tag直接回车
常用模板标签:for if with [csrf_token extends include block url load]见后续页面
for标签:循环遍历可迭代变量中的每一个元素,没有break和continue等复杂功能,相关操作类比python。
(1)遍历列表:
tagtest.html模板:
{% for name in name_list %}
<li>{{ name }}</li>
{% endfor %}
反向遍历:
{% for name in name_list reversed %}
<li>{{ name }}</li>
{% endfor %}
views.py视图:
def tagtest(request):
list=["zhang","wang","li"]
return render(request,"tagtest.html",{"name_list":list})
渲染结果:

(2)列表中字典取值:
tagtest.html模板:
{% for info_dic in name_list %}
<li>{{ info_dic.name }}</li>
{% endfor %}
views.py视图:
def tagtest(request):
list=[{"name":"le"},{"name":"yang"},{"name":"he"}]
return render(request,"tagtest.html",{"name_list":list})
渲染结果:
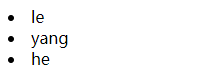
(3)遍历字典:
tagtest.html模板:
{% for k,v in info_dict.items %}
<li>{{ k }}:{{ v }}</li>
{% endfor %}
views.py视图:
def tagtest(request):
dic={"name":"yang","age":20,"sex":"male"}
return render(request,"tagtest.html",{"info_dict":dic})
渲染结果:

(4)for…empty…:for遍历一个空的变量或者未找到时执行empty
tagtest.html模板:
{% for info_dic in name_list %}
<li>{{ info_dic.name }}</li>
{% empty %}
<p>给出的变量为空或者未找到!</p>
{% endfor %}
views.py视图:
def tagtest(request):
list=[]
return render(request,"tagtest.html",{"name_list":list})
渲染结果:

(5)forloop使用案例:
tagtest.html模板:
{% for i in l %}
<li>{{ forloop }}---{{ i }}</li>
{% endfor %}
配合属性使用:
{% for i in l %}
<li>{{ forloop.counter }}---{{ i }}</li>
{% endfor %}
views.py视图:
def tagtest(request):
li=["python","mysql","web"]
return render(request,"tagtest.html",{"l":li})
渲染结果:

注:循环序号可以通过{{forloop}}显示,必须在循环内部用:
|
forloop.counter |
当前循环的索引值(从1开始),forloop是循环器,通过点来使用功能 |
|
forloop.counter0 |
当前循环的索引值(从0开始) |
|
forloop.revcounter |
当前循环的倒序索引值(从1开始) |
|
forloop.revcounter0 |
当前循环的倒序索引值(从0开始) |
|
forloop.first |
当前循环是不是第一次循环(布尔值) |
|
forloop.last |
当前循环是不是最后一次循环(布尔值) |
|
forloop.parentloop |
本层循环的外层循环的对象,再通过上面的几个属性来显示外层循环的计数等 |
if标签:判断变量的逻辑值是进行选择性的输出,类比python(< > = <= >= != == and or not not in is is not前后必须要有空格)
tagtest.html模板:
{% if num > 100 %}
<h1>大于100</h1>
{% elif num < 100 %}
<h1>小于100</h1>
{% else %}
<h1>等于100</h1>
{% endif %}
views.py视图:
def tagtest(request):
n=100
return render(request,"tagtest.html",{"num":n})
渲染结果:

with标签:多用于给一个复杂的变量起别名
注意:等号左右不要加空格。
{% with total=business.employees.count %}
{{ total }} <!--只能在with语句体内用-->
{% endwith %}
或
{% with business.employees.count as total %}
{{ total }}
{% endwith %}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号