NeHe OpenGL Lesson39 – Introduction to Physical Simulations
This sample gives us some basics information about Physical Simulations. Some terminologies like Mass, Force, acceleration, velocity, time, position and the relationships among them are described here.
For the simulation part, we need to use another delta time – simulation delta time instead of application delta time. The idea is that any given application delta time will be compared with the simulation threshold (the minimum delta time that could be acceptable), if the application delta time longer than this threshold, the application delta time will be separated into a several small delta time (the total value of those delta time will equal the application delta time), the code just like the following:
// milliseconds is the application delta time float dt = milliseconds / 1000.0f; float maxPossible_dt = 0.1f; int numOfIterations = (int)(dt / maxPossible_dt) + 1; // seperate into the simulation delta time if (numOfIterations != 0) dt = dt / numOfIterations; for (int a = 0; a < numOfIterations; ++a) { constantVelocity->operate(dt); motionUnderGravitation->operate(dt); massConnectedWithSpring->operate(dt); }
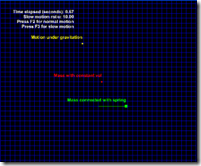
Then there are 3 different simulations provided:
1) moving with constant speed, no external force applied, no acceleration;
2) moving with the certain initial speed under the gravity, constant external force applied, constant acceleration;
3) moving with the spring model, various external force applied based on the distance, the acceleration also become vary as the distance changing.
When you set up the simulation model, one thing need to take special care is the unit choose. Make sure all element choose the correct and consistent unit.
The source code could be found here.

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号