《Spring in action 4》(五)SpringMVC起步
SpringMVC起步
介绍
SpringMVC基于模型-视图-通知器(Model-View-Controller,MVC)模式实现的,它能够帮助我们构建像Spring框架那样灵活和松耦合的Web应用程序。
跟踪SpringMVC流程
图示:
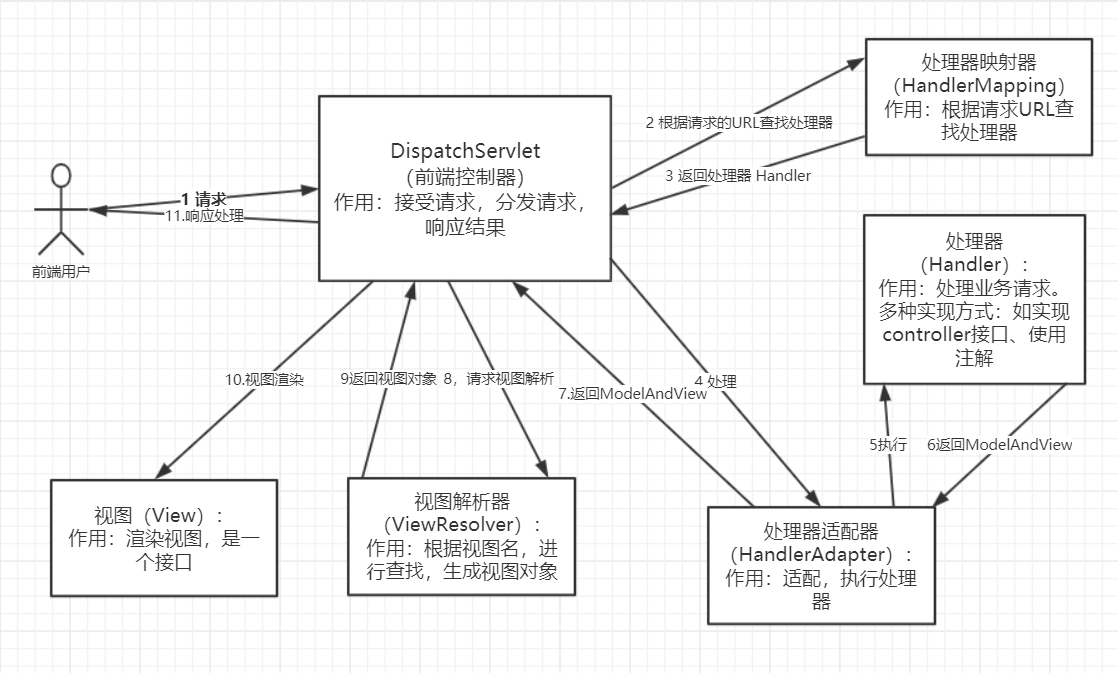
步骤说明:
-
用户发送请求到前端控制器(DispatchServlet),该控制器会过滤出哪些请求可以访问servlet、哪些不能访问。就是URL-Pattern的作用,并且会加载SpringMVC.xml配置文件。
-
前端控制器会找到处理器映射器(HandlerMapping),通过HandlerMapping完成URL到Controller映射的组件,简单来说,就是将在SpringMVC.xml中配置的或者注解的URL与对应的处理类找到并进行存储,用
Map<URL,handler>这样的方式来存储。 -
HandlerMapping有了映射关系,并且找到了URL对应的处理器,HandlerMapping就会将其处理器(Handler)返回,在放回前,会加上很多拦截器。
-
DispatchServlet拿到Handler之后,找到HandlerAdapter(处理器适配器),通过它来访问处理器,并执行处理器。
-
执行处理器。
-
处理器会返回一个ModelAndView对象到HandlerAdapter。
-
通过HandlerAdapter将ModelAndView对象返回到前端控制器DispatchServlet。
-
前端控制器请求视图解析器(ViewResolver)去进行视图解析,根据逻辑视图名解析成真真的视图(JSP),其实就是将ModelAndView对象中存放视图的名称进行查找,找到对应的页面形成视图对象。
-
返回视图对象到前端控制器。
-
视图渲染,就是将ModelAndView对象中的数据放到Request域中,用来让页面加载数据的。
-
通过第8步,通过名称找到了对应的页面,通过第10步,request域中有了所需要的数据,那么就可以进行视图渲染了。最后将其返回即可。
这里再附上网上的一张详细的图:
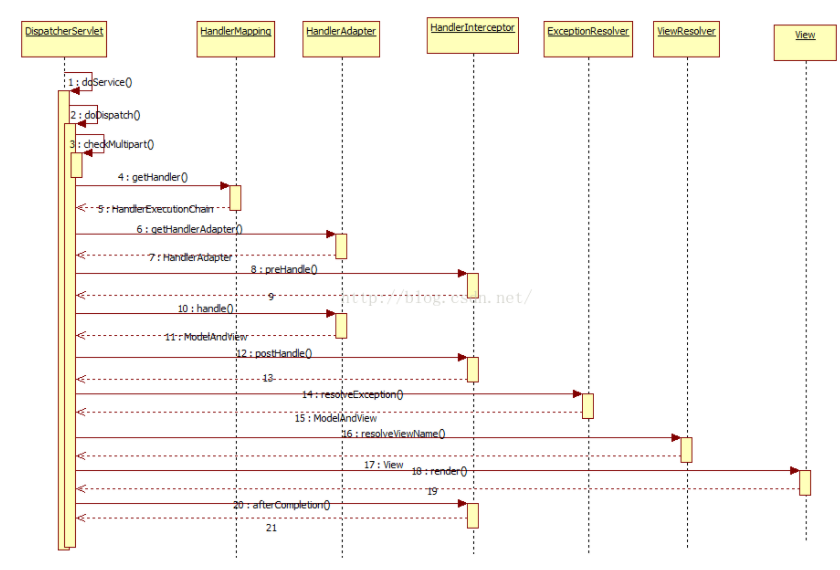
web.xml版本的Web项目
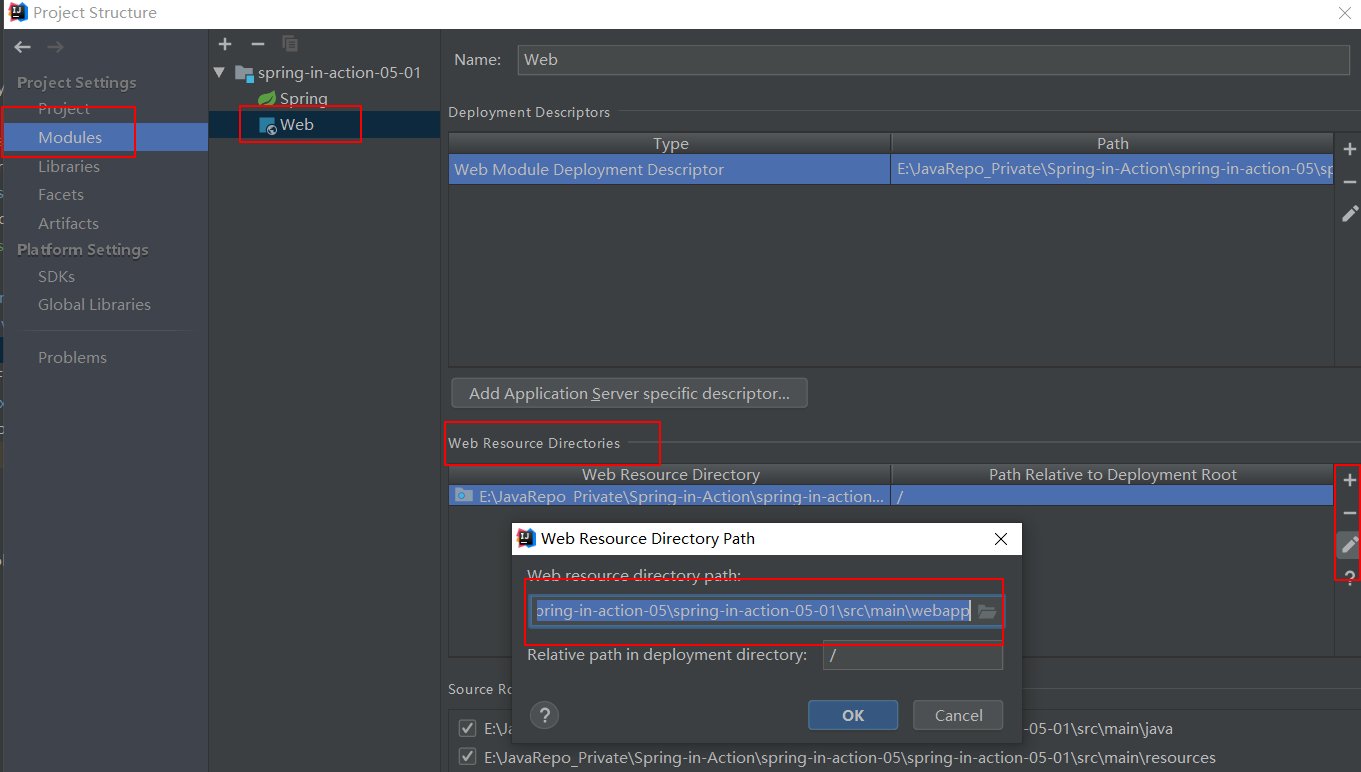
1. 项目结构
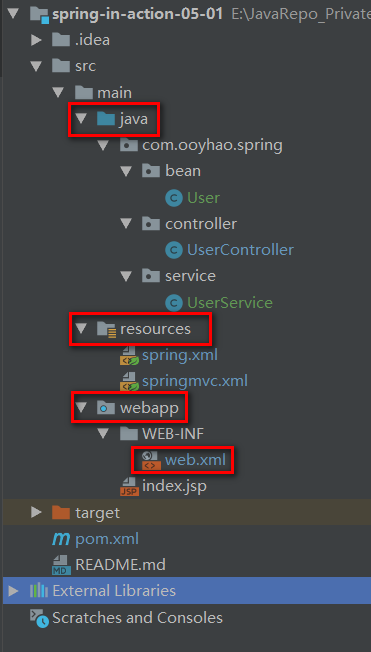
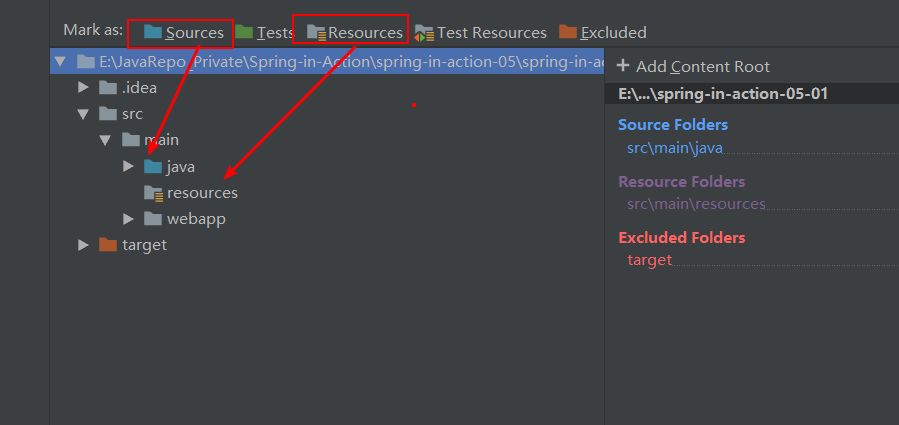
说明:蓝色的Java文件夹,标注为 sources,标有条形圆筒的resources文件夹标注为Resources。
- java文件夹用来存放java源码。
- resources文件夹用来存放资源文件:如spring配置文件,mapper文件。
- webapp目录则用来存放web相关的资源。
File-->Project Structure
2. Pom 文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.ooyhao.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-in-action-05-01</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>spring-in-action-05-01 Maven Webapp</name>
<url>http://www.example.com</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.7</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.7</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>4.3.15.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId>
<version>5.1.8.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- json 解析,不配置转化器和引入依赖,返回List则会抛出异常-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-annotations</artifactId>
<version>2.9.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
3. 生成web.xml
项目结构搭建好之后,需要生成web.xml文件并配置。
web.xml文件:
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >
<web-app>
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<!--配置applicationContext配置文件-->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!--配置编码过滤器-->
<filter>
<filter-name>encodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>
org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter
</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>utf-8</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>forceEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>encodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<!--配置Spring上下文加载器的监听器-->
<!--默认加载classpath:下面的applicationContext.xml文件。需要自定义可以配置
<context-param></context-param> 进行配合使用
-->
<listener>
<listener-class>
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
</listener-class>
</listener>
<!--配置前端控制器-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
4. 配置Spring和SpringMVC
springmvc.xml配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.ooyhao.spring.**.controller"/>
<!--注解驱动,配置controller返回的转换器-->
<mvc:annotation-driven>
<mvc:message-converters>
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter"/>
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter"/>
</mvc:message-converters>
</mvc:annotation-driven>
<!--解决@ResponseBody返回中文乱码情况-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter" >
<property name="messageConverters">
<list>
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter">
<property name="supportedMediaTypes">
<list>
<value>text/plain;charset=utf-8</value>
<value>text/html;charset=UTF-8</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!--静态页面,如html,css,js,images可以访问-->
<mvc:default-servlet-handler/>
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="viewClass"
value="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView"/>
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
</bean>
</beans>
spring.xml配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
">
<!--组件扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.ooyhao.spring">
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
</beans>
5. 编写逻辑代码
User类:
public class User implements Serializable {
private String username;
private Integer age;
private String sex;
//noArgsConstructor
//allArgsConstructor
//getter and setter
//toString
}
UserService类:
@Service
public class UserService {
public List<User> findAllUsers(){
List<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
users.add(new User("林黛玉",18,"女"));
users.add(new User("贾宝玉",20,"男"));
return users;
}
}
UserController类:
@Controller
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping("/hello")
@ResponseBody
public List<User> hello(){
return userService.findAllUsers();
}
}
6. 测试和结果
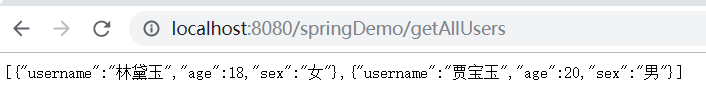
启动程序,并测试 localhost:8080/SpringDemo/getAllUsers
无配置文件的Web项目
如果使用过SpringBoot的都知道,SpringBoot可以做到零配置,即没有xml文件,这是因为Spring3.2之后,引入了WebApplicationInitializer。我们可以看一下这个类的源码中:
容在下,拿着这一级英语水平去翻译。
/**
Interface to be implemented in Servlet 3.0+ environments in order to configure the {@link ServletContext} programmatically as opposed to (or possibly in conjunction with) the traditional {@code web.xml}-based approach.
译:
在servlet3.0版本以上,通过实现接口以编程的方式进行配置ServletContext,这与传统的web.xml的形式近乎相反(不用web.xml文件,同样可以创建一个web应用)
Implementations of this SPI will be detected automatically by {@link
SpringServletContainerInitializer}, which itself is bootstrapped automatically by any Servlet 3.0 container.
译:
实现了这个SPI,将会被SpringServletContainerInitializer自动识别,并自动启动。
See {@linkplain SpringServletContainerInitializer its
Javadoc} for details on this bootstrapping mechanism.
译:
可以通过查看SpringServletContainerInitializer文档去了解自启动机制的详情。
<h2>Example</h2>
译:示例
<h3>The traditional, XML-based approach</h3>
译:传统基于Xml的方式
Most Spring users building a web application will need to register Spring's {@code DispatcherServlet}. For reference, in WEB-INF/web.xml, this would typically be done as,follows:
译:大部分Spring用户在构建一个web应用程序都需要去注册一个Spring的前端控制器(DispatchServlet),而其典型的就是在WEB-INF下的web.xml文件中注册。如下:
--->源码不是这样的,源码的尖括号使用了转义字符
* <servlet>
* <servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
* <servlet-class>
* org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
* </servlet-class>
* <init-param>
* <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
* <param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/dispatcher-config.xml</param-value>
* </init-param>
* <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
* </servlet>
*
* <servlet-mapping>
* <servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
* <url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
* </servlet-mapping>
以上配置就是使用传统的xml配置文件的方式,向servlet容器中注册一个DispatchServlet。
The code-based approach with {@code WebApplicationInitializer}
* Here is the equivalent {@code DispatcherServlet} registration logic,
* {@code WebApplicationInitializer}-style:
译:
通过使用WebApplicationInitializer的基于代码的方式,其与xml是一个相同的注册逻辑。WebApplicationInitializer代码方式:
* public class MyWebAppInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
* @Override
* public void onStartup(ServletContext container) {
* XmlWebApplicationContext appContext = new XmlWebApplicationContext();
* appContext.setConfigLocation("/WEB-INF/spring/dispatcher-config.xml");
*
* ServletRegistration.Dynamic dispatcher =
* container.addServlet("dispatcher", new
DispatcherServlet(appContext));
* dispatcher.setLoadOnStartup(1);
* dispatcher.addMapping("/");
* }
* }
*
* As an alternative to the above, you can also extend from {@link
org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer}.
译:你也可以通过集成自AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer来实现,以上二者任选其一
* As you can see, thanks to Servlet 3.0's new {@link ServletContext#addServlet} method we're actually registering an instance of the {@code DispatcherServlet}, and this means that the {@code DispatcherServlet} can now be treated like any other object receiving constructor injection of its application context in this case.
译:如你所见,正是由于servlet3.0 的新方法(ServletContext#addServlet)出现,我们可以通过它注册一个DispatchServlet的实例了。这也意味着DispatchServlet可以像其他对象那
样,通过构造注入的方式接受一个Application Context
This style is both simpler and more concise. There is no concern for dealing with init-params, etc, just normal JavaBean-style properties and constructor arguments. You are free to create and work with your Spring application contexts as necessary before injecting them into the {@code DispatcherServlet}.
译:这种方式既简单又简洁。我们不需要如何去处理初始化参数,等,仅仅需要处理像普通JavaBean那样的属性和构造方法参数。在你必须将他们注入到DispatchServlet中之前,你可以很自由的构建和处理你的spring应用程序。
Most major Spring Web components have been updated to support this style of registration. You'll find that {@code DispatcherServlet}, {@code FrameworkServlet},{@code ContextLoaderListener} and {@code DelegatingFilterProxy} all now support constructor arguments. Even if a component (e.g. non-Spring, other third party) has not been specifically updated for use within {@code WebApplicationInitializers}, they still
may be used in any case. The Servlet 3.0 {@code ServletContext} API allows for setting init-params, context-params, etc programmatically.
译:大部分Spring web 组件都进行了更新,以至于能够支持这个注册方式,你可以发现像 DispatcherServlet、FrameworkServlet、ContextLoaderListener和DelegatingFilterProxy ,现在全部都支持构造参数注入。甚至是一些非spring,其他第三方组织的组件在WebApplicationInitializers中使用的没有支持的也会更新,以至于一直可以使用。Servlet3.0 API 也可以通过编程的方式 去设置 初始化参数、容器参数等
A 100% code-based approach to configuration In the example above,
{@code WEB-INF/web.xml} was successfully replaced with code in
* the form of a {@code WebApplicationInitializer}, but the actual
* {@code dispatcher-config.xml} Spring configuration remained XML-based.
* {@code WebApplicationInitializer} is a perfect fit for use with Spring's code-based
* {@code @Configuration} classes.
See @{@link org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration Configuration} Javadoc for complete details, but the following example demonstrates refactoring to use Spring's {@link org.springframework.web.context.support.AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext} in lieu of {@code XmlWebApplicationContext}, and user-defined {@code @Configuration} classes {@code AppConfig} and {@code DispatcherConfig} instead of Spring XML files.
译 :上面是一个完全由代码的配置方式的案例,web.xml文件已经被一个WebApplicationInitializer 成功取代。当然,实际上 Spring的配置任然保持着基于xml方式,WebApplicationInitializer 是一个更加适合 Spring代码的 配置类。可以查看Configuration的文档,了解完整的详情。但是下面这个例子是使用Spring的 AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext 来代替XmlWebApplicationContext进行重构的。并且用户通过@Configuration,AppConfig,DispatcherConfig来代替xml配置文件。
This example also goes a bit beyond those above to demonstrate typical configuration of the 'root' application context and registration of the {@code ContextLoaderListener}:
译:这个例子比上面的例子更进一步,使用root application context 来重构的典型配置,并且注册ContextLoaderListener
* public class MyWebAppInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
* @Override
* public void onStartup(ServletContext container) {
* // Create the 'root' Spring application context
创建root Spring的应用上下文
* AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext rootContext =
* new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
* rootContext.register(AppConfig.class);
* // Manage the lifecycle of the root application context
管理root 应用上下文的生命周期
* container.addListener(new ContextLoaderListener(rootContext));
* // Create the dispatcher servlet's Spring application context
// 创建了Servlet的前端控制器的Spring应用上下文
* AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext dispatcherContext =
* new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
* dispatcherContext.register(DispatcherConfig.class);
* // Register and map the dispatcher servlet
//注册并且映射前端控制器
* ServletRegistration.Dynamic dispatcher =
* container.addServlet("dispatcher", new
DispatcherServlet(dispatcherContext));
* dispatcher.setLoadOnStartup(1);
* dispatcher.addMapping("/");
* }
* }
*
* As an alternative to the above, you can also extend from {@link
org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer}.
你也可以通过集成自AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer,以上二者任选其一。
Remember that {@code WebApplicationInitializer} implementations are
detected automatically -- so you are free to package them within your application as you see fit.
记住,WebApplicationInitializer 的实现类 都是自动识别的。所以,你可以自由的将他们打包到你认为合适的应用程序中。
Ordering {@code WebApplicationInitializer} execution
{@code WebApplicationInitializer} implementations may optionally be annotated at the
* class level with Spring's @{@link org.springframework.core.annotation.Order Order}
* annotation or may implement Spring's {@link org.springframework.core.Ordered Ordered}
* interface. If so, the initializers will be ordered prior to invocation. This provides
* a mechanism for users to ensure the order in which servlet container initialization
* occurs. Use of this feature is expected to be rare, as typical applications will likely
* centralize all container initialization within a single {@code WebApplicationInitializer}.
Caveats :说明、警告
web.xml versioning
web.xml版本
{@code WEB-INF/web.xml} and {@code WebApplicationInitializer} use are not mutually exclusive; for example, web.xml can register one servlet, and a {@code WebApplicationInitializer} can register another. An initializer can even modify registrations performed in {@code web.xml} through methods such as {@link ServletContext#getServletRegistration(String)}.
译:web.xml与WebApplicationInitializer不会相互排斥,例如,web.xml可注册一个Servlet,而WebApplicationInitializer可以注册另一个,后者甚至可以修改在xml中注册的。
However, if {@code WEB-INF/web.xml} is present in the application, its {@code version} attribute must be set to "3.0" or greater, otherwise {@code ServletContainerInitializer} bootstrapping will be ignored by the servlet container
译:然而,如果web.xml存在于应用中,那么它的版本必须在3.0或以上,否则ServletContainerInitializer 自己化启动将会被Servlet容器忽略。
* <h3>Mapping to '/' under Tomcat</h3>、
在tomcat下映射/
* <p>Apache Tomcat maps its internal {@code DefaultServlet} to "/", and on Tomcat versions
<= 7.0.14, this servlet mapping cannot be overridden programmatically
7.0.15 fixes this issue. Overriding the "/" servlet mapping has also been tested successfully under GlassFish 3.1
译:在tomcat7.0.14及以下,tomcat使用其自身的DefaultServlet去映射/,这个Servlet映射将不能被编程方式重写在7.0.15版本。在GlassFish 3.1下, 成功测试出可以重写/这个Servlet映射器。
*/
public interface WebApplicationInitializer {
/**
* Configure the given {@link ServletContext} with any servlets, filters, listeners context-params and attributes necessary for initializing this web application.
为你这个web容器配置任何必要的 filter,listener,servlet,及其参数和属性
See examples {@linkplain WebApplicationInitializer above}.
* @param servletContext the {@code ServletContext} to initialize
* @throws ServletException if any call against the given {@code ServletContext}
* throws a {@code ServletException}
*/
void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException;
}
当你耐心的看完源码和翻译,你大概就知道SpringBoot为何可以做到不用web.xml文件就可以搭建一个web项目。这是使用了WebApplicationInitializer。
其实当我们好好学习Spring,会发现曾经SpringBoot那些神秘面纱,慢慢被揭开了。这也是我学了SpringBoot基础之后,又回头学习Spring的原因。
废话不多说了,开始搭建我们无配置文件的wen项目。
1. 替代web.xml的InitWeb
web.xml这里使用InitWeb.java代替,这里使用的是AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer,WebApplicationInitializer的子类,代码如下:
public class InitWeb extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
//配置rootConfig,即原来的applicationContext.xml
return new Class[]{RootConfig.class};
}
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
//配置ServletConfig,即原来的springmvc.xml
return new Class[]{ServletConfig.class};
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
//配置servlet映射,即之前在web.xml中DispatchServlet中配置的。
return new String[]{"/"};
}
}
2. POM
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.ooyhao.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-in-action-05-02</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>spring-in-action-05-02 Maven Webapp</name>
<url>http://www.example.com</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.7</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.7</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-annotations</artifactId>
<version>2.9.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
3. RootConfig
/*相当于spring.xml*/
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.ooyhao.spring", useDefaultFilters = true,excludeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = EnableWebMvc.class)
})
public class RootConfig {
扫描基础包,使用默认的过滤器。即全部都扫描。排除标有Controller注解的。
4. ServletConfig
/*相当于springmvc.xml*/
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.ooyhao.spring.**.controller")
public class ServletConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
/*配置JSP视图解析器*/
@Bean
public ViewResolver viewResolver(){
InternalResourceViewResolver resolver =
new InternalResourceViewResolver();
resolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/views/");
resolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
resolver.setExposeContextBeansAsAttributes(true);
return resolver;
}
/*配置静态资源的处理*/
@Override
public void configureDefaultServletHandling(DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer configurer) {
configurer.enable();
}
}
可以看出,SpringMvc的配置文件,比前面的spring配置文件多了很多内容。扫描所有的Controller,配置视图解析器,配置静态资源处理。开启webmvc(@EnableWebMvc)
@EnableWebMvc 相当于之前在springmvc.xml文件中配置的<mvc:annotation-driven>
5. 编写逻辑代码
Article:
public class Article implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String title;
private String content;
private String author;
public Article() {}
public Article(Integer id, String title, String content,
String author) {
this.id = id;
this.title = title;
this.content = content;
this.author = author;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Article{" +
"id=" + id +
", title='" + title + '\'' +
", content='" + content + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
ArticleService:
@Service
public class ArticleService {
private static List<Article> articles = new ArrayList<>();
static {
Article article1 = new Article(1,"红楼梦","红楼梦","曹雪芹");
Article article2 = new Article(2,"三国演义","三国演义","罗贯中");
Article article3 = new Article(3,"水浒传","水浒传","施耐庵");
Article article4 = new Article(4,"西游记","西游记","吴承恩");
articles.add(article1);
articles.add(article2);
articles.add(article3);
articles.add(article4);
}
public List<Article> findAllArticle(){
return articles;
}
}
ArticleController:
@Controller
public class ArticleController {
@Autowired
private ArticleService articleService;
@RequestMapping("/findAllArticles")
@ResponseBody
public List<Article> findAllArticles(){
List<Article> articles = articleService.findAllArticle();
return articles;
}
}
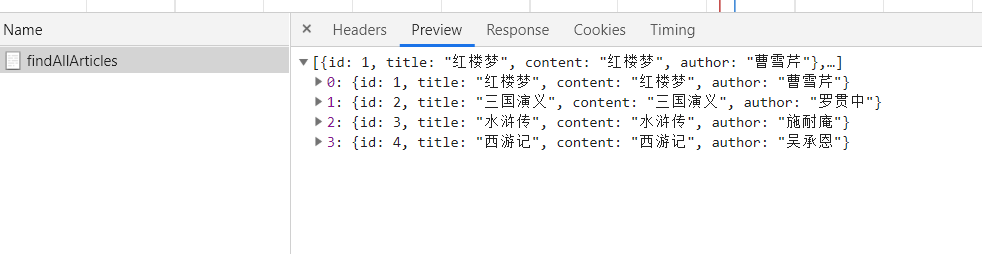
6. 测试和结果
接受请求参数的输入
SpringMVC允许以多种方式将客户端中的数据传送到控制器的处理器方法中,包括:
- 查询参数(Query Parameter)
- 表单参数(Form Patameter)
- 路径参数(Path Variable)
将上述示例进行了一定的修改,配合页面进行展示:
1. 查询参数
查询参数,我们以分页来做示例:
ArticleService:
@Service
public class ArticleService {
private static Map<Integer,Article> articles = new HashMap<>();
static {
Article article1 = new Article(1,"红楼梦","林黛玉、贾宝玉","曹雪芹");
Article article2 = new Article(2,"三国演义","诸葛亮、刘备","罗贯中");
Article article3 = new Article(3,"水浒传","鲁智深、武松","施耐庵");
Article article4 = new Article(4,"西游记","孙悟空、猪八戒","吴承恩");
articles.put(1,article1);
articles.put(2,article2);
articles.put(3,article3);
articles.put(4,article4);
}
public List<Article> findAllArticle(){
return new ArrayList<>(articles.values());
}
public Article findArticleById(Integer id) {
return articles.get(id);
}
public List<Article> findArticleByPage(Integer page, Integer size){
int firstIndex = (page-1) * size;
int lastIndex = page * size;
return new ArrayList<>
(articles.values()).subList(firstIndex,lastIndex);
}
}
ArticleController:
@Controller
public class ArticleController {
@Autowired
private ArticleService articleService;
@GetMapping("/article")
public String article(Model model,
@RequestParam(value = "page",defaultValue = "1") Integer page,
@RequestParam(value = "size",defaultValue = "2") Integer size){
List<Article> articles = articleService.findArticleByPage(page,
size);
model.addAttribute("articles",articles);
return "articleList";
}
}
articleList.jsp
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: ouYang
Date: 2019/9/1
Time: 11:13
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%--文章信息--%>
<h1>文章列表</h1>
<c:forEach items="${articles}" var="article">
<ul>
<li>ID:<c:out value="${article.id}"/></li>
<li>标题:<c:out value="${article.title}"/></li>
<li>内容:<c:out value="${article.content}"/></li>
<li>作者:<c:out value="${article.author}"/></li>
</ul>
</c:forEach>
</body>
</html>
测试及结果:
说明:
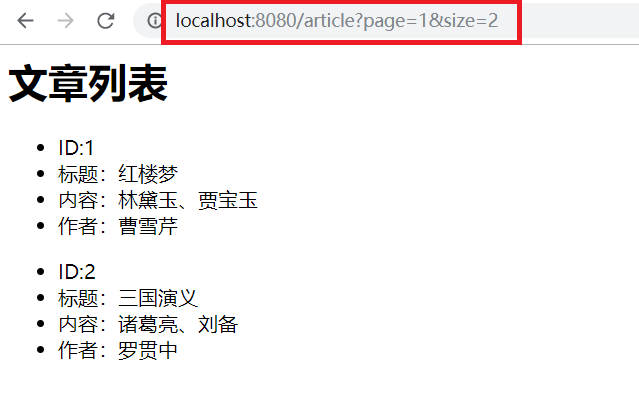
请求参数会拼接在请求路径后面使用?隔开,参数和值之间使用=连接。多个参数之间使用&进行拼接。Controller可以通过@RequestParam注解接收,可以设置默认值,当然,也可以省略@RequestParam注解。
2. 通过路径参数
ArticleController:
/*将参数写到路径上*/
@GetMapping("/article/{id}")
public String article(Model model,@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
Article article = articleService.findArticleById(id);
List<Article> articles = new ArrayList<>();
articles.add(article);
model.addAttribute("articles",articles);
return "articleList";
}
测试及结果:
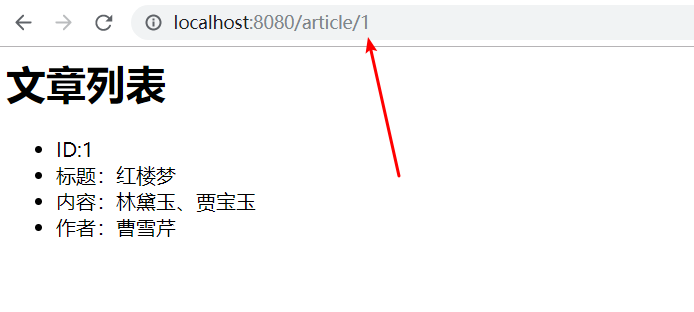
说明:
可以看出,路径参数与请求参数是不一样的,路径参数是请求地址中的一部分,在Controller中通过@PathVariable注解来注释接受。/article/{id} 在路径上使用{}来标注参数的位置。
3. 处理表单
处理表单参数,首先我们需要一个表单,这里以注册为例:
register jsp文件:
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%--
Created by IntelliJ IDEA.
User: ouYang
Date: 2019/9/1
Time: 10:29
To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates.
--%>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Blog</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>欢迎加入Spring的大家庭</h1>
<form method="post" >
用户名:<input name="username" type="text" ><br>
密码:<input name="password" type="password" ><br>
年龄:<input name="age" type="number" ><br>
<input type="submit" value="提交"><br>
</form>
</body>
</html>
一个普通的表单,使用post请求提交,当我们没有指定action属性的时候,点击提交之后,会使用原地址,即请求表单页面的地址,通过post请求提交,本例中是/register. 表单包括 用户名,密码和年龄三个属性。后台进行相应的Bean接受(User)
User:
public class User implements Serializable {
private String username;
private String password;
private Integer age;
//all/noArgConstructor, getter and setter, toString
}
UserService:
@Service
public class UserService {
private static List<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
public void saveUser(User user){
users.add(user);
}
}
IndexController:
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping("/")
public String home(){
return "home";
}
@GetMapping("/register")
public String toRegister(){
return "register";
}
/*处理表单数据,并验证*/
@PostMapping("/register")
public String register(User user){
userService.saveUser(user);
return "redirect:/registerSuccess";
}
@GetMapping("/registerSuccess")
public String registerSuccess(){
return "registerSuccess";
}
@GetMapping("/registerFail")
public String registerFail(){
return "registerFail";
}
}
通过上面代码可以看出,通过get请求类型,请求路径为/register,通过返回逻辑视图名,DispatchServlet将逻辑视图名去查找视图,并渲染返回,就可以进入注册表单页面。显而易见,前端提交的参数会自动填写到User对象中,这就是SpringMVC的强大之处,可以将数据自动与实体进行映射。
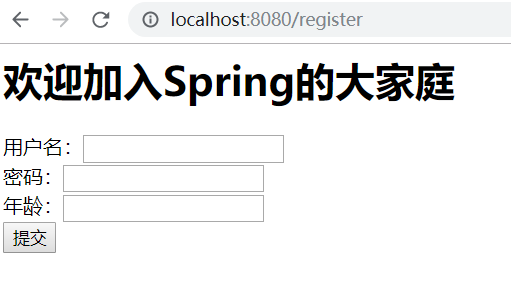
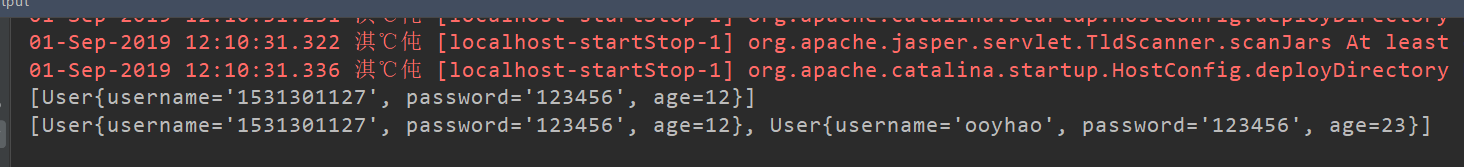
注册成功之后就会跳到注册成功的页面:
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Blog</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>注册成功~</h1>
</body>
</html>
如下:
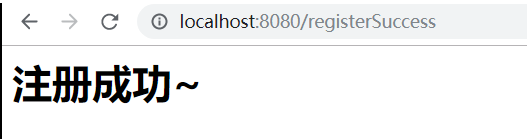
但是此时我们可以尝试,在页面不填写任何数据,同样是可以提交成功的,这明显不符合我们的业务要求。所以这里需要进行参数校验。
4. 参数校验
首先,我们需要导入一个Jar包
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.hibernate.validator/hibernate-validator -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate.validator</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>6.1.0.Alpha3</version>
</dependency>
其次我们需要修改我们的实体类
public class User implements Serializable {
@NotNull
@Size(min = 4,max = 20)
private String username;
@NotNull
@Size(min = 6,max = 32)
private String password;
@NotNull
@Min(1)
@Max(150)
private Integer age;
//all/noArgConstructor, getter and setter, toString
}
并且需要在Controller的方式接受参数的地方加上@Valid注解,如下:
/*处理表单数据,并验证*/
@PostMapping("/register")
public String register(@Valid User user, Errors errors){
if (errors.hasErrors()){
return "redirect:/registerFail";
}
userService.saveUser(user);
return "redirect:/registerSuccess";
}
可以看出这里有个Errors参数,这个参数必须紧跟在@Valid注解之后,并且可以通过它判断参数填写是否正确。因为即使加了@Valid,也无法阻止方法的执行,所以需要手动判断处理。
我们增加一个注册失败的提示页面。
registerFail:
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Blog</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>注册失败,请检查数据是否填写正确~</h1>
</body>
</html>
如未按要求填写数据就提交:
4.1 参数检验注解
| 注解 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| @AssertFalse | 所注解的元素必须是Boolean类型,并且值为false |
| @AssertTrue | 所注解的元素必须是Boolean类型,并且值为true |
| @DecimalMax | 所注解的元素必须是数字,并且它的值要小于或等于给定的BigDecimalString的值 |
| @DecimalMin | 所注解的元素必须是数字,并且它的值要大于或等于给定的BigDecimalString的值 |
| @Digists | 所注解的元素必须是数字,并且它的值必须有指定的位数 |
| @Future | 所注解的元素的值必须是一个将来的日期 |
| @Max | 所注解的元素必须是数字,并且它的值要小于或等于给定的值 |
| @Min | 所注解的元素必须是数字,并且它的值要大于或等于给定的值 |
| @NotNull | 所注解元素的值必须不能为null |
| @Null | 所注解元素的值必须为null |
| @Past | 所注解的元素的值必须是一个已过去的日期 |
| @Pattern | 所注解的元素的值必须匹配给定的正则表达式 |
| @Size | 所注解的元素的值必须是String,集合或数组,并且它的长度要符合给定的范围 |
5. 本地中的POM 文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.ooyhao.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-in-action-05-02</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>spring-in-action-05-02 Maven Webapp</name>
<url>http://www.example.com</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.7</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.7</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- @ResponseBody自动转JSON -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-annotations</artifactId>
<version>2.9.5</version>
</dependency>
<!-- servlet参数 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 参数校验 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate.validator</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>6.1.0.Alpha3</version>
</dependency>
<!--jsp中使用jstl标签-->
<dependency>
<groupId>jstl</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>spring-in-action-05-02</finalName>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-clean-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.0</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.22.1</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-install-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.5.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-deploy-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.8.2</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>
</project>
总结:
这一节主要是将web.xml构建web项目和WebApplicationInitializer构建项目对比,手动搭建一个无xml文件的web项目。同时也揭开了SpringBoot无配置文件启动的神秘面纱。并且连接了三种参数输入的方式。
案例地址:
https://gitee.com/ooyhao/JavaRepo_Public/tree/master/Spring-in-Action/spring-in-action-05
最后
如果觉得不错的话,那就关注一下小编哦!一起交流,一起学习



