蛙蛙推荐: LRU缓存的实现算法讨论
业务模型
读、写、删的比例大致是7:3:1,至少要支持500w条缓存,平均每条缓存6k,要求设计一套性能比较好的缓存算法。
算法分析
不考虑MemCached,Velocity等现成的key-value缓存方案,也不考虑脱离.net gc自己管理内存,不考虑随机读取数据及顺序读取数据的场景,目前想到的有如下几种LRU方案
|
算法 |
分析 |
|
SortedDictionary |
.net自带的,内部用二叉搜索树(应该不是普通树,至少是做过优化的树)实现的,检索为O(log n),比普通的Dictionay(O(1))慢一点。 |
|
Dictionary + PriorityQueue |
Dictionay可以保证检索是O(1); |
|
Dictionay + Binary heap |
二叉堆也是优先队列,分析应该同上,我没有详细评估。 |
|
b树 |
查找,删除,插入效率都很好,数据库都用它,但实现复杂,写一个没有BUG的B树几乎不可能。有人提到stl:map是自顶向下的红黑树,查找,删除,插入都是O(log n),但咱不懂c++,没做详细测试。 |
|
Dictionay + List |
Dict用来检索; |
|
Dictionay + LinkedList |
Dict用来检索; |
目前几种方案在多线程下应该都需要加锁,不太好设计无锁的方案,下面这个链接是一个支持多线程的方案,但原理至今没搞特明白
A High Performance Multi-Threaded LRU Cache
http://www.codeproject.com/KB/recipes/LRUCache.aspx
用普通链表简单实现LRU缓存
以下是最后一种方案的简单实现,大家讨论下这个方案值不值得优化,或者其它的哪个方案比较合适
readonly Dictionary<K, V> _dict;
readonly LinkedList<K> _queue = new LinkedList<K>();
readonly object _syncRoot = new object();
private readonly int _max;
public LRUCacheHelper(int capacity, int max) {
_dict = new Dictionary<K, V>(capacity);
_max = max;
}
public void Add(K key, V value) {
lock (_syncRoot) {
checkAndTruncate();
_queue.AddFirst(key); //O(1)
_dict[key] = value; //O(1)
}
}
private void checkAndTruncate() {
lock (_syncRoot) {
int count = _dict.Count; //O(1)
if (count >= _max) {
int needRemoveCount = count / 10;
for (int i = 0; i < needRemoveCount; i++) {
_dict.Remove(_queue.Last.Value); //O(1)
_queue.RemoveLast(); //O(1)
}
}
}
}
public void Delete(K key) {
lock (_syncRoot) {
_dict.Remove(key); //(1)
_queue.Remove(key); // O(n)
}
}
public V Get(K key) {
lock (_syncRoot) {
V ret;
_dict.TryGetValue(key, out ret); //O(1)
_queue.Remove(key); //O(n)
_queue.AddFirst(key); //(1)
return ret;
}
}
}
用双头链表代替普通链表
突然想起来了,可以把链表换成双头链表,然后在字典里保存链表节点,在Get方法的时候直接从字典里获取到要移动的节点,然后把这个节点的上一个节点的Next指针指向给下一个节点,下一个节点的Previous指针指向上一个节点,这样就把移动节点的操作简化成O(1)了,提高了缓存读取的效率。
_dict.TryGetValue(key, out ret); //O(1)
ret.Next.Previous = ret.Previous //O(1)
ret. Previous.Next. = ret.Next //O(1)
_queue.AddFirst(key); //O(1)
我改进后的链表就差不多满足需求了,
|
操作 |
基本操作 |
复杂度 |
|
读取 |
Dict.Get Queue.Move |
O 1 O 1 |
|
删除 |
Dict.Remove Queue.Remove |
O 1 O 1 |
|
增加 |
Dict.Add Queue.AddFirst |
O 1 O 1 |
|
截断 |
Dict.Remove Queue.RemoveLast |
O k O k K表示截断缓存元素的个数 |
其中截断的时候可以指定当缓存满的时候截断百分之多少的最少使用的缓存项。
其它的就是多线程的时候锁再看看怎么优化,字典有线程安全的版本,就把.net 3.0的读写锁扣出来再把普通的泛型字典保证成ThreadSafelyDictionay就行了,性能应该挺好的。
链表的话不太好用读写锁来做线程同步,大不了用互斥锁,但得考虑下锁的粒度,Move,AddFirst,RemoveLast的时候只操作一两个节点,是不是想办法只lock这几个节点就行了,Truncate的时候因为要批量操作很多节点,所以要上个大多链表锁,但这时候怎么让其它操作停止得考虑考虑,类似数据库的表锁和行锁。
实现代码
public T Value { get; set; }
public DoubleLinkedListNode<T> Next { get; set; }
public DoubleLinkedListNode<T> Prior { get; set; }
public DoubleLinkedListNode(T t) { Value = t; }
public DoubleLinkedListNode() { }
public void RemoveSelf() {
Prior.Next = Next;
Next.Prior = Prior;
}
}
public class DoubleLinkedList<T> {
protected DoubleLinkedListNode<T> m_Head;
private DoubleLinkedListNode<T> m_Tail;
public DoubleLinkedList() {
m_Head = new DoubleLinkedListNode<T>();
m_Tail = m_Head;
}
public DoubleLinkedList(T t)
: this() {
m_Head.Next = new DoubleLinkedListNode<T>(t);
m_Tail = m_Head.Next;
m_Tail.Prior = m_Head;
}
public DoubleLinkedListNode<T> Tail {
get { return m_Tail; }
}
public DoubleLinkedListNode<T> AddHead(T t) {
DoubleLinkedListNode<T> insertNode = new DoubleLinkedListNode<T>(t);
DoubleLinkedListNode<T> currentNode = m_Head;
insertNode.Prior = null;
insertNode.Next = currentNode;
currentNode.Prior = insertNode;
m_Head = insertNode;
return insertNode;
}
public void RemoveTail() {
m_Tail = m_Tail.Prior;
m_Tail.Next = null;
return;
}
}
public class LRUCacheHelper<K, V> {
class DictItem {
public DoubleLinkedListNode<K> Node { get; set; }
public V Value { get; set; }
}
readonly Dictionary<K, DictItem> _dict;
readonly DoubleLinkedList<K> _queue = new DoubleLinkedList<K>();
readonly object _syncRoot = new object();
private readonly int _max;
public LRUCacheHelper(int capacity, int max) {
_dict = new Dictionary<K, DictItem>(capacity);
_max = max;
}
public void Add(K key, V value) {
lock (this)
{
checkAndTruncate();
DoubleLinkedListNode<K> v = _queue.AddHead(key); //O(1)
_dict[key] = new DictItem() { Node = v, Value = value }; //O(1)
}
}
private void checkAndTruncate() {
int count = _dict.Count; //O(1)
if (count >= _max) {
int needRemoveCount = count / 10;
for (int i = 0; i < needRemoveCount; i++) {
_dict.Remove(_queue.Tail.Value); //O(1)
_queue.RemoveTail(); //O(1)
}
}
}
public void Delete(K key) {
lock (this) {
_dict[key].Node.RemoveSelf();
_dict.Remove(key); //(1)
}
}
public V Get(K key) {
lock (this) {
DictItem ret;
if (_dict.TryGetValue(key, out ret)) {
ret.Node.RemoveSelf();
_queue.AddHead(key);
return ret.Value;
}
return default(V);
}
}
}
性能测试
用双头链表测试了一下,感觉性能还可以接受,每秒钟读取可达80多w,每秒钟写操作越20多w。
程序初始化200w条缓存,然后不断的加,每加到500w,截断掉10分之一,然后继续加。
测试模型中每秒钟的读和写的比例是7:3,以下是依次在3个时间点截取的性能计数器图。
图1
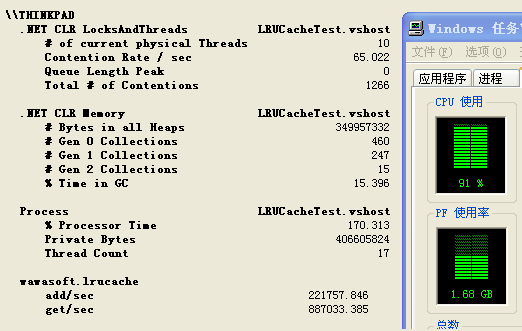
图2
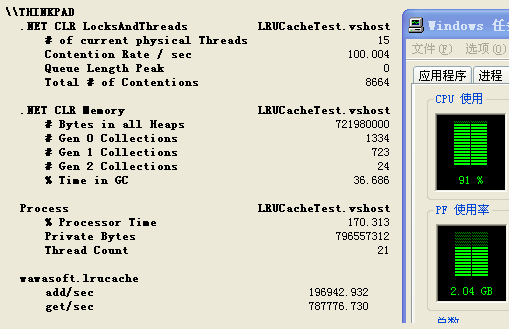
图3

内存最高会达到1g,cpu也平均百分之90以上,但测试到后期会发现每隔一段时间,就会有一两秒,吞吐量为0,如最后一张截图,后来观察发现,停顿的那一两秒是二代内存在回收,等不停顿的时候# gen 2 collections就会加1,这个原因应该是链表引起的,对链表中节点的添加和删除是很耗费GC的,因为会频繁的创建和销毁对象。
后续改进
1、 用游标链表来代替普通的双头链表,程序起来就收工分配固定大小的数组,然后用数组的索引来做链表,省得每次添加和删除节点都要GC的参与,这相当于手工管理内存了,但目前我还没找到c#合适的实现。
2、 有人说链表不适合用在多线程环境中,因为对链表的每个操作都要加互斥锁,连读写锁都用不上,我目前的实现是直接用互斥锁做的线程同步,每秒的吞吐量七八十万,感觉lock也不是瓶颈,如果要改进的话可以把Dictionary用ThreadSafelyDictionary来代替,然后链表还用互斥锁(刚开始设想的链表操作只锁要操作的几个节点以降低并发冲突的想法应该不可取,不严谨)。
3、 还有一个地方就是把锁细分以下,链表还用链表,但每个链表的节点是个HashSet,对HashSet的操作如果只有读,写,删,没有遍历的话应该不需要做线程同步(我感觉不用,因为Set就是一个集合,一个线程往里插入,一个线程往里删除,一个线程读取应该没问题,顶多读进来的数据可能马上就删除了,而整个Set的结构不会破坏)。然后新增数据的时候往链表头顶Set里插入,读取某个数据的时候把它所在的节点的Set里删除该数据,然后再链表头的Set里插入一个数据,这样反复操作后,链表的最后一个节点的Set里的数据都是旧数据了,可以安全的删除了,当然这个删除的时候应该是要锁整个链表的。每个Set应该有个大小上限,比如20w,但set不能安全的遍历,就不能得到当前大小,所以添加、删除Set的数据的时候应该用Interlocked.Decrement()和 Interlocked.Increment()维护一个Count,一遍一个Set满的时候,再到链表的头新增一个Set节点。
性能测试脚本
private static PerformanceCounter _addCounter;
private static PerformanceCounter _getCounter;
static void Main(string[] args) {
SetupCategory();
_addCounter = new PerformanceCounter("wawasoft.lrucache", "add/sec", false);
_getCounter = new PerformanceCounter("wawasoft.lrucache", "get/sec", false);
_addCounter.RawValue = 0;
_getCounter.RawValue = 0;
Random rnd = new Random();
const int max = 500 * 10000;
LRUCacheHelper<int, int> cache = new LRUCacheHelper<int, int>(200 * 10000, max);
for (int i = 10000*100000 - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
if(i % 10 > 7)
{
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(
delegate
{
cache.Add(rnd.Next(0, 10000), 0);
_addCounter.Increment();
});
}
else
{
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(
delegate
{
int pop = cache.Get(i);
_getCounter.Increment();
});
}
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
private static void SetupCategory() {
if (!PerformanceCounterCategory.Exists("wawasoft.lrucache")) {
CounterCreationDataCollection CCDC = new CounterCreationDataCollection();
CounterCreationData addcounter = new CounterCreationData();
addcounter.CounterType = PerformanceCounterType.RateOfCountsPerSecond32;
addcounter.CounterName = "add/sec";
CCDC.Add(addcounter);
CounterCreationData getcounter = new CounterCreationData();
getcounter.CounterType = PerformanceCounterType.RateOfCountsPerSecond32;
getcounter.CounterName = "get/sec";
CCDC.Add(getcounter);
PerformanceCounterCategory.Create("wawasoft.lrucache","lrucache",CCDC);
}
}
}
参考链接
不分先后,都是随时从网上找的,大多看不懂
潜心学习数据结构-C#语言描述系列文章
http://space.cnblogs.com/group/topic/6922/
《C++数据结构原理与经典问题求解》
http://www.huachu.com.cn/itbook/bookinfodetail.asp?lbbh=10087298&sort=ml
数据结构(C#):循环链表
http://www.cnblogs.com/zxjay/archive/2008/12/07/1349688.html
表的游标实现
http://www.comp.nus.edu.sg/~xujia/mirror/algorithm.myrice.com/datastructure/basic/list/chapter3_3.htm
我所理解的链表1
http://www.diybl.com/course/3_program/c/csuanfa/2007213/21570.html
cursor implementation of linked list
http://wiki.answers.com/Q/Explain_the_Cursor_implementation_of_linked_list
Sorting Algorithms In C#
http://www.codeproject.com/KB/recipes/cssorters.aspx
The C5 Generic Collection Library
http://www.itu.dk/research/c5/
当弱引用对象成为集合元素时
http://www.agiledon.com/post/Coding/Weakreference-Collection-CSharp.html
QuickSort in Functional C#
http://blogs.objectsharp.com/cs/blogs/jlee/archive/2008/05/23/quicksort-in-functional-c.aspx
LRU页面置换算法模拟
http://dev.csdn.net/article/73207.shtm








【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
2007-07-22 元搜索、热点发现、自动分类和相关性分析的简单实现
2007-07-22 蛙蛙推荐:用c#实现一个简单的分布式搜索