2.(图)-深度优先遍历DFS
从图的某个节点开始遍历,访问了则标记下来,然后访问此点所有邻域中任意点为新起点,且做上访问标记,通常通过递归和栈的技巧实现。
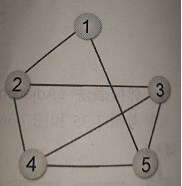
1:以1为起点,[5,2]入栈
2:弹出上面的2,2相邻且未标记访问的3,4入栈[5,4,3]
3:弹3,入4,5;[5,4,5,4]
4:弹4,入5;[5,4,5,5]
5:弹5,剩余[5,4,5]
6:[5,4,5]均被标记访问,依次弹出,不打印、访问节点
最终深度优先遍历依次访问节点:1,2,3,4,5
1.基于递归
class list_node:
def __init__(self):
self.val = 0
self.next = None
def dfs(current, run=[0] * 9):
'''
基于递归实现
:param current:
:param run:
:return:
'''
run[current] = 1
print('[%d]' % current, end=' ')
ptr = head[current].next
while ptr != None: # 遍历所有current节点连接的节点
if run[ptr.val] == 0: # 连接点未访问
dfs(ptr.val, run)
ptr = ptr.next
def graph_create(data):
'''
创建链表表示图
:return:
'''
global head
for i in range(len(head)):
head[i] = list_node()
head[i].val = i
head[i].next = None
ptr = head[i]
for j in range(len(data)):
if data[j][0] == i:
newnode = list_node()
newnode.val = data[j][1]
newnode.next = None
ptr.next = newnode
ptr = ptr.next
def print_head(head):
'''
打印函数
:return:
'''
for i in range(len(head)):
ptr = head[i]
print('顶点%d=>' % i, end=' ')
ptr = ptr.next
while ptr != None:
print('[%d] ' % ptr.val, end=' ')
ptr = ptr.next
print()
data = [[1, 2], [2, 1], [1, 3], [3, 1],
[2, 4], [4, 2], [2, 5], [5, 2],
[3, 6], [6, 3], [3, 7], [7, 3],
[4, 8], [8, 4], [5, 8], [8, 5],
[6, 8], [8, 6], [8, 7], [7, 8]]
head = [None] * 9
graph_create(data)
print_head(head)
print('1节点开始,递归深度优先遍历:')
dfs(1)
print()
2.基于栈
def dfs_stack(current):
'''
基于栈
:param current:
:return:
'''
node_stack = []
if len(node_stack) == 0:
node_stack.append(current)
run = [0] * 9
while len(node_stack) != 0:
out = node_stack.pop()
if run[out] == 0:
print('[%d]' % out, end=' ')
run[out] = 1
ptr = head[out].next
while ptr != None: # 遍历所有current节点连接的节点
if run[ptr.val] == 0: # 连接点未访问
node_stack.append(ptr.val)
ptr = ptr.next
run = [0] * 9
print('1节点开始,栈深度优先遍历:')
dfs_stack(1)
output:
顶点0=>
顶点1=> [2] [3]
顶点2=> [1] [4] [5]
顶点3=> [1] [6] [7]
顶点4=> [2] [8]
顶点5=> [2] [8]
顶点6=> [3] [8]
顶点7=> [3] [8]
顶点8=> [4] [5] [6] [7]
1节点开始,递归深度优先遍历:
[1] [2] [4] [8] [5] [6] [3] [7]
1节点开始,栈深度优先遍历:
[1] [3] [7] [8] [6] [5] [2] [4]



