第四章 第四节 使用RowLayout
RowLayout与FillLayout很相似:它把所有的控件放在一行或一列中。但是,它不会把所有的控件都设为相同的大小。如果空间不够,它会把控件放到另一行或另一列中。
RowLayout使用RowData的实例来决定控件的初始宽度和高度。可以通过给控件的setLayoutData()传递RowData的方法,把一个RowData对象关联到一个控件;layout从控件中获取RowData以决定控件的大小和排布(sizing and placement)。
注意:所有SWT控件的始祖,Widget类,有一个称作setData()的方法,与setLayoutData()一样,用对象(Object)作为参数。如果读者把一个layout data实例赋给一个控件,但它没有达到读者所预期的结果,检查一下是不是不小心调用了setData()而不是setLayoutData()。
RowData类有两个公有成员(public member):
| public int height public int width |
读者可以在构造RowData对象之后设置这些值。例如,下面的代码创建一个按钮并把它的宽设为100象素,高设为50象素。
| Button button = new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH); RowData rowData = new RowData(); rowData.height = 50; rowData.width = 100; button.setLayoutData(rowData); |
RowData提供了两个很方便的构造函数,使读者可以用两个整数或者一个Point来设置高和宽。代码如下:
| Button button = new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH); button.setLayoutData(new RowData(100, 50)); // width, height//宽度,高度 |
或使用如下代码:
| Button button = new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH); button.setLayoutData(new RowData(new Point(100, 50))); // width, height//宽度,高度 |
RowLayout像FillLayout一样,有一个公有(public)的属性样式(type),可以取SWT.HORIZONTAL或SWT.VERTICAL将layout设置为行或列。RowLayout还有其它一些可设置的属性(见表4-2)。
表4-2 RowLayout的属性
| 属性 | 说明 |
| boolean justify | Iftrue, justifies the entire row or column; it doesn't change the size of the controls, but rather spaces them evenly to fill the space. Think of a line of text in a newspaper story that has excess space between letters to preserve the justification of the column. The default isfalse. |
| int marginBottom | The size of the bottom margin, in pixels, for the layout. The default is 3. |
| int marginLeft | The size of the left margin, in pixels, for the layout. The default is 3. |
| int marginRight | The size of the right margin, in pixels, for the layout. The default is 3. |
| int marginTop | The size of the top margin, in pixels, for the layout. The default is 3. |
| boolean pack | Iftrue, tells all controls to use their preferred size. The default istrue. |
| int spacing | The size of the space, in pixels, between neighboring controls. The default is 3. |
| int type | The type of the layout; if it'sSWT.HORIZONTAL (the default), the layout will use rows. If it'sSWT.VERTICAL, the layout will use columns. Current implementations will useSWT.VERTICAL if an invalid value is specified. |
| boolean wrap | Iftrue, will wrap the controls to the next row or column if the current row or column is out of space. The default istrue. |
RowLayout有两个构造函数:一个空的构造函数;另一个用一个参数标明样式(样式值(type value)作为参数)。
考虑下面的代码:
| package examples.ch4;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.*; import org.eclipse.swt.layout.RowLayout; import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
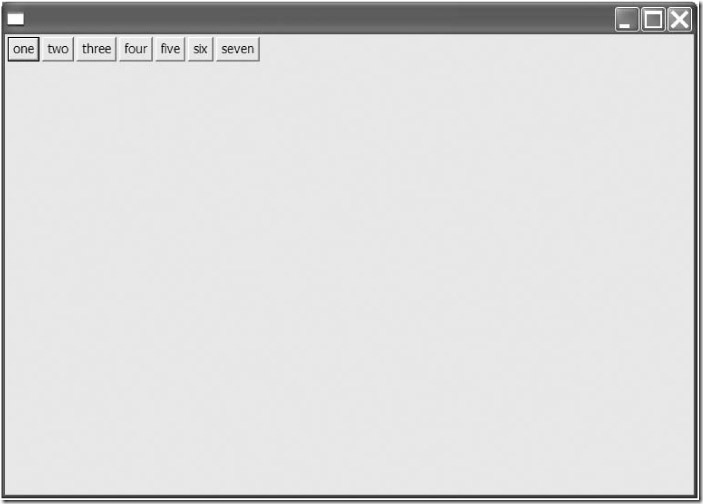
public class RowLayoutHorizontal { public static void main(String[] args) { Display display = new Display(); Shell shell = new Shell(display); shell.setLayout(new RowLayout(SWT.HORIZONTAL)); new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH).setText("one"); new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH).setText("two"); new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH).setText("three"); new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH).setText("four"); new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH).setText("five"); new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH).setText("six"); new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH).setText("seven"); shell.open(); while (!shell.isDisposed()) { if (!display.readAndDispatch()) { display.sleep(); } } display.dispose(); } } |
这段代码使用row layout的默认属性的值创建了一个水平的row layout。如果读者编译并运行这段代码,就可以看到如图4-3所示的窗体。
图4-3 默认的RowLayout
因为默认的属性会折行显示,所以改变窗口的大小会使控件显示到多行(见图4-4)。
图4-4 默认的RowLayout,改变大小后的情形
通过操作row layout的值和使用RowData对象,读者可以显著的改变layout的行为。清单4-2展示了这样的例子。
清单4-2 RowLayoutTest.java
| package examples.ch4;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.*; import org.eclipse.swt.layout.RowLayout; import org.eclipse.swt.layout.RowData; import org.eclipse.swt.SWT;
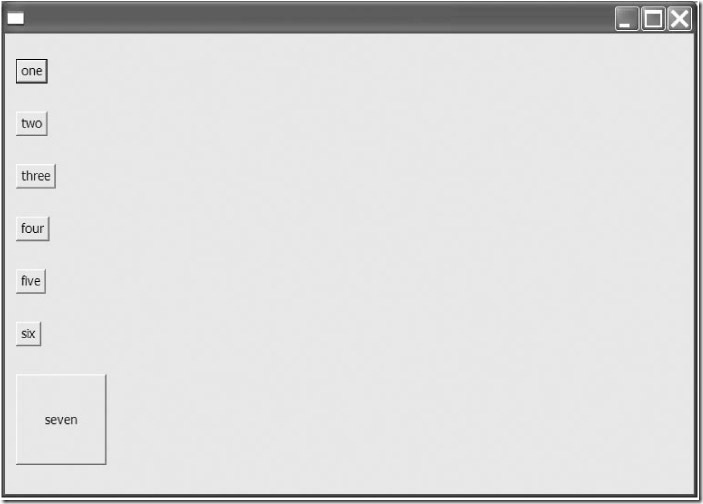
public class RowLayoutTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Display display = new Display(); Shell shell = new Shell(display); RowLayout layout = new RowLayout(SWT.VERTICAL); layout.marginLeft = 12; layout.marginTop = 0; layout.justify = true; shell.setLayout(layout); new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH).setText("one"); new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH).setText("two"); new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH).setText("three"); new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH).setText("four"); new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH).setText("five"); new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH).setText("six"); Button b = new Button(shell, SWT.PUSH); b.setText("seven"); b.setLayoutData(new RowData(100, 100)); shell.open(); while (!shell.isDisposed()) { if (!display.readAndDispatch()) { display.sleep(); } } display.dispose(); } } |
这段代码创建了一个垂直的row layout,改变了上边距和左边距(top and left margin),并对控件进行操作——使用一个RowData对象来设置标为“seven”的按钮的大小。编译并运行这段代码可以看到如图4-5所示的窗体。
图4-5 一个改变了部分属性的RowLayout
读者会看到,垂直的row layout看起来极像column layout;RowLayout的垂直(columnar)排列功能是在SWT 2.0中添加的。SWT的开发人员没有创建一个新的类并重复大量的代码,而是重用了RowLayout并添加了垂直(vertical)属性。当然,读者也可以创建一个叫做ColumnLayout的类,从RowLayout继承并把样式设为SWT.VERTICAL――如果这样感觉好些的话。大多数人还是接受这个“xx的名称”好了。
RowLayout的属性可以取代FillLayout,但还不足以用于复杂的layout。下一节的主题,GridLayout,使layout向前迈了一大步。