BZOJ 2725 [Violet 6]故乡的梦 线段树+最短路树
\(\color{#0066ff}{ 题目描述 }\)
.gif)
\(\color{#0066ff}{输入格式}\)
.gif)
\(\color{#0066ff}{输出格式}\)
.gif)
\(\color{#0066ff}{输入样例}\)
6 7
1 2 1
2 3 1
3 4 2
4 5 1
5 6 1
1 3 3
4 6 3
1 6
4
1 2
1 3
4 3
6 5
\(\color{#0066ff}{输出样例}\)
7
6
Infinity
7
\(\color{#0066ff}{数据范围与提示}\)
.gif)
\(\color{#0066ff}{ 题解 }\)
分别从s和t跑最短路,构建出最短路树
标记最短路树的点和边
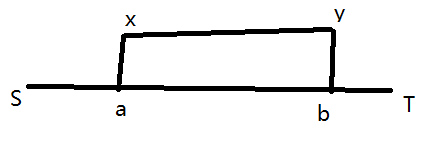
从最短路树上的每个点bfs,找到能影响的L和R
显然若上图a,b之间的某条边断了,x到y的边就可以用来更新这部分答案
从a找到所有x,b找到所有y
枚举所有边,只要不在最短路树上,就类似于上图更新(用线段树维护)
在\(O(nlogn)\)的复杂度下求出删去每条最短路树上的边的ans
对于询问,如果不是最短路树的边,ans就是最短路
否则用刚刚在线段树求的ans输出
跑dij的pair要开long long!!!!
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define LL long long
LL in() {
char ch; LL x = 0, f = 1;
while(!isdigit(ch = getchar()))(ch == '-') && (f = -f);
for(x = ch ^ 48; isdigit(ch = getchar()); x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48));
return x * f;
}
const int maxn = 2e6 + 100;
int L[maxn], R[maxn], S, T;
int n, m;
struct node {
int to;
LL dis;
bool vis;
node *nxt;
node(int to = 0, LL dis = 0, bool vis = false, node *nxt = NULL): to(to), dis(dis), vis(vis), nxt(nxt) {}
};
node *head[maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
LL diss[maxn], dist[maxn];
int st[maxn], cnt, rst[maxn];
LL ans[maxn];
const LL inf = 9999999999999LL;
using std::pair;
using std::make_pair;
struct Tree {
Tree *ch[2];
LL val;
int l, r;
Tree(LL val = 0, int l = 0, int r = 0): val(val), l(l), r(r) {}
}*root;
void build(Tree *&o, int l, int r) {
o = new Tree(inf, l, r);
if(l == r) return;
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
build(o->ch[0], l, mid);
build(o->ch[1], mid + 1, r);
}
void add(int from, int to, LL dis) {
head[from] = new node(to, dis, 0, head[from]);
}
void dij(int s, LL *dis) {
std::priority_queue<pair<LL, int>, std::vector<pair<LL, int> >, std::greater<pair<LL, int> > > q;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) vis[i] = 0, dis[i] = inf;
q.push(make_pair(dis[s] = 0, s));
while(!q.empty()) {
int tp = q.top().second;
q.pop();
if(vis[tp]) continue;
vis[tp] = true;
for(node *i = head[tp]; i; i = i->nxt)
if(dis[i->to] > dis[tp] + i->dis)
q.push(make_pair(dis[i->to] = dis[tp] + i->dis, i->to));
}
}
void bfs(int s, int *P, LL *dis) {
std::queue<int> v;
P[st[s]] = s;
v.push(st[s]);
while(!v.empty()) {
int tp = v.front(); v.pop();
for(node *i = head[tp]; i; i = i->nxt) {
if(dis[i->to] == dis[tp] + i->dis && !vis[i->to] && !P[i->to]) {
P[i->to] = s;
v.push(i->to);
}
}
}
}
void change(Tree *o, int l, int r, LL val) {
if(o->r < l || o->l > r) return;
if(l <= o->l && o->r <= r) return (void)(o->val = std::min(o->val, val));
change(o->ch[0], l, r, val), change(o->ch[1], l, r, val);
}
void query(Tree *o) {
if(o->l == o->r) return (void)(ans[o->l] = o->val);
o->ch[0]->val = std::min(o->ch[0]->val, o->val);
o->ch[1]->val = std::min(o->ch[1]->val, o->val);
query(o->ch[0]);
query(o->ch[1]);
}
int main() {
n = in(), m = in();
LL x, y, z;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
x = in(), y = in(), z = in();
add(x, y, z), add(y, x, z);
}
dij(S = in(), diss);
dij(T = in(), dist);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) vis[i] = 0;
for(int o = S; o != T;) {
st[rst[o] = ++cnt] = o;
vis[o] = true;
for(node *i = head[o]; i; i = i->nxt) {
if(diss[o] + dist[i->to] + i->dis == diss[T]) {
i->vis = true;
o = i->to;
break;
}
}
}
st[rst[T] = ++cnt] = T;
vis[T] = true;
for(int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) bfs(i, L, diss);
for(int i = cnt; i >= 1; i--) bfs(i, R, dist);
build(root, 1, cnt);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(node *j = head[i]; j; j = j->nxt) {
if(j->vis) continue;
if(L[i] < R[j->to] && L[i] && R[j->to]) change(root, L[i], R[j->to] - 1, diss[i] + dist[j->to] + j->dis);
}
query(root);
for(int q = in(); q --> 0;) {
x = in(), y = in();
if(rst[x] > 0 && rst[y] > 0 && abs(rst[x] - rst[y]) == 1) {
LL t = ans[std::min(rst[x], rst[y])];
if(t == inf) printf("Infinity\n");
else printf("%lld\n", t);
}
else if(diss[T] == inf) printf("Infinty\n");
else printf("%lld\n", diss[T]);
}
return 0;
}
----olinr


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号