一个Work Stealing Pool线程池的实现
一、一般来说实现一个线程池主要包括以下几个组成部分:
1)线程管理器 :用于创建并管理线程池 。
2)工作线程 :线程池中实际执行任务的线程 。 在初始化线程时会预先创建好固定数目的线程在池中 ,这些初始化的线程一般是处于空闲状态 ,不消耗CPU,占用较小的内存空间 。
3)任务接口 :每个任务必须实现的接口 ,当线程池中的可执行的任务时 ,被工作线程调试执行。 把任务抽象出来形成任务接口 ,可以做到线程池与具体的任务无关 。
4)任务队列 :用来存放没有处理的任务 ,提 供一种缓冲机制 。 实现这种结构有好几种方法 ,常用的是队列 ,主要是利用它先进先出的工作原理;另外一种是链表之类的数据结构 ,可以动态为它分配内存空间 ,应用中比较灵活 。
二、常用的线程池模型
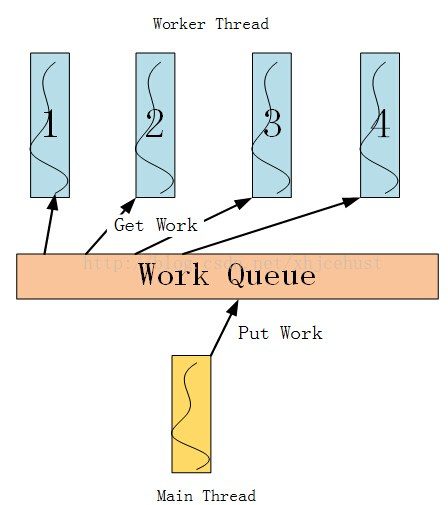
如上图所示,工作队列由主线程和工作者线程共享,主线程将任务放进工作队列,工作者线程从工作队列中取出任务执行。共享工作队列的操作需在互斥量的保护下安全进行,主线程将任务放进工作队列时若检测到当前待执行的工作数目小于工作者线程总数,则需使用条件变量唤醒可能处于等待状态的工作者线程。当然,还有其他地方可能也会使用到互斥量和条件变量,不再赘述。
三、无锁化线程池模型
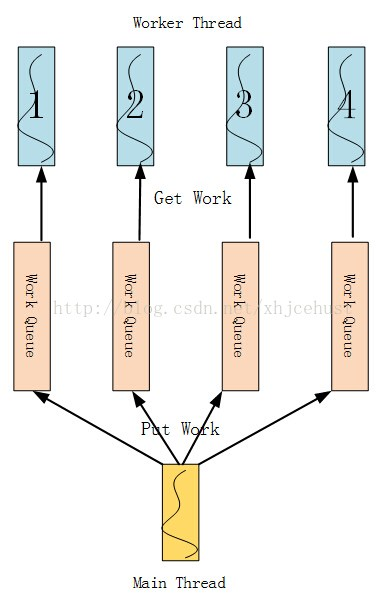
注:上述资料来自于:
四、我的线程池模型
我的线程池模型跟前面无锁化线程池模型很像,不过,它并不是无锁的。但是它是Work Stealing Pool.
这种线程模型对应于几种网络服务器编程模型中的是:Reactor + thread pool(主线程IO,工作线程计算)。
关于Work Stealing Pool的一些说明:
(1)Steal,翻译为偷窃,窃取。这里的意思是,如果当前工作线程处理完自己本地任务队列中的任务时,就会去全局队列或者其他工程线程的队列里面查找工作任务,帮助它们完成。
(2)利用Work Staling,可以更好实现负载均衡。因为每个工作线程的任务都是不一样的,完成的时间也不一样。
五、线程池具体实现
1. 这个线程池的优点:
(1)当添加任务时,唤醒一个空闲的工作线程,而不是一群线程,所以不会产生惊群现象。
(2)Work stealing pool,每个工作线程有自己的任务队列,当前完成自己本地的队列的任务时,会自动去全局队列里面获取任务来工作,或者去”偷“其他线程的队列里面的任务。
(3)当添加任务时,没有直接就把任务集中放在全局队列里面,避免工作线程集中去全局队列里面获取任务而造成频繁的锁开销。
2. 这个线程的缺点:
这个线程池有一个很明显的缺陷,就是,如果线程池里只有一个线程时,所添加的工作任务不支持任务递归,什么意思呢?就是说,在线程所要执行的工作任务,不能再添加新的工作任务到线程池中,否则,会造成死锁。
为什么会有这个问题呢?
其实,跟这个线程池的实现有很大关系(这不是废话嘛),线程在执行任务时,用了加锁操作,而且只有当当前任务执行完成后才通过信号量的方式通知主线程(等待结果的线程)计算结果已经完成了,所以,如果在任务中递归执行添加新的任务在线程池中,就会造成死锁,因为第一个在执行第一个任务之前就锁住了线程。
一些可能的解决办法:
要怎么解决这个问题呢?一个可能性的解决方法是,对应这种内部的任务,另外开一个线程去执行。不过,因为时间的关系,我还没有试过。
3. 这个线程的一些方面有待以后改进:
(1)在线程去streal 其他线程的工作任务时,是需要给其他线程加锁了,虽然是从队列尾端拿数据,而它本身的工作线程是从队列头端拿数据,其原因是考虑到一个情况就是,当队列里面只剩下一个任务时,有可能出现竞争的情况,所以,一个方法是,对于头尾指针要经过特别的初始化处理。(具体需要查找资料,网络上有博客说过,往了是哪里了)
(2)这个线程池的队列用了锁,但实际上可以用无锁队列来实现。网上有人写过,可以找来参考下。
4. 具体的代码
因为代码通俗易懂,也加上了很多注释,就不多做解释了。
threadpool.h

struct thread_pool; struct future; /* Create a new thread pool with no more than n threads. */ struct thread_pool * thread_pool_new(int nthreads); void thread_pool_shutdown_and_destroy(struct thread_pool *); typedef void * (* fork_join_task_t) (struct thread_pool *pool, void * data); struct future * thread_pool_submit( struct thread_pool *pool, fork_join_task_t task, void * data); void * future_get(struct future *); void future_free(struct future *);
threadpool.c

#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/time.h> #include <errno.h> #include <assert.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <semaphore.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include "threadpool.h" struct future { fork_join_task_t task; void *arg; //parameter void *result; sem_t *sem; int status; //0: not to do, 1: doing, 2: done int local; //1: internal task, 0: external task struct future *prev; struct future *next; }; struct thread_t { pthread_t id; pthread_mutex_t mutex; pthread_cond_t cond; int idle; //1: idle, 0: busy int index; //record the current thread index in pool int current_task_num; //total task number in current thread struct thread_pool *pool; //point to the pool area struct future *head; struct future *tail; }; struct thread_pool { int max_threads; pthread_mutex_t mutex; int shutdown; //1: shutdown, 0: normal struct thread_t *threads; struct future *head; struct future *tail; }; static void *thread_route(void *arg) { assert(arg != NULL); struct thread_t *thread = (struct thread_t *)arg; assert(thread != NULL); struct thread_pool *pool = thread->pool; assert(pool != NULL); struct future *future = NULL; while(1) { pthread_mutex_lock(&thread->mutex); if(future != NULL) { thread->idle = 0; future->status = 1; //doing future->result = future->task(pool, future->arg); future->status = 2; sem_post(future->sem); } while(thread->current_task_num == 0 && pool->shutdown == 0) { //wait for task assigment pthread_cond_wait(&thread->cond, &thread->mutex); } if(pool->shutdown == 1) { //pool is shutdown, destroy the local task list struct future *temp = NULL; while(thread->head != NULL) { temp = thread->head; thread->head = thread->head->next; free(temp); } pthread_mutex_unlock(&thread->mutex); pthread_exit(NULL); } //Fist, get task from local task list to do while(thread->head != NULL) { thread->idle = 0; future = thread->head; thread->head = thread->head->next; if(thread->tail == future) thread->tail = NULL; else thread->head->prev = NULL; //call the callback to do work thread->current_task_num--; future->status = 1; //doing #if 0 if(pool->max_threads == 1 && future->local == 1) { /* * TBD: in case there is only a thread in pool * and the task is local task * we can create a thread to do the task? */ } else #else { future->result = future->task(pool, future->arg); } #endif future->status = 2; sem_post(future->sem); //Let future_get know, the result is ok } pthread_mutex_unlock(&thread->mutex); thread->idle = 1; /* * The local task work are done, go to global task list to get task * or go to other work thread to get task. */ //Step1: Go to globacl task list to get task(From Head) pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutex); future = NULL; while(pool->head != NULL && pool->head->status == 0) { //printf("Worker %d get task from global task, current_task %d\n", thread->index, thread->current_task_num); future = pool->head; pool->head = pool->head->next; if(pool->tail == future) pool->tail = NULL; else pool->head->prev = NULL; //Get the future, then put into the local task list? #if 0 pthread_mutex_lock(&thread->mutex); if(thread->head != NULL) { future->next = thread->head; thread->head->prev = future; } else { thread->tail = future; } thread->head = future; thread->current_task_num++; pthread_mutex_unlock(&thread->mutex); if(thread->current_task_num == 9) { //Get 10 tasks, ok, get out, give some changes to other work threads break; } #else //printf("Worked %d get one task from globack task list.\n", thread->index); break; //get one task, break #endif } pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutex); //Step2: Go to other work thread task list to get task(From Tail) if(future == NULL && thread->current_task_num == 0) { //printf("Worker %d can not get task from global task, then try other work threads, current_task %d\n", thread->index, thread->current_task_num); future = pool->head; int i = 0; struct thread_t *other_thread = NULL; for(i=0; i<pool->max_threads; i++) { if(i == thread->index) continue; //myself if(pool->threads[i].current_task_num == 0) continue; //it has no task //lock it? pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->threads[i].mutex); other_thread = (struct thread_t *)&pool->threads[i]; while(other_thread->tail != NULL && other_thread->tail->status == 0) { future = other_thread->tail; other_thread->tail = other_thread->tail->prev; if(future == other_thread->head) other_thread->head = NULL; else other_thread->tail->next = NULL; //Get the future, then put into our local task list? #if 0 pthread_mutex_lock(&thread->mutex); if(thread->head != NULL) { future->next = thread->head; thread->head->prev = future; } else { thread->tail = future; } thread->head = future; thread->current_task_num++; printf("Worker %d get task from other thread task, current_task %d\n", thread->current_task_num); pthread_mutex_unlock(&thread->mutex); if(thread->current_task_num == 4) { //Get 4 tasks, ok, get out, give some changes to other work threads break; } #else //printf("Worked %d get one task from other worker %d.\n", thread->index, i); break; //get one task, break #endif } pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->threads[i].mutex); } } } } struct thread_pool * thread_pool_new(int nthreads) { struct thread_pool *pool = (struct thread_pool *)malloc(sizeof(struct thread_pool)); assert(pool != NULL); pool->max_threads = nthreads; pool->head = pool->tail = NULL; pthread_mutex_init(&pool->mutex, NULL); pool->threads = (struct thread_t *)malloc(nthreads * sizeof(struct thread_t)); assert(pool->threads != NULL); int i = 0; for(i=0; i<pool->max_threads; i++) { pthread_mutex_init(&pool->threads[i].mutex, NULL); pthread_cond_init(&pool->threads[i].cond, NULL); pool->threads[i].idle = 1; //idle pool->threads[i].index = i; pool->threads[i].pool = pool; //point to the pool area pool->threads[i].current_task_num = 0; pthread_create(&pool->threads[i].id, NULL, thread_route,(void *)(&pool->threads[i])); } return pool; } struct future * thread_pool_submit( struct thread_pool *pool, fork_join_task_t task, void * data) { assert(pool != NULL); struct future *future = (struct future *)malloc(sizeof(struct future)); assert(future); future->task = task; future->arg = data; future->prev = future->next = NULL; future->result = NULL; future->status = 0; future->local = 0; //default is external task int i = 0; unsigned long myself_pid = pthread_self(); for(i=0; i<pool->max_threads; i++) { if(pool->threads[i].id == myself_pid) { future->local = 1; //it is internal task break; } } future->sem = (sem_t *)malloc(sizeof(sem_t)); assert(future->sem != NULL); sem_init(future->sem, 0, 0); //find a idle work thread to put the task struct thread_t * thread = NULL; for(i = 0; i< pool->max_threads; i++) { thread = &pool->threads[i]; pthread_mutex_lock(&thread->mutex); if(thread->idle == 1) { //find it, insert the task from head if(thread->head != NULL) { future->next = thread->head; thread->head->prev = future; } else { thread->tail = future; } thread->head = future; thread->current_task_num++; //Just let work thread know, it has work to do if(thread->current_task_num == 1) { //printf("%s(): Let worker %d to start to work\n", __FUNCTION__, thread->index); pthread_cond_signal(&thread->cond); } pthread_mutex_unlock(&thread->mutex); return future; } pthread_mutex_unlock(&thread->mutex); } //can not find idle work thread, just put it into global task list //printf("%s(): no find idle work thread, just put into global task list\n", __FUNCTION__); pthread_mutex_lock(&pool->mutex); if(pool->head != NULL) { future->next = pool->head; pool->head->prev = future; } else { pool->tail = future; } pool->head = future; pthread_mutex_unlock(&pool->mutex); return future; } void * future_get(struct future *future) { assert(future); sem_wait(future->sem); //wait for the result ready return (void *)future->result; }
完整的代码,请看我的GitHub:
https://github.com/wolf623/Work-Stealing-Pool
如需转发,请注明出处:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号