Spring IoC
1. 控制反转是一个对象获取它所依赖的对象的引用。反转是指责任的反转。
对象的依赖关系的管理被反转了,转到了IoC容器,对象之间的相互依赖关系由IoC容器进行管理,并由IoC容器完成对象的注入。
很多对象依赖关系的建立和维护并不需要和系统运行状态有很强的关联性,所以可以把面向对象编程需要执行的诸如新建对象、为对象引用赋值等操作交给IoC容器统一完成。这样将散落在不同代码中的功能相同的
部分就集中成为容器的一部分,也就成为面向对象系统的基础设施的一部分。
2. IoC的设计与实现
2.1 如果深入到Spring的实现中看,我们通常所说的IoC容器,实际上代表着一系列功能各异的容器产品,只是容器的功能有大有小,有各自的特点。
2.2 BeanFactory与ApplicationContext
BeanFactory:
containsBean(String)
getAliases(String)
getBean(Class<T>)
getBean(Class<T>, Object...)
getBean(String)
getBean(String, Class<T>)
getBean(String, Object...)
getType(String)
isPrototype(String)
isSingleton(String)
isTypeMatch(String, Class<?>)
isTypeMatch(String, ResolvableType)
ApplicationContext:
getApplicationName()
getAutowireCapableBeanFactory()
getDisplayName()
getId()
getParent()
getStartupDate()
直接的BeanFactory的实现(XmlBeanFactory)是IoC的基本形式,而各种ApplicationContext的实现是IoC容器的高级表现形式。
BeanFactory与FactoryBean:
若myJndiObject是一个FactoryBean(可以生产对象),那么使用&myJndiObject得到的是FactoryBean,而不是myJndiObject这个工厂bean生产出来的对象。
//对FactoryBean的转义定义,因为如果使用bean的名字检索FactoryBean得到的对象是工厂生成的对象,
//如果需要得到工厂本身,需要转义
String FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX = "&";
2.3 IoC容器的初始化过程:Resource定位、载入、注册
编程式使用IoC容器:
1 ClassPathResource res = new ClassPathResource("beans.xml"); 2 DefaultListableBeanFactory factory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); 3 XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(factory); 4 reader.loadBeanDefinitions(res);
2.3.1.Resource定位过程
Resource定位指的是BeanDefinition的资源定位,它由ResouceLoader通过统一的Resouce接口来完成,这个Resouce对各种形式的BeanDefinition的
使用都提供了统一接口。比如,在文件系统中的Bean定义信息可以使用FileSystemResource来进行抽象;在类路径中的bean定义信息可以使用ClassPathResouce。
这个定位过程类似于容器寻找数据的过程。
以ApplicationContext的实现类FileSystenXmlApplicaiontContext为例分析Resource定位过程。
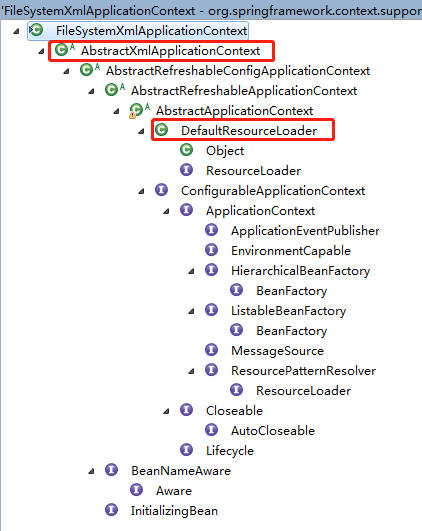
具体实现:
public class FileSystemXmlApplicationContext extends AbstractXmlApplicationContext { public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext() { } public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) { super(parent); } // configLocation是BeanDefinition所在的文件路径 public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation) throws BeansException { this(new String[] {configLocation}, true, null); } // configLocations包含多个BeanDefinition所在的文件路径 public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String... configLocations) throws BeansException { this(configLocations, true, null); } public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException { this(configLocations, true, parent); } public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh) throws BeansException { this(configLocations, refresh, null); } // 在对象的初始化过程中,调用refresh函数载入BeanDefinition // 这个refresh启动了BeanDefinition的载入过程 public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext( String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException { super(parent); setConfigLocations(configLocations); if (refresh) { refresh(); } } // 这是应用于文件系统中Resource的实现,通过构造一个 // FileSystemResource来得到一个在文件系统中定位的 // BeanDefinition,这个getResourceByPath是在 // BeanDefinitionReader的loadBeanDefinition中被调用的, // loadBeanDefinition采用了模板模式,具体的定位实现是由各个 // 子类完成的。 @Override protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) { if (path.startsWith("/")) { path = path.substring(1); } //这里使用文件系统资源对象来定义bean 文件 return new FileSystemResource(path); } }
在FileSystemXmlApplicationContext中,我们可以看到在构造函数中,实现了对configuration进行处理的功能,让所有配置在文件系统中的,以xml文件方式存在的BeanDefinition都能够得到有效的处理。
在FileSystemXmlApplicationContext可以看到,在对BeanDefinition定位的过程中,最初是由refresh触发的,这个refresh的调用是在FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的构造函数启动的。
分析refresh方法调用栈:



栈顶至栈底。
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext对容器的初始化:
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException { //如果已经有容器,销毁容器中的bean,关闭容器 if (hasBeanFactory()) { destroyBeans(); closeBeanFactory(); } try { //创建IOC容器 DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory(); beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId()); //对IOC容器进行定制化,如设置启动参数,开启注解的自动装配等 customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory); //调用载入Bean定义的方法,主要这里又使用了一个委派模式,在当前类中只定义了抽象的loadBeanDefinitions方法,具体的实现调用子类容器 loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) { this.beanFactory = beanFactory; } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex); } }
这是在上下文中创建DefaultListableBeanFactory的地方,而getInternalParentBeanFactory()的具体实现可以参见AbstractApplicationContext中的实现,会根据容器已有的双亲IoC容器的信息来生成DefaultListableBeanFactory的双亲IoC容器:
protected DefaultListableBeanFactory createBeanFactory() { return new DefaultListableBeanFactory(getInternalParentBeanFactory()); }
下面是使用BeanDefinitionReader载入bean定义的地方
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, @Nullable Set<Resource> actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { //获取在IoC容器初始化过程中设置的资源加载器 ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader(); if (resourceLoader == null) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Cannot import bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available"); } // 这里对Resource的路径模式进行解析,比如我们设定的各种Ant格式的路径定义,得到需要的Resource集合,这些Resource集合指向我们已经定义好的BeanDefinition信息,可以是多个文件 if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) { // Resource pattern matching available. try { //将指定位置的Bean定义资源文件解析为Spring IOC容器封装的资源 //加载多个指定位置的Bean定义资源文件 调用DefaultResouceLoader的getResource完成具体的Resource定位 Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location); //委派调用其子类XmlBeanDefinitionReader的方法,实现加载功能 int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resources); if (actualResources != null) { for (Resource resource : resources) { actualResources.add(resource); } } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]"); } return loadCount; } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", ex); } } else { // Can only load single resources by absolute URL. //将指定位置的Bean定义资源文件解析为Spring IOC容器封装的资源 //加载单个指定位置的Bean定义资源文件 Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location); //委派调用其子类XmlBeanDefinitionReader的方法,实现加载功能 int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resource); if (actualResources != null) { actualResources.add(resource); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location [" + location + "]"); } return loadCount; } } //重载方法,调用loadBeanDefinitions(String); @Override public int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { Assert.notNull(locations, "Location array must not be null"); int counter = 0; for (String location : locations) { counter += loadBeanDefinitions(location); } return counter; }
DefaultResourceLoader的getResource方法:
//获取Resource的具体实现方法 @Override public Resource getResource(String location) { Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null"); for (ProtocolResolver protocolResolver : this.protocolResolvers) { Resource resource = protocolResolver.resolve(location, this); if (resource != null) { return resource; } } //如果是类路径的方式,那需要使用ClassPathResource 来得到bean 文件的资源对象 if (location.startsWith("/")) { return getResourceByPath(location); } else if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) { return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader()); } else { try { // Try to parse the location as a URL... // 如果是URL 方式,使用UrlResource 作为bean 文件的资源对象 URL url = new URL(location); return (ResourceUtils.isFileURL(url) ? new FileUrlResource(url) : new UrlResource(url)); } catch (MalformedURLException ex) { // No URL -> resolve as resource path. //如果既不是classpath标识,又不是URL标识的Resource定位,则调用 //容器本身的getResourceByPath方法获取Resource return getResourceByPath(location); } } }
综述,
前面我们看到的getResourceByPath会被子类FileSystemXmlApplicationContext实现,这个方法返回的是一个FileSystemResource对象,通过这个对象,spring可以进行相关的I/O操作,完成BeanDefinition的定位。分析到这里已经一目了然,
它实现的就是对path进行解析,然后生成一个FileSystemResource对象并返回。
@Override protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) { if (path.startsWith("/")) { path = path.substring(1); } //这里使用文件系统资源对象来定义bean 文件 return new FileSystemResource(path); }
如果是其他的ApplicationContext,那么会对应生成其他种类的Resource,比如ClassPathResource、ServletContextResource等。
2.3.2.BeanDefinition的载入与解析
载入过程是把用户定义好的bean表示成IoC容器内部的数据结构,而这个容器内部的数据结构就是BeanDefinition。
BeanDefinition实际上就是POJO对象在IoC容器中的抽象,通过这个BeanDefinition定义的结构,使容器能够方便地对POJO对象也就是bean进行管理。
对容器的启动来说,refresh是一个很重要的方法。下面介绍下它的实现。该方法在AbstractApplicationContext类(它是FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的基类)中找到。它详细地描述了整个ApplicationContext的初始化过程,
比如BeanFactory的更新,MessageSource和PostProcessor的注册等。这里看起来更像是对ApplicationContext进行初始化的模板和执行提纲,这个执行过程为Bean的生命周期管理提供了条件。

@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. //调用容器准备刷新的方法,获取容器的当时时间,同时给容器设置同步标识 prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. //告诉子类启动refreshBeanFactory()方法,Bean定义资源文件的载入从 //子类的refreshBeanFactory()方法启动 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. //为BeanFactory配置容器特性,例如类加载器、事件处理器等 prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. //为容器的某些子类指定特殊的BeanPost事件处理器 postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. //调用所有注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor的Bean invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. //为BeanFactory注册BeanPost事件处理器. //BeanPostProcessor是Bean后置处理器,用于监听容器触发的事件 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. //初始化信息源,和国际化相关. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. //初始化容器事件传播器. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. //调用子类的某些特殊Bean初始化方法 onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. //为事件传播器注册事件监听器. registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. //初始化所有剩余的单例Bean finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. //初始化容器的生命周期事件处理器,并发布容器的生命周期事件 finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. //销毁已创建的Bean destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. //取消refresh操作,重置容器的同步标识. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches(); } } }
进入obtainFreshBeanFactory(),进入AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext的refreshBeanFactory()方法,在这个方法中创建了BeanFactory。在创建IoC容器以前,如果已经有容器存在,那么需要把已有的容器关闭和销毁,保证
在refresh以后使用的是新建立的IoC容器。

@Override protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException { //如果已经有容器,销毁容器中的bean,关闭容器 if (hasBeanFactory()) { destroyBeans(); closeBeanFactory(); } try { //创建IOC容器 DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory(); beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId()); //对IOC容器进行定制化,如设置启动参数,开启注解的自动装配等 customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory); //调用载入Bean定义的方法,主要这里又使用了一个委派模式,在当前类中只定义了抽象的loadBeanDefinitions方法,具体的实现调用子类容器 loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) { this.beanFactory = beanFactory; } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex); } }
这里调用的loadBeanDefinitions实际上是一个抽象方法,在AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext的子类AbstractXmlApplicationContext中实现。在loadBeanDefinitions中初始化了XmlBeanDefinitionReader,然后将这个读取器在IoC容器中设好,
最后启动读取器来完成BeanDefinition在IoC容器的载入。

protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException { // Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory. //创建XmlBeanDefinitionReader,即创建Bean读取器,并通过回调设置到容器中去,容 器使用该读取器读取Bean定义资源 XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory); // Configure the bean definition reader with this context's // resource loading environment. //为Bean读取器设置Spring资源加载器,AbstractXmlApplicationContext的 //祖先父类AbstractApplicationContext继承DefaultResourceLoader,因此,容器本身也是一个资源加载器 beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment()); beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this); //为Bean读取器设置SAX xml解析器 beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this)); // Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader, // then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions. //当Bean读取器读取Bean定义的Xml资源文件时,启用Xml的校验机制 initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader); //Bean读取器真正实现加载的方法 loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader); }
具体的载入过程是委托给BeanDefinitionReader完成的。

//Xml Bean读取器加载Bean定义资源 protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException { //获取Bean定义资源的定位 Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources(); if (configResources != null) { //Xml Bean读取器调用其父类AbstractBeanDefinitionReader读取定位 //的Bean定义资源 reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources); } //如果子类中获取的Bean定义资源定位为空,则获取FileSystemXmlApplicationContext构造方法中setConfigLocations方法设置的资源 String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations(); if (configLocations != null) { //Xml Bean读取器调用其父类AbstractBeanDefinitionReader读取定位 //的Bean定义资源 reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations); } }
2.3.3.向IoC容器注册这些BeanDefinition
这个过程是通过调用BeanDefinitionRegistry接口的实现来完成的。这个注册过程把载入过程中解析得到的BeanDefinition向IoC容器进行注册。通过分析我们可以看到,
在IoC容器内部将BeanDefinition注入到一个HashMap中去,IoC容器就是通过这个HashMap来持有这些BeanDefinition数据的。
在Spring IoC的设计中,Bean定义的载入和依赖注入是两个独立的过程。依赖注入一般发生在应用第一次通过getBean向容器索取bean的时候。但是有一个例外,在使用IoC容器时有一个
预实例化的配置,即lazyinit属性。通过这个配置,用户可以对容器初始化过程作一个微小的控制,从而改变这个被设置了lazyinit属性的bean的依赖注入过程。即这个Bean的依赖注入在容器
初始化时就预先完成了。




