Forever Winter
A snowflake graph is generated from two integers x and y, both greater than 11, as follows:
- Start with one central vertex.
- Connect x new vertices to this central vertex.
- Connect y new vertices to each of these x vertices.
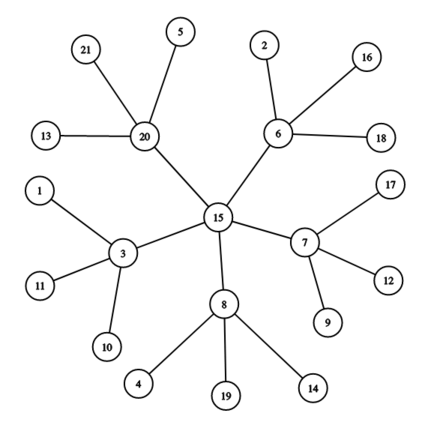
The snowflake graph above has a central vertex 1515, then x=5=5 vertices attached to it (33, 66, 77, 88, and 2020), and then y=3=3 vertices attached to each of those.
The first line contains a single integer t (1≤t≤10001≤≤1000) — the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains two integers n and m (2≤n≤2002≤≤200; 1≤m≤min(1000,n(n−1)2)1≤≤min(1000,(−1)2)) — the number of vertices and edges in the graph, respectively.
The next m lines each contain two integers each u and v (1≤u,v≤n1≤,≤, u≠v≠) — the numbers of vertices connected by an edge. The graph does not contain multiple edges and self-loops.
It is guaranteed that this graph is a snowflake graph for some integers x and y both greater than 11.
For each test case, on a separate line output the values of x and y, in that order, separated by a space.
The first test case is pictured in the statement. Note that the output 3 5 is incorrect, since x should be output before y.
__EOF__

本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/o-Sakurajimamai-o/p/17517686.html
关于博主:评论和私信会在第一时间回复。或者直接私信我。
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
声援博主:如果您觉得文章对您有帮助,可以点击文章右下角【推荐】一下。您的鼓励是博主的最大动力!




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)