Edgy Trees(dfs,并查集,快速幂,树形结构,红黑树)
You are given a tree (a connected undirected graph without cycles) of n vertices. Each of the n−1−1 edges of the tree is colored in either black or red.
You are also given an integer k. Consider sequences of k vertices. Let's call a sequence [a1,a2,…,ak][1,2,…,] good if it satisfies the following criterion:
- We will walk a path (possibly visiting same edge/vertex multiple times) on the tree, starting from a11 and ending at ak.
- Start at a11, then go to a22 using the shortest path between a1 and a2, then go to a3 in a similar way, and so on, until you travel the shortest path between ak−1−1 and ak.
- If you walked over at least one black edge during this process, then the sequence is good.
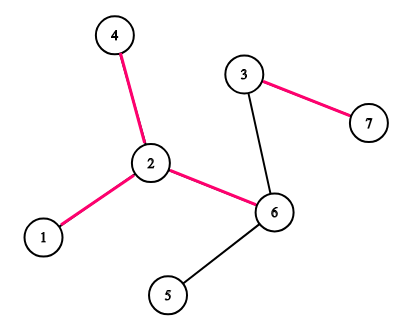
Consider the tree on the picture. If k=3=3 then the following sequences are good: [1,4,7], [5,5,3] and [2,3,7][2,3,7]. The following sequences are not good: [1,4,6][1,4,6], [5,5,5][5,5,5], [3,7,3]
There are nk sequences of vertices, count how many of them are good. Since this number can be quite large, print it modulo 109+7109+7.
The first line contains two integers n and k (2≤n≤1052≤≤105, 2≤k≤1002≤≤100), the size of the tree and the length of the vertex sequence.
Each of the next n−1lines contains three integers ui, vi and xi (1≤ui,vi≤n1≤,≤, xi∈{0,1}∈{0,1}), where ui and vi denote the endpoints of the corresponding edge and xi is the color of this edge (00 denotes red edge and 11 denotes black edge).
Print the number of good sequences modulo 109+7109+7.
In the first example, all sequences (4444) of length 44 except the following are good:
- [1,1,1,1]
- [2,2,2,2]
- [3,3,3,3]
- [4,4,4,4]
1|0
__EOF__

本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/o-Sakurajimamai-o/p/17485698.html
关于博主:评论和私信会在第一时间回复。或者直接私信我。
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
声援博主:如果您觉得文章对您有帮助,可以点击文章右下角【推荐】一下。您的鼓励是博主的最大动力!




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)