基础-快速排序(基本)
简单的快排就是定义一个基准数和一左一右两个“哨兵”,右侧哨兵找比不大于基准数的值,左侧找不小于基准的数,找到后交换两个哨兵对应值的位置,然后继续向左,向右寻找符合条件的数,知道左、右哨兵相遇后,将基准值和左哨兵值交换即可,此时,交换后的基准值左侧都是小于它的值,右侧都是大于它的值,然后以此方式分别处理左侧数据和右侧数据
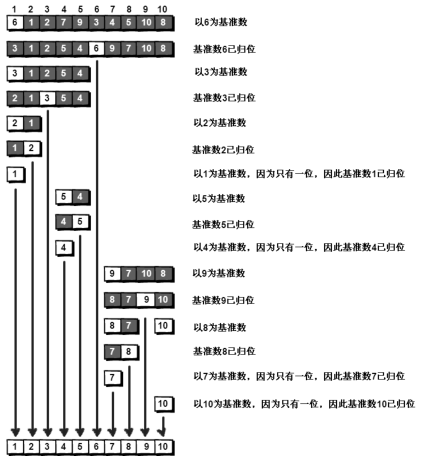
package com.nxz.blog.otherTest; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Test t = new Test(); int[] ints = {2, 1, 4, 5, 6, 3, 8, 1, 0, 22, 33, 12, 1, 2}; t.quickSort(ints, 0, ints.length - 1); for (int i : ints) { System.out.print(i + " "); } } /** * 基本的快排,就最左侧数设置为基准数,设置l,r索引,分别代表左侧索引值,和右侧索引值,r递减从右侧开始找比基准小的数,l递增从左侧开始找比基准大的数, * 然后将两个数调换位置,循环多次知道l==r时,终止循环,最终将基准数和l值调换位置, * 然后递归调用quickSort(left,i-1),quickSort(i+1,right) * * @param arr */ public void quickSort(int[] arr, int left, int right) { //递归终止条件 if (left > right) { return; } int base = arr[left]; int l = left; int r = right; //l=r时就不用再次循环比较了 一趟代表只调换了两个值,以一个值为基准时,会多次调换值,因此需要循环,直到l==r时,代表该基准值左右侧已经调换完毕,最后 //再将基准值和l值调换即可(也就是讲基准值归位,左侧为小于基准的数,右侧为大于基准的数) while (l != r) { //从右侧找小于基准的数 while (l < r && arr[r] >= base) { r--; } //从左侧找大于基准的数 while (l < r && arr[l] <= base) { l++; } if (l < r) { swapInt(arr, l, r); } } //基准和l调换 swapInt(arr, left, l); //递归左侧和右侧数组 (采用分治的思想,两个递归方法调用完毕后,就认为左右两侧已经排好) quickSort(arr, left, l - 1); quickSort(arr, l + 1, right); } /** * 交换数组中的两个数 * * @param arr * @param left * @param right */ private void swapInt(int[] arr, int left, int right) { int temp = arr[left]; arr[left] = arr[right]; arr[right] = temp; } }

