BERT源码分析(一)---预训练
undefined
整个代码文件如下:

BertModel类实现了BERT模型,代码位于modeling.py模块中。
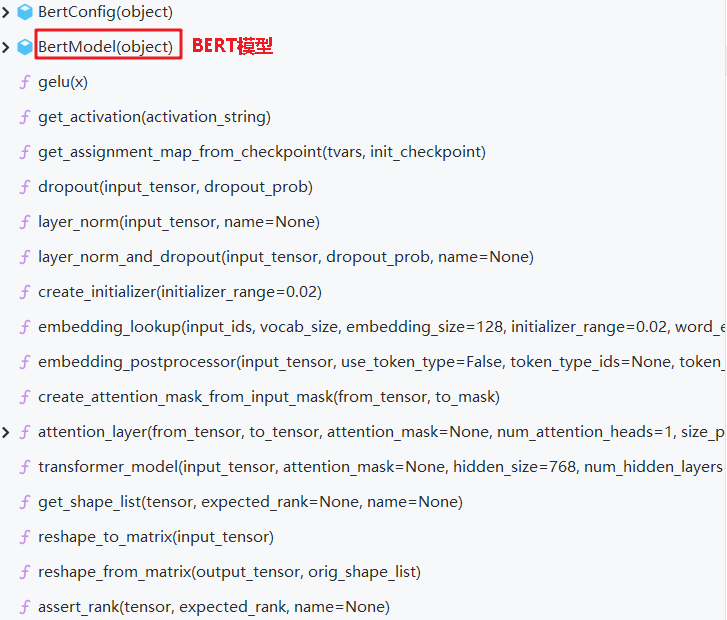
1.配置类(BertConfig)
这段代码定义了BERT模型的一些默认参数和4个文件处理函数。
参数:
- vocab_size:词表大小
- hidden_size:隐藏层神经元数
- num_hidden_layers:Transformer encoder中的隐藏层数
- num_attention_heads:multi-head attention 的head数
- intermediate_size:encoder的“中间”隐层神经元数(例如feed-forward layer)
- hidden_act:隐藏层激活函数
- hidden_dropout_prob:隐层dropout率
- attention_probs_dropout_prob:注意力部分的dropout
- max_position_embeddings:最大位置编码
- type_vocab_size:token_type_ids的词典大小
- initializer_range:truncated_normal_initializer初始化方法的stdev
函数:
- from_dict(cls,json_object):从字典中获取config参数;
- from_json(cls,json_file):从json文件中获取config参数;
- to_dict():将实例序列化为Python字典;
- to_json_string():将此实例序列化为JSON字符串。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 | class BertConfig(object): """Configuration for `BertModel`.""" def __init__(self, vocab_size, # 词表大小 hidden_size=768, # 隐藏层神经元数 num_hidden_layers=12, # transformer encoder中的隐藏层数 num_attention_heads=12, # multi-head attention中head的数量 intermediate_size=3072, # encoder的"中间"隐层神经元数 hidden_act="gelu",# 隐藏层激活函数 hidden_dropout_prob=0.1, # 隐层dropout率 attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1, # 注意力部分的dropout max_position_embeddings=512, # 最大位置编码 type_vocab_size=16, # token_type_ids的词典大小 initializer_range=0.02): # 初始化方法的stdev """Constructs BertConfig. Args: vocab_size: Vocabulary size of `inputs_ids` in `BertModel`. hidden_size: Size of the encoder layers and the pooler layer. num_hidden_layers: Number of hidden layers in the Transformer encoder. num_attention_heads: Number of attention heads for each attention layer in the Transformer encoder. intermediate_size: The size of the "intermediate" (i.e., feed-forward) layer in the Transformer encoder. hidden_act: The non-linear activation function (function or string) in the encoder and pooler. hidden_dropout_prob: The dropout probability for all fully connected layers in the embeddings, encoder, and pooler. attention_probs_dropout_prob: The dropout ratio for the attention probabilities. max_position_embeddings: The maximum sequence length that this model might ever be used with. Typically set this to something large just in case (e.g., 512 or 1024 or 2048). type_vocab_size: The vocabulary size of the `token_type_ids` passed into `BertModel`. initializer_range: The stdev of the truncated_normal_initializer for initializing all weight matrices. """ self.vocab_size = vocab_size self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.num_hidden_layers = num_hidden_layers self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads self.hidden_act = hidden_act self.intermediate_size = intermediate_size self.hidden_dropout_prob = hidden_dropout_prob self.attention_probs_dropout_prob = attention_probs_dropout_prob self.max_position_embeddings = max_position_embeddings self.type_vocab_size = type_vocab_size self.initializer_range = initializer_range @classmethod def from_dict(cls, json_object): """Constructs a `BertConfig` from a Python dictionary of parameters.""" config = BertConfig(vocab_size=None) for (key, value) in six.iteritems(json_object): config.__dict__[key] = value return config @classmethod def from_json_file(cls, json_file): """Constructs a `BertConfig` from a json file of parameters.""" with tf.gfile.GFile(json_file, "r") as reader: text = reader.read() return cls.from_dict(json.loads(text)) def to_dict(self): """Serializes this instance to a Python dictionary.""" output = copy.deepcopy(self.__dict__) return output def to_json_string(self): """Serializes this instance to a JSON string.""" return json.dumps(self.to_dict(), indent=2, sort_keys=True) + "\n" |
2.获取词向量(embedding_lookup)
1 2 3 4 5 6 | def embedding_lookup(input_ids, vocab_size, embedding_size=128, initializer_range=0.02, word_embedding_name="word_embeddings", use_one_hot_embeddings=False) |
功能:输入每句话每个单词的id,返回这句话的embedding表示(获得token embedding)
参数:
- input_ids:word id 【batch_size, seq_length】
- vocab_size:embedding词表
- embedding_size:embedding维度
- initializer_range:embedding初始化范围
- word_embedding_name:embeddding table命名
- use_one_hot_embeddings:是否使用one-hot embedding
返回:
- output:输出对应单词的词向量
[batch_size, seq_length, num_inputs*embedding_size] - embedding table:单词对应embedding的表【batch_size, seq_length, embedding_size】
如果使用one-hot,则先对输入word_ids进行one-hot处理,再乘以embedding_table,得到对应word的词向量;不使用one-hot,直接用从embedding_table中获取对应word_ids的词向量。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 | def embedding_lookup(input_ids, vocab_size, embedding_size=128, initializer_range=0.02, word_embedding_name="word_embeddings", use_one_hot_embeddings=False): """Looks up words embeddings for id tensor. 获取词向量 Args: input_ids: int32 Tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length] containing word ids. vocab_size: int. Size of the embedding vocabulary. embedding_size: int. Width of the word embeddings. initializer_range: float. Embedding initialization range. word_embedding_name: string. Name of the embedding table. use_one_hot_embeddings: bool. If True, use one-hot method for word embeddings. If False, use `tf.gather()`. Returns: float Tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length, embedding_size]. """ # This function assumes that the input is of shape [batch_size, seq_length, # num_inputs]. # # If the input is a 2D tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length], we # reshape to [batch_size, seq_length, 1]. if input_ids.shape.ndims == 2: input_ids = tf.expand_dims(input_ids, axis=[-1]) embedding_table = tf.get_variable( name=word_embedding_name, shape=[vocab_size, embedding_size], initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range)) flat_input_ids = tf.reshape(input_ids, [-1]) #【batch_size*seq_length*input_num】 if use_one_hot_embeddings: one_hot_input_ids = tf.one_hot(flat_input_ids, depth=vocab_size) output = tf.matmul(one_hot_input_ids, embedding_table) else: output = tf.gather(embedding_table, flat_input_ids) input_shape = get_shape_list(input_ids) output = tf.reshape(output, input_shape[0:-1] + [input_shape[-1] * embedding_size]) return (output, embedding_table) |
3.词向量的后续处理(embedding_postprocessor)
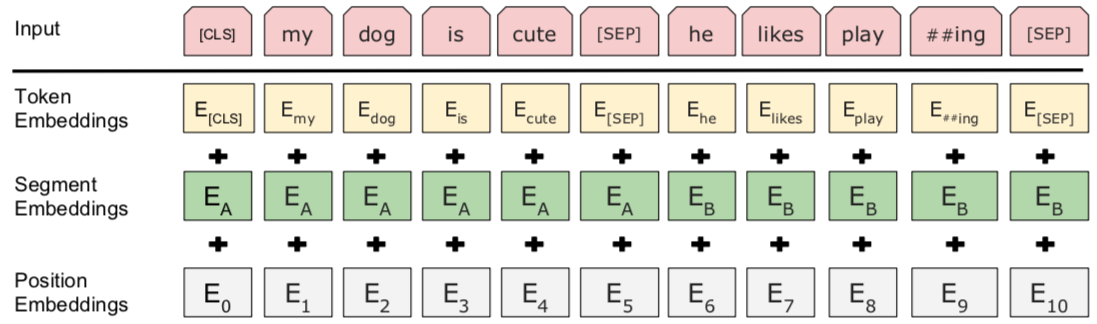
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | def embedding_postprocessor(input_tensor, use_token_type=False, token_type_ids=None, token_type_vocab_size=16,# 一般是2 token_type_embedding_name="token_type_embeddings", use_position_embeddings=True, position_embedding_name="position_embeddings", initializer_range=0.02, max_position_embeddings=512,#最大位置编码,必须大于等于max_seq_len dropout_prob=0.1): |
功能:在token embedding的基础上,增加segment embedding和position embedding。
输入:
- input_tensor:float,[batch_size, seq_length, embedding_size].
- use_token_type: 布尔,是否添加‘token_type_ids’的embedding
- token_type_ids: (可选) int32,[batch_size, seq_length]. 只有use_token_type为True情况下使用
- token_type_vocab_size: int. “ token_type_ids”的词汇量
- token_type_embedding_name: string,token type ids的embedding table表名称
- use_position_embeddings: 布尔,是否添加position embeddings
- position_embedding_name: string,positional embedding的embedding table表名称
- initializer_range: float,权重初始化范围
- max_position_embeddings: int,此模型可能曾经使用的最大sequence长度。 该长度可以比input_tensor的序列长度长,但不能短。
- dropout_prob: float,应用于最终输出张量的dropout概率
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 | def embedding_postprocessor(input_tensor, use_token_type=False, token_type_ids=None, token_type_vocab_size=16,# 一般是2 token_type_embedding_name="token_type_embeddings", use_position_embeddings=True, position_embedding_name="position_embeddings", initializer_range=0.02, max_position_embeddings=512,#最大位置编码,必须大于等于max_seq_len dropout_prob=0.1): """Performs various post-processing on a word embedding tensor. Args: input_tensor: float Tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length, embedding_size]. use_token_type: bool. Whether to add embeddings for `token_type_ids`. token_type_ids: (optional) int32 Tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length]. Must be specified if `use_token_type` is True. token_type_vocab_size: int. The vocabulary size of `token_type_ids`. token_type_embedding_name: string. The name of the embedding table variable for token type ids. use_position_embeddings: bool. Whether to add position embeddings for the position of each token in the sequence. position_embedding_name: string. The name of the embedding table variable for positional embeddings. initializer_range: float. Range of the weight initialization. max_position_embeddings: int. Maximum sequence length that might ever be used with this model. This can be longer than the sequence length of input_tensor, but cannot be shorter. dropout_prob: float. Dropout probability applied to the final output tensor. Returns: float tensor with same shape as `input_tensor`. Raises: ValueError: One of the tensor shapes or input values is invalid. """ input_shape = get_shape_list(input_tensor, expected_rank=3)#【batch_size,seq_length,embedding_size】 batch_size = input_shape[0] seq_length = input_shape[1] width = input_shape[2] output = input_tensor # Segment position信息 if use_token_type: if token_type_ids is None: raise ValueError("`token_type_ids` must be specified if" "`use_token_type` is True.") token_type_table = tf.get_variable( name=token_type_embedding_name, shape=[token_type_vocab_size, width], initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range)) # This vocab will be small so we always do one-hot here, since it is always # faster for a small vocabulary. flat_token_type_ids = tf.reshape(token_type_ids, [-1]) one_hot_ids = tf.one_hot(flat_token_type_ids, depth=token_type_vocab_size) token_type_embeddings = tf.matmul(one_hot_ids, token_type_table) token_type_embeddings = tf.reshape(token_type_embeddings, [batch_size, seq_length, width]) output += token_type_embeddings # Position embedding信息 if use_position_embeddings: # 确保seq_length小于等于max_position_embeddings assert_op = tf.assert_less_equal(seq_length, max_position_embeddings) with tf.control_dependencies([assert_op]): full_position_embeddings = tf.get_variable( name=position_embedding_name, shape=[max_position_embeddings, width], initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range)) # Since the position embedding table is a learned variable, we create it # using a (long) sequence length `max_position_embeddings`. The actual # sequence length might be shorter than this, for faster training of # tasks that do not have long sequences. # # So `full_position_embeddings` is effectively an embedding table # for position [0, 1, 2, ..., max_positin_embeddings-1], and the current # sequence has positions [0, 1, 2, ... seq_length-1], so we can just # perform a slice. position_embeddings = tf.slice(full_position_embeddings, [0, 0], [seq_length, -1]) num_dims = len(output.shape.as_list()) # word embedding之后的tensor是[batch_size, seq_length, width] # 因为位置编码是与输入内容无关,它的shape总是[seq_length, width] # 我们无法把位置Embedding加到word embedding上 # 因此我们需要扩展位置编码为[1, seq_length, width] # 然后就能通过broadcasting加上去了。 # Only the last two dimensions are relevant (`seq_length` and `width`), so # we broadcast among the first dimensions, which is typically just # the batch size. position_broadcast_shape = [] for _ in range(num_dims - 2): position_broadcast_shape.append(1) position_broadcast_shape.extend([seq_length, width]) position_embeddings = tf.reshape(position_embeddings, position_broadcast_shape) output += position_embeddings output = layer_norm_and_dropout(output, dropout_prob) return output |
4.构造attention_mask
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | def create_attention_mask_from_input_mask(from_tensor, to_mask): """Create 3D attention mask from a 2D tensor mask. Args: from_tensor: 2D or 3D Tensor of shape [batch_size, from_seq_length, ...]. to_mask: int32 Tensor of shape [batch_size, to_seq_length]. Returns: float Tensor of shape [batch_size, from_seq_length, to_seq_length]. """ |
功能:从2维的mask生成3维的attention mask。
参数:
- from_tensor:padding后的input_ids,2D或者3D张量,[batch_size, from_seq_length,…]
- to_mask:mark标记向量[batch_size, to_seq_length]
返回:
- mask:[batch_size, from_seq_length, to_seq_length]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | def create_attention_mask_from_input_mask(from_tensor, to_mask): """Create 3D attention mask from a 2D tensor mask. Args: from_tensor: 2D or 3D Tensor of shape [batch_size, from_seq_length, ...]. to_mask: int32 Tensor of shape [batch_size, to_seq_length]. Returns: float Tensor of shape [batch_size, from_seq_length, to_seq_length]. """ from_shape = get_shape_list(from_tensor, expected_rank=[2, 3]) batch_size = from_shape[0] from_seq_length = from_shape[1] to_shape = get_shape_list(to_mask, expected_rank=2) to_seq_length = to_shape[1] to_mask = tf.cast( tf.reshape(to_mask, [batch_size, 1, to_seq_length]), tf.float32) # We don't assume that `from_tensor` is a mask (although it could be). We # don't actually care if we attend *from* padding tokens (only *to* padding) # tokens so we create a tensor of all ones. # # `broadcast_ones` = [batch_size, from_seq_length, 1] broadcast_ones = tf.ones( shape=[batch_size, from_seq_length, 1], dtype=tf.float32) # Here we broadcast along two dimensions to create the mask. mask = broadcast_ones * to_mask return mask |
5.注意力层(attention layer)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | def attention_layer(from_tensor, to_tensor, attention_mask=None, num_attention_heads=1, size_per_head=512, query_act=None, key_act=None, value_act=None, attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.0, initializer_range=0.02, do_return_2d_tensor=False, batch_size=None, from_seq_length=None, to_seq_length=None) |
功能:实现multi-head attention,考虑key-query-value形式的attention,输入的from_tensor当做是query, to_tensor当做是key和value,当两者相同的时候即为self-attention。
参数:
- from_tensor:[batch_size, from_seq_length, from_width]
- to_tensor:[batch_size, to_seq_length, to_width]
- attention_mask=None:[batch_size,from_seq_length, to_seq_length]
- num_attention_heads=1:attention head numbers
- size_per_head=512:每个head的大小
- query_act=None:query变换的激活函数
- key_act=None:key变换的激活函数
- value_act=None:value变换的激活函数
- attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.0:attention层的dropout
- initializer_range=0.02:初始化取值范围
- do_return_2d_tensor=False:是否返回2d张量,
- 如果True,输出形状[batch_size*from_seq_length,num_attention_heads*size_per_head]
- 如果False,输出形状[batch_size, from_seq_length, num_attention_heads*size_per_head]
- batch_size=None:如果输入是3D的, #那么batch就是第一维,但是可能3D的压缩成了2D的,所以需要告诉函数batch_size
- from_seq_length=None:同上
- to_seq_length=None:同上
具体过程参照:https://www.cnblogs.com/nxf-rabbit75/p/11945130.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 | def attention_layer(from_tensor, to_tensor, attention_mask=None, num_attention_heads=1, size_per_head=512, query_act=None, key_act=None, value_act=None, attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.0, initializer_range=0.02, do_return_2d_tensor=False, batch_size=None, from_seq_length=None, to_seq_length=None): """Performs multi-headed attention from `from_tensor` to `to_tensor`. This is an implementation of multi-headed attention based on "Attention is all you Need". If `from_tensor` and `to_tensor` are the same, then this is self-attention. Each timestep in `from_tensor` attends to the corresponding sequence in `to_tensor`, and returns a fixed-with vector. This function first projects `from_tensor` into a "query" tensor and `to_tensor` into "key" and "value" tensors. These are (effectively) a list of tensors of length `num_attention_heads`, where each tensor is of shape [batch_size, seq_length, size_per_head]. Then, the query and key tensors are dot-producted and scaled. These are softmaxed to obtain attention probabilities. The value tensors are then interpolated by these probabilities, then concatenated back to a single tensor and returned. In practice, the multi-headed attention are done with transposes and reshapes rather than actual separate tensors. Args: from_tensor: float Tensor of shape [batch_size, from_seq_length, from_width]. to_tensor: float Tensor of shape [batch_size, to_seq_length, to_width]. attention_mask: (optional) int32 Tensor of shape [batch_size, from_seq_length, to_seq_length]. The values should be 1 or 0. The attention scores will effectively be set to -infinity for any positions in the mask that are 0, and will be unchanged for positions that are 1. num_attention_heads: int. Number of attention heads. size_per_head: int. Size of each attention head. query_act: (optional) Activation function for the query transform. key_act: (optional) Activation function for the key transform. value_act: (optional) Activation function for the value transform. attention_probs_dropout_prob: (optional) float. Dropout probability of the attention probabilities. initializer_range: float. Range of the weight initializer. do_return_2d_tensor: bool. If True, the output will be of shape [batch_size * from_seq_length, num_attention_heads * size_per_head]. If False, the output will be of shape [batch_size, from_seq_length, num_attention_heads * size_per_head]. batch_size: (Optional) int. If the input is 2D, this might be the batch size of the 3D version of the `from_tensor` and `to_tensor`. from_seq_length: (Optional) If the input is 2D, this might be the seq length of the 3D version of the `from_tensor`. to_seq_length: (Optional) If the input is 2D, this might be the seq length of the 3D version of the `to_tensor`. Returns: float Tensor of shape [batch_size, from_seq_length, num_attention_heads * size_per_head]. (If `do_return_2d_tensor` is true, this will be of shape [batch_size * from_seq_length, num_attention_heads * size_per_head]). Raises: ValueError: Any of the arguments or tensor shapes are invalid. """ def transpose_for_scores(input_tensor, batch_size, num_attention_heads, seq_length, width): output_tensor = tf.reshape( input_tensor, [batch_size, seq_length, num_attention_heads, width]) output_tensor = tf.transpose(output_tensor, [0, 2, 1, 3]) return output_tensor from_shape = get_shape_list(from_tensor, expected_rank=[2, 3]) to_shape = get_shape_list(to_tensor, expected_rank=[2, 3]) if len(from_shape) != len(to_shape): raise ValueError( "The rank of `from_tensor` must match the rank of `to_tensor`.") if len(from_shape) == 3: batch_size = from_shape[0] from_seq_length = from_shape[1] to_seq_length = to_shape[1] elif len(from_shape) == 2: if (batch_size is None or from_seq_length is None or to_seq_length is None): raise ValueError( "When passing in rank 2 tensors to attention_layer, the values " "for `batch_size`, `from_seq_length`, and `to_seq_length` " "must all be specified.") # Scalar dimensions referenced here: # B = batch size (number of sequences) # F = `from_tensor` sequence length # T = `to_tensor` sequence length # N = `num_attention_heads` # H = `size_per_head` from_tensor_2d = reshape_to_matrix(from_tensor) to_tensor_2d = reshape_to_matrix(to_tensor) # `query_layer` = [B*F, N*H] query_layer = tf.layers.dense( from_tensor_2d, num_attention_heads * size_per_head, activation=query_act, name="query", kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range)) # `key_layer` = [B*T, N*H] key_layer = tf.layers.dense( to_tensor_2d, num_attention_heads * size_per_head, activation=key_act, name="key", kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range)) # `value_layer` = [B*T, N*H] value_layer = tf.layers.dense( to_tensor_2d, num_attention_heads * size_per_head, activation=value_act, name="value", kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range)) # query_layer` = [B, N, F, H] query_layer = transpose_for_scores(query_layer, batch_size, num_attention_heads, from_seq_length, size_per_head) # `key_layer` = [B, N, T, H] key_layer = transpose_for_scores(key_layer, batch_size, num_attention_heads, to_seq_length, size_per_head) # Take the dot product between "query" and "key" to get the raw # attention scores. # `attention_scores` = [B, N, F, T] attention_scores = tf.matmul(query_layer, key_layer, transpose_b=True) attention_scores = tf.multiply(attention_scores, 1.0 / math.sqrt(float(size_per_head))) if attention_mask is not None: # `attention_mask` = [B, 1, F, T] attention_mask = tf.expand_dims(attention_mask, axis=[1]) # Since attention_mask is 1.0 for positions we want to attend and 0.0 for # masked positions, this operation will create a tensor which is 0.0 for # positions we want to attend and -10000.0 for masked positions. adder = (1.0 - tf.cast(attention_mask, tf.float32)) * -10000.0 # Since we are adding it to the raw scores before the softmax, this is # effectively the same as removing these entirely. attention_scores += adder # Normalize the attention scores to probabilities. # `attention_probs` = [B, N, F, T] attention_probs = tf.nn.softmax(attention_scores) # This is actually dropping out entire tokens to attend to, which might # seem a bit unusual, but is taken from the original Transformer paper. attention_probs = dropout(attention_probs, attention_probs_dropout_prob) # `value_layer` = [B, T, N, H] value_layer = tf.reshape( value_layer, [batch_size, to_seq_length, num_attention_heads, size_per_head]) # `value_layer` = [B, N, T, H] value_layer = tf.transpose(value_layer, [0, 2, 1, 3]) # `context_layer` = [B, N, F, H] context_layer = tf.matmul(attention_probs, value_layer) # `context_layer` = [B, F, N, H] context_layer = tf.transpose(context_layer, [0, 2, 1, 3]) if do_return_2d_tensor: # `context_layer` = [B*F, N*H] context_layer = tf.reshape( context_layer, [batch_size * from_seq_length, num_attention_heads * size_per_head]) else: # `context_layer` = [B, F, N*H] context_layer = tf.reshape( context_layer, [batch_size, from_seq_length, num_attention_heads * size_per_head]) return context_layer |
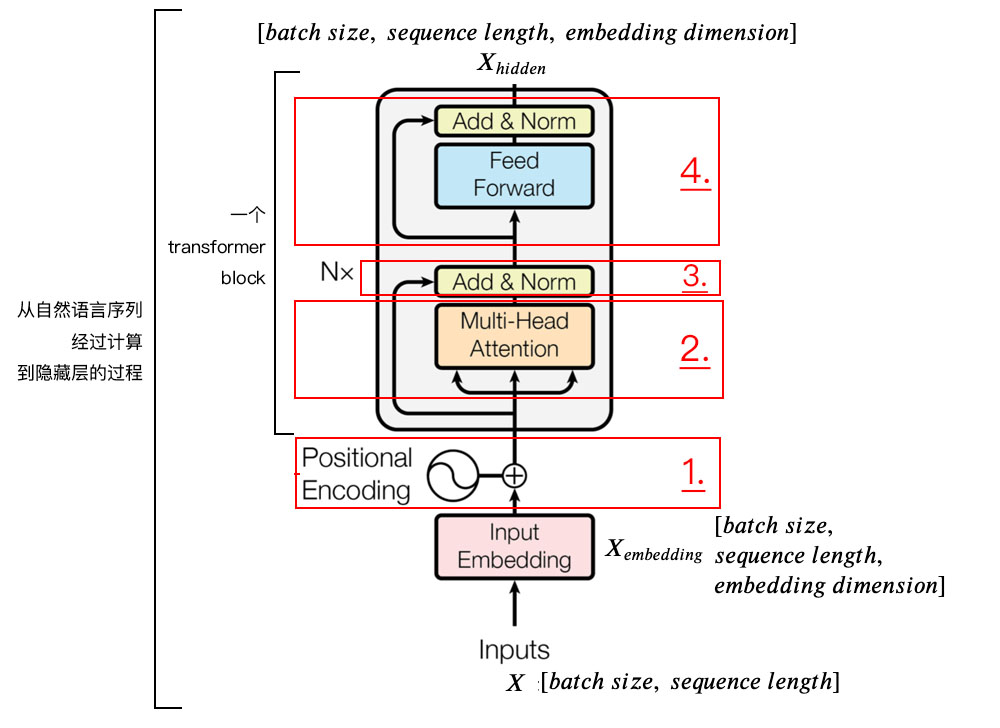
6.Transformer
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | def transformer_model(input_tensor, # 【batch_size, seq_length, hidden_size】 attention_mask=None, # 【batch_size, seq_length, seq_length】 hidden_size=768, num_hidden_layers=12, num_attention_heads=12, intermediate_size=3072, intermediate_act_fn=gelu, # feed-forward层的激活函数 hidden_dropout_prob=0.1, attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1, initializer_range=0.02, do_return_all_layers=False) |
功能:实现Transformer模型
参数:
- input_tensor:[batch_size, seq_length, hidden_size]
- attention_mask=None:[batch_size, seq_length, seq_length]
- hidden_size=768:Transformer隐藏层大小
- num_hidden_layers=12:Transformer的层(block)数
- num_attention_heads=12:attention头的数目
- intermediate_size=3072:transformer的“中间”隐层神经元数
- intermediate_act_fn=gelu:feed-forward层的激活函数
- hidden_dropout_prob=0.1
- attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1
- initializer_range=0.02
- do_return_all_layers=False
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 | def transformer_model(input_tensor, attention_mask=None, hidden_size=768, num_hidden_layers=12, num_attention_heads=12, intermediate_size=3072, intermediate_act_fn=gelu, hidden_dropout_prob=0.1, attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1, initializer_range=0.02, do_return_all_layers=False): """Multi-headed, multi-layer Transformer from "Attention is All You Need". This is almost an exact implementation of the original Transformer encoder. See the original paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762 Also see: https://github.com/tensorflow/tensor2tensor/blob/master/tensor2tensor/models/transformer.py Args: input_tensor: float Tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length, hidden_size]. attention_mask: (optional) int32 Tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length, seq_length], with 1 for positions that can be attended to and 0 in positions that should not be. hidden_size: int. Hidden size of the Transformer. num_hidden_layers: int. Number of layers (blocks) in the Transformer. num_attention_heads: int. Number of attention heads in the Transformer. intermediate_size: int. The size of the "intermediate" (a.k.a., feed forward) layer. intermediate_act_fn: function. The non-linear activation function to apply to the output of the intermediate/feed-forward layer. hidden_dropout_prob: float. Dropout probability for the hidden layers. attention_probs_dropout_prob: float. Dropout probability of the attention probabilities. initializer_range: float. Range of the initializer (stddev of truncated normal). do_return_all_layers: Whether to also return all layers or just the final layer. Returns: float Tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length, hidden_size], the final hidden layer of the Transformer. Raises: ValueError: A Tensor shape or parameter is invalid. """ if hidden_size % num_attention_heads != 0: raise ValueError( "The hidden size (%d) is not a multiple of the number of attention " "heads (%d)" % (hidden_size, num_attention_heads)) attention_head_size = int(hidden_size / num_attention_heads) input_shape = get_shape_list(input_tensor, expected_rank=3) batch_size = input_shape[0] seq_length = input_shape[1] input_width = input_shape[2] # The Transformer performs sum residuals on all layers so the input needs # to be the same as the hidden size. if input_width != hidden_size: raise ValueError("The width of the input tensor (%d) != hidden size (%d)" % (input_width, hidden_size)) # We keep the representation as a 2D tensor to avoid re-shaping it back and # forth from a 3D tensor to a 2D tensor. Re-shapes are normally free on # the GPU/CPU but may not be free on the TPU, so we want to minimize them to # help the optimizer. prev_output = reshape_to_matrix(input_tensor) all_layer_outputs = [] for layer_idx in range(num_hidden_layers): with tf.variable_scope("layer_%d" % layer_idx): layer_input = prev_output with tf.variable_scope("attention"): attention_heads = [] with tf.variable_scope("self"): attention_head = attention_layer( from_tensor=layer_input, to_tensor=layer_input, attention_mask=attention_mask, num_attention_heads=num_attention_heads, size_per_head=attention_head_size, attention_probs_dropout_prob=attention_probs_dropout_prob, initializer_range=initializer_range, do_return_2d_tensor=True, batch_size=batch_size, from_seq_length=seq_length, to_seq_length=seq_length) attention_heads.append(attention_head) attention_output = None if len(attention_heads) == 1: attention_output = attention_heads[0] else: # In the case where we have other sequences, we just concatenate # them to the self-attention head before the projection. attention_output = tf.concat(attention_heads, axis=-1) # Run a linear projection of `hidden_size` then add a residual # with `layer_input`. with tf.variable_scope("output"): attention_output = tf.layers.dense( attention_output, hidden_size, kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range)) attention_output = dropout(attention_output, hidden_dropout_prob) attention_output = layer_norm(attention_output + layer_input) # The activation is only applied to the "intermediate" hidden layer. with tf.variable_scope("intermediate"): intermediate_output = tf.layers.dense( attention_output, intermediate_size, activation=intermediate_act_fn, kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range)) # Down-project back to `hidden_size` then add the residual. with tf.variable_scope("output"): layer_output = tf.layers.dense( intermediate_output, hidden_size, kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range)) layer_output = dropout(layer_output, hidden_dropout_prob) layer_output = layer_norm(layer_output + attention_output) prev_output = layer_output all_layer_outputs.append(layer_output) if do_return_all_layers: final_outputs = [] for layer_output in all_layer_outputs: final_output = reshape_from_matrix(layer_output, input_shape) final_outputs.append(final_output) return final_outputs else: final_output = reshape_from_matrix(prev_output, input_shape) return final_output |
7.函数入口(init)
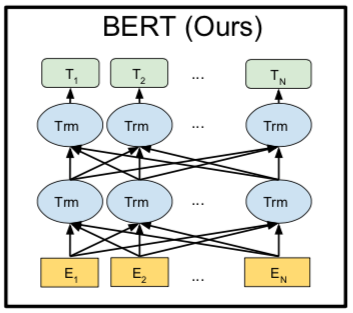
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 | def __init__(self, config, # BertConfig对象 is_training, input_ids, # 【batch_size, seq_length】 input_mask=None, # 【batch_size, seq_length】 token_type_ids=None, # 【batch_size, seq_length】 use_one_hot_embeddings=False, # 是否使用one-hot;否则tf.gather() scope=None): config = copy.deepcopy(config) if not is_training: config.hidden_dropout_prob = 0.0 config.attention_probs_dropout_prob = 0.0 input_shape = get_shape_list(input_ids, expected_rank=2) batch_size = input_shape[0] seq_length = input_shape[1] # 不做mask,即所有元素为1 if input_mask is None: input_mask = tf.ones(shape=[batch_size, seq_length], dtype=tf.int32) if token_type_ids is None: token_type_ids = tf.zeros(shape=[batch_size, seq_length], dtype=tf.int32) with tf.variable_scope(scope, default_name="bert"): with tf.variable_scope("embeddings"): # word embedding (self.embedding_output, self.embedding_table) = embedding_lookup( input_ids=input_ids, vocab_size=config.vocab_size, embedding_size=config.hidden_size, initializer_range=config.initializer_range, word_embedding_name="word_embeddings", use_one_hot_embeddings=use_one_hot_embeddings) # 添加position embedding和segment embedding # layer norm + dropout self.embedding_output = embedding_postprocessor( input_tensor=self.embedding_output, use_token_type=True, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, token_type_vocab_size=config.type_vocab_size, token_type_embedding_name="token_type_embeddings", use_position_embeddings=True, position_embedding_name="position_embeddings", initializer_range=config.initializer_range, max_position_embeddings=config.max_position_embeddings, dropout_prob=config.hidden_dropout_prob) with tf.variable_scope("encoder"): # input_ids是经过padding的word_ids: [25, 120, 34, 0, 0] # input_mask是有效词标记: [1, 1, 1, 0, 0] attention_mask = create_attention_mask_from_input_mask( input_ids, input_mask) # transformer模块叠加 # `sequence_output` shape = [batch_size, seq_length, hidden_size]. self.all_encoder_layers = transformer_model( input_tensor=self.embedding_output, attention_mask=attention_mask, hidden_size=config.hidden_size, num_hidden_layers=config.num_hidden_layers, num_attention_heads=config.num_attention_heads, intermediate_size=config.intermediate_size, intermediate_act_fn=get_activation(config.hidden_act), hidden_dropout_prob=config.hidden_dropout_prob, attention_probs_dropout_prob=config.attention_probs_dropout_prob, initializer_range=config.initializer_range, do_return_all_layers=True) # `self.sequence_output`是最后一层的输出,shape为【batch_size, seq_length, hidden_size】 self.sequence_output = self.all_encoder_layers[-1] # ‘pooler’部分将encoder输出【batch_size, seq_length, hidden_size】 # 转成【batch_size, hidden_size】 with tf.variable_scope("pooler"): # 取最后一层的第一个时刻[CLS]对应的tensor, 对于分类任务很重要 # sequence_output[:, 0:1, :]得到的是[batch_size, 1, hidden_size] # 我们需要用squeeze把第二维去掉 first_token_tensor = tf.squeeze(self.sequence_output[:, 0:1, :], axis=1) # 然后再加一个全连接层,输出仍然是[batch_size, hidden_size] self.pooled_output = tf.layers.dense( first_token_tensor, config.hidden_size, activation=tf.tanh, kernel_initializer=create_initializer(config.initializer_range)) |
举例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | # Already been converted into WordPiece token ids input_ids = tf.constant([[31, 51, 99], [15, 5, 0]]) input_mask = tf.constant([[1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 0]]) token_type_ids = tf.constant([[0, 0, 1], [0, 1, 0]]) config = modeling.BertConfig(vocab_size=32000, hidden_size=512, num_hidden_layers=8, num_attention_heads=6, intermediate_size=1024) model = modeling.BertModel(config=config, is_training=True, input_ids=input_ids, input_mask=input_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids) label_embeddings = tf.get_variable(...) pooled_output = model.get_pooled_output() logits = tf.matmul(pooled_output, label_embeddings) |
参考文献:
【3】tf.one_hot()函数简介 - nini_coded的博客



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 按钮权限的设计及实现
2018-12-19 Keras 源码分析