Tensorflow 搭建神经网络及tensorboard可视化
分类:
TensorFlow
1. session对话控制
1 2 3 | matrix1 = tf.constant([[3,3]])matrix2 = tf.constant([[2],[2]])product = tf.matmul(matrix1,matrix2) #类似于numpy的np.dot(m1,m2) |
方法1:
1 2 3 4 | sess = tf.Session()result = sess.run(product)print(result) # [[12]]sess.close() |
方法2:
1 2 3 | with tf.Session() as sess:#不需要手动关闭sess result2 = sess.run(product) print(result2) # [[12]] |
2. Variable变量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | state = tf.Variable(0,name='counter')#定义常量 oneone = tf.constant(1)#定义加法步骤(注:此步并没有直接计算)new_value = tf.add(state,one)#将 State 更新成 new_valueupdate = tf.assign(state,new_value)# 如果定义 Variable, 就一定要 initialize# init = tf.initialize_all_variables() # tf 马上就要废弃这种写法init = tf.global_variables_initializer() # 替换成这样就好with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init) for _ in range(3): sess.run(update) print(sess.run(state))>>>123 |
3. placeholder
Tensorflow 如果想要从外部传入data, 那就需要用到 tf.placeholder(), 然后以这种形式传输数据 sess.run(***, feed_dict={input: **}).
接下来, 传值的工作交给了 sess.run() , 需要传入的值放在了feed_dict={} 并一一对应每一个 input. placeholder 与 feed_dict={} 是绑定在一起出现的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | input1 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) #大部分只能处理float32input2 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) #两行两列[2,2]output = tf.multiply(input1,input2)with tf.Session() as sess: print(sess.run(output,feed_dict={input1:[2.],input2:[1.]}))>>>[2.] |
4. 添加层def add_layer()
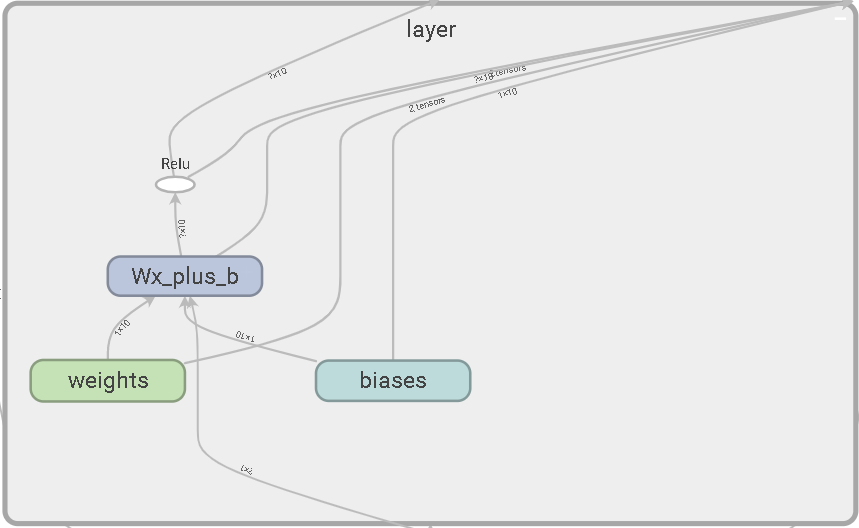
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | import tensorflow as tfdef add_layer(inputs,in_size,out_size,activation_function=None): with tf.name_scope('layer'): with tf.name_scope('weights'): Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size,out_size]),name='W') biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,out_size])+0.1) Wx_plus_biase = tf.add(tf.matmul(inputs,Weights),biases) if activation_function == None: outputs = Wx_plus_biase else: outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_biase) return outputs |
5. 搭建神经网络
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | import numpy as npx_data = np.linspace(-1,1,300)[:,np.newaxis]noise = np.random.normal(0,0.05,x_data.shape).astype(np.float32)y_data = np.square(x_data) - 0.5 + noise# 利用占位符定义我们所需的神经网络的输入。 tf.placeholder()就是代表占位符,这里的None代表无论输入有多少都可以,因为输入只有一个特征,所以这里是1。with tf.name_scope('inputs'): xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1],name='x_input') ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1],name='y_input')#层l1 = add_layer(xs,1,10,activation_function=tf.nn.relu)prediction = add_layer(l1,10,1,activation_function=None)#lossloss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys-prediction), reduction_indices=1))#优化器train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1).minimize(loss)# init = tf.initialize_all_variables() # tf 马上就要废弃这种写法init = tf.global_variables_initializer() # 替换成这样就好sess = tf.Session()sess.run(init)for i in range(1000): sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={xs:x_data,ys:y_data}) if i % 50 == 0: # to see the step improvement print(sess.run(loss, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data})) |
结果如下:

6. 结果可视化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | import matplotlib.pyplot as pltfig = plt.figure()ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)ax.scatter(x_data,y_data)# plt.ion() #plt.ion()用于连续显示# plt.show()# 每隔50次训练刷新一次图形,用红色、宽度为5的线来显示我们的预测数据和输入之间的关系,并暂停0.1s。for i in range(1000): sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={xs:x_data,ys:y_data}) if i % 50 == 0: try: ax.lines.remove(lines[0]) except Exception: pass prediction_value = sess.run(prediction,feed_dict={xs:x_data}) lines = ax.plot(x_data,prediction_value,'r-',lw=5)#线宽度=5# ax.lines.remove(lines[0])#去除lines的第一个线段 plt.pause(0.1) #暂停0.1s# plt.show() |

7. TensorFlow的优化器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizertf.train.AdadeltaOptimizertf.train.AdagradDAOptimizertf.train.MomentumOptimizertf.train.AdamOptimizertf.train.FtrlOptimizertf.train.RMSPropOptimizer |
8. 可视化神经网络
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 | # 图纸搭建 指定这里名称的会将来在可视化的图层inputs中显示出来import tensorflow as tfwith tf.name_scope('inputs'): # define placeholder for inputs to network xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1],name='x_in') ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1],name='y_in')def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None): # add one more layer and return the output of this layer with tf.name_scope('layer'): with tf.name_scope('weights'): Weights = tf.Variable( tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size],name='W'), name='W') with tf.name_scope('biases'): biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1,name='b') with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'): Wx_plus_b = tf.add( tf.matmul(inputs, Weights), biases) if activation_function is None: outputs = Wx_plus_b else: outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b, ) return outputs#层l1 = add_layer(xs,1,10,activation_function=tf.nn.relu)prediction = add_layer(l1,10,1,activation_function=None)# the error between prediciton and real datawith tf.name_scope('loss'): loss = tf.reduce_mean( tf.reduce_sum( tf.square(ys - prediction),# eduction_indices=[1] ))with tf.name_scope('train'): train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss)sess = tf.Session() # get session# tf.train.SummaryWriter soon be deprecated, use followingwriter = tf.summary.FileWriter("E:/logs", sess.graph)sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) |
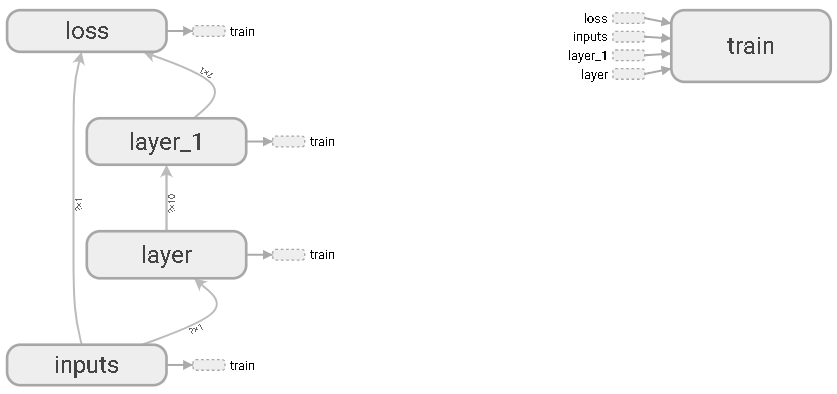
inputs输入层

隐藏层layer
隐藏层layer1

损失函数

训练

9. 可视化训练过程
输入数据:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | import tensorflow as tfimport numpy as np# 图纸搭建 指定这里名称的会将来在可视化的图层inputs中显示出来with tf.name_scope('inputs'): # define placeholder for inputs to network xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1],name='x_in') ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1],name='y_in') ## make up some data x_data= np.linspace(-1, 1, 300, dtype=np.float32)[:,np.newaxis] noise= np.random.normal(0, 0.05, x_data.shape).astype(np.float32) y_data= np.square(x_data) -0.5+ noise |
添加层:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | def add_layer(inputs , in_size, out_size,n_layer, activation_function=None): ## add one more layer and return the output of this layer layer_name='layer%s'%n_layer with tf.name_scope(layer_name): with tf.name_scope('weights'): Weights= tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]),name='W') # tf.histogram_summary(layer_name+'/weights',Weights) tf.summary.histogram(layer_name + '/weights', Weights) # tensorflow >= 0.12 with tf.name_scope('biases'): biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,out_size])+0.1, name='b') # tf.histogram_summary(layer_name+'/biase',biases) tf.summary.histogram(layer_name + '/biases', biases) # Tensorflow >= 0.12 with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'): Wx_plus_b = tf.add(tf.matmul(inputs,Weights), biases) if activation_function is None: #最后一层不需要激活 outputs=Wx_plus_b else: outputs= activation_function(Wx_plus_b) # tf.histogram_summary(layer_name+'/outputs',outputs) tf.summary.histogram(layer_name + '/outputs', outputs) # Tensorflow >= 0.12 return outputs |
损失函数:
1 2 3 4 5 | with tf.name_scope('loss'): loss= tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum( tf.square(ys- prediction), reduction_indices=[1])) # tf.scalar_summary('loss',loss) # tensorflow < 0.12 tf.summary.scalar('loss', loss) # tensorflow >= 0.12 |
接下来,开始合并打包。 tf.merge_all_summaries()方法会对我们所有的summaries合并到一起。因此在原有代码片段中添加:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | sess= tf.Session()# merged= tf.merge_all_summaries() # tensorflow < 0.12merged = tf.summary.merge_all() # tensorflow >= 0.12# writer = tf.train.SummaryWriter('logs/', sess.graph) # tensorflow < 0.12writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("logs/", sess.graph) # tensorflow >=0.12# sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables()) # tf.initialize_all_variables() # tf 马上就要废弃这种写法sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) # 替换成这样就好 |
训练
1 2 3 4 5 | for i in range(1000): sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={xs:x_data,ys:y_data}) if i % 50 == 0: result = sess.run(merged,feed_dict={xs:x_data,ys:y_data}) writer.add_summary(result,i) |
(1)DISTRIBUTIONS

(2)EVENTS
1 2 | # tf.scalar_summary('loss',loss) # tensorflow < 0.12 tf.summary.scalar('loss', loss) # tensorflow >= 0.12 |

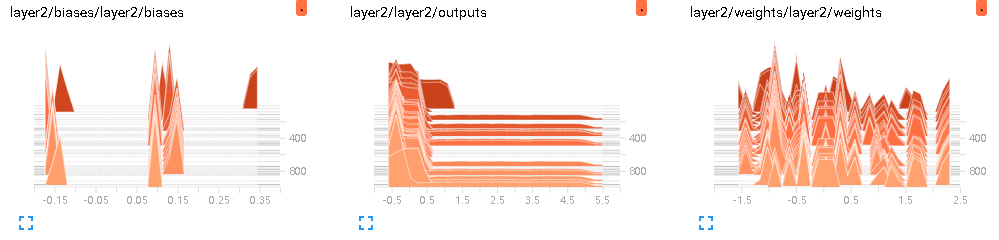
(3)HISTOGRAMS
1 2 | # tf.histogram_summary(layer_name+'/biase',biases) # Tensorflow < 0.12tf.summary.histogram(layer_name + '/biases', biases) # Tensorflow >= 0.12 |
参考文献:
【1】莫烦Python



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 按钮权限的设计及实现