201871010105-曹玉中《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十三周学习总结
| 项目 | 内容 |
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ |
| 这个作业的要求在哪里 | https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p/11888568.html |
| 作业学习目标 |
(1) 掌握事件处理的基本原理,理解其用途; (2) 掌握AWT事件模型的工作机制; (3) 掌握事件处理的基本编程模型; (4) 了解GUI界面组件观感设置方法; (5) 掌握WindowAdapter类、AbstractAction类的用法; (6) 掌握GUI程序中鼠标事件处理技术。 |
第一部分:理论知识
一、Java的事件处理机制
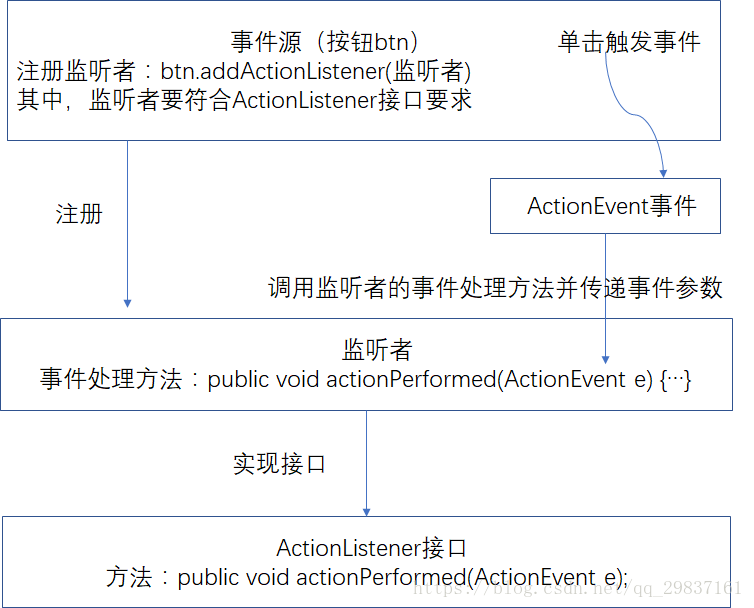
二、事件处理流程
1、给事件源对象注册监听者
事件监听者是在事件发生时要对事件进行处理的对象。AWT定义了各种类型的事件,每一种事件有相应的事件监听者接口 ,在接口中描述了处理相应事件应该实现的基本行为。若事件类名为XxxEvent,则事件监听接口的命名为XxxListener,给部件注册监听者的方法为addXxxListener(XxxListener a)。
列子:只要用户点击按钮,JButton对象就会创建一个ActionEvent对象,然后调用listener.actionPerformed(event)传递事件对象。
内嵌类的方法:
MyListener listener = new MyListener();
JButton button = new JButton("OK");
button.addActionListener(listener);
class MyListener implements ActionListener{
...
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event){
...
}
}
lambda 表达式:
exitButton.addActionListener(event -> Systeu.exit(O));
使用匿名类:
exitButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener()
{
public void actionPerformed(new ActionEvent)
{
System.exit(0);
}
});
2、给监听者编写事件处理代码
3、发生事件时调用监听者的方法进行相关处理
java的事件处理机制称为委托事件处理,事件源发生事件时由监听者处理。监听者中定义事件处理方法,事件源不需要实现任何接口,但其内部有个列表记录该事件源注册了哪些监听者,从而保证发生事件时能去调用监听者的方法。
三、适配器类adapter:
鉴于简化的目的,每个含有 多个方法的 AWT 监听器接口都配有一个适配器(XxxAdapter) 类,这个类实现了接口中的所有方 法, 但每个方法没有做任何事情。可以通过继承适配器类来指定对某些事件的响应动作,而不必实现接口中的每 个方法(ActionListener 这样的接口只有一个方法,因此没必要提供适配器类)。
内部类方法:
class Terminator extends WindowAdapter
{
public void windowCIosing(WindowEvent e)
{
if {useragrees) System.exit(O);
}
}
frame.addWindowListener(new Terminator());
匿名内部类方法:
frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter()
{
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e)
{
if (useragrees) System.exit(0);
}
});
四、动作
通常, 激活一个命令可以有多种方式。用户可以通过菜单、击键或工具栏上的按钮选择 特定的功能。在 AWT 事件模型中实现这些非常容易:将所有事件连接到同一个监听器上。
Swing包提供了一种非常实用的机制来封装命令,并将它们连接到多个事件源,这就是 Action 接口。
有一个类实现了这个接口除 actionPerformed 方法之外的所有方 法,它就是 AbstractAction。这个类存储了所有名 / 值对, 并管理着属性变更监听器。我们可 以直接扩展 AbstractAction 类,并在扩展类中实现 actionPerformed方法。
五、AWT事件继承层次
AWT事件类的继承关系图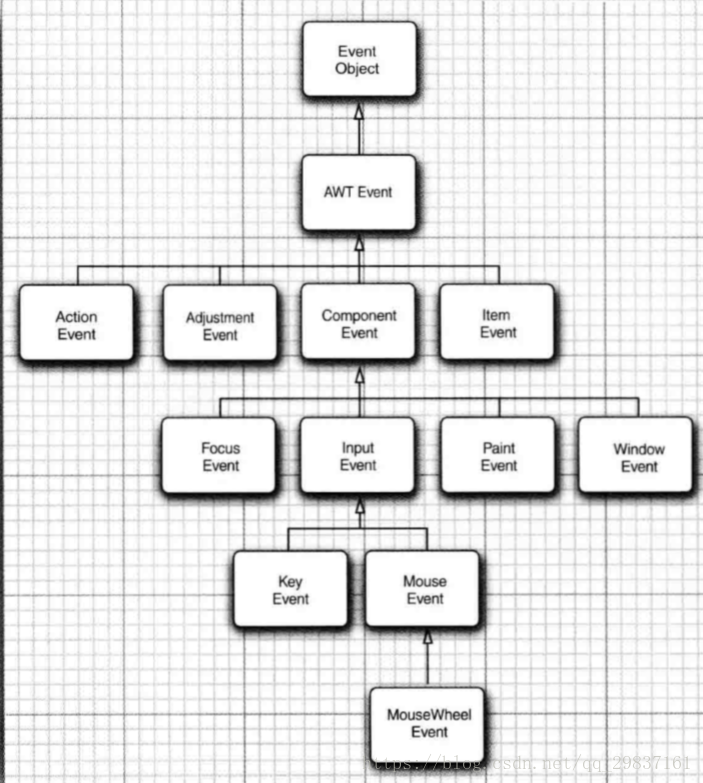
事件处理总结:
AWT将事件分为底层low-level)事件和语义semantic)事件。语义事件是表示用户动作的事件,底层事件是形成那些事件的事件。
下面是 java.awt.event 包中最常用的语义事件类:
•ActionEvent (对应按钮点击、 菜单选择、选择列表项或在文本框中 ENTER);
•AdjustmentEvent (用户调节滚动条);
•ItemEvem (用户从复选框或列表框中选择一项)。
常用的 5 个底层事件类是:
•KeyEvent (一个键被按下或释放);
•MouseEvent (鼠标键被按下、 释放、 移动或拖动);
•MouseWheelEvent (鼠标滚轮被转动);
•FocusEvent (某个组件获得焦点或失去焦点);
•WindowEvent ( 窗口状态被改变)
所有的Listener接口都继承于EventListener,位于java.util包中。
第二部分:实验
实验1: 导入第11章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
● 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材443页-444页程序11-1,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
● 在事件处理相关代码处添加注释;
● 用lambda表达式简化程序;
● 掌握JButton组件的基本API;
● 掌握Java中事件处理的基本编程模型。
代码如下:
package button;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* A frame with a button panel.
*/
public class ButtonFrame extends JFrame
{
private JPanel buttonPanel;
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200;
public ButtonFrame()
{
setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT);
// 创建了三个按钮对象
var yellowButton = new JButton("Yellow");
var blueButton = new JButton("Blue");
var redButton = new JButton("Red");
//创建了一个面板对象
buttonPanel = new JPanel();
//将三个按钮添加到面板中
buttonPanel.add(yellowButton);
buttonPanel.add(blueButton);
buttonPanel.add(redButton);
// add panel to frame
add(buttonPanel);
// create button actions
var yellowAction = new ColorAction(Color.YELLOW);
var blueAction = new ColorAction(Color.BLUE);
var redAction = new ColorAction(Color.RED);
// 将动作和按钮联系起来
yellowButton.addActionListener(yellowAction);
blueButton.addActionListener(blueAction);
redButton.addActionListener(redAction);
}
/**
* An action listener that sets the panel's background color.
*/
private class ColorAction implements ActionListener
{
private Color backgroundColor;
public ColorAction(Color c)
{
backgroundColor = c;
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
buttonPanel.setBackground(backgroundColor);
}
}
}
package button;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* @version 1.35 2018-04-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ButtonTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
var frame = new ButtonFrame();
frame.setTitle("ButtonTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
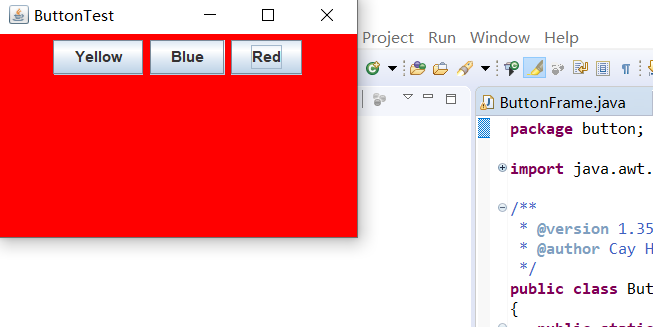
运行结果如下:
简化后的代码:
package button;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* A frame with a button panel.
*/
public class ButtonFrame extends JFrame
{
private JPanel buttonPanel;
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200;
public ButtonFrame() {
setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT);
buttonPanel = new JPanel();
makeButton("yellow", Color.yellow);
makeButton("blue", Color.blue);
makeButton("red", Color.red);
add(buttonPanel);
}
protected void makeButton(String name,Color backgound) {
// create buttons
JButton button = new JButton(name);
// add buttons to panel
buttonPanel.add(button);
button.addActionListener((e)->{
buttonPanel.setBackground(backgound);
});
}
}
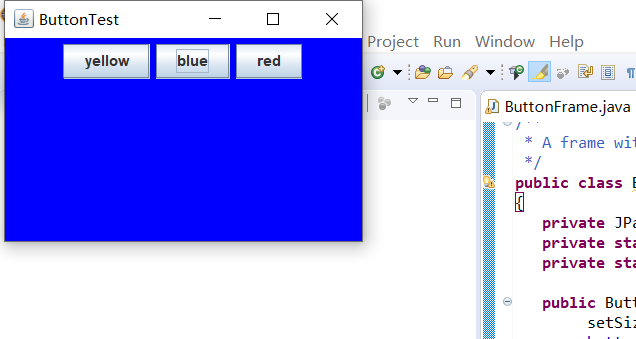
运行结果如下:
测试程序2:
● 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材449页程序11-2,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
● 在组件观感设置代码处添加注释;
● 了解GUI程序中观感的设置方法。
代码如下:
package button;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.SwingUtilities;
import javax.swing.UIManager;
/**
* 带有按钮面板的框架,用于更改外观和感觉
*/
public class PlafFrame extends JFrame
{
private JPanel buttonPanel;
public PlafFrame()//构造器
{
buttonPanel = new JPanel();
UIManager.LookAndFeelInfo[] infos = UIManager.getInstalledLookAndFeels();
for (UIManager.LookAndFeelInfo info : infos)
makeButton(info.getName(), info.getClassName());
add(buttonPanel);
pack();
}
/**
* 创建一个按钮来更改可插入的外观.
* @param name the button name
* @param className the name of the look-and-feel class
*/
private void makeButton(String name, String className)
{
//添加按钮到面板
JButton button = new JButton(name);
buttonPanel.add(button);
//设置按钮要进行的操作
button.addActionListener(event -> {
// 按钮操作结果: 切换到新的外观
try //可能出错的代码放入try子句中
{
UIManager.setLookAndFeel(className);
SwingUtilities.updateComponentTreeUI(this);
pack();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
package button;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* @version 1.32 2015-06-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PlafTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new PlafFrame();
frame.setTitle("PlafTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
运行结果如下:
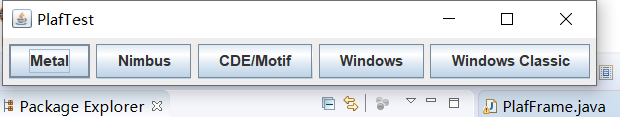
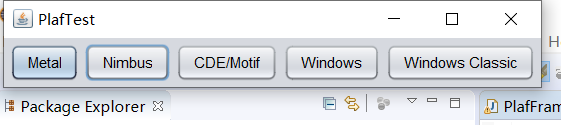


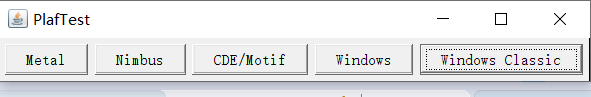
测试程序3:
● 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材457页-458页程序11-3,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
● 掌握AbstractAction类及其动作对象;
● 掌握GUI程序中按钮、键盘动作映射到动作对象的方法。
代码如下:
package action;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* A frame with a panel that demonstrates color change actions.
*/
public class ActionFrame extends JFrame
{
private JPanel buttonPanel;
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200;
public ActionFrame()
{
setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT);
buttonPanel = new JPanel();
// 定义动作
var yellowAction = new ColorAction("Yellow", new ImageIcon("yellow-ball.gif"),
Color.YELLOW);
var blueAction = new ColorAction("Blue", new ImageIcon("blue-ball.gif"), Color.BLUE);
var redAction = new ColorAction("Red", new ImageIcon("red-ball.gif"), Color.RED);
// add buttons for these actions
buttonPanel.add(new JButton(yellowAction));
buttonPanel.add(new JButton(blueAction));
buttonPanel.add(new JButton(redAction));
add(buttonPanel);
// 将Y,B,R这些键与名称联系起来
/*
*可以使用getInputMap方法从组件中得到输入映射
* WHEN_ANCESTOR_OF_FOCUSED_COMPONENT条件意味着在当前组件包含了拥有键盘焦点的组件时会查看这个映射
*/
InputMap inputMap = buttonPanel.getInputMap(JComponent.WHEN_ANCESTOR_OF_FOCUSED_COMPONENT);
inputMap.put(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke("ctrl Y"), "panel.yellow");
inputMap.put(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke("ctrl B"), "panel.blue");
inputMap.put(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke("ctrl R"), "panel.red");
// associate the names with actions
ActionMap actionMap = buttonPanel.getActionMap();
actionMap.put("panel.yellow", yellowAction);
actionMap.put("panel.blue", blueAction);
actionMap.put("panel.red", redAction);
}
public class ColorAction extends AbstractAction
{
/**
* Constructs a color action.
* @param name the name to show on the button
* @param icon the icon to display on the button
* @param c the background color
*/
public ColorAction(String name, Icon icon, Color c)
{
//将所有信息存储在AbstractAction类提供的名/值对表中
putValue(Action.NAME, name);
putValue(Action.SMALL_ICON, icon);
putValue(Action.SHORT_DESCRIPTION, "Set panel color to " + name.toLowerCase());
putValue("color", c);
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
//获取名/值对表中名为color的值并将其强制转换为颜色对象
var color = (Color) getValue("color");
buttonPanel.setBackground(color);
}
}
}
package action;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* @version 1.34 2015-06-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ActionTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
var frame = new ActionFrame();
frame.setTitle("ActionTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
运行结果如下:
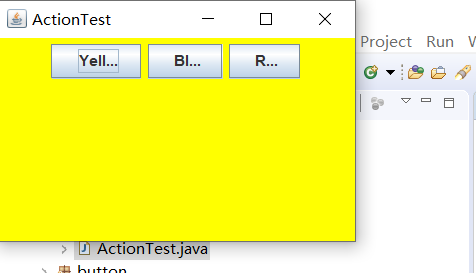
测试程序4:
● 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材462页程序11-4、11-5,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
● 掌握GUI程序中鼠标事件处理技术。
代码如下:
package mouse;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* 带有鼠标操作的用于添加和删除正方形的组件。
*/
public class MouseComponent extends JComponent
{
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200;
private static final int SIDELENGTH = 10;
private ArrayList<Rectangle2D> squares;
private Rectangle2D current; //包含鼠标光标的正方形
public MouseComponent()
{
squares = new ArrayList<>();
current = null;
addMouseListener(new MouseHandler());
addMouseMotionListener(new MouseMotionHandler());
}
public Dimension getPreferredSize()
{
return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT);
}
public void paintComponent(Graphics g)
{
var g2 = (Graphics2D) g;
// 遍历正方形集合,并将每个正方形绘制出来
for (Rectangle2D r : squares)
g2.draw(r);
}
/**
* Finds the first square containing a point.
* @param p a point
* @return the first square that contains p
*/
public Rectangle2D find(Point2D p)
{
for (Rectangle2D r : squares)
{
if (r.contains(p)) return r;
}
return null;
}
/**
* Adds a square to the collection.
* @param p the center of the square
*/
public void add(Point2D p)
{
double x = p.getX();
double y = p.getY();
current = new Rectangle2D.Double(x - SIDELENGTH / 2, y - SIDELENGTH / 2,
SIDELENGTH, SIDELENGTH);
squares.add(current);
repaint();
}
/**
* Removes a square from the collection.
* @param s the square to remove
*/
public void remove(Rectangle2D s)
{
if (s == null) return;
if (s == current) current = null;
squares.remove(s);
repaint();
}
private class MouseHandler extends MouseAdapter
{
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent event)
{
// add a new square if the cursor isn't inside a square
current = find(event.getPoint());
if (current == null) add(event.getPoint());
}
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent event)
{
//如果光标所在位置在正方形集合中包含并且鼠标点击次数>=2,则删除此位置的正方形
current = find(event.getPoint());
if (current != null && event.getClickCount() >= 2) remove(current);
}
}
private class MouseMotionHandler implements MouseMotionListener
{
public void mouseMoved(MouseEvent event)
{
// set the mouse cursor to cross hairs if it is inside a rectangle
if (find(event.getPoint()) == null) setCursor(Cursor.getDefaultCursor());
else setCursor(Cursor.getPredefinedCursor(Cursor.CROSSHAIR_CURSOR));
}
public void mouseDragged(MouseEvent event)
{
if (current != null)
{
int x = event.getX();
int y = event.getY();
// 拖动当前矩形使其居中(x,y)
current.setFrame(x - SIDELENGTH / 2, y - SIDELENGTH / 2, SIDELENGTH, SIDELENGTH);
repaint();
}
}
}
}
package mouse;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* A frame containing a panel for testing mouse operations
*/
public class MouseFrame extends JFrame
{
public MouseFrame()
{
add(new MouseComponent());
pack();
}
}
package mouse;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* @version 1.35 2018-04-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class MouseTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
var frame = new MouseFrame();
frame.setTitle("MouseTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
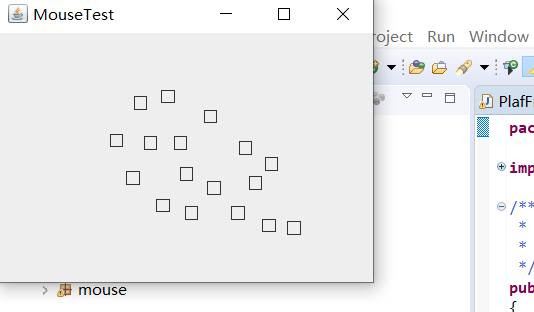
运行结果如下:
实验2:结对编程练习
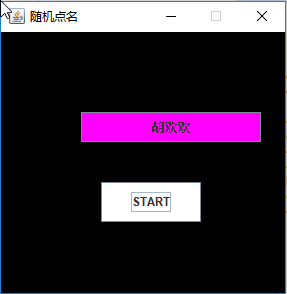
利用班级名单文件、文本框和按钮组件,设计一个有如下界面(图1)的点名器,要求用户点击开始按钮后在文本输入框随机显示2018级计算机科学与技术(1)班同学姓名,如图2所示,点击停止按钮后,文本输入框不再变换同学姓名,此同学则是被点到的同学姓名。
代码如下:
package chart13;
import java.util.*;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.awt.Frame;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
public class ButtonFrame extends JFrame implements ActionListener{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
//serialVersionUID适用于Java的序列化机制,简单来说,Java的序列化机制是通过判断类的
private JButton but ;
private JButton show;
private static boolean flag = true;
public static void main(String arguments []) {
new ButtonFrame();
}
public ButtonFrame(){
but = new JButton("START");//创建一个“开始”按钮
but.setBounds(100,150,100,40);
show = new JButton("随机点名");//创建一个“随机点名”按钮
show.setBounds(80,80,180,30);
add(but);//将按钮添加到面板中
add(show);
setLayout(null);
setVisible(true);//面板的可视化处理
setResizable(false);
setBounds(100,100,300,300);
this.getContentPane().setBackground(Color.black);//面板背景色为白色
setTitle("随机点名");//设置框架标题
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//关闭该面板
but.addActionListener(this);
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
int i=0;
String names[]=new String[50];//创建一个数组,大小为50
try {
Scanner in=new Scanner(new File("D:\\student.txt"));//将文件写入程序
while(in.hasNextLine())
{
names[i]=in.nextLine();//读取文件,遍历全班姓名
i++;
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();//异常处理
}
//点击开始后的操作
if(but.getText()=="START"){
show.setBackground(Color.GREEN);
flag=true;
new Thread(){
public void run(){
while(ButtonFrame.flag){
Random r = new Random(); //随机点名
int i= r.nextInt(43);
show.setText(names[i]);
}
}
}.start();
but.setText("STOP");
but.setBackground(Color.BLUE);
}
else if(but.getText()=="STOP"){
flag = false;
but.setText("START");
but.setBackground(Color.WHITE);
show.setBackground(Color.magenta);
}
}
}
运行结果如下:
学习总结:
通过本章的学习,了解了如何对事件进行处理,比如通过点击按钮或者鼠标对界面进行操控,通过实验课上学长演示实验,再用lambda表达式以及匿名类等简化程序,
使得自己对实验有了更多的了解。第一部分的验证理解实验难度相对较小一点,但在结对编程的过程中出现了较多的问题,也是通过借助他人力量完成本次实验,希望
学长和老师能够详细讲解一下结对编程部分内容,以便有更深刻的理解。



