一、Flume简明笔记
一、Flume概述
1.1 Flume定义
Flume是Cloudera提供的一个高可用、高可靠的分布式的海量日志采集、聚合和传输的系统。
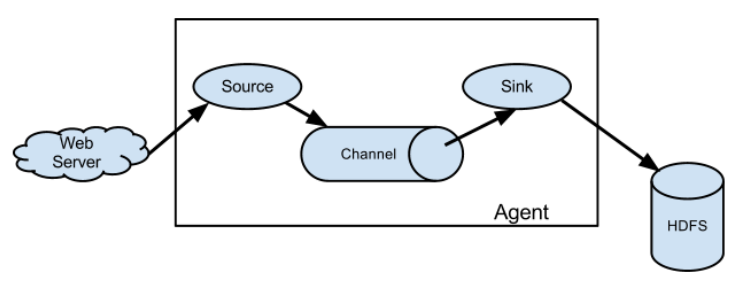
1.2 Flume基础机构
-
Agent
Agent是一个JVM进程,它以事件的形式将数据从源头送至目的。
Agent主要由三个部分组成:Source、Channel、Sink
-
Source
Source是负责接收数据到Flume Agent的组件。Source组件可以处理各种类型、各种格式的日志数据,包括avro、thrift、exec、jms、spooling directory、netcat、sequence generator、syslog、http、legacy。
-
Channel
Channel是位于Source和Sink之间的缓冲区。因此,Channel允许Source和Sink运作在不同的速率上。Channel是线程安全的,可以同时处理几个Source的写入操作和几个Sink的读取操作。
Flume自带两种Channel:Memory Channel和File Channel 以及 Kafka Channel。
-
Memory Channel是内存中的队列。
Memory Channel在不需要关系数据丢失的情景下适用。如果需要关心数据丢失,那么Memory Channel就不应该使用,程序死亡、机器宕机或者重启都会导致数据丢失。
-
File Channel
File Channel将所有事件写到磁盘。所以在程序关闭或机器宕机的情况下不会丢失数据。
-
-
Sink
Sink不断地轮询Channel中的事件且批量地移除它们,并将这些事件批量写入到存储或索引系统、或者被发送到另一个Flume Agent。
Sink组件目的地包括:hdfs、logger、avro、thrift、ipc、file、HBase、solr、自定义组件
-
-
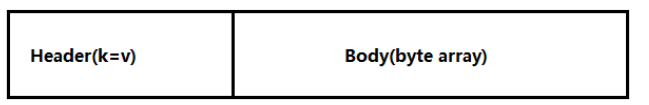
Event
传输单元,Flume数据传输的基本单元,以Event的形式将数据从源头送至目的地。
Event由Header和Body两部分组成,Header用来存放该event的一些属性,为K-V结构,Body用来存放该条数据,形式为字节数组。
二、Flume快速入门
2.1 安装部署
-
官网
-
安装部署
-
将下载文件解压到
opt/software目录下 -
将
$FLUME_HOME/conf下的flume-env.sh.template文件修改为flume-env.sh,并配置其中的JAVA_HOME属性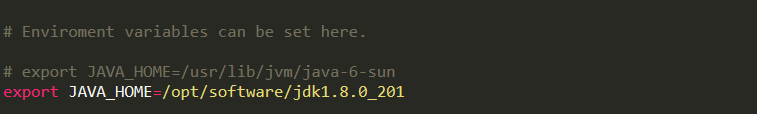
-
2.2 入门案例
2.2.1 监控端口数据官方案例:netcat-flume-logger.conf
可以参考如下官方案例说明:
-
需求
使用Flume监听一个端口,收集该端口数据,并打印到控制台

-
配置文件
-
安装netcat工具:
sudo yum install nc -y -
检查44444端口是否被占用:
netstat -unltp | grep 44444 -
创建Flume Agent配置文件 netcat-flume-logger.conf
-
在$FLUME_HOME创建job文件夹:
mkdir $FLUME_HOME/job -
在job文件夹下创建Flume Agent配置文件
netcat-flume-logger.conf# Name the components of this agent # a1:表示agent的名称 a1.sources=r1 # r1:表示a1的source名称 a1.sinks=k1 # k1:表示a1的sink名称 a1.channels=c1 # c1:表示c1的channel名称 #Discribe/Configure the source a1.sources.r1.type=netcat # 表示a1的输入源类型为netcat类型 a1.sources.r1.bind=localhost # 表示a1的监听主机 a1.sources.r1.port=44444 # 表示a1的监听端口号 #Discribe the sink a1.sinks.k1.type=logger # 表示a1的输出目的地是控制台logger类型 #Use a channel which buffers events in memory a1.channels.c1.type=memory # 表示a1的channel类型是memory内存型 a1.channels.c1.capacity=1000 # 表示a1的channel总容量为1000个event a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=100 # 表示a1的channel传输时收集到了100条event以后再去提交事务 #Bind the source and sink to the channel a1.sources.r1.channels=c1 # 表示将source和channel关联 # 注意a1.sinks.k1.channel环节的channel,不能写成channels,应为channel与sink的关系是一对多(即 1:n) a1.sinks.k1.channel=c1 # 表示将sink和channel关联
-
-
-
测试
-
开启服务端
# 方式一 [nuochengze@pc001 job]$ flume-ng agent --conf conf --conf-file $FLUME_HOME/job/netcat-flume-logger.conf --name a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console # 方式二(简写) [nuochengze@pc001 job]$ flume-ng agent -c conf -f $FLUME_HOME/jobs/netcat-flume-logger.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console- --conf/-c:表示配置文件存储在
$FLUME_HOME/conf目录中 - --name/-n:表示给agent起的名称
- --conf -file/-f :flume本次启动读取的配置文件是在
$FLUME_HOME/job文件下的netcat-flume-logger.conf文件 - -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console:-D表示flume运行时动态修改flume.root.logger参数属性值,并将控制台日志打印级别设置为INFO级别。日志级别包括:log、info、warn、error
- --conf/-c:表示配置文件存储在
-
开启客户端
nc localhost 44444-
在客户端发送数据

-
在服务端接收数据

-
-
2.2.2 实时监控单个追加文件案例:exec-flume-hdfs.conf
-
需求
实时监控Hive日志,并上传到HDFS中
-
配置文件
http://flume.apache.org/releases/content/1.7.0/FlumeUserGuide.html#exec-source
http://flume.apache.org/releases/content/1.7.0/FlumeUserGuide.html#flume-sinks
# singlefilehive_flume_hdfs.conf # Name the components of this agent a1.sources=r1 a1.sinks=k1 a1.channels=c1 # Discribe/Configure the source a1.sources.r1.type=exec a1.sources.r1.command="tail -F /$HIVE_HOME/logs/hive.log" # Discribe the sink a1.sinks.k1.type=hdfs a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path="hdfs://pc001:8082" a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix=logs- # 上传文件前缀 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round=true # 是否按照时间滚动文件夹 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue=1 # 多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit=hour # 重新定义时间单位 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.userLocalTimeStamp=true # 是否使用本地时间戳 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize=1000 # 积累多少个Event才flush到HDFS一次 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType=DataStream # 设置文件类型,可支持压缩 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval=30 # 多久生成一个新的文件 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize=134217700 # 设置每个文件的滚动大小,比128M小一点 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount=0 # 文件的滚动与Event数量无关 # Use a channel which buffers events in memory a1.channels.c1.type=memory a1.channels.c1.capacity=1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a1.sources.r1.channels=c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel=c1注意:
对于所有与时间相关的转义序列,Event Header 中必须存在以 “timestamp”的 key(除非 hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp 设置为 true,此方法会使用 TimestampInterceptor 自动添加 timestamp)。
2.2.3 实时监控目录下多个新文件:spooldir-flume-hdfs.conf
-
需求
使用 Flume 监听整个目录的文件,并上传至 HDFS
-
配置文件
# Name the components of this agent a3.sources = r3 a3.sinks = k3 a3.channels = c3 # Describe/configure the source a3.sources.r3.type = spooldir # 定义监控目录 a3.sources.r3.spoolDir = /opt/software/flume-1.7.0/upload # 定义上传文件后缀名 a3.sources.r3.fileSuffix = .COMPLETED # 是否有文件头 a3.sources.r3.fileHeader = true #忽略所有以.tmp 结尾的文件,不上传 a3.sources.r3.ignorePattern = ([^ ]*\.tmp) # Describe the sink a3.sinks.k3.type = hdfs a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.path = hdfs://pc001:8082/flume/upload/%Y%m%d/%H #上传文件的前缀 a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.filePrefix = upload- #是否按照时间滚动文件夹 a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.round = true #多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹 a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.roundValue = 1 #重新定义时间单位 a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.roundUnit = hour #是否使用本地时间戳 a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true #积攒多少个 Event 才 flush 到 HDFS 一次 a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.batchSize = 100 #设置文件类型,可支持压缩 a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.fileType = DataStream #多久生成一个新的文件 a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.rollInterval = 60 #设置每个文件的滚动大小大概是 128M a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700 #文件的滚动与 Event 数量无关 a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.rollCount = 0 # Use a channel which buffers events in memory a3.channels.c3.type = memory a3.channels.c3.capacity = 1000 a3.channels.c3.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a3.sources.r3.channels = c3 a3.sinks.k3.channel = c3 -
说明
在使用Spooling Directory Source时,不要再监控目录中创建并持续修改文件
2.2.4 实时监控目录下的多个追加文件:taildir-flume-hdfs.conf
Exec source 适用于监控一个实时追加的文件,但不能保证数据不丢失;Spooldir Source 能够保证数据不丢失,且能够实现断点续传,但延迟较高,不能实时监控;而 Taildir Source 既能够实现断点续传,又可以保证数据不丢失,还能够进行实时监控
-
需求
使用 Flume 监听整个目录的实时追加文件,并上传至 HDFS
-
配置文件
# Name the components of this agent a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source a1.sources.r1.type = TAILDIR # 指定position_file位置 a1.sources.r1.positionFile = /opt/software/flume-1.7.0/tail_dir.json # 注意,存在多个f时,分别指定监控目录文件,否则会覆盖上一个 a1.sources.r1.filegroups = f1 # 定义监控目录文件 a1.sources.r1.filegroups.f1 = /opt/software/flume-1.7.0/files/file.* # Describe the sink a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://pc001:8082/flume/taildir/%Y%m%d/%H #上传文件的前缀 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = upload- #是否按照时间滚动文件夹 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true #多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 1 #重新定义时间单位 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = hour #是否使用本地时间戳 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true #积攒多少个 Event 才 flush 到 HDFS 一次 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize = 100 #设置文件类型,可支持压缩 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream #多久生成一个新的文件 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 60 #设置每个文件的滚动大小大概是 128M a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700 #文件的滚动与 Event 数量无关 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 0 # Use a channel which buffers events in memory a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 -
说明
Taildir Source 维护了一个 json 格式的 position File,其会定期的往 position File 中更新每个文件读取到的最新的位置,因此能够实现断点续传:
[{"inode":69133564,"pos":6,"file":"/opt/software/flume-1.7.0/files/file1.txt"},{"inode":69133565,"pos":6,"file":"/opt/software/flume-1.7.0/files/file2.txt"}]注:Linux 中储存文件元数据的区域就叫做 inode,每个 inode 都有一个号码,操作系统用 inode 号码来识别不同的文件,Unix/Linux 系统内部不使用文件名,而使用 inode 号码来识别文件
三、Flume进阶
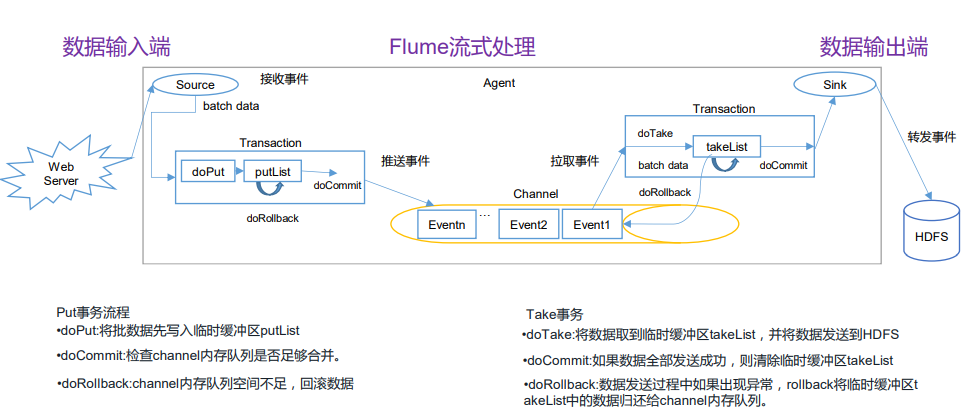
3.1 Flume事务
3.2 Flume Agent内部原理
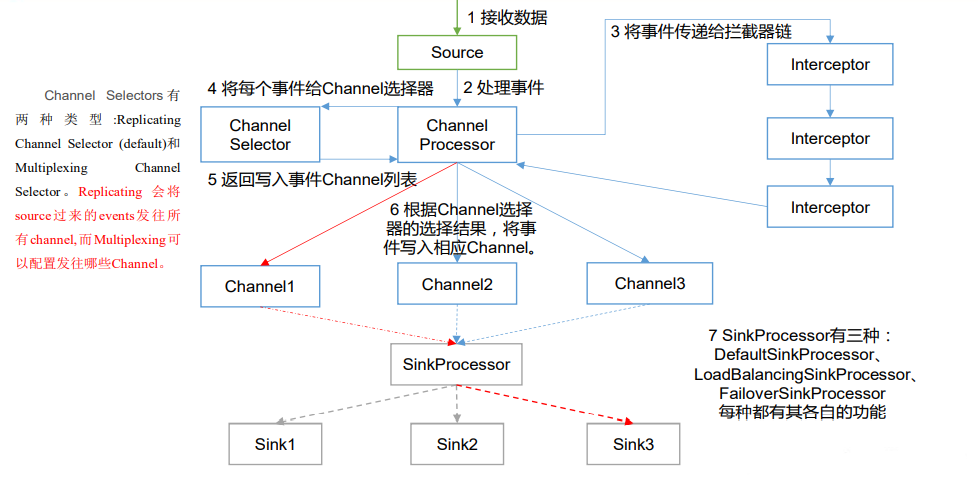
-
ChannelSelector
ChannelSelector的作用就是选出Event将要被发送哪个Channel。
其共有两种类型,分别是Replicating(复制)和 Multiplexing(多路复用)。
- ReplicatingSelector会将同一个Event发往所有的Channel。
- Multiplexing会根据相应的原则,将不同的Event发往不同的Channel。
-
SinkProcessor
SinkProcessor共有三种类型,分别是DefaultSinkProcessor、LoadBalancingSinkProcessor和FailoverSinkProcessor
- DefaultSinkProcessor对应的是单个的Sink
- LoadBalancingSinkProcessor和FailoverSinkProcessor对应的是Sink Group
- LoadBalancingSinkProcessor可以实现负载均衡的功能
- FailoverSinkProcessor可以实现故障转移的功能
3.3 Flume拓扑结构
3.3.1 简单串联
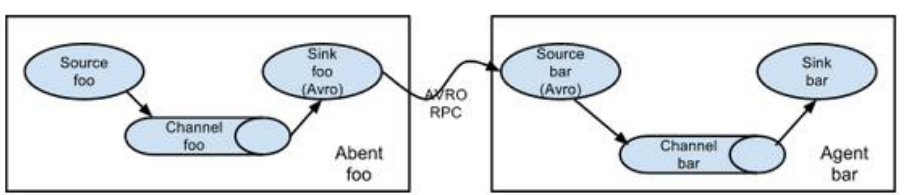
将多个flume顺序连接起来了,从最初的source开始到最终sink传送的目的地存储系统。
当桥接过多的flume数量,flume数量过多不仅会影响传输速率,而且一旦传输过程中某个节点flume宕机,会影响整个传输系统。
3.3.2 复制和多路复用
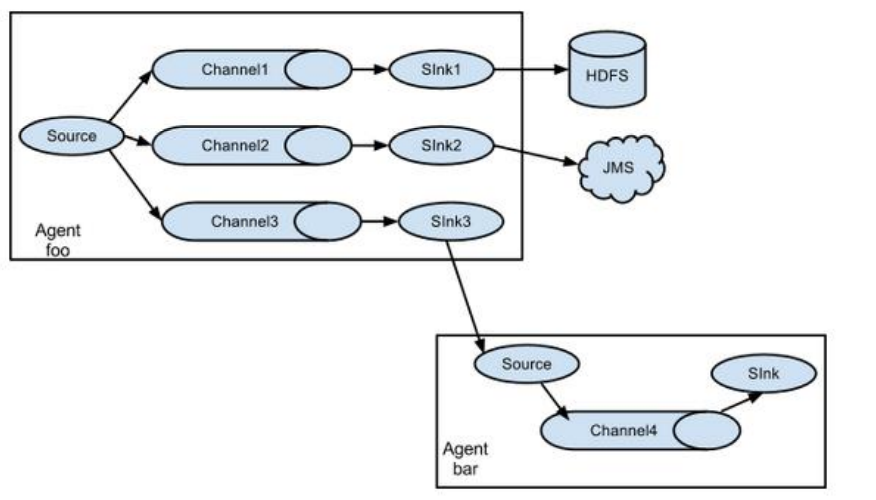
Flume支持将事件流向一个或者多个目的地,这种模式可以将相同数据复制到多个channel中,或者将不同数据分发到不同的channel中,sink可以选择传送到不同的目的地。
3.3.3 负载均衡和故障转移
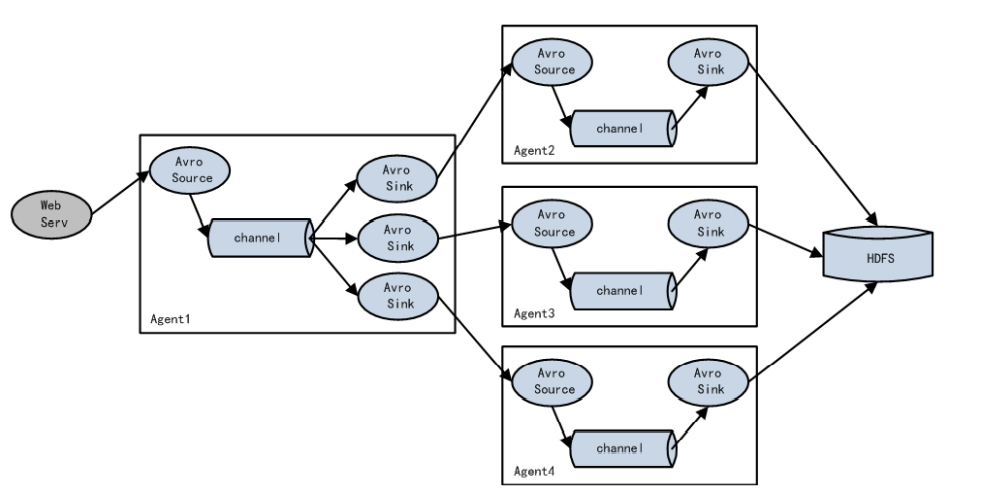
Flume支持使用将多个Sink逻辑上分到一个Sink组,Sink组配合不同的SinkProcessor可以实现均衡负载和错误恢复的功能。
3.3.4 聚合

每台服务器部署一个flume采集日志,传输到一个集中收集日志的flume,再有此flume上传到hdfs、hive、hbase等,进行日志分析。
四、案例
4.1 复制和多路复用
-
案例需求
使用 Flume-1 监控文件变动,Flume-1 将变动内容传递给 Flume-2,Flume-2 负责存储 到 HDFS。同时 Flume-1 将变动内容传递给 Flume-3,Flume-3 负责输出到 Local FileSystem。
-
需求分析
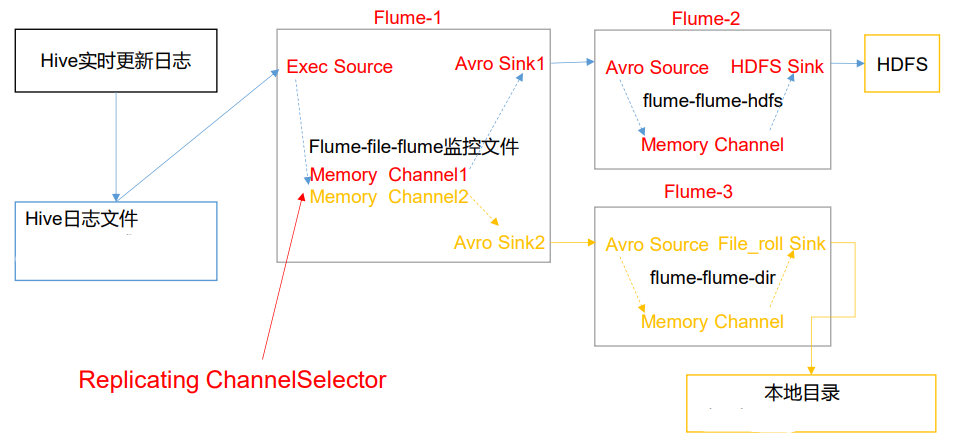
-
实现步骤
-
准备工作
- 创建conf文件夹,并创建文件hive_flume_avro.conf、avro_flume_hdfs.conf、avro_flume_localfile.conf
-
hive_flume_avro.conf文件创建:1个source,2个channel,2个sink
# Name the components of this agent is a1 a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 k2 a1.channels = c1 c2 # 将数据流复制给所有 channel a1.sources.r1.selector.type=replicationg # Describe/configure the source a1.sources.r1.type = TAILDIR # 指定position_file位置 a1.sources.r1.positionFile = /opt/software/flume-1.7.0/datas/position_file/tail_dir.json # 注意,存在多个f时,分别指定监控目录文件,否则会覆盖上一个 a1.sources.r1.filegroups = f1 # 定义监控目录文件 a1.sources.r1.filegroups.f1 = /opt/software/hive-3.1.2/logs/hive.log # Describe the sink # k1 a1.sinks.k1.type=avro a1.sinks.k1.hostname=pc001 a1.sinks.k1.port=4141 # k2 a1.sinks.k2.type=avro a1.sinks.k2.hostname=pc001 a1.sinks.k2.port=4142 # Use a channel which buffers events in memory # c1 a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # c2 a1.channels.c2.type = memory a1.channels.c2.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 a1.sinks.k2.channel = c2 -
avro_flume_hdfs.conf文件创建:1个source,1个channel,1个sink
# Name the components of this agent is a2 a2.sources = r1 a2.sinks = k1 a2.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source a2.sources.r1.type=avro a2.sources.r1.bind=pc001 a2.sources.r1.port=4141 # Describe the sink a2.sinks.k1.type = hdfs a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://pc001:8082/flume/group_test1/%Y%m%d/%H #上传文件的前缀 a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = upload- #是否按照时间滚动文件夹 a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true #多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹 a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 1 #重新定义时间单位 a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = hour #是否使用本地时间戳 a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true #积攒多少个 Event 才 flush 到 HDFS 一次 a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize = 100 #设置文件类型,可支持压缩 a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream #多久生成一个新的文件 a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 60 #设置每个文件的滚动大小大概是 128M a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700 #文件的滚动与 Event 数量无关 a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 0 # Use a channel which buffers events in memory a2.channels.c1.type = memory a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a2.sources.r1.channels = c1 a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1 -
avro_flume_localfile.conf文件创建:1个source,1个channel,1个sink
# Name the components of this agent is a3 a3.sources = r1 a3.sinks = k1 a3.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source a3.sources.r1.type=avro a3.sources.r1.bind=pc001 a3.sources.r1.port=4142 # Describe the sink # 输出的本地目录必须是已经存在的目录,如果该目录不存在,并不会创建新的目录 a3.sinks.k1.type=file_roll a3.sinks.k1.sink.directory=/opt/software/flume-1.7.0/datas/group_test1_output_file # Use a channel which buffers events in memory a3.channels.c1.type = memory a3.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a3.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a3.sources.r1.channels = c1 a3.sinks.k1.channel = c1 -
执行配置文件
注意启动的顺序
[1] flume-ng agent --conf conf --conf-file /opt/software/flume-1.7.0/jobs/group_test1/avro_flume_localfile.conf --name a3 [2] flume-ng agent --conf conf --conf-file /opt/software/flume-1.7.0/jobs/group_test1/avro_flume_hdfs.conf --name a2 [3] flume-ng agent --conf conf --conf-file /opt/software/flume-1.7.0/jobs/group_test1/hive_flume_avro.conf --name a1 -
效果
-
HDFS
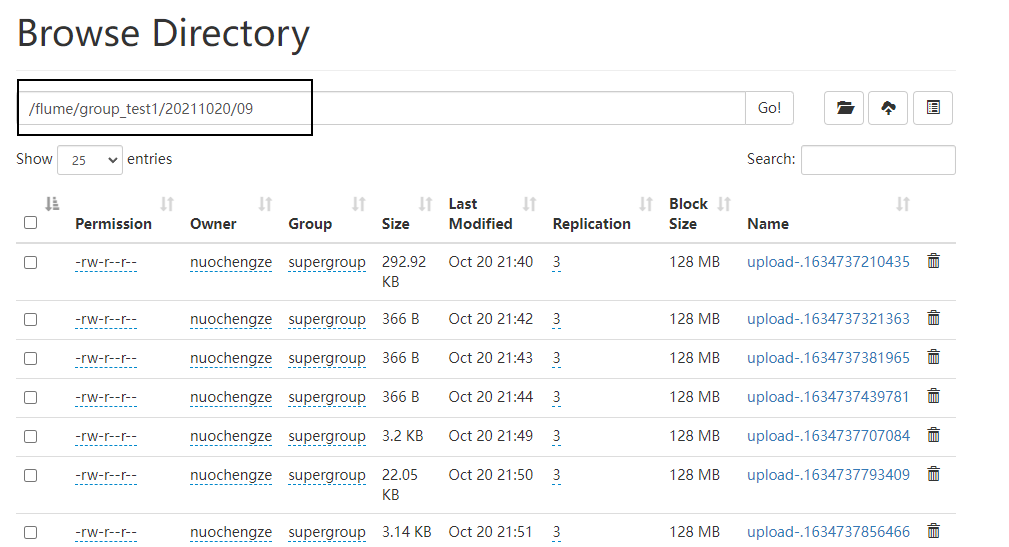
-
localFile

-
-
4.2 负载均衡和故障转移
-
案例需求
使用 Flume1 监控一个端口,其 sink 组中的 sink 分别对接 Flume2 和 Flume3,采用 FailoverSinkProcessor,实现故障转移的功能。
-
需求分析
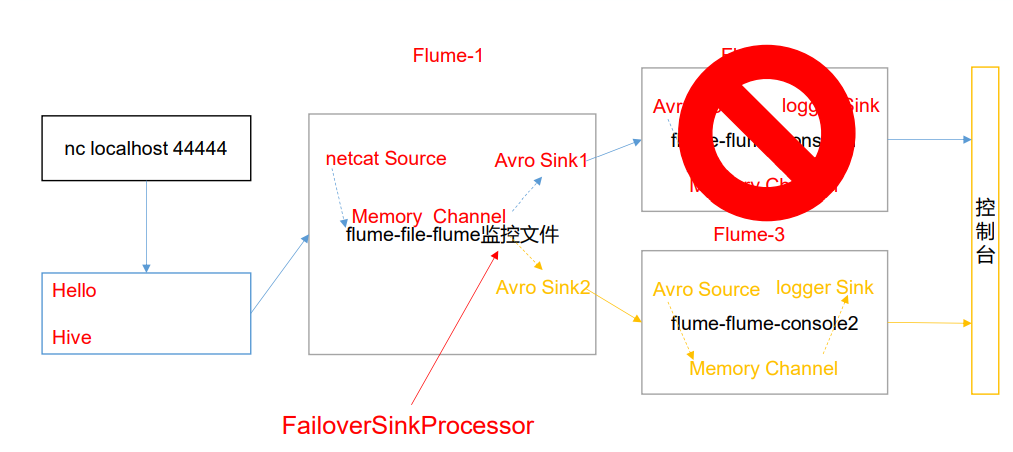
-
实现步骤
-
准备工作
创建conf文件夹,并创建文件netcat_flume_avro.conf、avro_flume_logger1.conf、avro_flume_logger2.conf
-
netcat_flume_avro.conf文件创建:1个source,1个channel,2个sink(在一个组中)
# Name the components of this agent is a1 a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 k2 a1.channels = c1 a1.sinkgroups = g1 #Discribe/Configure the source a1.sources.r1.type=netcat a1.sources.r1.bind=pc001 a1.sources.r1.port=44444 # Discribe then sinkgroup -- 多路复用(二选一) a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type=failover a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.priority.k1=5 a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.priority.k2=10 a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.maxpenalty=10000 # Discribe then sinkgroup -- 均衡负载(二选一) a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type = load_balance a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.backoff = true a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.selector = random # Describe the sink # k1 a1.sinks.k1.type=avro a1.sinks.k1.hostname=pc001 a1.sinks.k1.port=4141 # k2 a1.sinks.k2.type=avro a1.sinks.k2.hostname=pc001 a1.sinks.k2.port=4142 # Use a channel which buffers events in memory a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinkgroups.g1.sinks= k1 k2 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 a1.sinks.k2.channel = c1 -
avro_flume_logger1.conf文件创建:1个source,1个channel,1个sink
# Name the components of this agent is a2 a2.sources = r1 a2.sinks = k1 a2.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source a2.sources.r1.type=avro a2.sources.r1.bind=pc001 a2.sources.r1.port=4141 # Describe the sink a2.sinks.k1.type = logger # Use a channel which buffers events in memory a2.channels.c1.type = memory a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a2.sources.r1.channels = c1 a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1 -
avro_flume_logger2.conf文件创建:1个source,1个channel,1个sink
# Name the components of this agent is a3 a3.sources = r1 a3.sinks = k1 a3.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source a3.sources.r1.type=avro a3.sources.r1.bind=pc001 a3.sources.r1.port=4142 # Describe the sink a3.sinks.k1.type = logger # Use a channel which buffers events in memory a3.channels.c1.type = memory a3.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a3.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a3.sources.r1.channels = c1 a3.sinks.k1.channel = c1 -
启动命令
[1] flume-ng agent --conf conf --conf-file /opt/software/flume-1.7.0/jobs/group_test2/avro_flume_logger2.conf --name a3 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console [2] flume-ng agent --conf conf --conf-file /opt/software/flume-1.7.0/jobs/group_test2/avro_flume_logger1.conf --name a2 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console [3] flume-ng agent --conf conf --conf-file /opt/software/flume-1.7.0/jobs/group_test2/netcat_flume_avro.conf --name a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
-
4.3 聚合
-
案例需求
在pc001上监控文件flume_test.log,数据发送至avro;
在pc002上监控端口4141,发送数据到avro;
在pc003上汇总数据,并将数据打印到控制台;
-
执行步骤
-
taildir_flume_avro.conf文件创建:1个source,1个channel,1个sink
# Name the components of this agent is a1 a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source a1.sources.r1.type = TAILDIR a1.sources.r1.positionFile = /opt/software/flume-1.7.0/datas/tail_dir.json a1.sources.r1.filegroups = f1 a1.sources.r1.filegroups.f1 = /opt/software/flume-1.7.0/datas/test_data1/flume.log # Describe the sink a1.sinks.k1.type=avro a1.sinks.k1.hostname=pc003 a1.sinks.k1.port=4141 # Use a channel which buffers events in memory a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 -
netcat_flume_avro.conf文件创建:1个source,1个channel,1个sink
# Name the components of this agent is a1 a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 #Discribe/Configure the source a1.sources.r1.type=netcat a1.sources.r1.bind=pc002 a1.sources.r1.port=44444 # Describe the sink a1.sinks.k1.type=avro a1.sinks.k1.hostname=pc003 a1.sinks.k1.port=4141 # Use a channel which buffers events in memory a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 -
avro_flume_avro.conf文件创建:1个source,1个channel,1个sink
# Name the components of this agent is a1 a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 #Discribe/Configure the source a1.sources.r1.type=avro a1.sources.r1.bind=pc003 a1.sources.r1.port=4141 # Describe the sink a1.sinks.k1.type=logger # Use a channel which buffers events in memory a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 -
效果
-
pc002

-
pc001

-
pc003

-
-
五、自定义
5.1 自定义拦截器
-
案例需求
使用flume采集服务器日志,按照日志类型的不同,将不同种类的日志发往不同的分析系统
-
需求分析
Flume 拓扑结构中的 Multiplexing 结构,Multiplexing 的原理是,根据 event 中 Header 的某个 key 的值,将不同的 event 发送到不同的 Channel中,所以我们需要自定义一个 Interceptor,为不同类型的 event 的 Header 中的 key 赋予不同的值。
以端口数据模拟日志。
-
实现步骤
-
创建maven项目,导入依赖
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.flume</groupId> <artifactId>flume-ng-core</artifactId> <version>1.7.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies> -
定义 CustomInterceptor 类并实现 Interceptor 接口
package com.nuochengze.interceptor; import org.apache.flume.Context; import org.apache.flume.Event; import org.apache.flume.interceptor.Interceptor; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; public class TypeInterceptor implements Interceptor { private List<Event> hasAddHeaderEvents; @Override public void initialize() { // 初始化 hasAddHeaderEvents = new ArrayList<>(); } @Override public Event intercept(Event event) { // 获取事件中的头信息 Map<String, String> headers = event.getHeaders(); // 获取事件中的body信息 String bodyString = new String(event.getBody()); // 按内容,添加头信息 if (bodyString.contains("nuochengze")){ headers.put("own","nuochengze"); }else{ headers.put("own","other"); } return event; } @Override public List<Event> intercept(List<Event> events) { for (Event event : events) { hasAddHeaderEvents.add(intercept(event)); } return hasAddHeaderEvents; } @Override public void close() { } public static class Builder implements Interceptor.Builder{ @Override public Interceptor build() { return new TypeInterceptor(); } @Override public void configure(Context context) { } } } -
将程序打包并上传到
$FLUME_HOME/lib目录中 -
编写配置文件
-
pc001上创建配置文件netcat-flume-avro.conf:1个source,2个memory channel,2个avro sink,并配置相应的 ChannelSelector 和 interceptor
# Name the components of this agent is a1 a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 k2 a1.channels = c1 c2 # 定义拦截器 a1.sources.r1.interceptors = i1 # 注意:别忘记在主类后面$上静态类 a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type = com.nuochengze.interceptor.TypeInterceptor$Builder # 定义选择器 a1.sources.r1.selector.type = multiplexing a1.sources.r1.selector.header = own a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.nuochengze = c1 a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.other = c2 #Discribe/Configure the source a1.sources.r1.type=netcat a1.sources.r1.bind=pc001 a1.sources.r1.port=44444 # Describe the sink # k1 a1.sinks.k1.type=avro a1.sinks.k1.hostname=pc002 a1.sinks.k1.port=4141 # k2 a1.sinks.k2.type=avro a1.sinks.k2.hostname=pc003 a1.sinks.k2.port=4141 # Use a channel which buffers events in memory # c1 a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # c2 a1.channels.c2.type = memory a1.channels.c2.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 a1.sinks.k2.channel = c2 -
pc002上创建配置文件avro-flume-logger.conf
# Name the components of this agent is a2 a2.sources = r1 a2.sinks = k1 a2.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source a2.sources.r1.type=avro a2.sources.r1.bind=pc002 a2.sources.r1.port=4141 # Describe the sink a2.sinks.k1.type = logger # Use a channel which buffers events in memory a2.channels.c1.type = memory a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a2.sources.r1.channels = c1 a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1 -
pc003上创建配置文件avro-flume-logger.conf
# Name the components of this agent is a3 a3.sources = r1 a3.sinks = k1 a3.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source a3.sources.r1.type=avro a3.sources.r1.bind=pc003 a3.sources.r1.port=4141 # Describe the sink a3.sinks.k1.type = logger # Use a channel which buffers events in memory a3.channels.c1.type = memory a3.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a3.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a3.sources.r1.channels = c1 a3.sinks.k1.channel = c1
-
-
pc003、pc002、pc001上分别启动
-
效果
-
pc001

-
pc002

-
pc003

-
-
5.2 自定义Source
Source 是负责接收数据到 Flume Agent 的组件。Source 组件可以处理各种类型、各种格式的日志数据,包括 avro、thrift、exec、jms、spooling directory、netcat、sequence generator、syslog、http、legacy。
官方也提供了自定义 source 的接口:自定义 MySource 需要继承 AbstractSource 类并实现 Configurable 和 PollableSource 接口。
实现相应方法:
- getBackOffSleepIncrement()//暂不用
- getMaxBackOffSleepInterval()//暂不用
- configure(Context context)//初始化 context(读取配置文件内容)
- process()//获取数据封装成 event 并写入 channel,这个方法将被循环调用。
使用场景:读取 MySQL 数据或者其他文件系统。
参考:
http://flume.apache.org/releases/content/1.7.0/FlumeDeveloperGuide.html#source
-
需求分析
使用flume接收数据,并给每条数据添加前缀,输出到控制台。
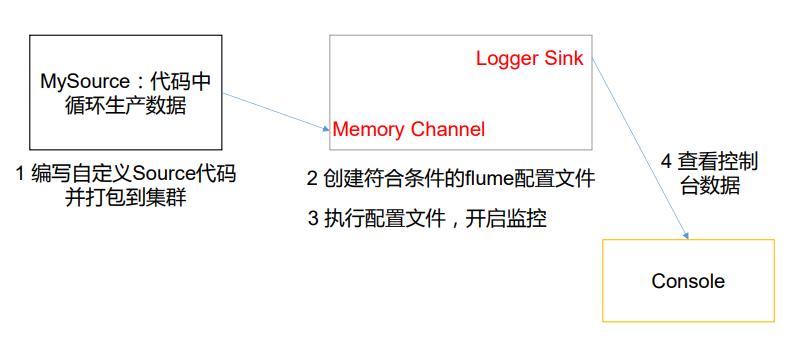

-
实现步骤
-
创建maven项目,导入依赖
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.flume</groupId> <artifactId>flume-ng-core</artifactId> <version>1.7.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies> -
编写代码
package com.nuochengze.source; import org.apache.flume.Context; import org.apache.flume.Event; import org.apache.flume.EventDeliveryException; import org.apache.flume.PollableSource; import org.apache.flume.conf.Configurable; import org.apache.flume.event.SimpleEvent; import org.apache.flume.source.AbstractSource; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.HashMap; public class MySource extends AbstractSource implements Configurable, PollableSource { // 定义全局的前缀和后缀 private String header_string; private String body_string; @Override public void configure(Context context) { // 读取配置文件 body_string = context.getString("body_string"); header_string = context.getString("header_string", "test_mysource"); } @Override public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException { Status status = null; try { // 接收数据 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { // 创建事件头信息 HashMap<String, String> header_map = new HashMap<String, String>(); // 构建事件对象 SimpleEvent event = new SimpleEvent(); // 给事件设置值 header_map.put("customer",header_string); event.setHeaders(header_map); event.setBody((body_string+"--"+i+"--"+ Arrays.toString(event.getBody())).getBytes()); // 将事件写入channel中 getChannelProcessor().processEvent(event); status=Status.READY; } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); status=Status.BACKOFF; } try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return status; } @Override public long getBackOffSleepIncrement() { return 0; } @Override public long getMaxBackOffSleepInterval() { return 0; } } -
编写配置
# Name the components of this agent is a1 a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 #Discribe/Configure the source a1.sources.r1.type=com.nuochengze.source.MySource a1.sources.r1.header_string = this is header of mysource a1.sources.r1.body_string = nuochengze # Describe the sink a1.sinks.k1.type=logger # Use a channel which buffers events in memory a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 -
将打包好的代码放置在
$FLUME_HOME/lib中 -
结果
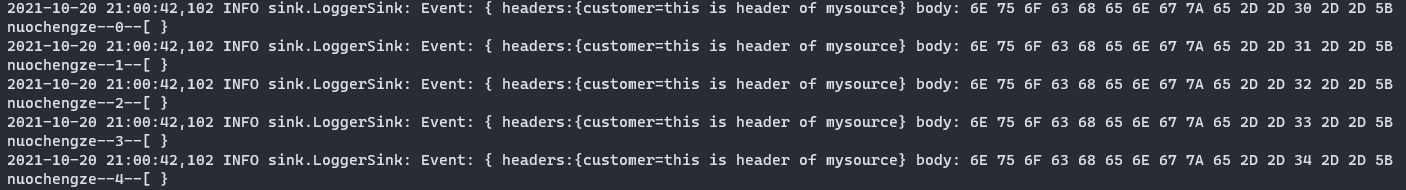
-
5.3 自定义Sink
Sink 不断地轮询 Channel 中的事件且批量地移除它们,并将这些事件批量写入到存储 或索引系统、或者被发送到另一个 Flume Agent。
Sink 是完全事务性的。在从 Channel 批量删除数据之前,每个 Sink 用 Channel 启动一 个事务。批量事件一旦成功写出到存储系统或下一个 Flume Agent,Sink 就利用 Channel 提 交事务。事务一旦被提交,该 Channel 从自己的内部缓冲区删除事件。
Sink 组件目的地包括 hdfs、logger、avro、thrift、ipc、file、null、HBase、solr、 自定义。自定义 MySink 需要继承 AbstractSink 类并实现 Configurable 接口。
实现相应方法:
- configure(Context context)//初始化 context(读取配置文件内容)
- process()//从 Channel 读取获取数据(event),这个方法将被循环调用。
使用场景:读取channel数据后写入mysql或其他文件系统
参考:
http://flume.apache.org/releases/content/1.7.0/FlumeDeveloperGuide.html#sink
-
需求分析
使用 flume 接收数据,并在 Sink 端给每条数据添加前缀和后缀,输出到控制台。前后 缀可在 flume 任务配置文件中配置
-
实现步骤
-
代码
package com.nuochengze.sink; import org.apache.flume.*; import org.apache.flume.conf.Configurable; import org.apache.flume.sink.AbstractSink; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import java.util.Arrays; public class MySink extends AbstractSink implements Configurable { private String content_sink; // 创建logger对象 private final Logger logger= LoggerFactory.getLogger(MySink.class); @Override public void configure(Context context) { content_sink = context.getString("content_sink", "!@!"); } @Override public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException { Status status = null; // 获取channel Channel channel = getChannel(); // 获取channel中的事务 Transaction channel_transaction = channel.getTransaction(); // 开始事务 channel_transaction.begin(); try { // 从channel获取数据 Event event = channel.take(); if (event != null) { // 处理事件 String s = content_sink + " " +new String(event.getBody()) + " " + content_sink; logger.info(s); } // 提交事务,就算没有事件,也要提交 channel_transaction.commit(); // 提交成功后,修改状态信息 status = Status.READY; } catch (ChannelException e) { e.printStackTrace(); status = Status.BACKOFF; }finally { channel_transaction.close(); } return status; } } -
配置信息
# Name the components of this agent is a1 a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 #Discribe/Configure the source a1.sources.r1.type = netcat a1.sources.r1.bind = pc001 a1.sources.r1.port = 44444 # Describe the sink a1.sinks.k1.type=com.nuochengze.sink.MySink a1.sinks.k1.content_sink=!@! # Use a channel which buffers events in memory a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 -
启动命令
flume-ng agent --conf conf --conf-file ./netcat-flume-logger.conf --name a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console -
结果


-

