Asp.net Core Mvc EF- Migrations使用
2019-01-26 15:35 糯米粥 阅读(9308) 评论(0) 收藏 举报 Migragtion的命令,左边是手动命令,右边是代码方式
首先来看命令方式:
创建一个mvc项目,默认已经集成了EF包
创建的项目包含了Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity.EntityFramewordCore包,这将使用Entity Framework Core通过SQL Server来储存身份识别的数据和表信息。
添加Sql连接字符串:
{ "Logging": { "LogLevel": { "Default": "Warning" } }, "AllowedHosts": "*", "ConnectionStrings": { "conn": "Data Source=pc;User ID=sa;Password=12;database=CoreDb;Connect Timeout=30;Encrypt=False;
TrustServerCertificate=False;ApplicationIntent=ReadWrite;MultiSubnetFailover=False" } }
注意这个:ConnectionStrings 是必须要这样写的,默认是根据这个名字读取,后面会说
Net Core 身份 Identity 允许向应用中添加登陆功能。用户可创建一个账户并进行登陆,登陆时可使用用户名、密码
Server数据库存储用户名字、密码和配置文件数据。另外,你可使用其他已有的存储空间存储数据
创建ApplicationUser, ApplicationRole 分别继承IdentityRole IdentityUser
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Threading.Tasks; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity; namespace IdentityDemo.Models { public class ApplicationRole:IdentityRole { } }
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity; namespace IdentityDemo.Models { public class ApplicationUser : IdentityUser { } }
创建上下文类:
using IdentityDemo.Models; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity.EntityFrameworkCore; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; namespace IdentityDemo.Date { public class ApplicationDbContext : IdentityDbContext<ApplicationUser> { public ApplicationDbContext(DbContextOptions<ApplicationDbContext> options) : base(options) { } } }
ConfigureServices 中注册服务
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { services.Configure<CookiePolicyOptions>(options => { // This lambda determines whether user consent for non-essential cookies is needed for a given request. options.CheckConsentNeeded = context => true; options.MinimumSameSitePolicy = SameSiteMode.None; }); services.AddAuthentication(CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme) .AddCookie(options => { options.LoginPath = "/Login"; }); services.AddDbContext<ApplicationDbContext>(options => { //配置文件前面必须是;ConnectionStrings //因为默认是:GetSection("ConnectionStrings")[name]. options.UseSqlServer(Configuration.GetConnectionString("conn")); //options.UseSqlServer(Configuration["Data:DefaultConnection:ConnectionString"])); }); services.AddIdentity<ApplicationUser, ApplicationRole>() .AddEntityFrameworkStores<ApplicationDbContext>() .AddDefaultTokenProviders(); //配置密码注册方式 services.Configure<IdentityOptions>(options => { options.Password.RequireLowercase = false; options.Password.RequireNonAlphanumeric = false; options.Password.RequireUppercase = false; options.Password.RequiredLength = 1; }); services.AddMvc().SetCompatibilityVersion(CompatibilityVersion.Version_2_2); }
我这里用了Cookie验证,所以应该添加中间件 app.UseAuthentication();
创建用户:通过依赖注入: UserManager 和 SignInManager 依赖:Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity;
private readonly UserManager<ApplicationUser> _userManager; private readonly SignInManager<ApplicationUser> _signinManager; public LoginController(UserManager<ApplicationUser> userManager, SignInManager<ApplicationUser> signinManager) { _userManager = userManager; _signinManager = signinManager; }
注册代码
[HttpPost] public async Task<IActionResult> Registe(LoginViewModel model) { var identityUser = new ApplicationUser { UserName = model.UserName, PasswordHash = model.PassWorld, NormalizedEmail = model.UserName }; var identityResult = await _userManager.CreateAsync(identityUser, model.PassWorld); if (identityResult.Succeeded) { return RedirectToAction("Index", "Home"); } return View(); }
注册之前,我们先通过命令生成数据库
命令依赖于:Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools包,不过默认也有了
可以输入dotnet ef migrations --help 看看帮助

输入后命令:dotnet ef migrations add identity
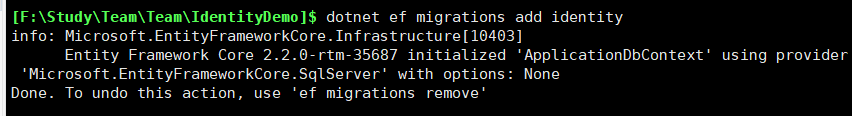
项目中会生成一个Migrations的文件夹和文件
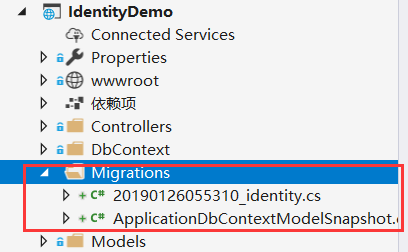
然后更新数据库:dotnet ef migrations update
可以看到生成了数据库和表,但AspNetUsers表的组建ID默认是字符串类型的,一连串GUID,待会会说改成常用的int类型
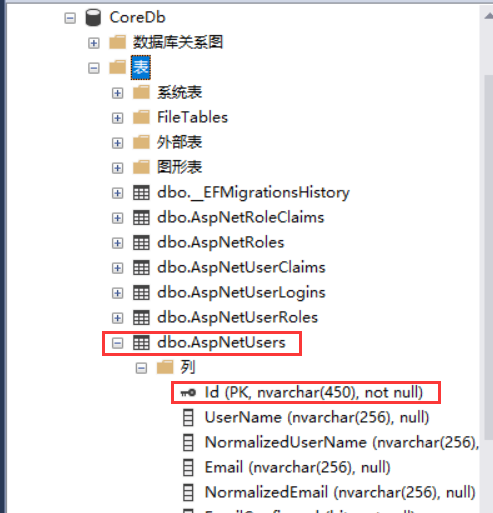
好了。现在注册一个看看
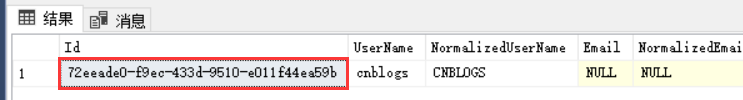
看看默认的: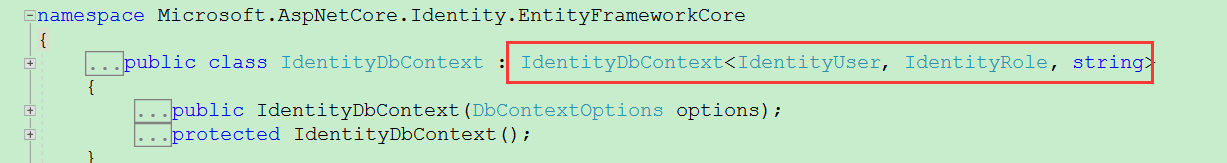
接下来我们修改默认的主键为int类型。只需要改成:IdentityUser<int> ,IdentityRole<int>
上下文改成:

因为是重新生成数据库,需要删除数据库,并且把Migrations的文件都删除,或者直接删除Migrations文件夹
可以执行命令删除库:dotnet ef database drop
否则EF会当作升级和降级处理,不会重新生成数据库
然后重新migragins add ,update 注册看看,已经是int类型了
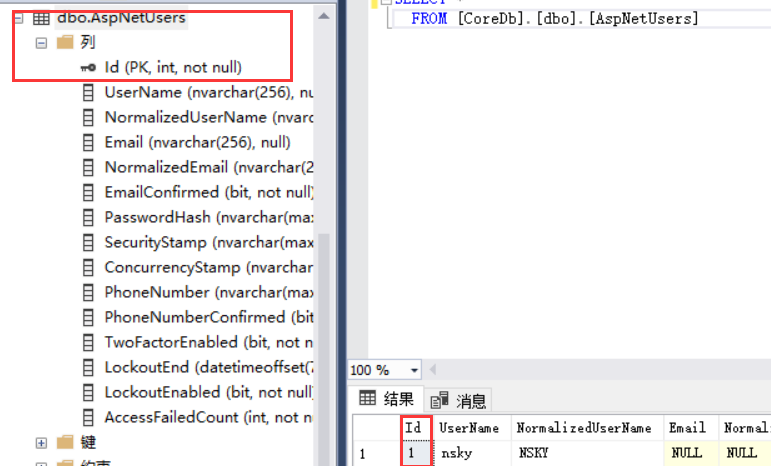
然后给表升级,在用户表添加一列 TrueName,首先看用户名表。默认是没有该列的
我们在ApplicationUser类新增字段
然后命令:dotnet ef migrations add AddTrueName //AddTrueName名字是任意取的
此时在Migrations文件夹生成了对呀的类

然后update,这里的update只会找最新的migrations 这里的最新的migrations就是20190126061435_identity
数据库已经有了
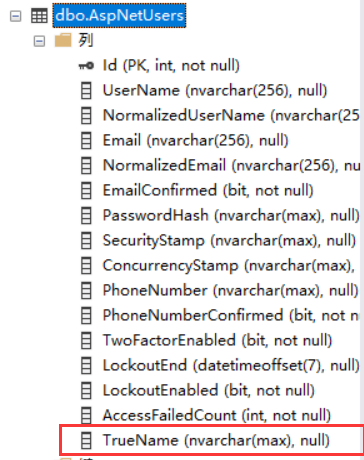
比如我们在添加一个Address列,然后在还原到只有TrueName的状态
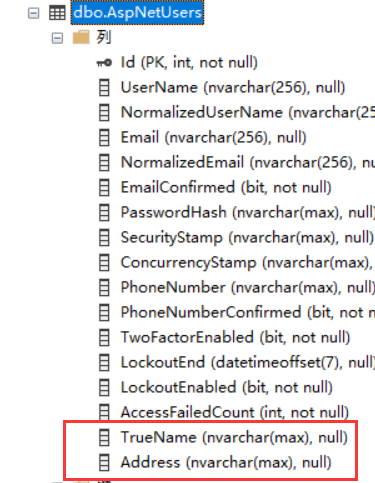
现在Migrations有3个Migration
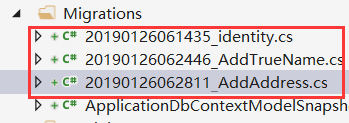
然后我们通过update回滚
dotnet ef database update 回滚的migration
我们这里回滚到AddTrueName 那么命令就是:dotnet ef database update AddTrueName
回滚之后。表也更新了

其实__EFMigrationsHistory表是保存了当前所有的Migration
回滚前
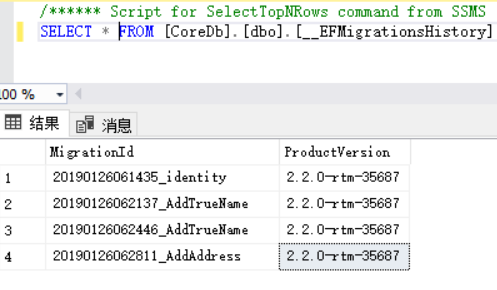
回滚后
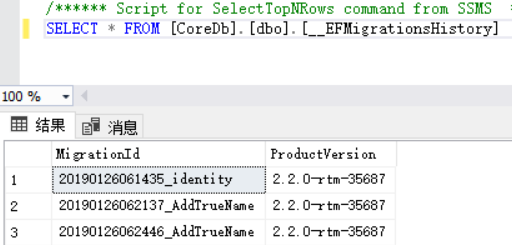
这里有两个AddTrueName是因为我add了两次,可以不用管
主要是对比之前和之后,AddAddress没有了
然后看:dotnet ef migrations script 生成脚本
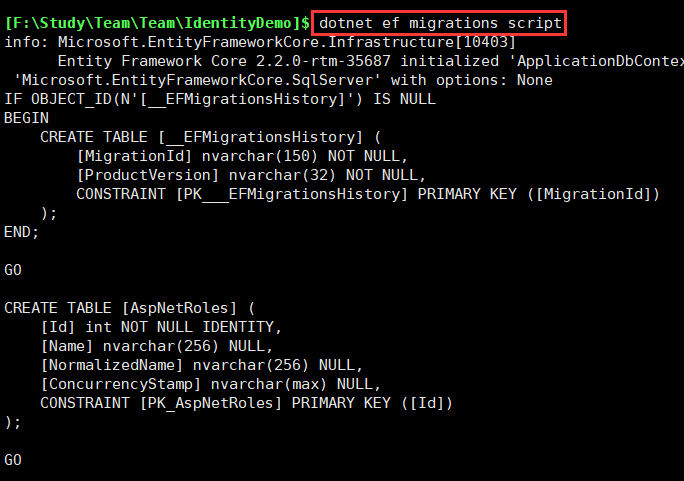
生成脚本在屏幕中,还得拷贝出来,多不友好,看看--help,是可以指定路径的

执行: dotnet ef migrations script -o d:\script\user.sql
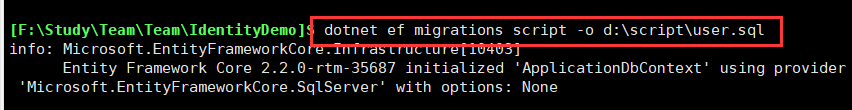
打开生成的文件看看
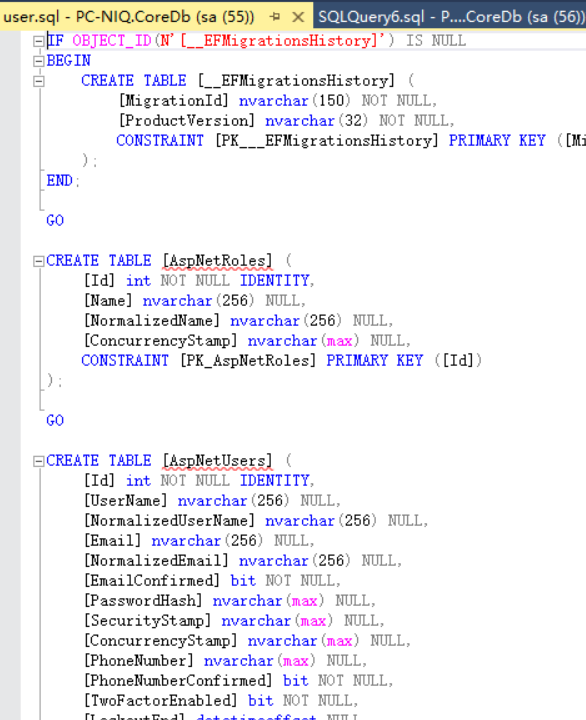
dotnet ef migratoins remove 是移除最新的一个migration,remove一次就移除一次,
前提是该migration没有update到database,如果细心你会发现,当你add migration时候,会提示,可以remove 移除
我们添加3个 migration 分别是 temp01,temp02,temp03
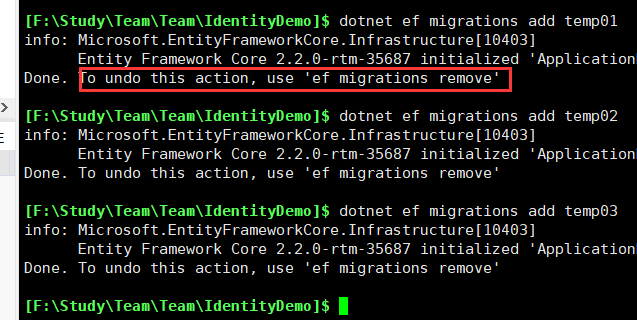
此时已经添加了3个测试的
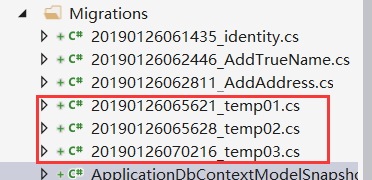
记住,我这里都没有执行update的,所以在__EFMigrationsHistory也不会记录。该表记录的是已经update到database的migration

我们执行一次命令:dotnet ef migrations remove
因为temp03是最后添加的,所以先删除,是不是像入栈出栈
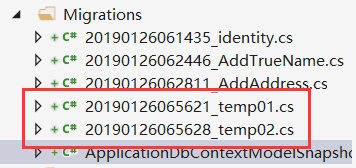
在remove一次,按照上面说的,应该是移除temp02

就不一一测试了
来看看,如果update 后。能不能remove,上面已经还原到了TrueName
我们先升级到Address
执行命令:dotnet ef database update Addaddress
表字段和历史纪录也都有了
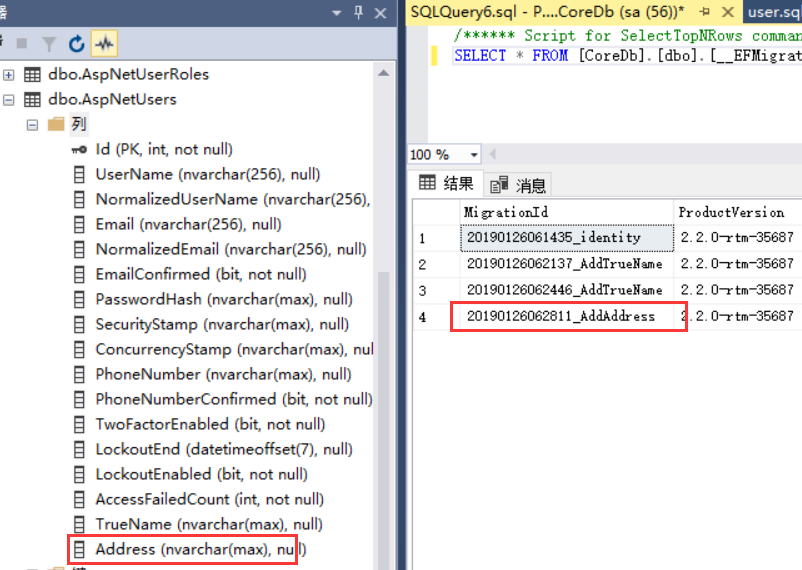
然后我们执行命令:dotnet ef migrations remove
这里要注意一点,我们是加了Adress后,我为了测试,又加了temp01,02,03,上面测试只remove了03,02
如果你没有remove01的话,现在remove是remove的01,注意下就好了
现在我们默认01,02,03都已经remove了。最新的肯定就是address了
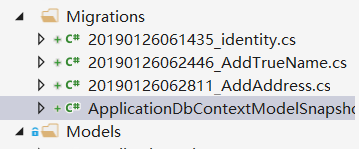
好了,有点啰嗦。执行命令:dotnet ef migrations remove

info提示该migratin已经udate到database
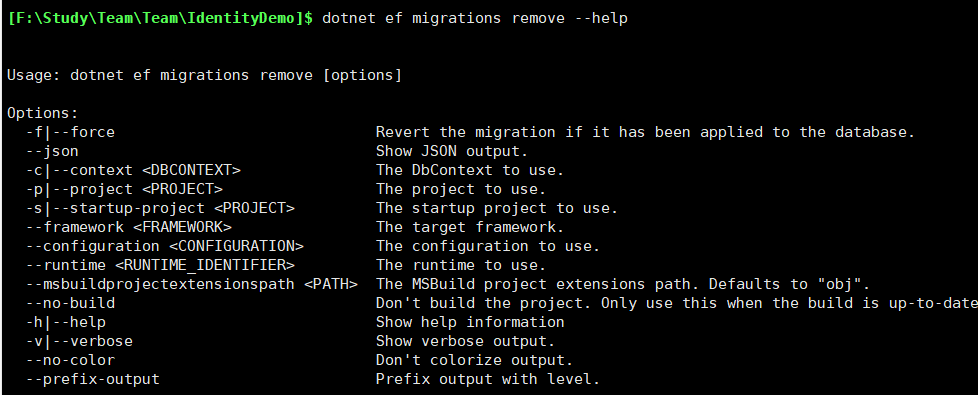
通过dotnet ef migrations remove --help
可以看到有其他选项,有兴趣的可以自行研究
上面都是手动执行命令,我们来看看在代码里面怎么做
在程序初始化的时候,添加一个默认管理员的账号,实例代码如下
创建一个ApplicationDbContextSeed类,用于创建默认用户
using IdentityDemo.Models; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity; using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection; using System; using System.Linq; using System.Threading.Tasks; using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging; namespace IdentityDemo.Date { public class ApplicationDbContextSeed { private UserManager<ApplicationUser> _userManger; /// <summary> /// /// </summary> /// <param name="context">上下文</param> /// <param name="server">依赖注入的容器,这里可以获取依赖注入</param> /// <returns></returns> public async Task AsyncSpeed(ApplicationDbContext context, IServiceProvider server) { try { _userManger = server.GetRequiredService<UserManager<ApplicationUser>>(); var logger = server.GetRequiredService<ILogger<ApplicationDbContext>>(); logger.LogInformation("speed Init"); //如果没有用户,则创建一个 if (!_userManger.Users.Any()) { var defaultUser = new ApplicationUser { UserName = "Admin", dEmail = "cnblogs@163.com" }; var userResult = await _userManger.CreateAsync(defaultUser, "123456"); if(!userResult.Succeeded) { logger.LogError("创建失败"); //logger.LogInformation("初始化用户失败"); userResult.Errors.ToList().ForEach(e => { logger.LogError(e.Description); }); } } } catch (Exception ex) { throw new Exception("初始化用户失败"); } } } }
添加一个对IWebHost扩展的类:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection; using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging; using System; namespace IdentityDemo.Date { public static class WebHostMigrationExtensions { public static IWebHost MigrationDbContext<TContext>(this IWebHost host, Action<TContext, IServiceProvider> sedder) where TContext : DbContext { using (var scope = host.Services.CreateScope()) { //拿到依赖注入容器 var servers = scope.ServiceProvider; //var logger = servers.GetRequiredService<ILogger<TContext>>(); var logger = servers.GetService<ILogger<TContext>>(); var context = servers.GetService<TContext>(); try { context.Database.Migrate(); sedder(context, servers); logger.LogInformation($"执行DbContex{typeof(TContext).Name}seed方法成功"); } catch (Exception ex) { logger.LogError(ex, $"执行DbContex{typeof(TContext).Name}seed方法失败"); } } return host; } } }
这样就可以在Program.cs的main方法中调用
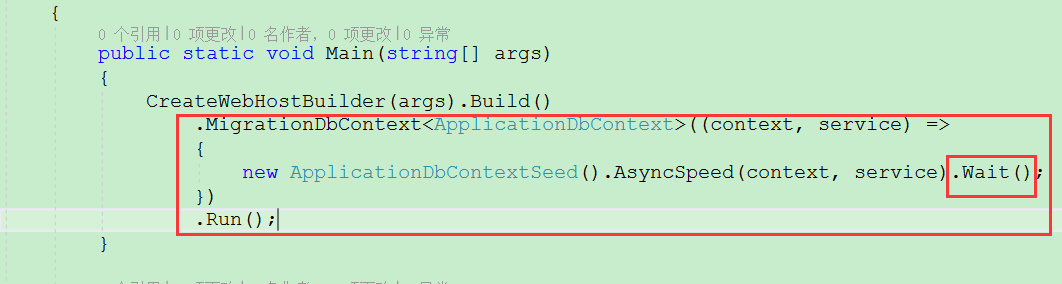
因为方法是异步方法,所以用Wait()方法改为同步的
然后删除Migration中的所有文件,重新add,可以 不update,因为代码会:context.Database.Migrate();
然后数据库已经初始化了

通过var user = _userManager.FindByEmailAsync("cnblogs@163.com").Result;可以查找用户,
[HttpPost] public IActionResult Login(LoginViewModel model) { var user = _userManager.FindByEmailAsync(model.Email).Result; if (user!=null) { var claims = new List<Claim> { new Claim("name",model.UserName) }; var claimsIdentity = new ClaimsIdentity(claims, CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme); var cliamsPrincipal = new ClaimsPrincipal(claimsIdentity); HttpContext.SignInAsync(CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme, cliamsPrincipal); return RedirectToAction("Index", "Home"); } return RedirectToAction("Index"); }
本文主要讲了magration的操作和identity身份的验证
源码:https://github.com/byniqing/AspNetCore-identity
参考资料
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/migration/proper-to-2x/?view=aspnetcore-2.2
https://www.cnblogs.com/jqdy/p/5941248.html
https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/ef/core/miscellaneous/cli/dotnet#dotnet-ef-migrations-remove

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号