[one-shot医学图像分割]LT-Net: Label Transfer by Learning Reversible Voxel-wise Correspondence for One-shot Medical Image Segmentation
前言
- 核心
- 问题:解决one-shot医学图像分割
- 方案: 传统的基于Atlas的医学图像分割对于解决one-shot问题很有帮助,通过使用神经网络进行替代传统纹理计算的方式计算一致性
引入强化学习,充分利用训练数据 - 结论: 思路方法很好,通过方法的结合进行提出新的方案是一个很好的思路。
- Atlas-based segmentation: 基于图谱的图像分割
Atlas:指人工标记完备的数据集,可以翻译为"地图集",如BrainWeb中的Atlas:在三维脑部CT数据中医生标注完备的各种脑部结构。 - non-rigid registration: 非刚性配准,用于label传播
- patch-based segmentation: 使用非局部思想(nonolocal concept) 进行patch-patch而不是one-one的对应关系。
- 深度卷积神经网络:DCNNs,deep convolutional neural networks
Abstract
- an intriguing characteristic of ..:一个有趣的特点是
1.为了解决缺少标注的问题,借助经典的atlas-based方法的分割思想来解决one-shot分割问题。
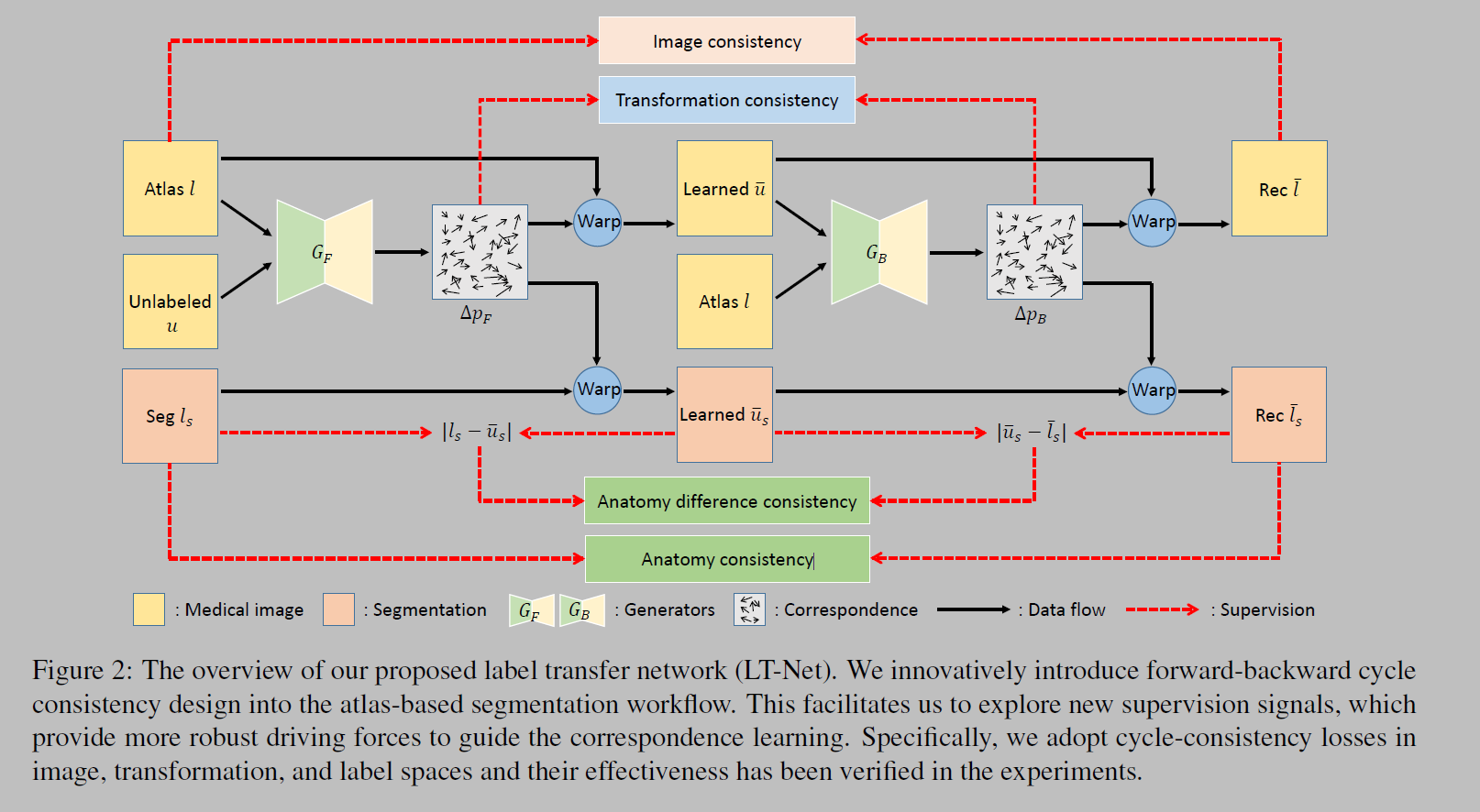
2.以端到端方式将对应映射关系的学习扩展到one-shot分割框架中,其中前向和反向构成的循环一致性 (forward-backward cycle-consistency)在图像、转换和标签空间中起到了额外监督的重要作用。 - 图像之间的真是标注的对应关系一般难以建立
- We demonstrate the superiority of our method over both deep learning-based one-shot seg-mentation methods and a classical multi-atlas segmentation method via thorough experiments.
- the state-of-the-art(SOTA):当前的最好方法
- 解释拓展:In addition, we impose supervision in three involved spaces, namely, the image space, the transformation space, and the label space, which has been verified effective in our experiments.
Introduction
- DCNN-based segmentation methods that require only one or few examples of annotation for training are highly desirable to enable efficient development and deployment of practical solutions
实际解决方案的部署问题 - 基于图谱的医学图像分割只需要很少的标注数据,这与深度学习中的少样本学习(few-shot/one-shot learning)概念相似。
- 传统基于图谱的医学图像分割的核心是标注数据和待分割数据之间的相似度匹配问题,传统方法都是通过纹理等特征进行局部特征计算。
- DCNNs在处理多尺度语义特征更加强大,通过DGCNNs进行基于图谱的医学图像分割更加合适。
- 我们提出的方法是直接使用深度学习方法来模拟基于图谱的医学图像分割
- 方法的输入是地图集和目标图片,并预测前者到后者的对应图。
- 主要使用神经网络学习对应关系(理解就是使用神经网络进行未标记图片和已经标记图片之间的像素点相似度进行预测,相似度高的使用对应的已经标记的类别)
- 为了有效训练,增加了鉴别网络进行对抗训练。
- correspondence problem: 一致性问题,即相似度的计算。forward-backward consistency,即先通过atlas数据对应到未标记数据上,经过预测后得到的结果(warped atlas)再对应回到original atlas中。
Method
参考

