美团笔试
算法第一题
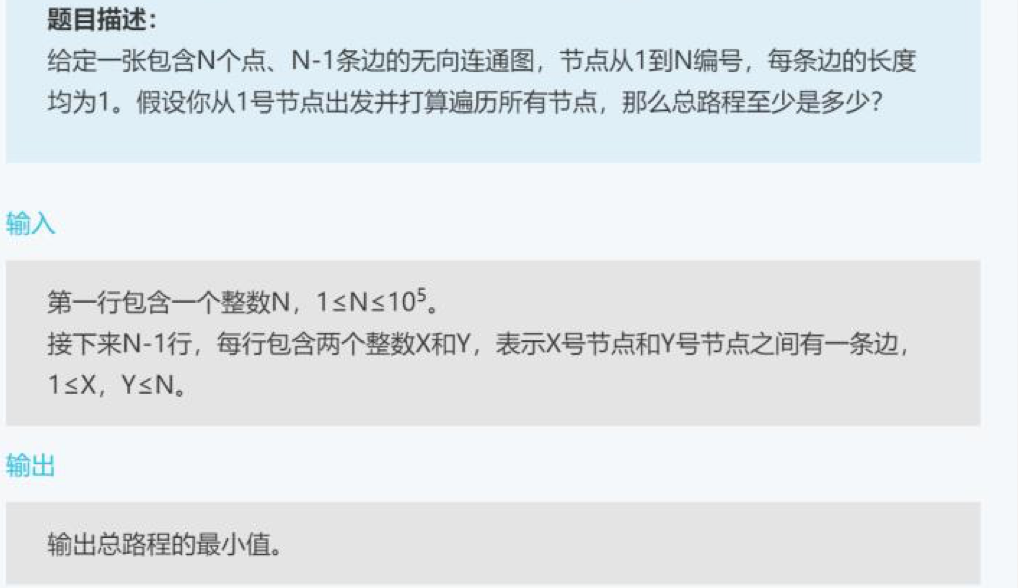 

example
input:
4
1 2
1 3
3 4
output:
4
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
int maxRoadLength(unordered_map<int, vector<int>> &adjList, int root) {
vector<int> successors = adjList[root];
size_t size = successors.size();
if (size == 0) return 0;
int maxLen = 0;
for (int successor : successors) {
maxLen = max(maxLen, maxRoadLength(adjList, successor));
}
return maxLen + 1;
}
int main() {
int N;
cin >> N;
unordered_map<int, vector<int>> adjList;
int pioneer, successor;
for (int i = 0; i < N-1; i++) {
cin >> pioneer >> successor;
adjList[pioneer].push_back(successor);
}
int ans = maxRoadLength(adjList, 1);
ans = 2 * (N-1) - ans;
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
算法第二题
这个是一个考察队列的题, 很精髓, 下次遇到这种顺序求解的题, 要注意
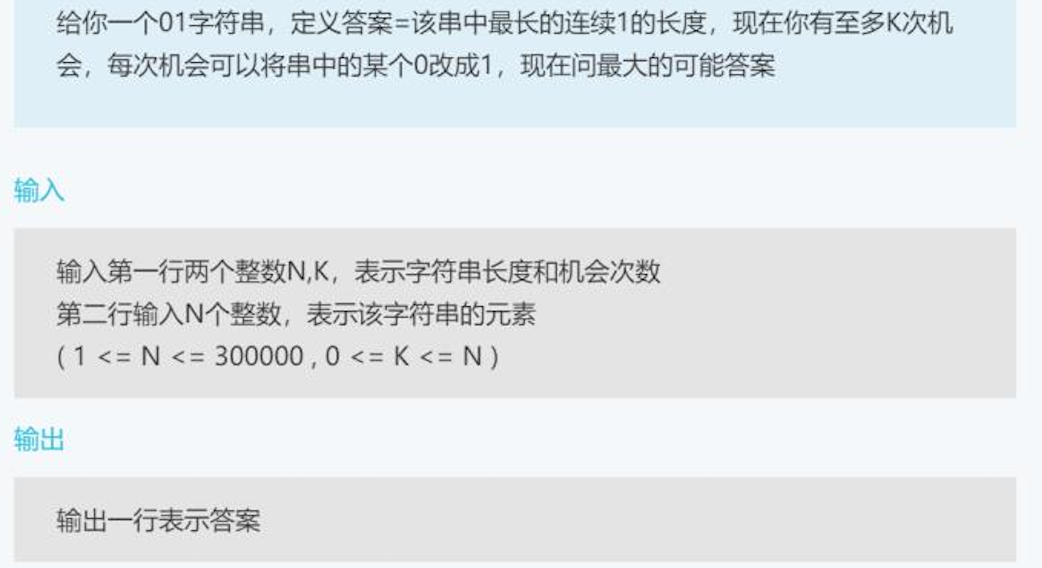 

example
input:
10 2
1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1
output: 5
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int N, K;
cin >> N >> K;
vector<int> nums(N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
cin >> nums[i];
}
// 连续的 1 串, 必定连续
// 看从 (start, end] 区间连续的 1 串的长度
queue<int> zero_queue;
int max_length = 0;
int cur_length = 0;
for(int end = 0; end < N; end++) {
if (nums[end] == 1) {
cur_length++;
max_length = max(max_length, cur_length);
continue;
}
if (zero_queue.size() < K){
zero_queue.push(end);
cur_length++;
max_length = max(max_length, cur_length);
} else {
int start = zero_queue.front();
zero_queue.pop();
zero_queue.push(end);
cur_length = end-start;
}
}
cout << max_length << endl;
return 0;
}

