Leetcode刷题第六周
回溯算法
回溯的本质是穷举,所以不是高效的算法
回溯法,一般可以解决如下几种问题:
组合问题:N个数里面按一定规则找出k个数的集合
注意区分一个集合取组合和多个集合取组合的细节。
切割问题:一个字符串按一定规则有几种切割方式
子集问题:一个N个数的集合里有多少符合条件的子集
排列问题:N个数按一定规则全排列,有几种排列方式
棋盘问题:N皇后,解数独等等
需要注意问题是有一个解还是多个解,一个解的需要返回值,一旦找到解就逐级返回,多个解的不需要返回值
因为回溯算法需要的参数可不像二叉树递归的时候那么容易一次性确定下来,所以一般是先写逻辑,然后需要什么参数,就填什么参数。
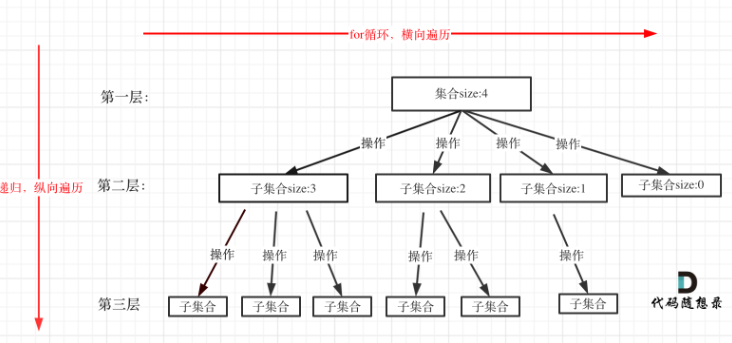

从图中看出for循环可以理解是横向遍历,backtracking(递归)就是纵向遍历
77、组合

class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public List<Integer> temp = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
int index = 1;
travesal(n,k,index);
return result;
}
public void travesal(int n, int k, int index){
// 终止条件,得到k个数的组合
if(temp.size() == k){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
return;
}
for (int i = index; i <= n - (k - temp.size()) + 1; i++) {
temp.add(i);
travesal(n,k,i+1);//递归
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);//回溯
}
}
}
216、组合总和 III

class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
public int sum;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {
sum = 0;
find(k,1,n);
return result;
}
public void find(int k, int left, int right){
if(temp.size() == k){
if(sum == right){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
}
return;
}
for(int i = left; i <= 9 - (k - temp.size()) + 1; i++){
if(sum > right){
continue;
}
temp.add(i);
sum += i;
find(k,i+1,right);
sum -= temp.get(temp.size() - 1);
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
}
}
17、电话号码的字母组合

class Solution {
public List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
public StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer();
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
// 边界条件
if(digits == null || digits.length() == 0){
return result;
}
char[] digitsArr = digits.toCharArray();
// 映射关系
String[] find = {"","","abc","def","ghi","jkl","mno","pqrs","tuv","wxyz"};
int index = 0;
letterCombinationsHelper(digitsArr, find, index);
return result;
}
public void letterCombinationsHelper(char[] digitsArr, String[] find, int index){
if(index == digitsArr.length){
result.add(new String(str));
return;
}
// 第index个数字对应的字母
String strTemp = find[digitsArr[index] - '0'];
for(int i = 0; i < strTemp.length(); i++){
str.append(strTemp.charAt(i));//加入第Index个数字对应的字母的第i个
letterCombinationsHelper(digitsArr,find,index+1);
str.deleteCharAt(str.length() - 1);
}
}
}
39、组合总和
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
int sum = 0;
int index = 0;
Arrays.sort(candidates);
combinationSumHelper(candidates,index,sum,target);
return result;
}
public void combinationSumHelper(int[] candidates, int index, int sum,int target){
if(sum >= target){
if(sum == target){
result.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(temp));
}
return;
}
for(int i = index; i < candidates.length; i++){
sum += candidates[i];
temp.add(candidates[i]);
combinationSumHelper(candidates,i,sum,target);
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
sum -= candidates[i];
}
}
}
40、 组合总和 II

class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
int sum = 0;
int index = 0;
Arrays.sort(candidates);
combinationSumHelper(candidates, target, index, sum);
return result;
}
public void combinationSumHelper(int[] candidates, int target, int index, int sum){
if(sum >= target){
if(sum == target){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
}
return;
}
// 每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次
for(int i = index; i < candidates.length; i++){
// 去重逻辑,同层剪枝,同枝可取
if(i > 0 &&i > index && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]){
continue;
}
temp.add(candidates[i]);
sum += candidates[i];
combinationSumHelper(candidates, target, i + 1, sum);
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
sum -= candidates[i];
}
}
}
131、分割回文串

class Solution {
public List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<List<String>>();
public List<String> temp = new ArrayList<String>();
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
int index = 0;
partitionHelper(s, index);
return result;
}
public void partitionHelper(String s, int index){
if(index == s.length()){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
return;
}
for(int i = index; i < s.length(); i++){
String s1 = s.substring(index, i + 1);
if(!check(s1,0,s1.length() - 1)){
continue;//字符子串不回文的话直接跳过该次分割方案
}
temp.add(s1);
partitionHelper(s,i+1);
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
}
// 判断是否回文
public boolean check(String s1, int left, int right){
while(left < right){
if(s1.charAt(left) == s1.charAt(right)){
left++;
right--;
}else{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
93、复原 IP 地址
class Solution {
public List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
public List<String> temp = new ArrayList<>();
public List<String> restoreIpAddresses(String s) {
find(0,s,s.length());
return result;
}
public void find(int index, String s, int length){
if(index == length){
if(temp.size() == 4){
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer();
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
buf.append(temp.get(i)).append(".");
}
buf.append(temp.get(3));
result.add(new String(buf));
}
return;
}
for(int i = index; i < length; i++){
int num = Integer.parseInt(s.substring(index,i+1));
if(num > 255){
break;
}
if(s.charAt(index) == '0'){
temp.add(s.substring(index,i+1));
find(i+1,s,length);
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
break;
}
temp.add(s.substring(index,i+1));
find(i+1,s,length);
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
}
}
78、子集
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
subsetsHandler(nums, 0);
return result;
}
public void subsetsHandler(int[] nums, int index){
if(index == nums.length){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
return;
}
result.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
for(int i = index; i < nums.length; i++){
temp.add(nums[i]);
subsetsHandler(nums,i+1);
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
}
}
90、子集 II

class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
subsetsWithDupHandler(nums, 0);
return result;
}
public void subsetsWithDupHandler(int[] nums, int index){
if(index == nums.length){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
return;
}
result.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
for(int i = index; i < nums.length; i++){
// 不能 包含重复的子集
if(i > 0 &&i > index && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]){
continue;
}
temp.add(nums[i]);
subsetsWithDupHandler(nums, i + 1);
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
}
}
491、递增子序列

class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public List<List<Integer>> findSubsequences(int[] nums) {
// 递增子序列中 至少有两个元素
findSubsequencesHandler(nums, 0);
return result;
}
public void findSubsequencesHandler(int[] nums, int index){
if(temp.size() > 1){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
}
int[] used = new int[201];
for(int i = index; i < nums.length; i++){
if(temp.size() != 0 && nums[i] < temp.get(temp.size() - 1) || (used[nums[i] + 100] == 1)){
continue;
}
used[nums[i] + 100] = 1;
temp.add(nums[i]);
findSubsequencesHandler(nums, i + 1);
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
}
}
46、全排列

class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
public int[] used;
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
used = new int[nums.length];
find(nums);
return result;
}
public void find(int[] nums){
if(temp.size() == nums.length){
result.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(temp));
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if(used[i] == 1){
continue;
}
temp.add(nums[i]);
used[i] = 1;
find(nums);
temp.remove(temp.size()-1);
used[i] = 0;
}
}
}
47、全排列 II

class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
public int[] used;
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
used = new int[nums.length];
Arrays.sort(nums);
find(nums);
return result;
}
public void find(int[] nums){
if(temp.size() == nums.length){
result.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(temp));
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if(used[i] == 1){
continue;
}
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i-1] != 1){
continue;
}
temp.add(nums[i]);
used[i] = 1;
find(nums);
temp.remove(temp.size()-1);
used[i] = 0;
}
}
}
332、重新安排行程
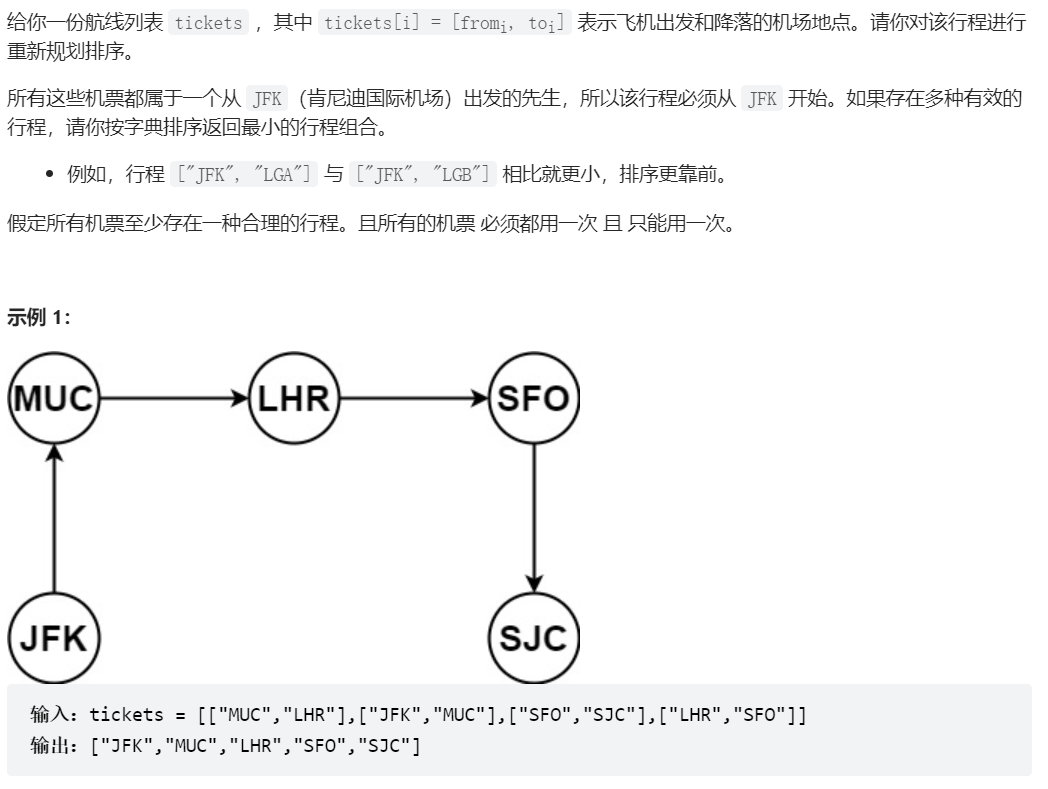
//基本参考代码随想录
class Solution {
public LinkedList<String> result;
public LinkedList<String> path = new LinkedList<String>();
public List<String> findItinerary(List<List<String>> tickets) {
Collections.sort(tickets,(a,b)->a.get(1).compareTo(b.get(1)));//字典排序
path.add("JFK");
int[] used = new int[tickets.size()];
findItineraryHanlder(tickets, used);
return result;
}
public boolean findItineraryHanlder(List<List<String>> tickets, int[] used){
if(path.size() == tickets.size() + 1){
result = new LinkedList<String>(path);
return true;
}
for(int i = 0; i < tickets.size(); i++){
if(used[i] != 1 && tickets.get(i).get(0).equals(path.getLast())){
path.add(tickets.get(i).get(1));
used[i] = 1;
if(findItineraryHanlder(tickets,used)){
return true;
}
path.removeLast();
used[i] = 0;
}
}
return false;
}
}
51、N 皇后

class Solution {
public List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<List<String>>();
public int[][] arr;
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
arr = new int[n][n];
find(n,0);
return result;
}
public void find(int n, int count){
if(count == n){
List<String> temp = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
String str = "";
for(int j= 0; j < n; j++){
if(arr[i][j] == 1){
str = str + "Q";
}else{
str = str + ".";
}
}
temp.add(str);
}
result.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(check(i,n,count)){
arr[count][i] = 1;
find(n,count+1);
arr[count][i] = 0;
}
}
}
public boolean check(int index,int n,int count){
for(int j = count - 1; j >= 0; j--){
if(arr[j][index] == 1){
return false;
}
}
for(int j = count - 1, index1 = index - 1; j >= 0 &&index1 >= 0; j-- , index1--){
if(arr[j][index1]==1){
return false;
}
}
for(int j = count - 1, index2 = index + 1; j >= 0 && index2<n; j-- ,index2++){
if(arr[j][index2]==1){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
37、解数独
class Solution {
public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
solveSudokuHander(board);
}
public boolean solveSudokuHander(char[][] board){
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < 9; j++){
if(board[i][j] != '.'){
continue;
}
for(char k = '1'; k <= '9'; k++){
if(judge(board,i,j,k)){
board[i][j] = k;
if(solveSudokuHander(board)){
return true;
}
board[i][j] = '.';
}
}
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public boolean judge(char[][] board, int i, int j, char k){
for(int m = 0; m < 9; m++){
if(board[i][m]==k){
return false;
}
}
for(int n = 0; n < 9; n++){
if(board[n][j]==k){
return false;
}
}
int startRow = (i/3)*3;
int startCol = (j/3)*3;
for(int m = startRow; m < startRow+3; m++){
for(int n = startCol; n < startCol+3; n++){
if(board[m][n]==k){
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号