Leetcode刷题第五周
二叉树:
种类:满二叉树、完全二叉树、二叉搜索树、平衡二叉搜索树
存储方式:链式存储、线式存储(顺序存储)
二叉数遍历:深度优先搜索(前序、中序、后序):使用递归实现(实际用栈来实现)、迭代法(非递归的方式、栈),广度优先搜索(层序遍历):用队列
递归三步走写法:1、确定递归函数的参数和返回值。2、确定终止条件。3、确定单层递归的逻辑。
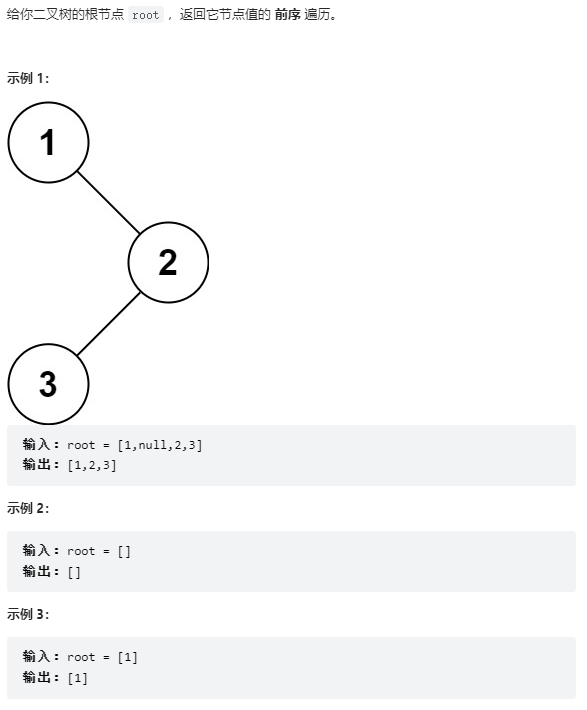
144、二叉树的前序遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
// 方法一:递归法
// public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
// List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
// preorder(root, result);
// return result;
// }
// public void preorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> result){
// if(root == null){
// return;
// }
// result.add(root.val);
// preorder(root.left, result);
// preorder(root.right, result);
// }
// 方法二:非递归的方法
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode cur = stack.pop();
if(cur != null){
result.add(cur.val);
stack.push(cur.right);
stack.push(cur.left);
}else{
continue;
}
}
return result;
}
// 方法三:统一风格的非递归
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
if(root != null){
stack.push(root);
}
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
if(stack.peek() != null){
TreeNode cur = stack.pop();
if(cur.right != null){
stack.push(cur.right);
}
if(cur.left != null){
stack.push(cur.left);
}
stack.push(cur);
stack.push(null);
}else{
stack.pop();
TreeNode cur = stack.pop();
result.add(cur.val);
}
}
return result;
}
}
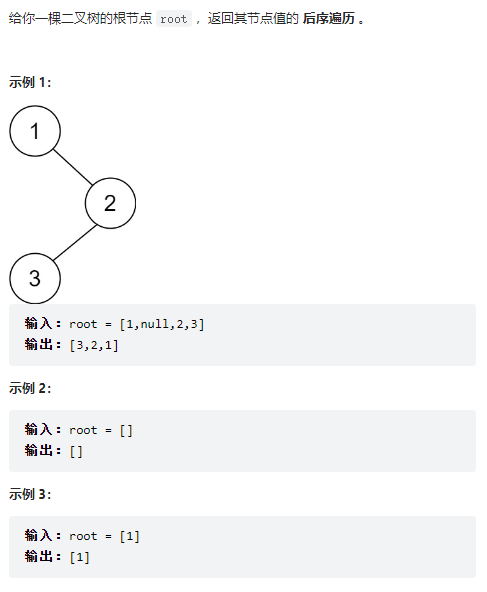
145、二叉树的后序遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
// 方法一:递归法
// public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
// List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
// postOrder(root, result);
// return result;
// }
// public void postOrder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> result){
// if(root == null){
// return;
// }
// postOrder(root.left, result);
// postOrder(root.right, result);
// result.add(root.val);
// }
// 方法二:非递归
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return result;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode cur = stack.pop();
result.add(cur.val);
if(cur.left != null){
stack.push(cur.left);
}
if(cur.right != null){
stack.push(cur.right);
}
}
Collections.reverse(result);
return result;
}
// 方法三:统一风格的非递归
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
if(root != null){
stack.push(root);
}
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
if(stack.peek() != null){
TreeNode cur = stack.pop();
stack.push(cur);
stack.push(null);
if(cur.right != null){
stack.push(cur.right);
}
if(cur.left != null){
stack.push(cur.left);
}
}else{
stack.pop();
TreeNode cur = stack.pop();
result.add(cur.val);
}
}
return result;
}
}
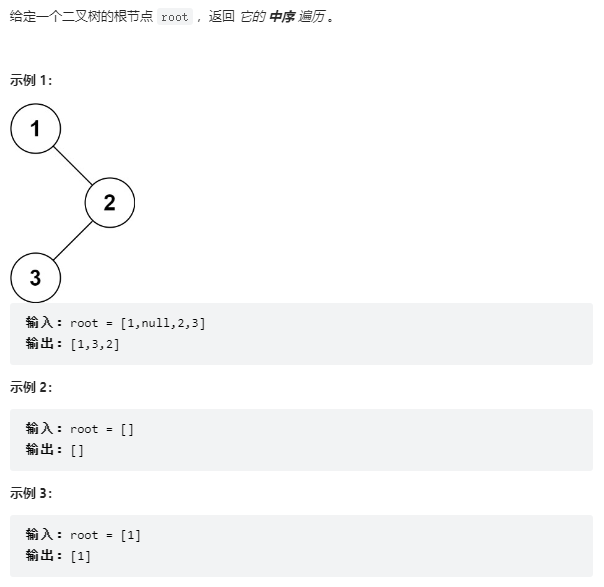
94、二叉树的中序遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
// 方法一:递归法
// public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
// List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
// infixOrder(root, result);
// return result;
// }
// public void infixOrder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> result){
// if(root == null){
// return;
// }
// infixOrder(root.left, result);
// result.add(root.val);
// infixOrder(root.right, result);
// }
// 方法二:非递归
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return result;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while(cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()){
if(cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}else{
cur = stack.pop();
result.add(cur.val);
cur = cur.right;
}
}
return result;
}
// 方法三:统一风格的非递归
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
if(root != null){
stack.push(root);
}
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
if(stack.peek() != null){
TreeNode cur = stack.pop();
if(cur.right != null){
stack.push(cur.right);
}
stack.push(cur);
stack.push(null);
if(cur.left != null){
stack.push(cur.left);
}
}else{
stack.pop();
TreeNode cur = stack.pop();
result.add(cur.val);
}
}
return result;
}
}
广度优先搜索:层序遍历
102、二叉树的层序遍历

class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int size = 0;
if(root != null){
queue.offer(root);
size = 1;
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
while(size > 0){
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
list1.add(cur.val);
if(cur.left != null){
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if(cur.right != null){
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
size--;
}
size = queue.size();
list.add(list1);
}
return list;
}
}
107、二叉树的层序遍历 II

class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int size = queue.size();
if(root != null){
queue.offer(root);
size = queue.size();
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
while(size > 0){
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
list1.add(cur.val);
if(cur.left != null){
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if(cur.right != null){
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
size--;
}
size = queue.size();
list.add(list1);
}
Collections.reverse(list);
return list;
}
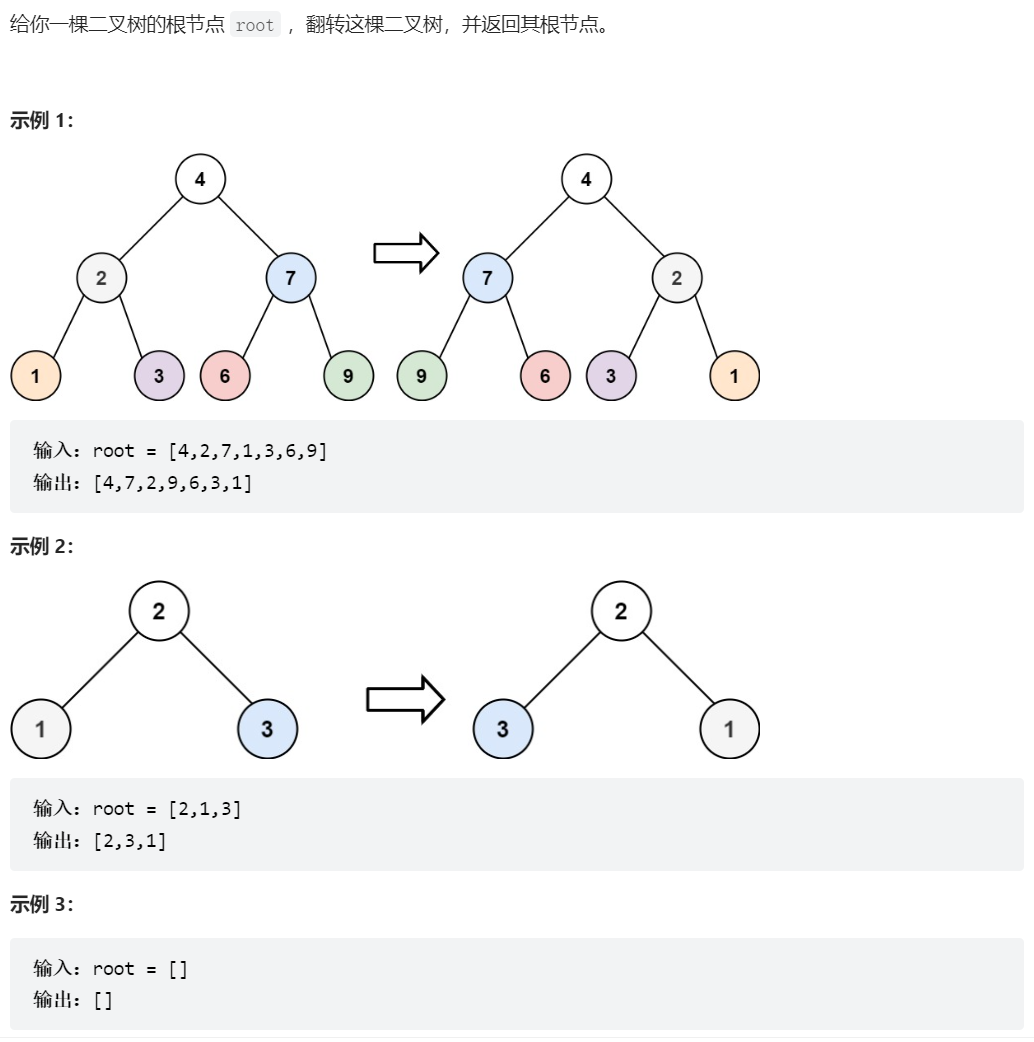
226、翻转二叉树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
// 方法一:层次遍历,广度优先算法
// public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
// Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// int size = queue.size();
// if(root != null){
// queue.offer(root);
// size = queue.size();
// }
// while(!queue.isEmpty()){
// while(size > 0){
// TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
// if(cur.left != null){
// queue.offer(cur.left);
// }
// if(cur.right != null){
// queue.offer(cur.right);
// }
// swapChildren(cur);
// size--;
// }
// size = queue.size();
// }
// return root;
// }
// public void swapChildren(TreeNode cur){
// TreeNode temp = cur.left;
// cur.left = cur.right;
// cur.right = temp;
// }
// 方法二:递归法,后序
// public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
// if(root == null){
// return root;
// }
// invertTree(root.left);
// invertTree(root.right);
// swapChildren(root);
// return root;
// }
// public void swapChildren(TreeNode cur){
// TreeNode temp = cur.left;
// cur.left = cur.right;
// cur.right = temp;
// }
// 方法三:迭代法:中序,统一风格
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
if(root != null){
stack.push(root);
}
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
if(stack.peek() != null){
TreeNode cur = stack.pop();
if(cur.right != null)
stack.push(cur.right);
if(cur.left != null)
stack.push(cur.left);
stack.push(cur);
stack.push(null);
swapChildren(cur);
}else{
stack.pop();
stack.pop();
}
}
return root;
}
public void swapChildren(TreeNode cur){
TreeNode temp = cur.left;
cur.left = cur.right;
cur.right = temp;
}
}
590、N 叉树的后序遍历
101、对称二叉树

class Solution {
// 方法一:递归,后序遍历
// public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
// return compare(root.left, root.right);
// }
// public boolean compare(TreeNode left, TreeNode right){
// if(left == null && right != null){
// return false;
// }
// if(right == null && left != null){
// return false;
// }
// if(right == null && left == null){
// return true;
// }
// if(left.val != right.val){
// return false;
// }
// boolean resultLeft = compare(left.left, right.right);
// boolean resultRight = compare(left.right, right.left);
// return resultLeft && resultRight;
// }
// 方法二:迭代
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode> deque = new LinkedList<>();
deque.offerFirst(root.left);
deque.offerLast(root.right);
while(!deque.isEmpty()){
TreeNode left = deque.pollFirst();
TreeNode right = deque.pollLast();
if(left == null && right == null){
continue;
}
if(left == null && right != null){
return false;
}
if(left != null && right == null){
return false;
}
if(left.val != right.val){
return false;
}
deque.offerFirst(left.left);
deque.offerFirst(left.right);
deque.offerLast(right.right);
deque.offerLast(right.left);
}
return true;
}
}
589、N 叉树的前序遍历
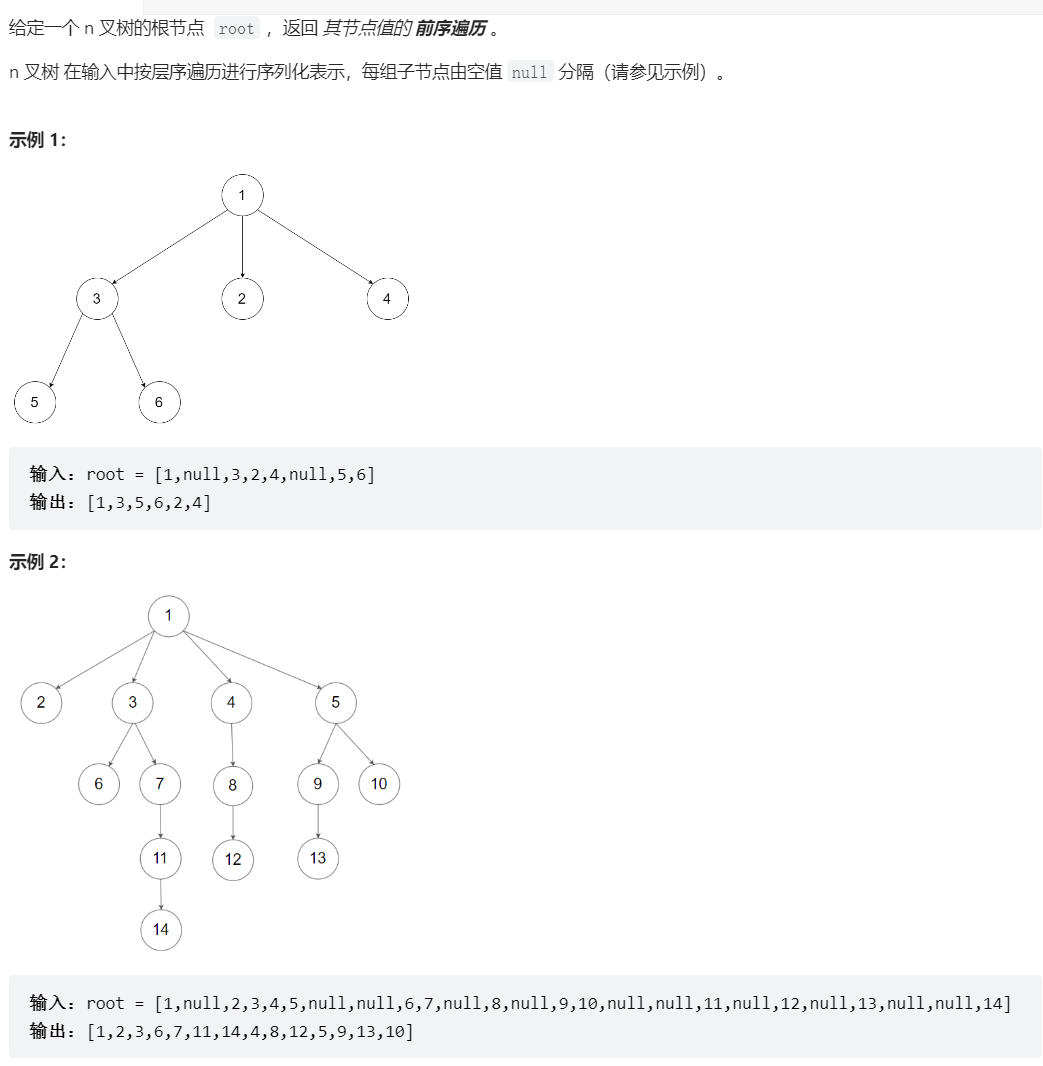
class Solution {
// 方法一:递归
// public List<Integer> resultList = new ArrayList<>();
// public List<Integer> preorder(Node root) {
// if(root == null){
// return resultList;
// }
// resultList.add(root.val);
// for(Node node : root.children){
// preorder(node);
// }
// return resultList;
// }
// 方法二:迭代,统一风格
public List<Integer> preorder(Node root) {
List<Integer> resultList = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
if(root != null){
stack.push(root);
}
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
if(stack.peek() != null){
Node cur = stack.pop();
List<Node> list = new ArrayList<>();
list = cur.children;
for(int i = list.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--){
if(list.get(i) != null){
stack.push(list.get(i));
}
}
stack.push(cur);
stack.push(null);
}else{
stack.pop();
Node cur = stack.pop();
resultList.add(cur.val);
}
}
return resultList;
}
}
559、N 叉树的最大深度

class Solution {
public int maxDepth(Node root) {
// 非递归
// if(root == null){
// return 0;
// }
// Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// queue.offer(root);
// int size = 1;
// int count = 0;
// while(!queue.isEmpty()){
// count++;
// while(size > 0 ){
// Node temp = queue.poll();
// for(Node k : temp.children){
// if(k != null){
// queue.offer(k);
// }
// }
// size--;
// }
// size = queue.size();
// }
// return count;
// 递归法:后序遍历
return find(root);
}
public int find(Node root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int depth = 0;
if(root.children != null){
for(Node k : root.children){
depth = Math.max(find(k),depth);
}
}
return depth + 1;
}
}
117、填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II
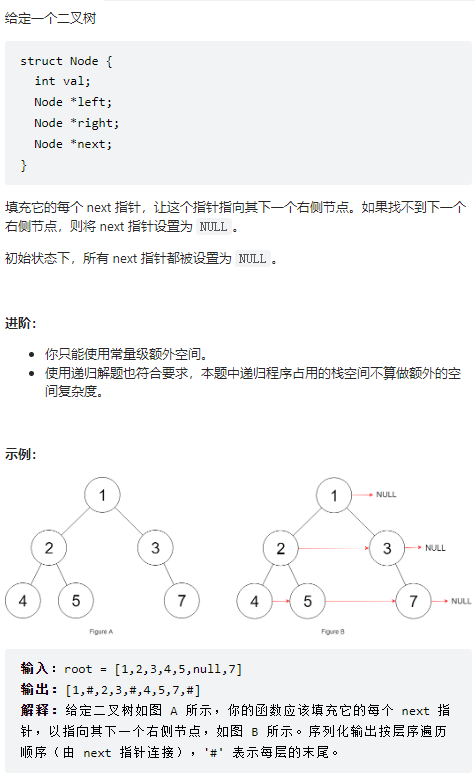
同上!
104、二叉树的最大深度
![]
(https://img2022.cnblogs.com/blog/3018498/202211/3018498-20221121204402960-1570599807.png)
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
// 非递归
// if(root == null){
// return 0;
// }
// Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// queue.offer(root);
// int count = 0;
// int size = 1;
// while(!queue.isEmpty()){
// count++;
// while(size > 0){
// TreeNode temp = queue.poll();
// if(temp.left != null){queue.offer(temp.left);}
// if(temp.right != null){queue.offer(temp.right);}
// size--;
// }
// size = queue.size();
// }
// return count;
// 递归
return find(root, 0);
}
public int find(TreeNode root, int depth){
if(root == null){
return depth;
}
int left = find(root.left, depth);
int right = find(root.right, depth);
depth = Math.max(left,right) + 1;
return depth;
}
}
111、二叉树的最小深度
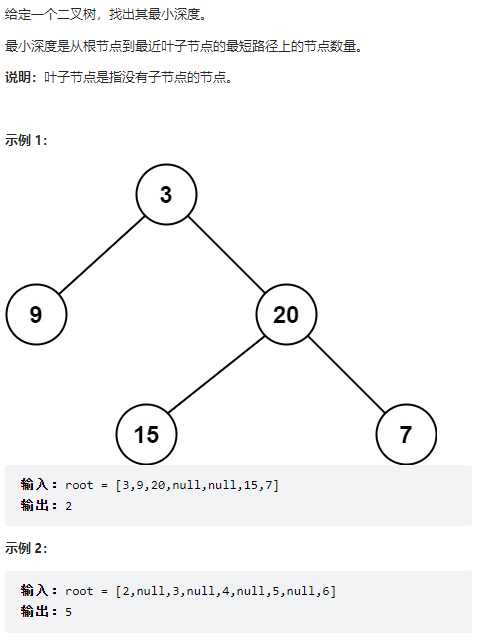
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
// 非递归,层序遍历
// if(root == null){
// return 0;
// }
// Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// queue.offer(root);
// int size = 1;
// int count = 0;
// while(!queue.isEmpty()){
// count++;
// while(size > 0){
// TreeNode temp = queue.poll();
// if(temp.left != null){
// queue.offer(temp.left);
// }
// if(temp.right != null){
// queue.offer(temp.right);
// }
// if(temp.left == null && temp.right == null){
// return count;
// }
// size--;
// }
// size = queue.size();
// }
// return count;
// 递归
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int left = minDepth(root.left);
int right = minDepth(root.right);
if(root.left == null && root.right != null){
return 1 + right;
}
if(root.right == null && root.left != null){
return 1 + left;
}
return Math.min(left, right) + 1;
}
}
222、完全二叉树的节点个数
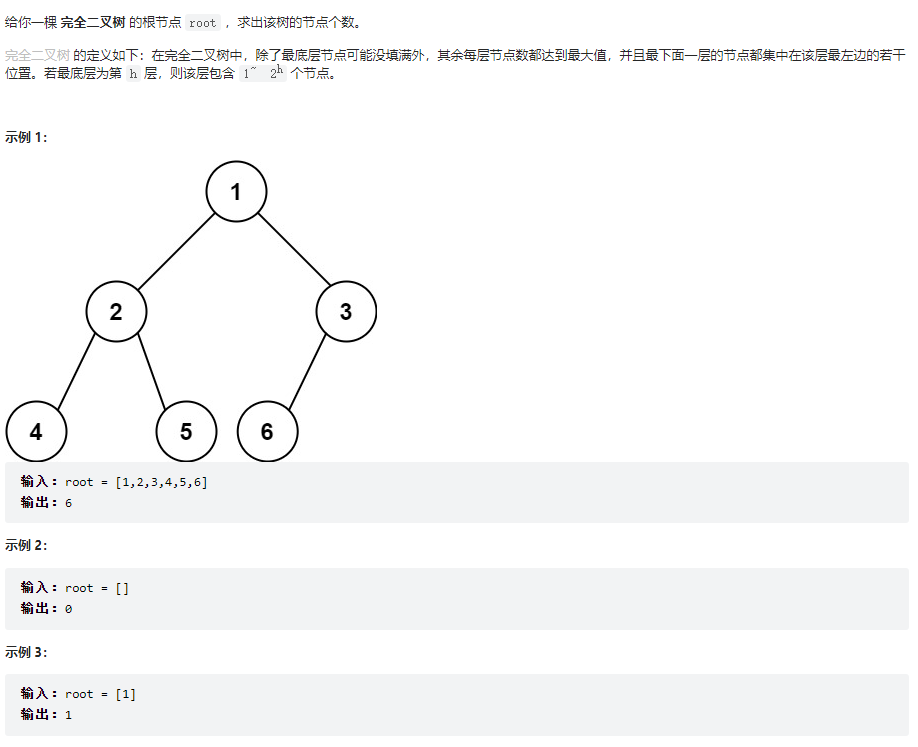
class Solution {
public int count = 0;
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return count;
}
count++;
countNodes(root.left);
countNodes(root.right);
return count;
}
}
110、平衡二叉树
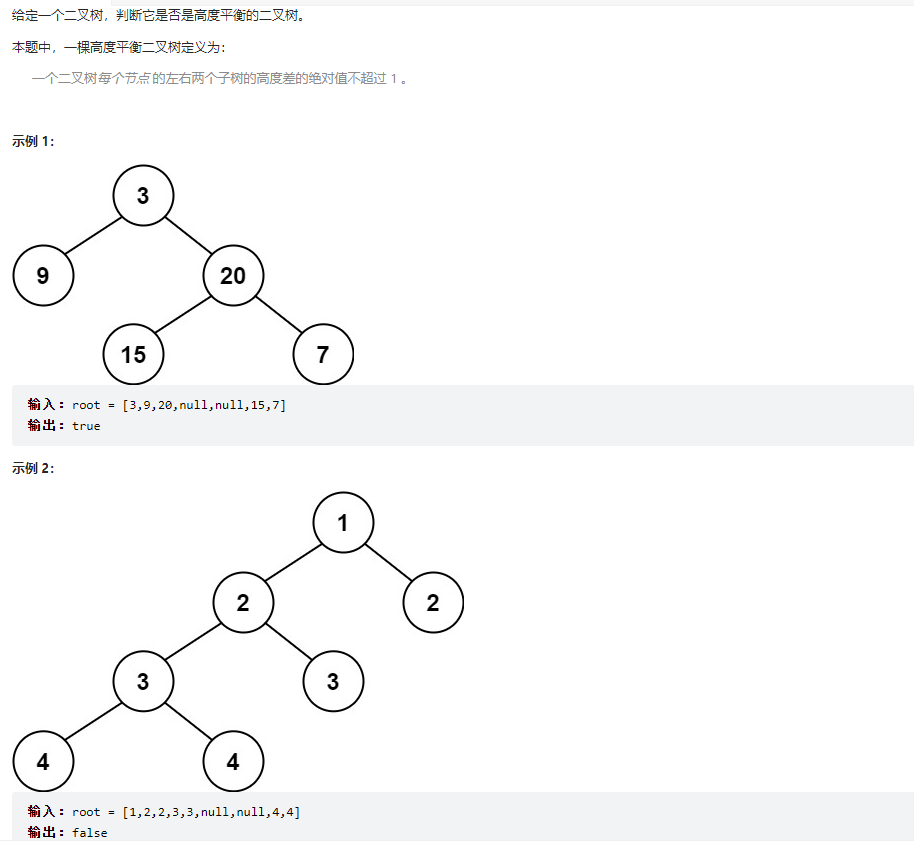
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return true;
}
return check(root) != -1;
}
public int check(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int left = check(root.left);
if(left == -1){return -1;}
int right = check(root.right);
if(right == -1){return -1;}
int result;
if(Math.abs(left - right) > 1){
return -1;
}else{
result = 1 + Math.max(left, right);
}
return result;
}
}
257、二叉树的所有路径
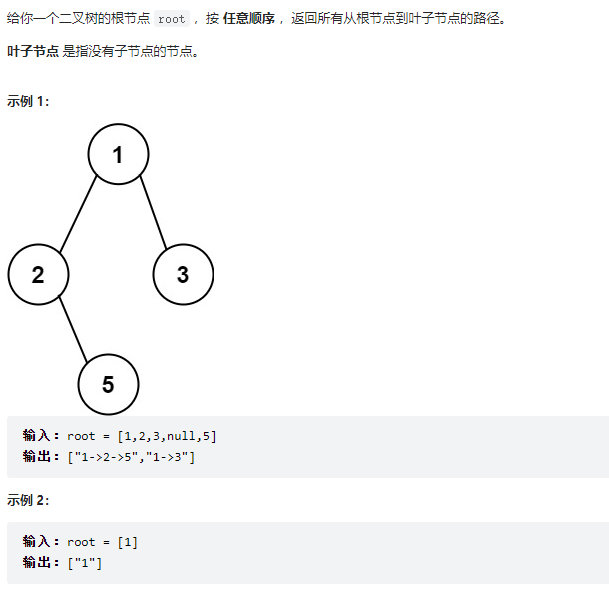
class Solution {
public List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return result;
}
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
TreePaths(root, list);
return result;
}
public void TreePaths(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list){
list.add(root.val);
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer();
for(int i = 0; i < list.size() - 1; i++){
buf.append(list.get(i)).append("->");
}
buf.append(list.get(list.size() - 1));
result.add(new String(buf));
return;
}
if(root.left != null){
TreePaths(root.left,list);
list.remove(list.size() - 1);
}
if(root.right != null){
TreePaths(root.right,list);
list.remove(list.size() - 1);
}
}
}
404、左叶子之和
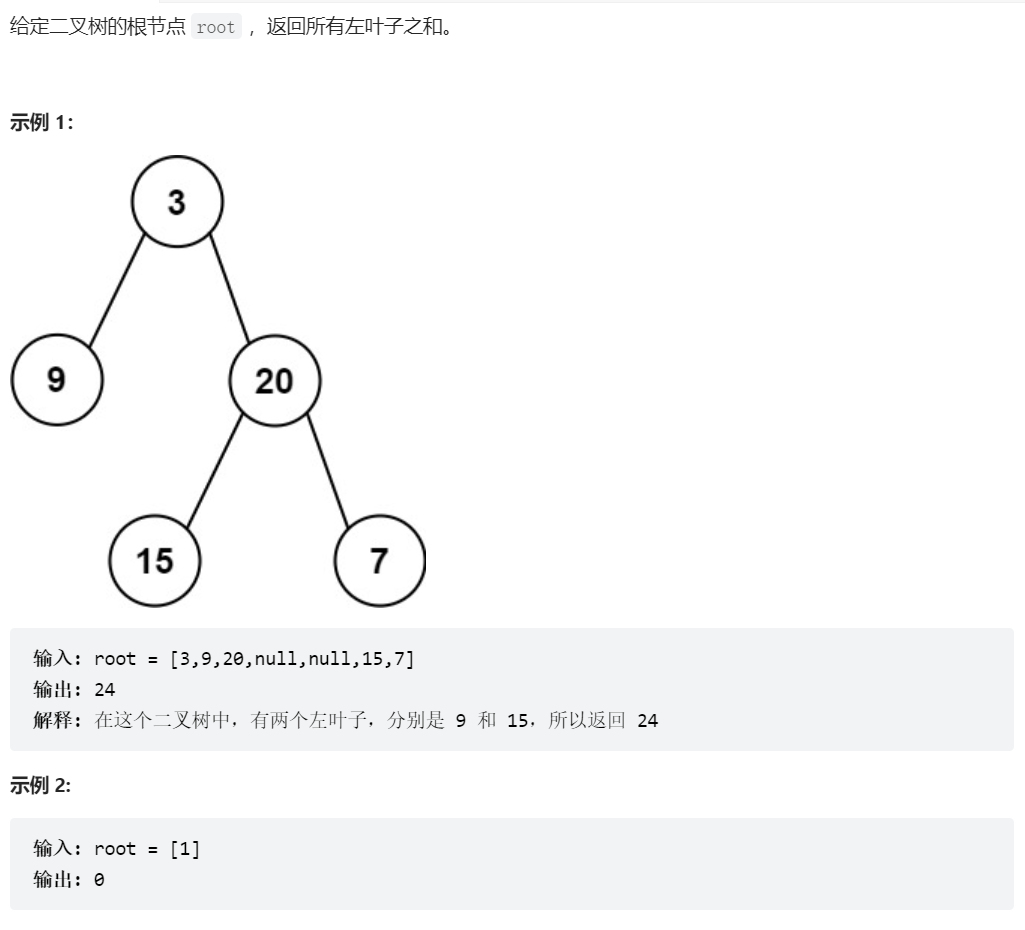
class Solution {
public int result = 0;
public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {
// 层序遍历
// int result = 0;
// if(root == null){
// return result;
// }
// Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// queue.offer(root);
// int size = 1;
// while(!queue.isEmpty()){
// while(size > 0){
// TreeNode temp = queue.poll();
// if(temp.left != null){
// queue.offer(temp.left);
// if(temp.left.left == null && temp.left.right == null){
// result += temp.left.val;
// }
// }
// if(temp.right != null){
// queue.offer(temp.right);
// }
// size--;
// }
// size = queue.size();
// }
// return result;
// 前序遍历
if(root == null){
return result;
}
sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left);
if(root.left != null && root.left.left == null && root.left.right == null){
result += root.left.val;
}
sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);
return result;
}
}
513找树左下角的值
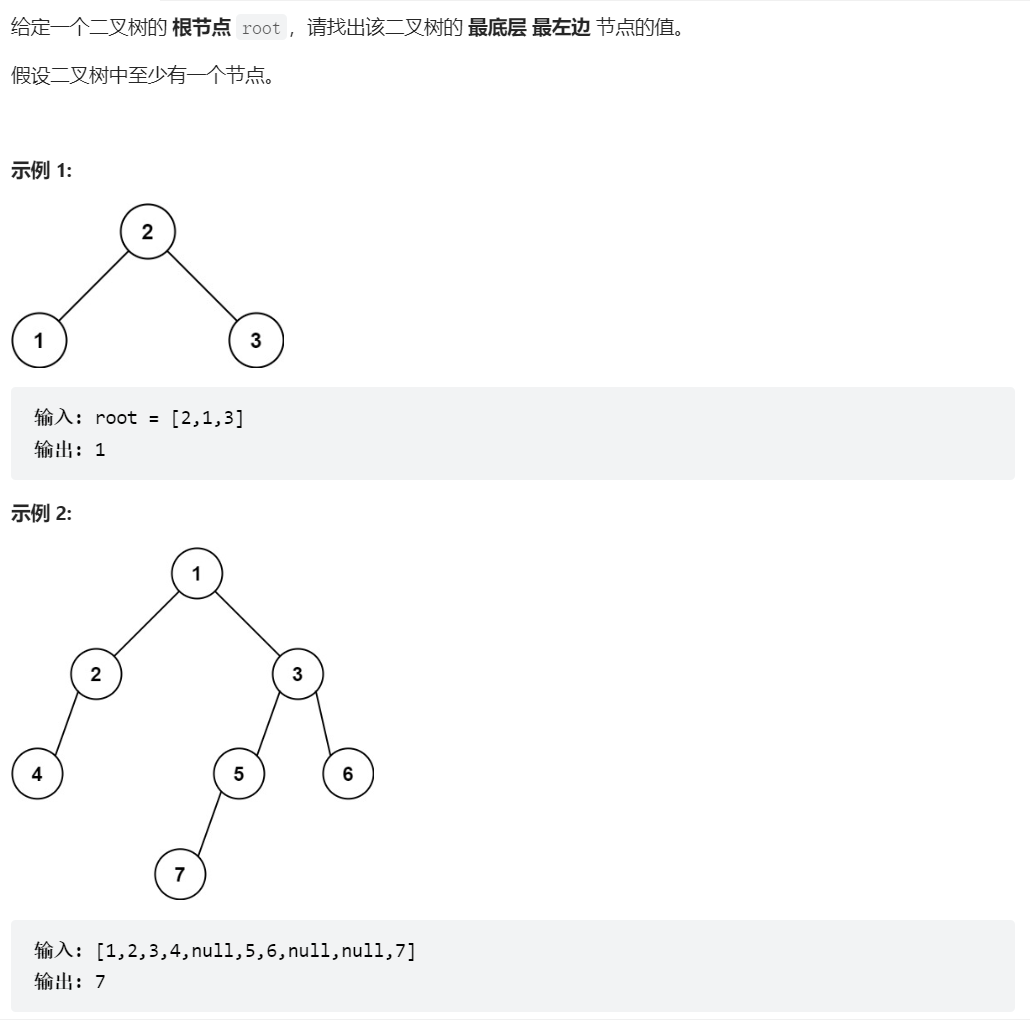
class Solution {
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int size = queue.size();
if(root != null){
queue.offer(root);
size = queue.size();
}
int find = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Queue<TreeNode> result = new LinkedList<>();
while(size > 0){
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
result.offer(cur);
if(cur.left != null){
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if(cur.right != null){
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
size--;
}
size = queue.size();
find = result.peek().val;
}
return find;
}
}
112、路径总和
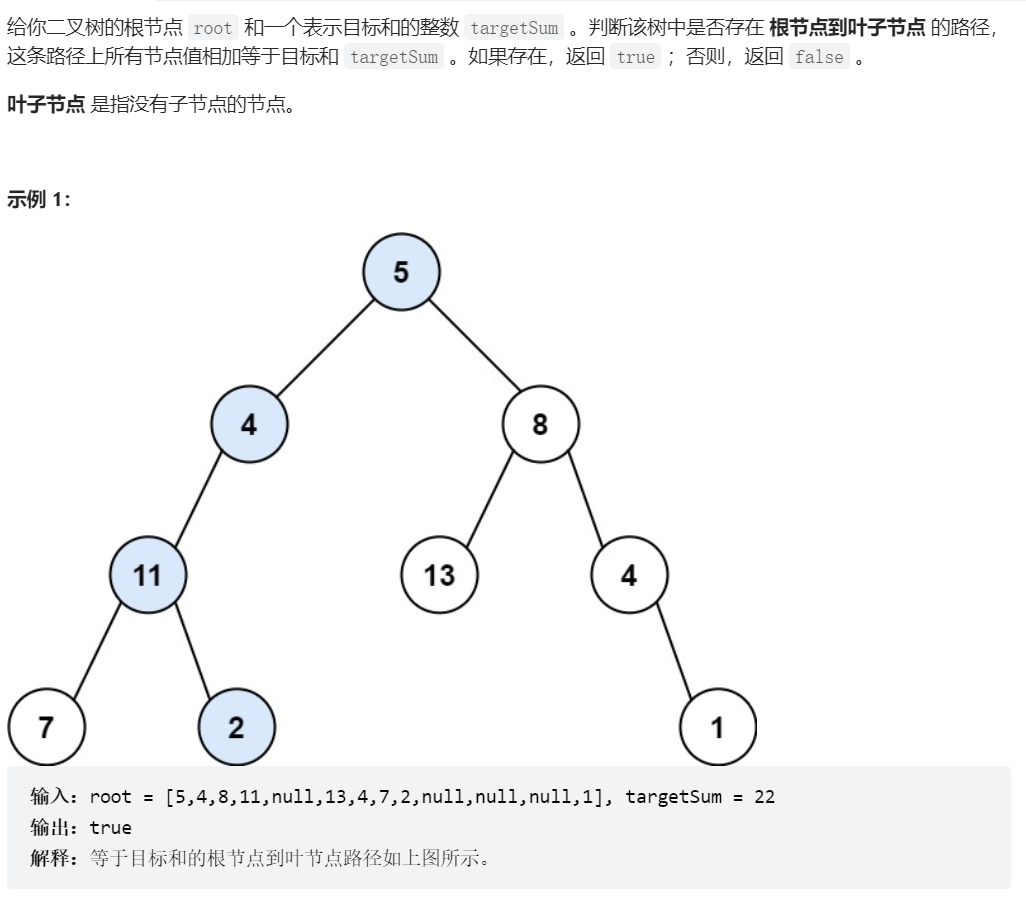
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root == null){
return false;
}
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
pathSum(root, result, temp);
return result.contains(targetSum);
}
public void pathSum(TreeNode root, List<Integer> result, List<Integer> temp){
temp.add(root.val);
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < temp.size(); i++){
sum += temp.get(i);
}
result.add(sum);
}
if(root.left != null){
pathSum(root.left, result, temp);
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
if(root.right != null){
pathSum(root.right, result, temp);
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
}
}
113、路径总和 II
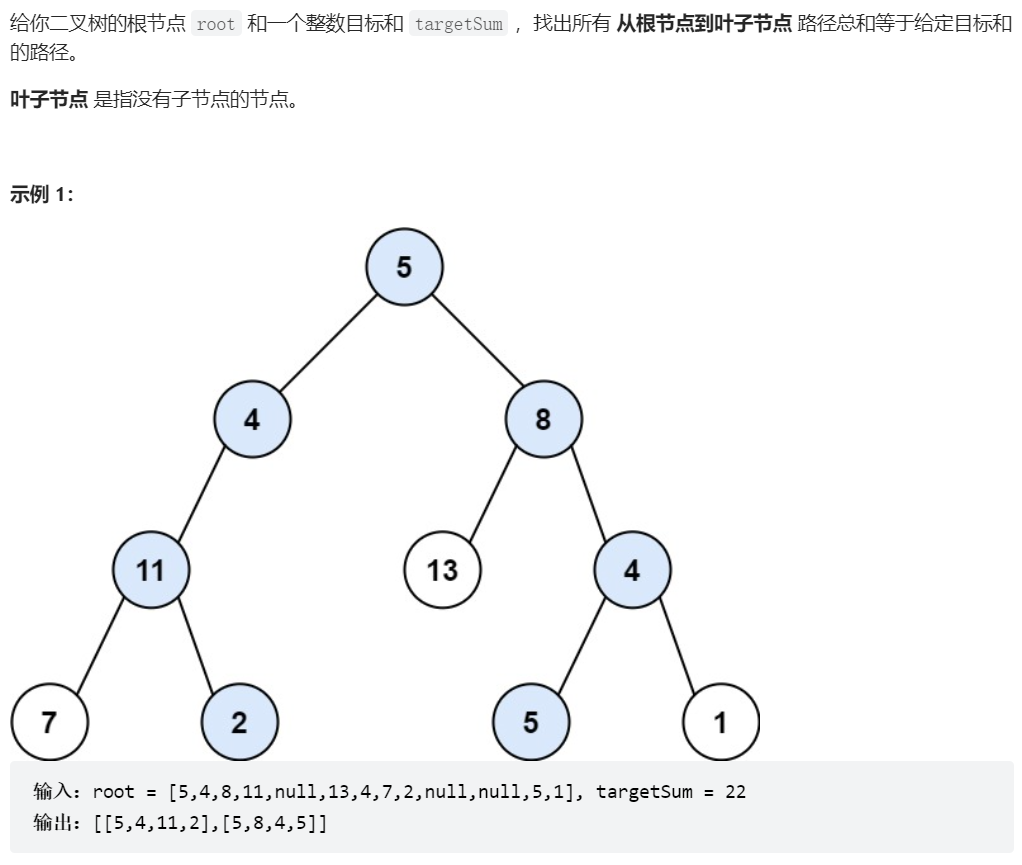
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return result;
}
find(root, result, temp, targetSum);
return result;
}
public void find(TreeNode root, List<List<Integer>> result, List<Integer> temp, int targetSum){
temp.add(root.val);
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < temp.size(); i++){
sum += temp.get(i);
}
if(sum == targetSum){
result.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(temp));
}
}
if(root.left != null){
find(root.left, result, temp, targetSum);
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
if(root.right != null){
find(root.right, result, temp, targetSum);
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
}
}
106、从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
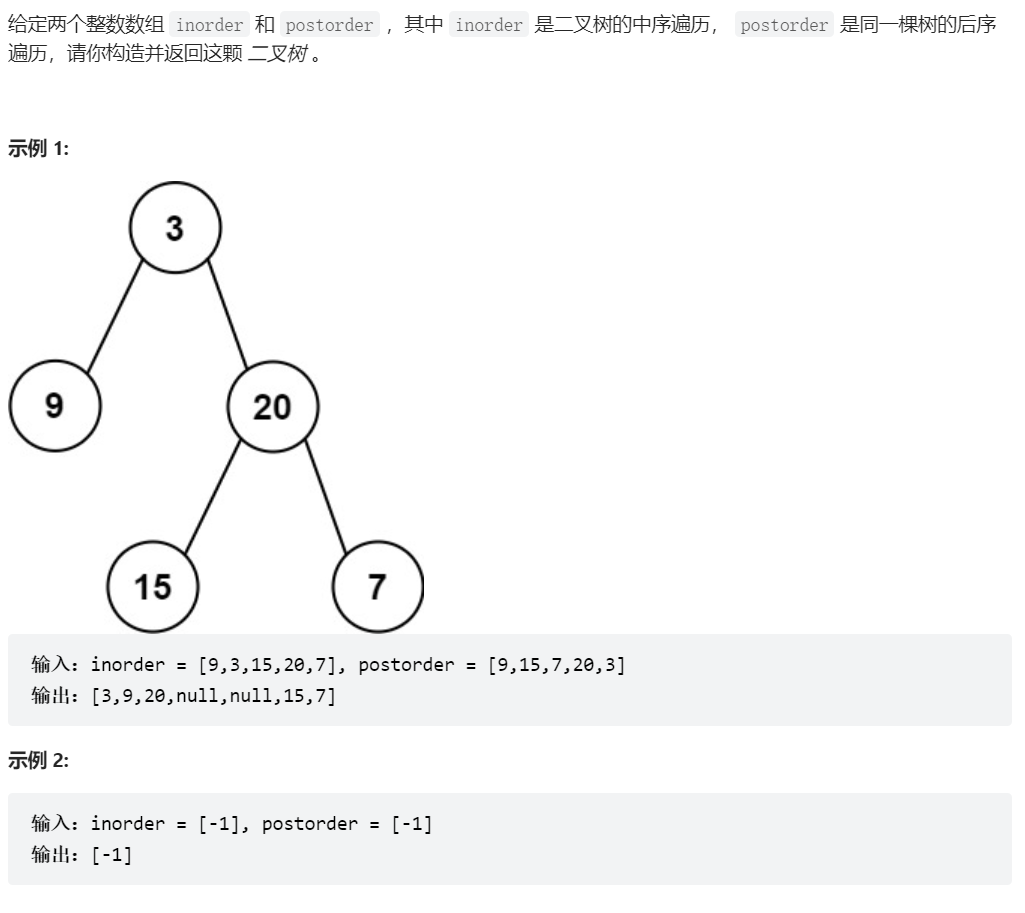
class Solution {
public Map<Integer, Integer> map;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++){
map.put(inorder[i], i);
}
return find(inorder, 0, inorder.length, postorder, 0, postorder.length);
}
public TreeNode find(int[] inorder, int inbegin, int inend, int[] postorder, int pobegin, int poend){
if(inbegin >= inend || pobegin >= poend){
return null;
}
int temp = map.get(postorder[poend - 1]);
int len = temp - inbegin;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(inorder[temp]);
root.left = find(inorder, inbegin, temp, postorder, pobegin, pobegin + len);
root.right = find(inorder, temp + 1, inend, postorder, pobegin + len, poend - 1);
return root;
}
}
105、从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
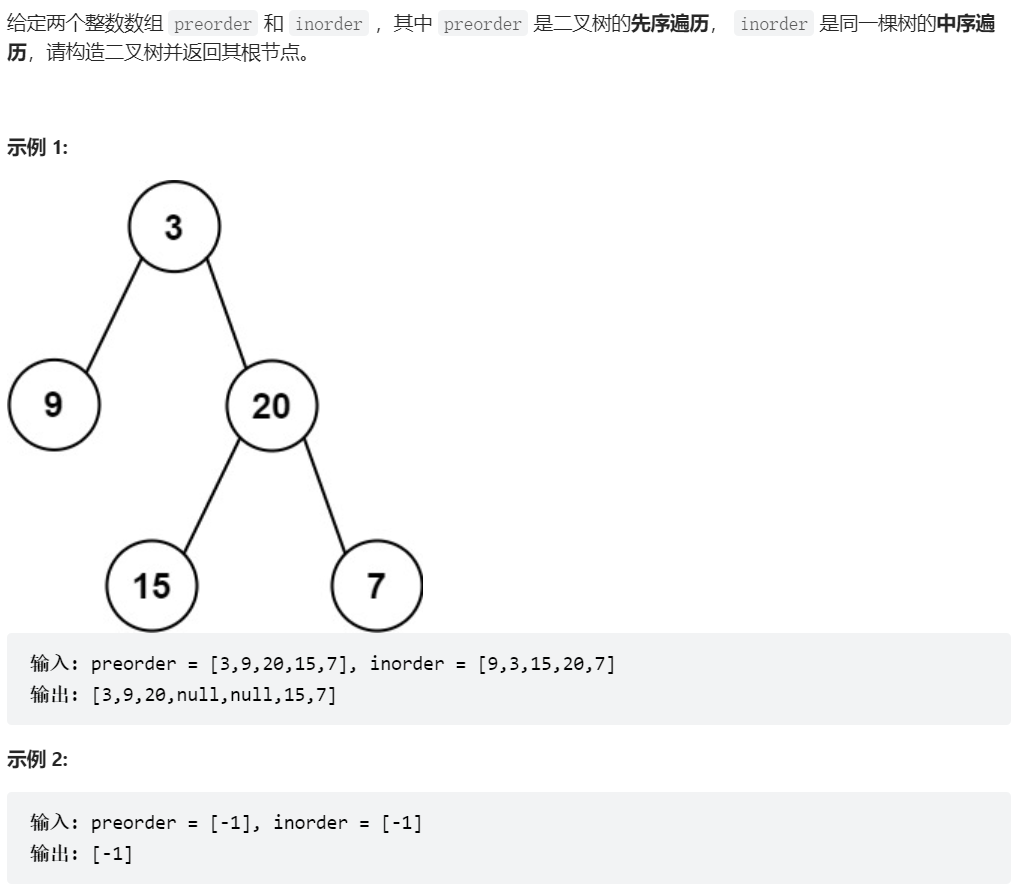
class Solution {
public Map<Integer, Integer> map;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++){
map.put(inorder[i], i);
}
return find(inorder, 0, inorder.length, preorder, 0, preorder.length);
}
public TreeNode find(int[] inorder, int inbegin, int inend, int[] preorder, int prbegin, int prend){
if(inbegin >= inend || prbegin >= prend){
return null;
}
int temp = map.get(preorder[prbegin]);
int len = temp - inbegin;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(inorder[temp]);
root.left = find(inorder, inbegin, temp, preorder, prbegin + 1, prbegin + len + 1);
root.right = find(inorder, temp + 1, inend, preorder, prbegin + len + 1, prend);
return root;
}
}
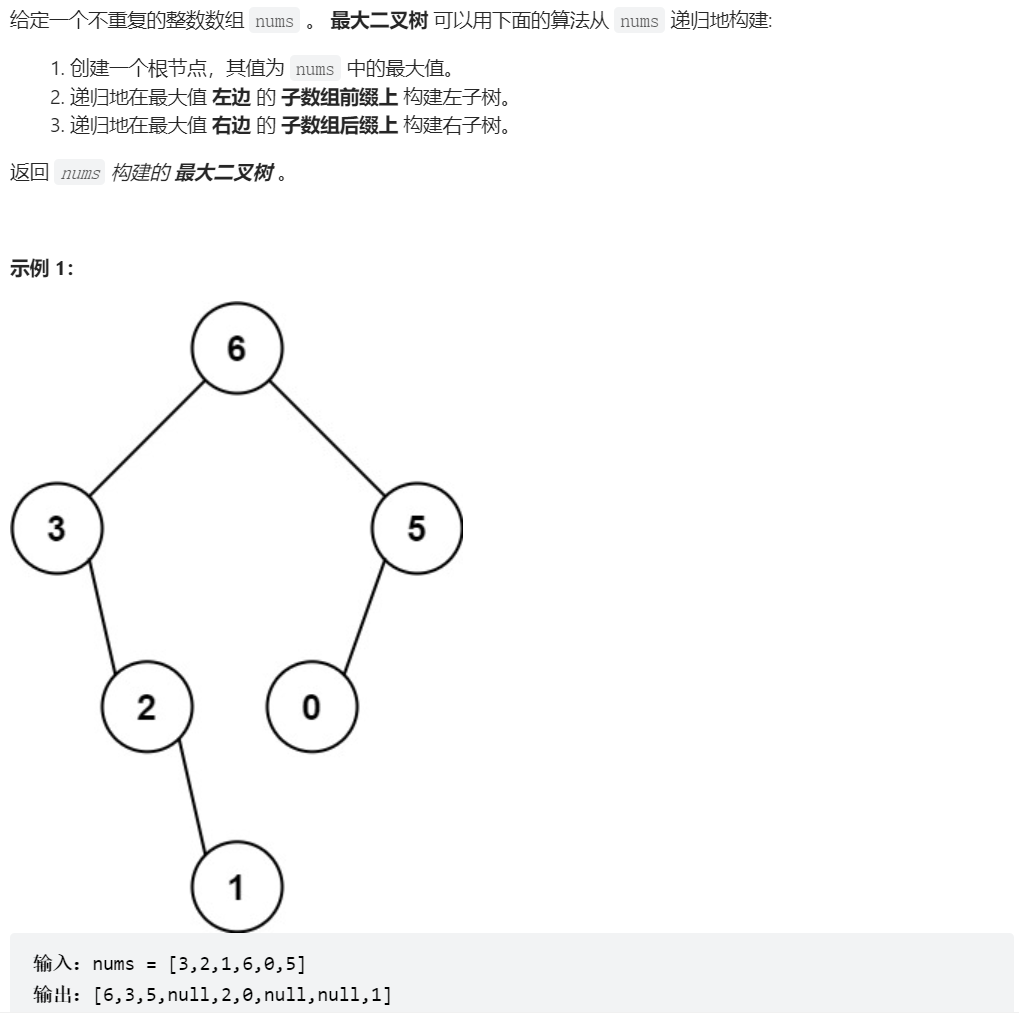
654、最大二叉树
class Solution {
public Map<Integer, Integer> map;
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) {
map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
map.put(nums[i], i);
}
return binaryTree(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode binaryTree(int[] nums, int left, int right){
int max = -1;
for(int i = left; i <= right; i++){
max = max > nums[i] ? max : nums[i];
}
if(max == -1){
return null;
}else{
int index = map.get(max);
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(max);
root.left = binaryTree(nums, left, index - 1);
root.right = binaryTree(nums, index + 1, right);
return root;
}
}
}
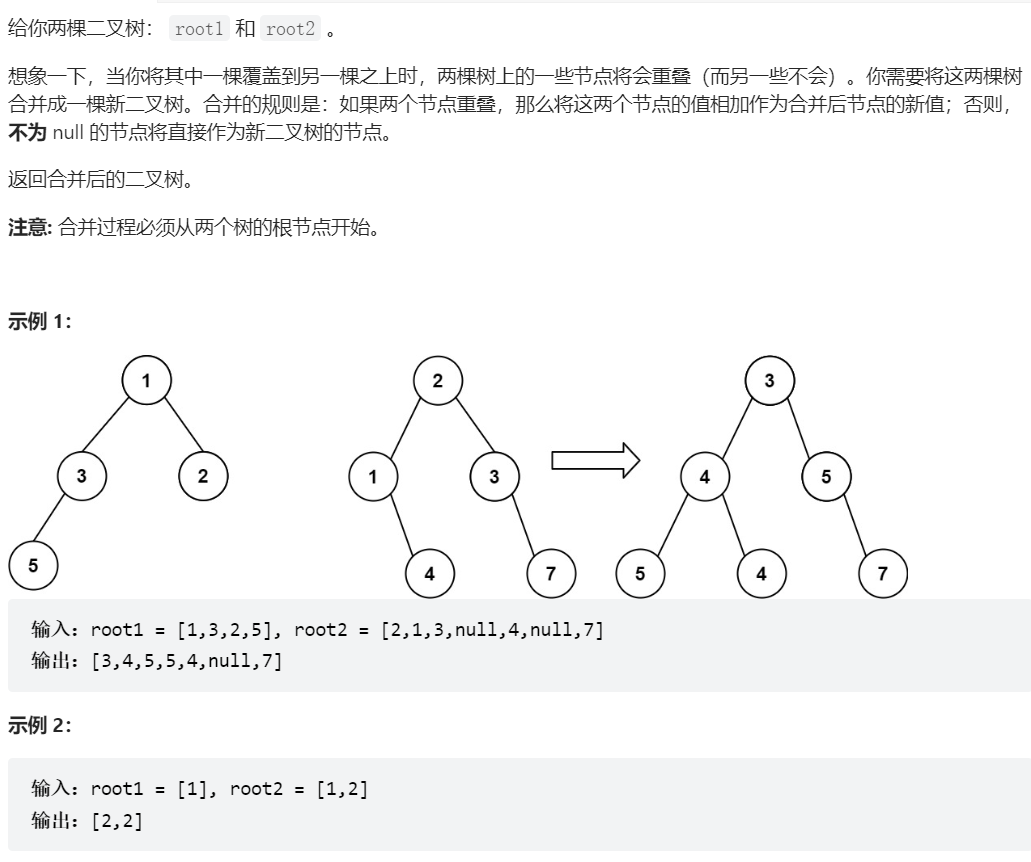
617、合并二叉树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode result = new TreeNode();
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
// 前序遍历,递归
// if(root1 == null){
// return root2;
// }
// if(root2 == null){
// return root1;
// }
// root1.val += root2.val;
// root1.left = mergeTrees(root1.left,root2.left);
// root1.right = mergeTrees(root1.right,root2.right);
// return root1;
// 使用栈迭代
// if(root1 == null){
// return root2;
// }
// if(root2 == null){
// return root1;
// }
// Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
// stack.push(root1);
// stack.push(root2);
// while(!stack.isEmpty()){
// TreeNode cur2 = stack.pop();
// TreeNode cur1 = stack.pop();
// cur1.val += cur2.val;
// if(cur1.left != null && cur2.left != null){
// stack.push(cur1.left);
// stack.push(cur2.left);
// }else{
// if(cur1.left == null){
// cur1.left = cur2.left;
// }
// }
// if(cur1.right != null && cur2.right != null){
// stack.push(cur1.right);
// stack.push(cur2.right);
// }else{
// if(cur1.right == null){
// cur1.right = cur2.right;
// }
// }
// }
// return root1;
// 使用队列迭代
if(root1 == null){
return root2;
}
if(root2 == null){
return root1;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root1);
queue.offer(root2);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode cur1 = queue.poll();
TreeNode cur2 = queue.poll();
cur1.val += cur2.val;
if(cur1.left != null && cur2.left != null){
queue.offer(cur1.left);
queue.offer(cur2.left);
}else{
if(cur1.left == null){
cur1.left = cur2.left;
}
}
if(cur1.right != null && cur2.right != null){
queue.offer(cur1.right);
queue.offer(cur2.right);
}else{
if(cur1.right == null){
cur1.right = cur2.right;
}
}
}
return root1;
}
}
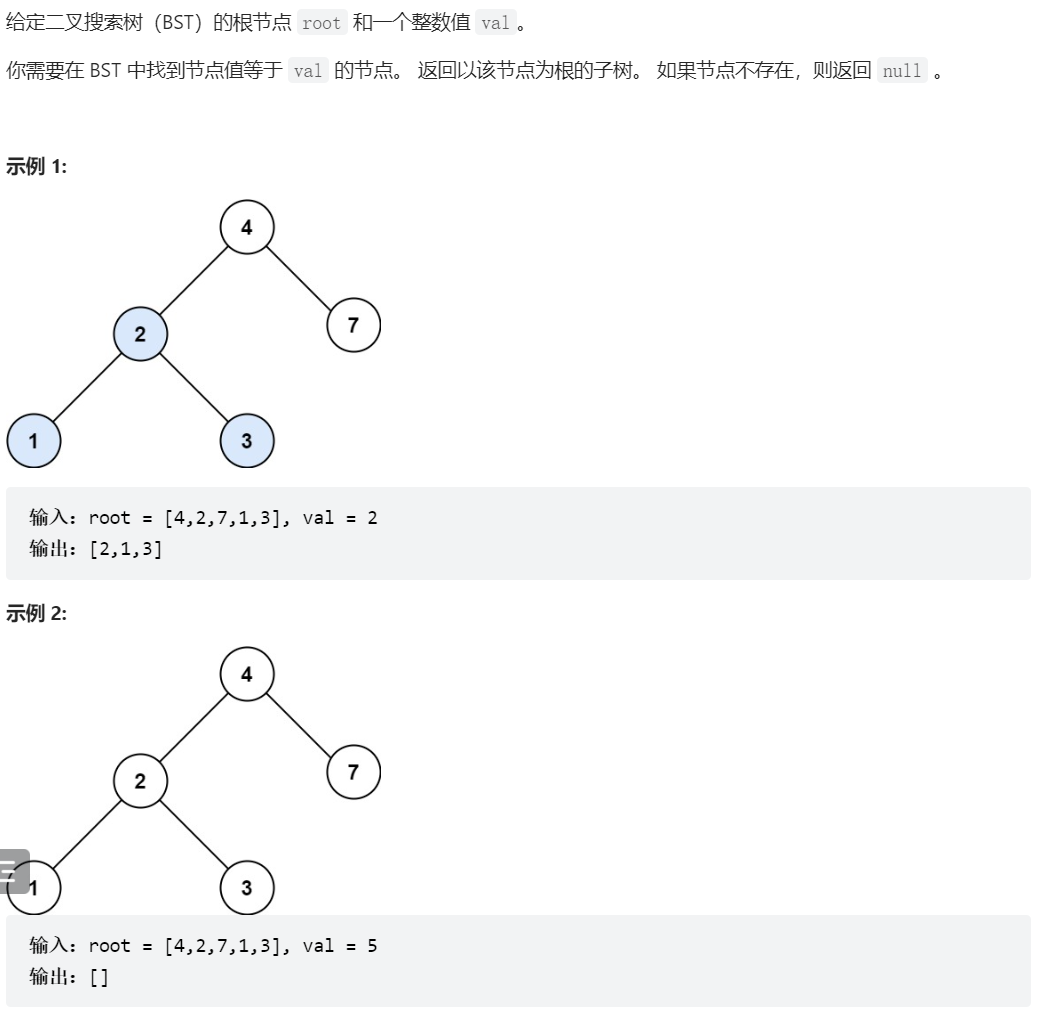
700、二叉搜索树中的搜索
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
// 递归
// if(root == null){
// return null;
// }
// TreeNode result = new TreeNode();
// if(root.val == val){
// result = root;
// }else if(root.val < val){
// result = searchBST(root.right,val);
// }else{
// result = searchBST(root.left,val);
// }
// return result;
// 迭代
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode cur = stack.pop();
if(cur.val == val){
return cur;
}else if(cur.val < val){
if(cur.right == null){
return null;
}
stack.push(cur.right);
}else{
if(cur.left == null){
return null;
}
stack.push(cur.left);
}
}
return null;
}
}
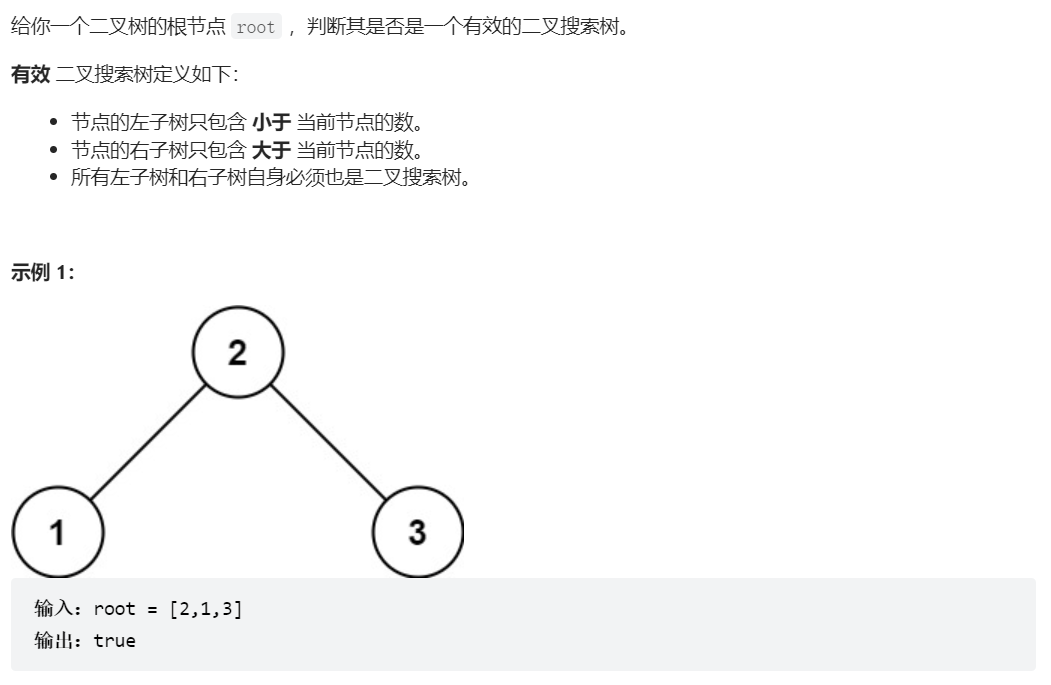
98、验证二叉搜索树
class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
// 需要从底层往上传递判断结果,所以采用后序遍历
if(root == null){
return true;
}
return isValidBST1(root,Long.MIN_VALUE,Long.MAX_VALUE);
}
public boolean isValidBST1(TreeNode root,long left, long right){
if(root == null){
return true;
}
if(root != null && (root.val <= left || root.val >= right)){
return false;
}
boolean leftFlag = isValidBST1(root.left,left,root.val);
boolean rightFlag = isValidBST1(root.right,root.val,right);
if(leftFlag == false || rightFlag == false){
return false;
}
return leftFlag && rightFlag;
}
}
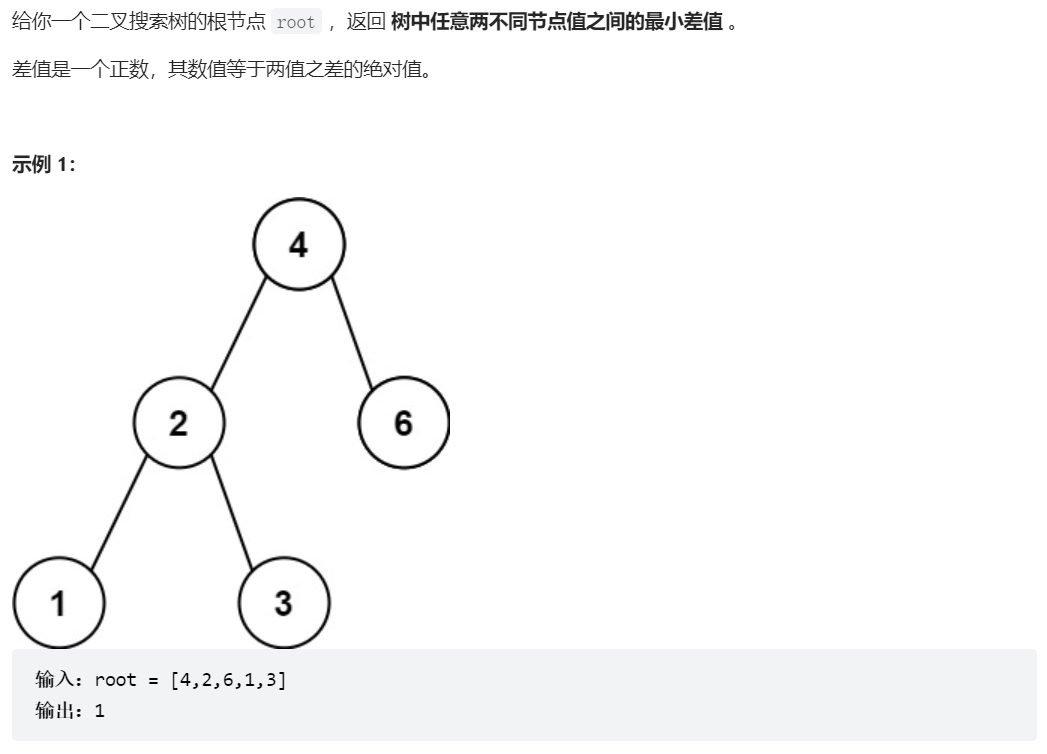
530、二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
class Solution {
public int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
TreeNode pre;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return result;
}
traversal(root);
return result;
}
public void traversal(TreeNode cur){
if(cur == null){
return;
}
traversal(cur.left);
if(pre != null){
result = Math.min(result, cur.val - pre.val);
}
pre = cur;
traversal(cur.right);
}
}
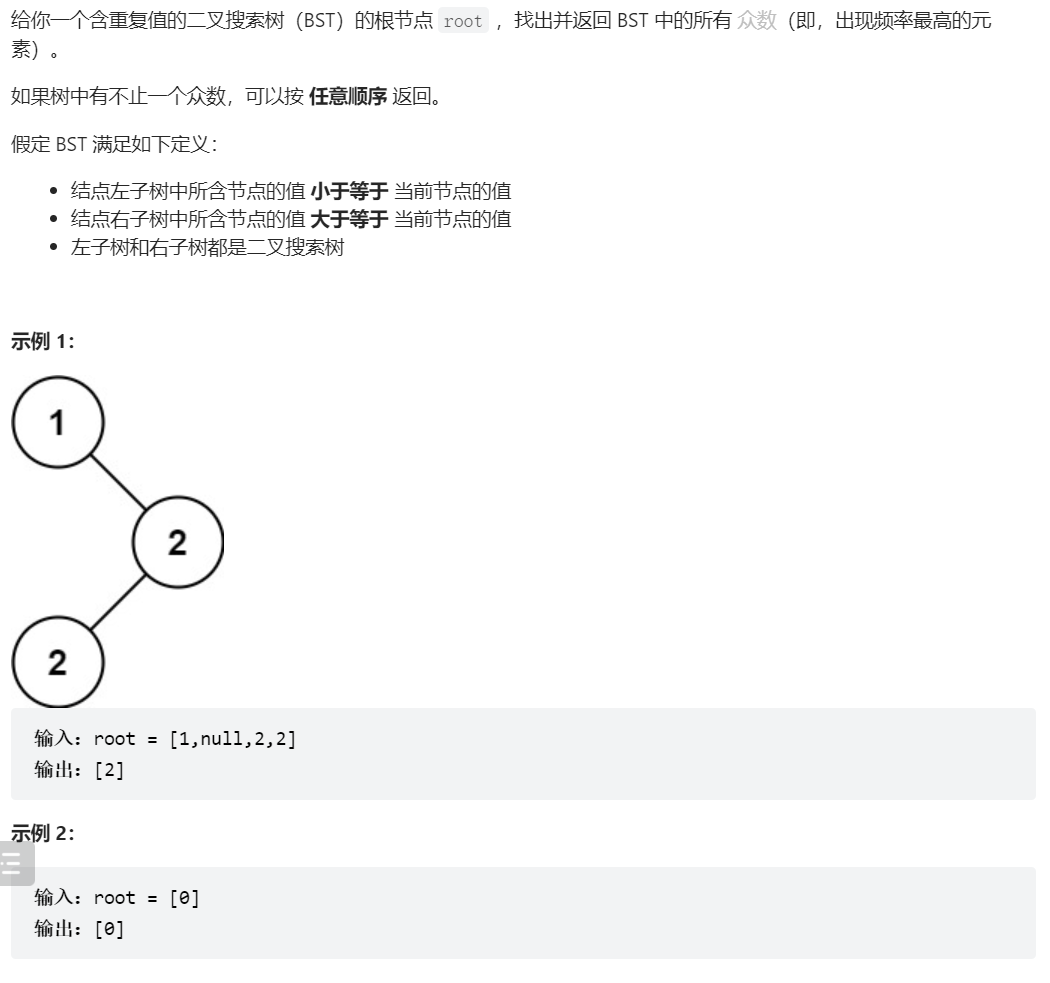
501、二叉搜索树中的众数
class Solution {
public int Maxcount;
public int count;
public List<Integer> result;
public TreeNode pre;
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
Maxcount = 0;
count = 0;
result = new ArrayList<>();
pre = null;
traversal(root);
int[] find = new int[result.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++){
find[i] = result.get(i);
}
return find;
}
public void traversal(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return;
}
traversal(root.left);
if(pre == null || root.val != pre.val){
count = 1;
}else{
count++;
}
pre = root;
if(count > Maxcount){
result.clear();
result.add(root.val);
Maxcount = count;
}else if(count == Maxcount){
result.add(root.val);
}
traversal(root.right);
}
}
236、二叉树的最近公共祖先

class Solution {
public TreeNode result = null;
// public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
// // 1、后序遍历,从下往上传递,从遇到p或q开始,往上传递true,当某个节点也叶子节点都为true时,找到最近工祖先
// // 递归
// postOrder(root,p.val,q.val);
// return result;
// }
// public boolean postOrder(TreeNode root, int p, int q){
// if(root == null){
// return false;
// }
// boolean leftFlag = postOrder(root.left,p,q);
// boolean rightFlag = postOrder(root.right,p,q);
// if(leftFlag && rightFlag){
// result = root;
// return true;
// }
// if((root.val == q || root.val == p) && (leftFlag || rightFlag)){
// result = root;
// return true;
// }
// if(root.val == q || root.val == p){
// return true;
// }
// if(leftFlag || rightFlag){
// return true;
// }
// return false;
// }
}
235、二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先

class Solution {
public TreeNode result = null;
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
int min = p.val < q.val ? p.val : q.val;
int max = p.val > q.val ? p.val : q.val;
find(root,min,max);
return result;
}
public void find(TreeNode root, int pval, int qval){
if(root == null){
return;
}
if(root.val >= pval && root.val <= qval){
result = root;
return;
}
find(root.left,pval,qval);
find(root.right,pval,qval);
}
}
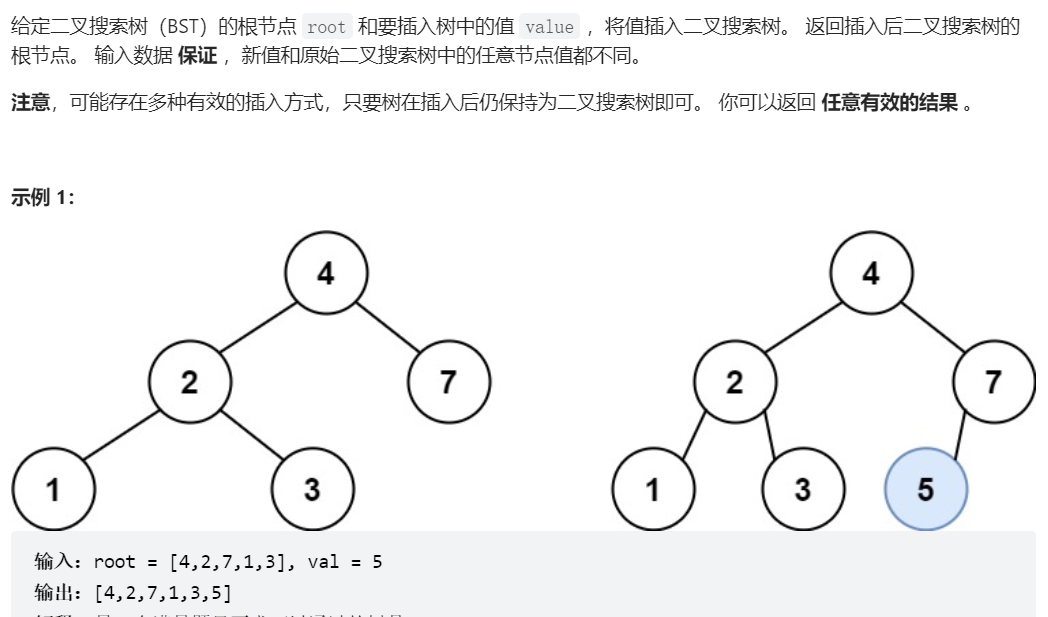
701、二叉搜索树中的插入操作
class Solution {
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if(root == null){
return new TreeNode(val);
}
TreeNode result = root;
travesal(root,val);
return result;
}
public void travesal(TreeNode root, int val){
if(root == null){
return;
}
if(root.val < val){
if(root.right == null){
root.right = new TreeNode(val);
return;
}else{
travesal(root.right,val);
}
}else{
if(root.val > val && root.left == null){
root.left = new TreeNode(val);
return;
}else{
travesal(root.left,val);
}
}
}
}
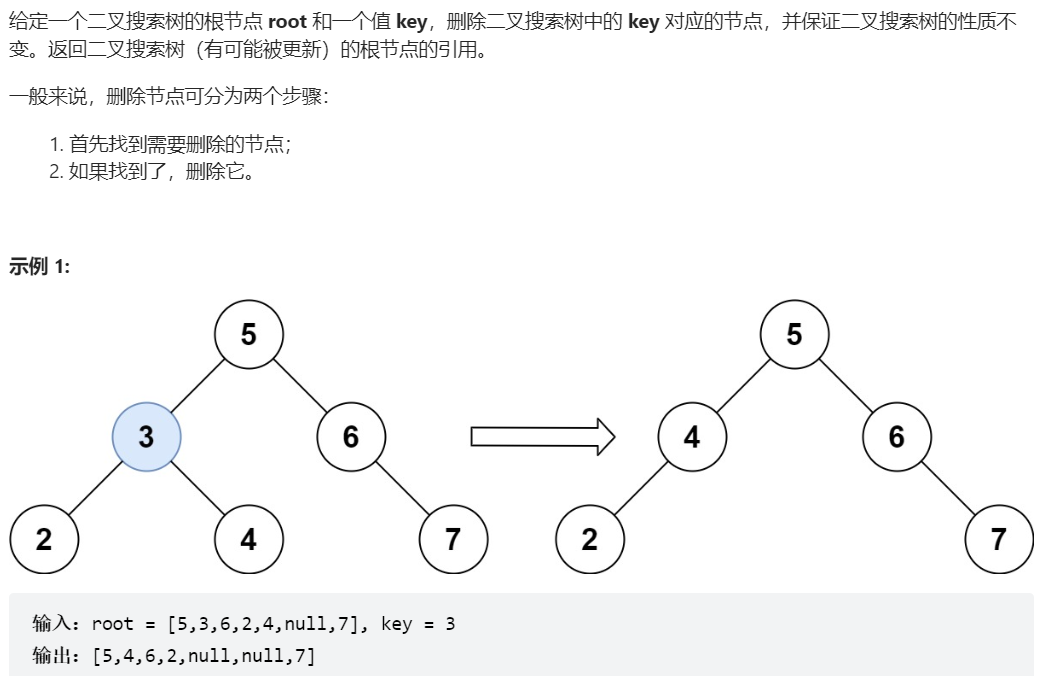
450、删除二叉搜索树中的节点
class Solution {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
root = delete(root,key);
return root;
}
public TreeNode delete(TreeNode root,int key){
if(root == null){
return null;
}
if(root.val < key){
root.right = delete(root.right,key);
}else if(root.val > key){
root.left = delete(root.left,key);
}else{
if(root.left == null)
return root.right;
if(root.right == null)
return root.left;
TreeNode cur = root.right;
TreeNode temp = root.right;
while(temp.left != null){
temp = temp.left;
}
temp.left = root.left;
return cur;
}
return root;
}
}
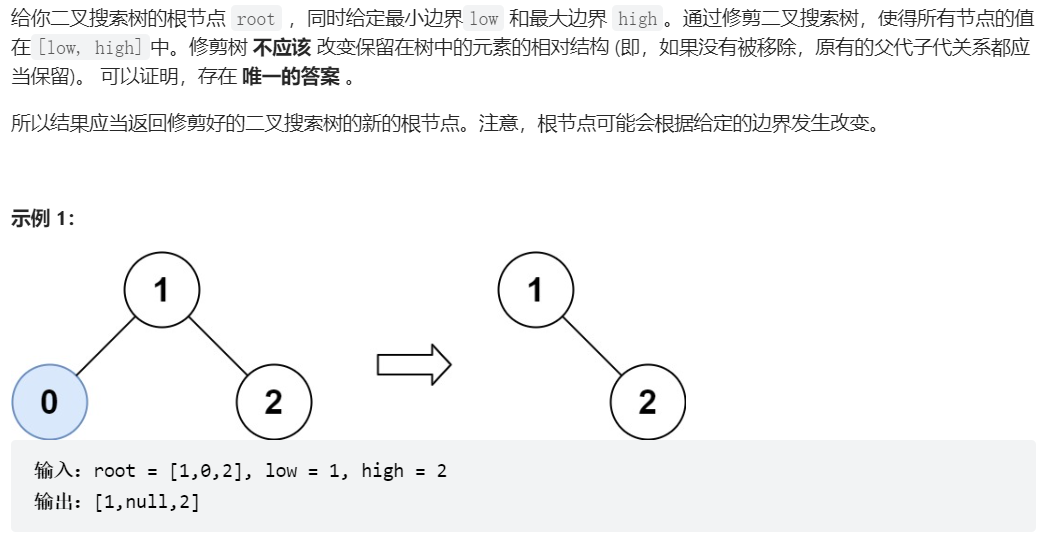
669、修剪二叉搜索树
class Solution {
public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
if(root == null){
return null;
}
if(root.val < low){
return trimBST(root.right,low,high);
}
if(root.val > high){
return trimBST(root.left,low,high);
}
root.left = trimBST(root.left,low,high);
root.right = trimBST(root.right,low,high);
return root;
}
}
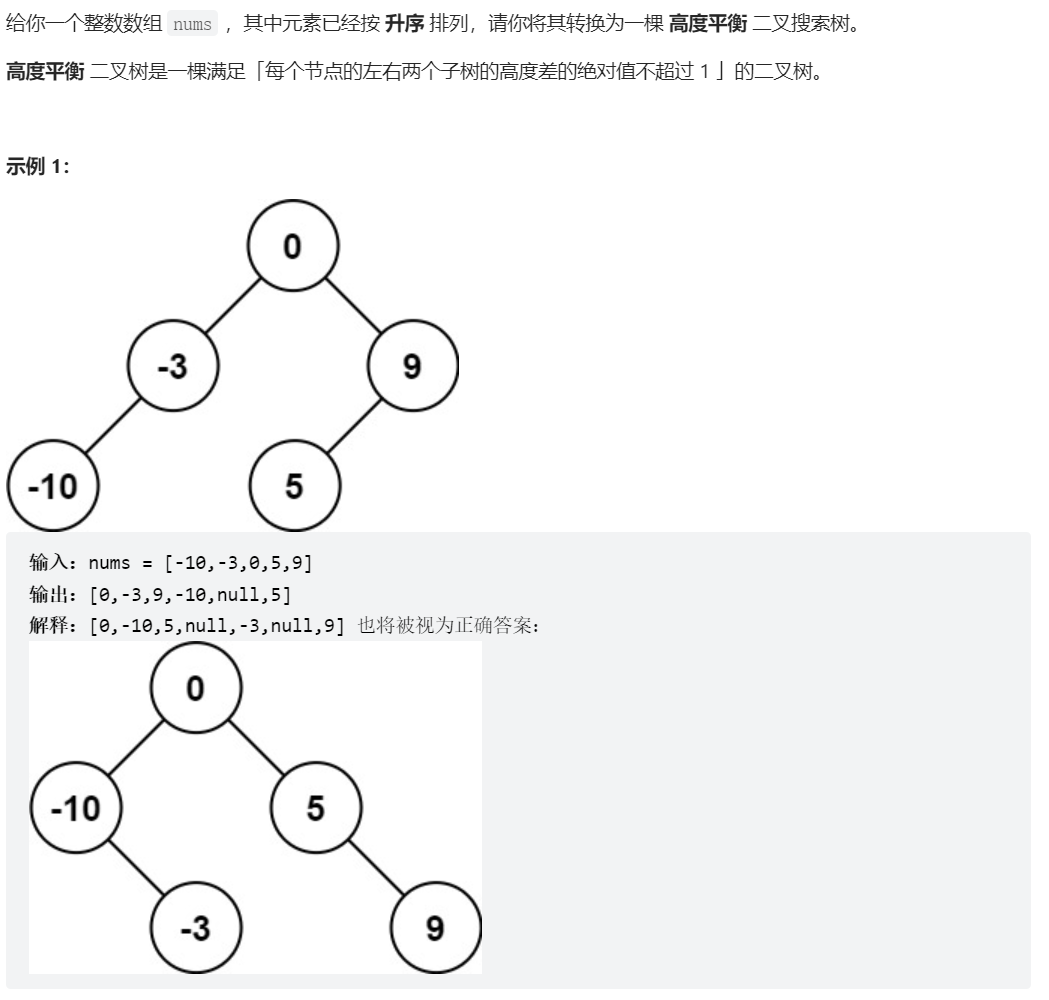
108、将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
return travesal(nums,0,nums.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode travesal(int[] nums, int left, int right){
if(left > right){
return null;
}
int mid = left + (right - left)/2;
TreeNode result = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
result.left = travesal(nums,left,mid - 1);
result.right = travesal(nums,mid + 1, right);
return result;
}
}
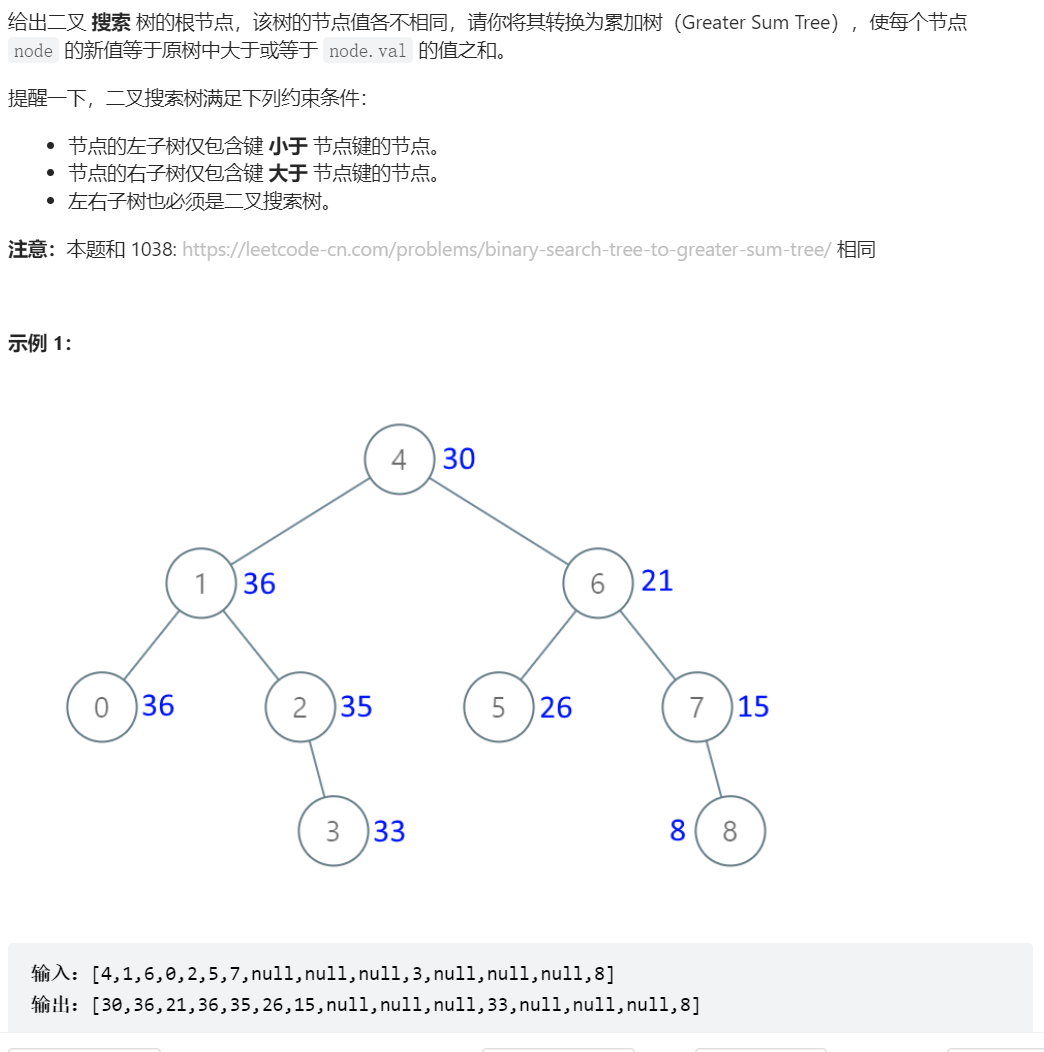
538、把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
class Solution {
public int sum = 0;
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return null;
}
convertBST(root.right);
root.val += sum;
sum = root.val;
convertBST(root.left);
return root;
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号