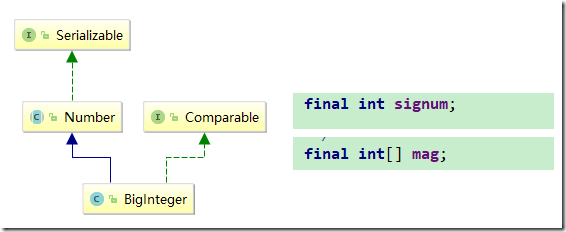
[十六]基础类型BigInteger简介
属性简介
| 负数 | -1 |
| 0 | 0 |
| 正数 | 1 |
字节序为大端模式,大端模式就是低地址存储高位
|
对于BigInteger 他的数据打开就是这么一种形式
[ 101....32位....1] [ 110....32个....1] ....N个..... [ 0110....32个....1]
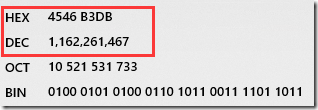
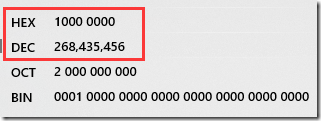
它的真值的计算方法与其他的二进制序列一样的
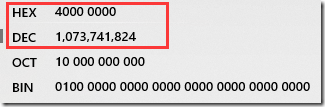
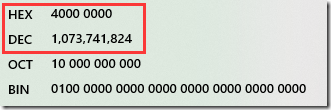
二进制为 0111 1110 的十进制为126 相信谁都会计算,BigInteger也是如此的
尤其是对于BigInteger字符串参数的构造形式
千万不要以为就是把字符的编码或者字符转换成数字切段存放到int数组中
他存放的都是转换后的真值
下面会详细介绍
|
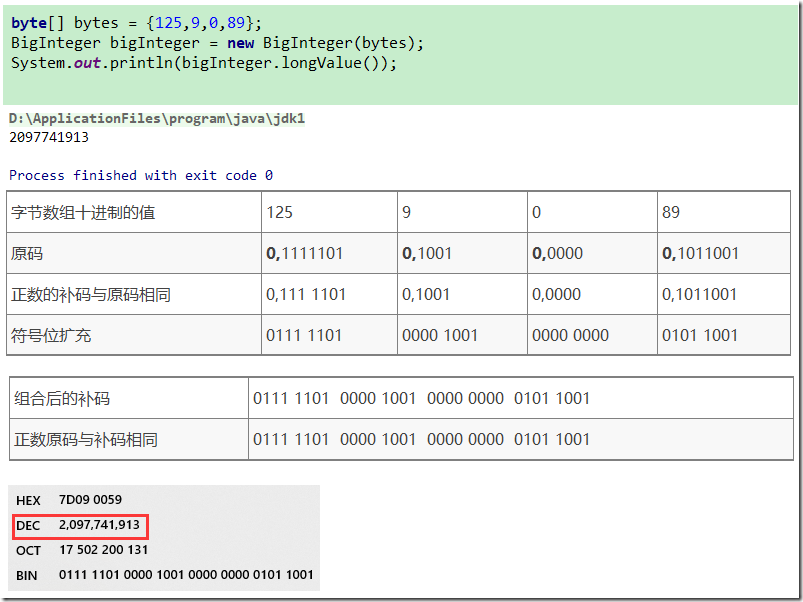
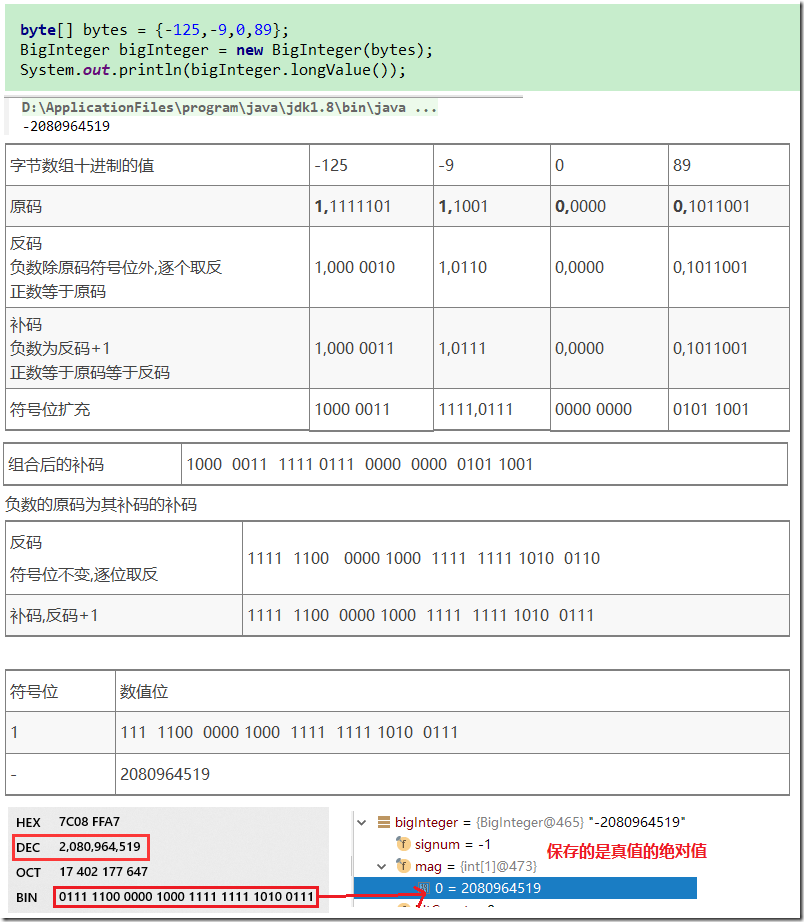
使用字节数组构造
- 如果是一个负数,会先得到真值的绝对值
- 如果有前导零,还会去掉所有的前导零
原码/反码/补码
| 原码 |
符号位+数值位
符号位为0 表示正数,符号位为1 表示负数
数值位就是真值的绝对值
又被称为带符号的绝对值表示
|
| 反码 | 正数的反码为其原码 负数的反码为其原码的除符号位外,逐位取反 |
| 补码 | 正数的补码为其原码 负数的补码为其反码+1 |
补码计算步骤
| 第一步求原码: 先写出来她的原码--->符号位+数值位(绝对值) |
|
第二步求反码:
如果是正数 反码与原码一样
如果是负数 反码为原码取反(除符号位外,逐位翻转)
|
| 第三步求补码: 如果是正数 补码与原码一样 如果是负数 补码为反码 + 1 |
| 第四步扩充: 如果不足数据类型的宽度,将需要填充到指定宽度 符号位扩充,也就是正数补0 负数补1 |
| 总结 不管什么形式,第一位始终都是符号位,0 表示正数, 1表示负数 正数原码/反码/补码 全都一样,知道一种就直接得到另外的形式 负数如果知道补码,想要得到他的原码,只需要对补码再一次的求补码即可 |
示例1
示例2
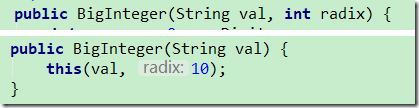
使用String构造
算法基础
| BigInteger内部使用int数组表示 普通数值使用每个数值位上的数字进行表示 |
| 一个BigInteger有多个int 一个普通数值有多个数字位 |
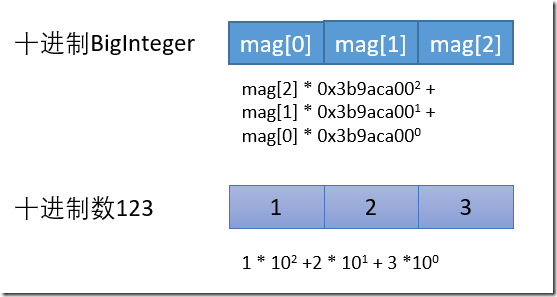
每个int能够表示的指定进制的最大值--intRadix 中保存的数据
其实 就是 BigInteger 的基于每个int作为一个元素的进制基数
|
|
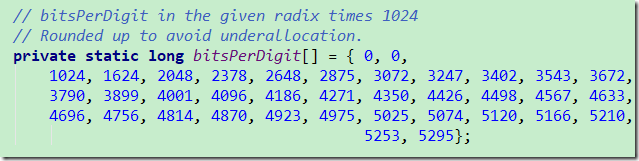
digitsPerInt 表示不同基数(进制)下一个int 能够表示的数字的长度 ,这个位数其实就是按照多长进行分割组装
intRadix 就是基数
bitsPerDigit 是用来推算需要多少个int的,也就是int数组的长度
|
构造方法源码解析
public BigInteger(String val, int radix) {
//定义了两个变量一个光标,光标记录着应该要处理的数据索引下标
//另一个numDigits 用来保存需要处理的数字位数 也就是有效长度,比如去掉前导零后的
int cursor = 0, numDigits;
final int len = val.length();//传递进来的字符数组的长度
//如果给定的基数,不在合法范围内,那么抛出异常,不会默认处理
if (radix < Character.MIN_RADIX || radix > Character.MAX_RADIX)
throw new NumberFormatException("Radix out of range");
//如果字符串长度为0 也是一种非法的参数
if (len == 0)
throw new NumberFormatException("Zero length BigInteger");
// Check for at most one leading sign
int sign = 1;
int index1 = val.lastIndexOf('-');
int index2 = val.lastIndexOf('+');
//符号- + 只能出现一个,而且还必须是第一个位置,否则都不合法
//根据最后一个的索引与0 进行比较,可以简便的判断符号位是否合法
if (index1 >= 0) {
if (index1 != 0 || index2 >= 0) {
throw new NumberFormatException("Illegal embedded sign character");
}
sign = -1;
cursor = 1;
} else if (index2 >= 0) {
if (index2 != 0) {
throw new NumberFormatException("Illegal embedded sign character");
}
cursor = 1;
}
//经过前面的判断,如果有符号位的话,光标的值更新为1 也就是后续不处理符号位
//如果此时光标的值等于字符长度,说明没有有效数字了,将会抛出异常
if (cursor == len)
throw new NumberFormatException("Zero length BigInteger");
// Skip leading zeros and compute number of digits in magnitude
//如果有前导0 ,将会去掉这些,光标的位置也会跟着一起移动
while (cursor < len &&
Character.digit(val.charAt(cursor), radix) == 0) {
cursor++;
}
//跳过了所有的0之后就不再有有效数据了,说明他就是个0
//哪怕他原来设置的负数的0 将会变为0 的标记
if (cursor == len) {
signum = 0;
mag = ZERO.mag;
return;
}
//记录实际需要处理的数据长度以及对符号位使用signum进行记录
numDigits = len - cursor;
signum = sign;
// Pre-allocate array of expected size. May be too large but can
// never be too small. Typically exact.
//根据前面的公式计算实际需要的二进制位数 numDigits需要处理的数字的长度
//bitsPerDigit 里面记录了每个进制1位数需要的二进制位数,但是放大了1024倍,所以还要除以1024 也就是右移10
//真正的值可能是小数个,除以1024之后变成了取整了,然后再加上一,百分百够用,需要的比特位数保存到numBits
long numBits = ((numDigits * bitsPerDigit[radix]) >>> 10) + 1;
if (numBits + 31 >= (1L << 32)) {
reportOverflow();
}
//numWords 记录的是实际需要的int类型数据的个数,也就是数组的长度
//右移5位就是除以32 就是计算数组的长度,除法会取整,防止1个不足32位的时候,就会变成0了所以numBits加上31 之后再除以32
int numWords = (int) (numBits + 31) >>> 5;
//此时创建真正的保存数据的int数组了
int[] magnitude = new int[numWords];
// Process first (potentially short) digit group
//numDigits 需要处理的数字的个数
//digitsPerInt 保存的是每一个int能够保存的指定数制下的字符长度
//如果有余数,说明有一个不足最大长度的位数
//如果没有余数,那么每一组都是刚好能够保存的最大长度
int firstGroupLen = numDigits % digitsPerInt[radix];
if (firstGroupLen == 0)
firstGroupLen = digitsPerInt[radix];
//第一组数据存放到数组的最后一个
String group = val.substring(cursor, cursor += firstGroupLen);
magnitude[numWords - 1] = Integer.parseInt(group, radix);
if (magnitude[numWords - 1] < 0)
throw new NumberFormatException("Illegal digit");
// Process remaining digit groups
int superRadix = intRadix[radix];
int groupVal = 0;
while (cursor < len) {
group = val.substring(cursor, cursor += digitsPerInt[radix]);
groupVal = Integer.parseInt(group, radix);
if (groupVal < 0)
throw new NumberFormatException("Illegal digit");
// 这个方法是用来累计计算的,方法内部写的很复杂
//其实逻辑很简单,比如一个数字序列1234,求他表示的值是多少
// ( ( (1*10)+2 )*10+3 )*10 +4 = 1234
//这个方法就是用来计算的,只不过每一个位置是一个int 低32位当做数值 高32位当做进位
destructiveMulAdd(magnitude, superRadix, groupVal);
}
// Required for cases where the array was overallocated.
mag = trustedStripLeadingZeroInts(magnitude);
if (mag.length >= MAX_MAG_LENGTH) {
checkRange();
}
}
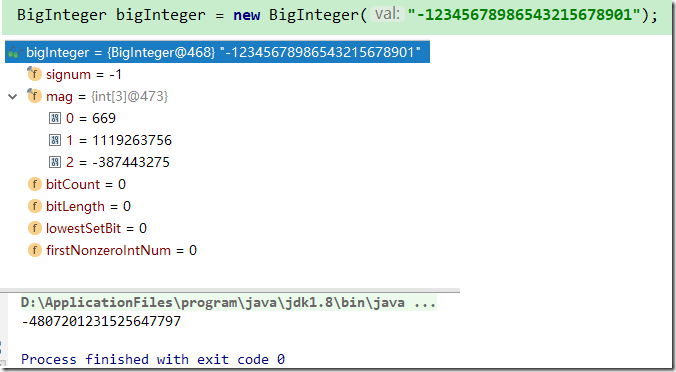
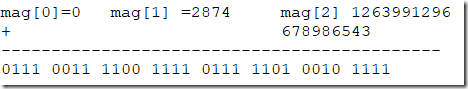
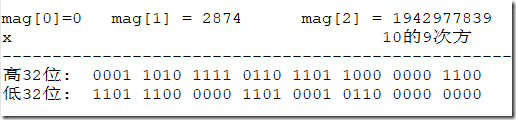
构造方法运行步骤
字符串构造方法计算示例
其他构造方法
方法简介
基础方法
| 获取符号位 signum() |
| 常用数学函数 negate() 取负 abs() 绝对值 pow(int) 求幂
gcd(BigInteger) 最大公约数
min(BigInteger) 最小值
max(BigInteger) 最大值
|
|
四则运算与取整求余
add(BigInteger) 加法
subtract(BigInteger) 减法
multiply(BigInteger) 乘法
divide(BigInteger) 除法(取整)
remainder(BigInteger) 求余
divideAndRemainder(BigInteger) 取整和求余 返回的是一个数组
|
|
获取基本类型的值
不同于基本数值类型的包装类,此处并不是直接强转的
如果太大intValue 和 longValue 将分别返回低的32位和64位
longValue 和 doubleValue可能会被转换为无穷
intValue()
longValue()
floatValue()
doubleValue()
|
|
数值类型的准确值
longValueExact()
intValueExact()
shortValueExact()
byteValueExact()
所谓准确就是不会舍入或者转换,因为他们会进行数据长度的校验
否则将会抛出异常
比如
|
|
位操作相关
and(BigInteger) 与
or(BigInteger) 或
not() 非
xor(BigInteger) 异或
andNot(BigInteger) 返回其值为 (this & ~val) 的 BigInteger 等效于 and(val.not())
shiftLeft(int) 左移
shiftRight(int) 右移
|
取模与求余对比
|
计算过程相同
对于整型数a,b来说,取模运算或者求余运算的方法都是:
求模运算和求余运算在第一步不同:
取余运算在取c的值时,向0 方向舍入;
而取模运算在计算c的值时,向负无穷方向舍入;
因此,求模时结果的符号与b一致,求余时结果的符号与a一致
如果a,b都是正整数的话,求模与求余没有区别
|
|
mod(BigInteger)
返回其值为 (this mod m) 的 BigInteger,取模不同于 remainder
BigInteger modPow(BigInteger exponent,BigInteger m)
BigInteger modInverse(BigInteger m)
|
bitCount与bitLength
| public int bitCount() 返回此 BigInteger 的二进制补码表示形式中与符号不同的位的数量 特别注意这个方法的含义 不是二进制补码表示形式的 1 位的数量,而是与符号不同的 |
| bitLength 最小的二进制补码表示形式的位数,不包括 符号位 对于正 BigInteger,这等于常规二进制表示形式中的位数 就是去掉符号位占用的长度 |
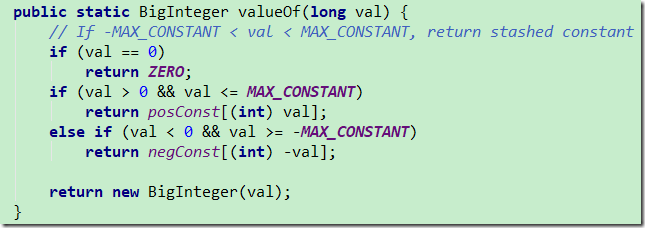
valueOf(long)
equals(Object)
toString hashCode CompareTo
|
public String toString(int radix) 转换为指定基数
toString()
|
| hashCode() |
|
compareTo(BigInteger)
小于、等于或大于 时,返回 -1,0,或 1
|
素数相关
|
是否素数
public boolean isProbablePrime(int certainty)
如果此 BigInteger 可能为素数,则返回 true,如果它一定为合数,则返回 false
如果 certainty <= 0,则返回 true
参数:
certainty - 调用方允许的不确定性的度量
如果该调用返回 true,则此 BigInteger 是素数的概率超出 ( 1 - 1/(2的certainty次方) )
此方法的执行时间与此参数的值是成比例的
返回:
如果此 BigInteger 可能为素数,则返回 true,如果它一定为合数,则返回 false
|
|
public static BigInteger probablePrime(int bitLength,
Random rnd)
返回有可能是素数的、具有指定长度的正 BigInteger此方法返回的 BigInteger 是合数的概率不超出 2的-100次方 参数:
bitLength - 返回的 BigInteger 的 bitLength。
rnd - 随机比特源,用这些随机比特选择用来进行质数测试的候选数
|
|
nextProbablePrime
public BigInteger nextProbablePrime()
返回大于此 BigInteger 的可能为素数的第一个整数
此方法返回的数是合数的概率不超出 2的-100次方
|
特殊的"位操作"
|
testBit(int) 计算 (this & (1<<n)) != 0
setBit(int) 计算 this | (1<<n)
clearBit(int) 计算 this & ~(1<<n)
flipBit(int) 计算 this ^ (1<<n)
|
|
getLowestSetBit()
返回此 BigInteger 最右端(最低位)1 比特位的索引
也就是从最右边开始数找到的第一个1
此字节的右端开始到本字节中最右端 1 之间的 0 比特的位数
如果此 BigInteger 不包含1位,则返回 -1
计算 this==0? -1 : log2(this & -this)
|
toByteArray
| public byte[] toByteArray() |
| BigInteger 内部使用int数组进行数据保存 一个int包含4个byte BigInteger可以使用byte数组构造 也自然能够分解成byte数组进行保存 |






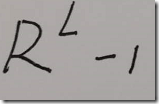
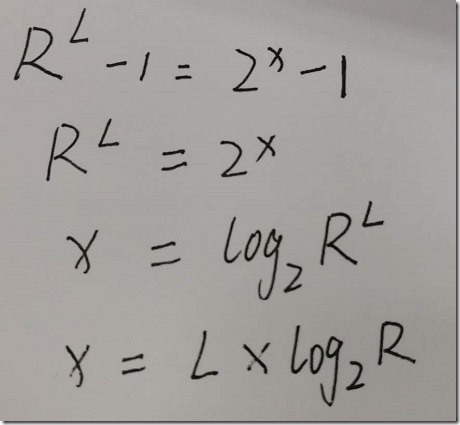





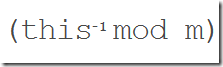


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号